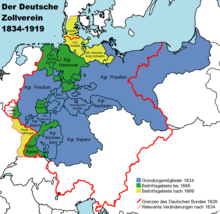
Territory of the German Customs Union
In 1834, the territory of the German Customs Union consisted of the founding states and the smaller countries and enclaves that had already been affiliated to them. Other states were added later.
Customs areas of the Zollverein on January 1, 1834
- Prussia with its affiliated states and enclaves - Anhalt-Bernburg (since June 17, 1826), Anhalt-Dessau (since July 17, 1828), Anhalt-Köthen (since July 17, 1828), Waldeck (since April 16, 1831 ), enclaved areas of Schwarzburg-Sondershausen (since October 25, 1819), enclave areas of Schwarzburg-Rudolstadt (since June 24, 1822), enclave Allstedt (to Sachsen-Weimar ) (since June 27, 1823), enclave of Oldisleben (to Sachsen-Weimar) (since June 27, 1823), enclave Rossow (in Mecklenburg-Schwerin ) (since December 2, 1826), enclave Netzeband (in Mecklenburg-Schwerin) (since December 2, 1826), enclave Schönberg (in Mecklenburg- Schwerin) (since December 2, 1826), Enclave Volkenroda (to Saxe-Coburg and Gotha ) (since July 4, 1829), Enclave Oberamt Meisenheim (to Hesse-Homburg ) (since December 31, 1829), Enclave of Principality of Birkenfeld (to Oldenburg ) (since July 24, 1830)
- Grand Duchy of Hesse (since February 14, 1828 with the Prussian-Hessian Customs Association )
- Electorate of Hesse (since July 25, 1831 with the Prussian-Hessian Customs Association ) without the Grafschaft Schaumburg (Hesse-Kassel had been a member of the Central German Trade Association since 1828)
- Bavaria (since January 18, 1828 with the Süddeutschen Zollverein) with the attached enclave Amt Königsberg (to Saxe-Coburg and Gotha ) (since June 14, 1831)
- Württemberg (since January 18, 1828 with the Süddeutschen Zollverein) with the affiliated states - Hohenzollern-Sigmaringen (since July 28, 1824), Hohenzollern-Hechingen (since July 28, 1824)
- Saxony (through membership treaty dated March 30, 1833) (Saxony had been a member of the Central German Trade Association since 1828)
- Customs and Trade Association of the Thuringian States (through accession treaty of May 11, 1833), i.e. Saxe-Weimar-Eisenach , Saxe-Coburg and Gotha , Saxe-Meiningen , Saxe-Altenburg , Schwarzburg-Rudolstadt (without their enclaved areas; see Prussia) , Schwarzburg-Sondershausen (without their enclaved areas; see Prussia), Reuss-Greiz , Reuss-Schleiz , Reuss-Lobenstein-Ebersdorf , Schmalkalden district (in Hesse-Kassel ) (since May 10, 1833), Erfurt city and district ( zu Prussia) (since May 10, 1833) (The Thuringian states had been a member of the Central German Trade Association since 1828)
Acceding States and Territories after January 1, 1834
- Hessen-Homburg (by treaty of February 20, 1835) (the Oberamt Homburg was assigned to the customs area of the Grand Duchy of Hesse and the Oberamt Meisenheim to the customs area of Prussia; Hessen-Homburg was therefore only an indirect member of the Zollverein) (Hessen-Homburg was already since 1828 member of the Central German Trade Association)
- Baden (by contract of May 12, 1835) (part of the Klettgau (including the municipality of Büsingen am Hochrhein ) remained outside the customs area of the Zollverein (see Article 6 of the Zollverein contract of July 8, 1867))
- Nassau (by treaty of December 10, 1835) (Nassau had been a member of the Central German Trade Association since 1828)
- Frankfurt am Main (by contract dated January 2, 1836) (Frankfurt am Main had been a member of the Central German Trade Association since 1828)
- Lippe-Detmold (by contract of October 18, 1841) (the national territory was assigned to the customs territory of Prussia, so that Lippe-Detmold was only an indirect member of the customs association) (Lippe-Detmold had been a member of the Central German Trade Association since 1828)
- Braunschweig (by contract of October 19, 1841) (Braunschweig had been a member of the Central German Trade Association since 1828)
- Grafschaft Schaumburg (part of Hessen-Kassel ) (by contract of November 13, 1841) (The county had been part of the Central German Trade Association since 1828)
- Hanover (by contract of September 7, 1851, came into force on January 1, 1854) (Hanover had been a main member of the Central German Trade Association since 1828; the Central German Trade Association expired when it joined the German Customs Union)
- Schaumburg-Lippe (Schaumburg-Lippe had been part of the Hanover customs area since 1828 ; with this it became part of the German Customs Union)
- Oldenburg (by treaty of March 1, 1852, in force since January 1, 1854) excluding the Principality of Lübeck and the Principality of Birkenfeld (which, however, was assigned to the Prussian customs area) (Oldenburg had been a member of the Central German Trade Association since 1828)
- Luxembourg (by treaty of February 8, 1842) (Luxembourg belonged to the Zollverein as an "ordinary" member until 1867, but since then as a special member until 1919, as Luxembourg was not a party to the treaty of July 8, 1867; The treaties under which Luxembourg was a member of the Customs Union were the treaty of the Customs Union states with Luxembourg of February 8, 1842 (duration: April 1, 1842 to March 31, 1846), the extension agreements of April 2, 1847 (term of April 1, 1846 to December 31, 1853) and December 26/31, 1853 (term: January 1, 1854 to December 31, 1877) According to Article 40 of the Treaty of Versailles , Luxembourg was withdrawn set by the Zollverein on January 1, 1919)
- Alsace-Lorraine (through the Peace of Frankfurt of May 10, 1871)
Acceding Hanseatic cities
- Hanseatic City of Lübeck (by treaty of 1868)
- Hanseatic City of Hamburg (by treaty of 1881, entered into force in 1888)
- Hanseatic City of Bremen (by treaty of 1884, entered into force in 1888)
Areas of the German Confederation outside of the customs union
- Mecklenburg-Strelitz
- Mecklenburg-Schwerin
- the Austro-Prussian condominium Schleswig-Holstein (1864–1866)
- Liechtenstein
- the Principality of Lübeck belonging to Oldenburg (within Schleswig-Holstein)
- Austria (later with the exception of the Austrian municipality of Jungholz and the Austrian Kleinwalsertal )
Special regulations
According to Article 33 of the constitution of the North German Confederation of July 1, 1867, the North