Duero
|
Duero Portuguese: Douro |
||
|
The Duero and its tributary Pisuerga |
||
| Data | ||
| location | Spain , Portugal | |
| River system | Duero | |
| Headwaters |
Picos de Urbión in the province of Soria 42 ° 0 ′ 25 ″ N , 2 ° 52 ′ 51 ″ W |
|
| Source height | 2160 msnm | |
| muzzle |
Atlantic Ocean near Porto Coordinates: 41 ° 8 ′ 43 " N , 8 ° 39 ′ 24" W 41 ° 8 ′ 43 " N , 8 ° 39 ′ 24" W |
|
| Mouth height | 0 msnm | |
| Height difference | 2160 m | |
| Bottom slope | 2.4 ‰ | |
| length | 897 km | |
| Catchment area | 98,400 km² | |
| Drain |
MQ |
700 m³ / s |
| Left tributaries | Águeda , Yeltes , Paiva , Távora , Tormes , Adaja | |
| Right tributaries | Corgo , Esla , Valderaduey , Pisuerga , Tâmega , Tua | |
| Big cities | Porto , Vila Nova de Gaia | |
| Medium-sized cities | Soria , Zamora , Aranda de Duero , Peso da Régua | |
|
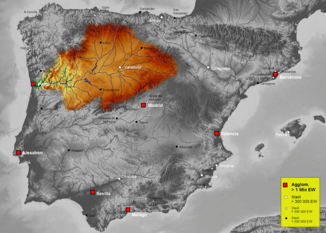
Catchment area of the Duero |
||
The Duero [ 'dweɾo ] ( Portuguese name Douro [ ˈdoɾu ]) is the third longest river on the Iberian Peninsula . It rises in the Spanish province of Soria , flows through northern Spain and northern Portugal and flows into the Atlantic Ocean at Porto . It is about 897 kilometers long.
geography
The Duero rises in the Picos de Urbión in the northern Spanish province of Soria at an altitude of 2080 meters. It flows through the autonomous community of Castile and León along the cities of Soria , Almazán , Aranda de Duero , Tordesillas and Zamora . At 112 km in length it forms the Spanish-Portuguese border , on which the river landscape lies on both sides in protected nature parks: Arribes del Duero and Douro Internacional . From here it flows 213 km in Portugal, passing the cities of Miranda do Douro , Pinhão and Peso da Régua as well as the Alto Douro wine-growing region . The Duero flows into the Atlantic at Porto and Vila Nova de Gaia .
North of its central reaches in Portugal lies the high plateau of the Serra de Aboboreira with the megalithic complex Chã da Parada . In the Neolithic , the entire area north of the Duero, including Galicia, was a single cultural area.
The most important right tributaries in Spain are Esla , Valderaduey and Pisuerga , in Portugal the Tâmega , the Tua and the Corgo coming from Galicia . Left tributaries are Águeda , Yeltes and Tormes . There are also a number of rivers with very little water flow such as the Riaza , the Duratón , the Cega , the Adaja , the Zapardiel , the Guareña and the Trabancos .
Anthropogenic pollution
The exposure to microplastics in the Duero is serious. In one study, more MP particles than fish larvae were found.
history
The ancient name of the Duero was Durius ; Numantia was the most important city on its shore.
In the early phase of the Reconquista up to the dissolution of the Caliphate of Cordoba (1031), the Duero marked the border area between the Christian north of Spain ( Kingdom of Asturias / Kingdom of León ) and al-Andalus in the south. Some still-preserved Moorish watchtowers ( atalayas ) in the Spanish province of Soria and the Peñafiel castle in the north of the province of Valladolid give evidence of this former border .
traffic
Between Porto and Pocinho , the Portuguese railway runs on the Linha do Douro, mostly along the river bank. The international long-distance hiking trail GR 14 Senda del Duero also runs from the source to the mouth .
There is evidence that the Duero was used as a shipping route until the time of the Roman occupation. Today the Duero is almost only navigable in Portuguese territory. From its mouth to the border region at Vega Terrón, it is navigable over 210 kilometers of the river through five locks with vehicles up to 83 m long, up to 11.40 m wide and a draft of up to 3.80 m.
| Surname | Construction year | Duero kilometers | Max. Drop height [m] |
Usable length [m] |
Usable width [m] |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Pocinho lock | 1983 | 180.5 | 22nd | 83 | 11.4 |
| Valeira lock | 1976 | 145 | 33.0 | ||
| Régua lock | 1973 | 105 | 28.5 | ||
| Carrapatelo lock | 1971 | 65 | 35.0 | 87 | |
| Crestuma lock | 1986 | 21.5 | 13.9 | 83 |
economy
Viticulture
From the Spanish-Portuguese border to Mesão Frio , the area around the Duero forms the Alto Douro wine region , the strictly demarcated port wine growing area . In earlier times, the barrels from this region and its historic center Peso da Régua were shipped on boats to the port wine cellars in Vila Nova de Gaia and Porto . Alto Douro was in 1756 the world's first protected wine region in all and since 2001 the World Heritage of UNESCO . In addition to the port wine, the red wines are also important here.
On the Spanish side, near Aranda de Duero, is the Ribera del Duero wine-growing region , where Tempranillo red wine is mainly grown.
Power plants and reservoirs
Looking downstream, the Duero is dammed for the following power plants to form the reservoirs of the same name:
| power plant | operator | Max. Power (MW) |
Reservoir | Surface (km²) |
Volume (million m³) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cuerda del Pozo | Iberdrola | 7th | Cuerda del Pozo | 21.76 | 229 |
| Los Rábanos | Iberdrola | 4th | Los Rábanos | 0.98 | 8th |
| San Jose | 2.2 | San Jose | 1.92 | 5.5 | |
| Villalcampo | Iberdrola | 206 | Villalcampo | 4.45 | 66 |
| Castro | Iberdrola | 190 | Castro | 1.8 | 27 |
| Miranda | EDP | 390 | Miranda | 1.2 | 28 |
| Picote | EDP | 426 | Picote | 63 | |
| Bemposta | EDP | 401 | Bemposta | 4.05 | 129 |
| Aldeadávila | Iberdrola | 1,139 | Aldeadávila | 3.68 | 114.3 |
| Saucelle | Iberdrola | 525 | Saucelle | ||
| Pocinho | EDP | 186 | Pocinho | 8.29 | 83 |
| Valeira | EDP | 216 | Valeira | 7.95 | 97 |
| Régua | EDP | 156 | Régua | 8.5 | 95 |
| Carrapatelo | EDP | 201 | Carrapatelo | 9.52 | 148.4 |
| Crestuma lever | EDP | 108 | Crestuma lever | 12.98 | 110 |
photos
Spanish part of the Duero near Toro
Spanish part of the Duero near Zamora
International part of the Duero, Arribes del Duero Natural Park near Fermoselle (Spain)
International part of the Duero from the dam at Aldeadávila de la Ribera (Spain)
Portuguese part of the Douro near Porto
See also
Web links
Individual evidence
- ↑ SM Rodrigues, C. Marisa R. Almeida, D. Silva, J. Cunha, C. Antunes, V. Freitas, S. Ramos: Microplastic contamination in an urban estuary: Abundance and distribution of microplastics and fish larvae in the Douro estuary . In: Science of The Total Environment. 659, 2019, p. 1071, doi : 10.1016 / j.scitotenv.2018.12.273 .
- ↑ Via Navegável - Introdução. Instituto Portuário e dos Transportes Marítimos, accessed March 9, 2014 (Portuguese).
- ^ Hans-Joachim Uhlemann: Canals and hydraulic structures in Spain and Portugal. (PDF; 1.5MB) Report on a trip through France and Portugal to study shipping canals, lifts and locks from April 24 to May 21, 1995. In: peter haas. 2007, archived from the original on March 9, 2014 ; accessed on March 9, 2014 .
- ↑ Distances et durée de déplacement entre les principaux quais, ports et écluses de navigation de la voie navigable du Douro. (PDF; 88kB) Instituto Portuário e dos Transportes Marítimos, accessed on March 9, 2014 (Portuguese).
- ^ Canal de Navegação. Instituto Portuário e dos Transportes Marítimos, accessed March 9, 2014 (Portuguese).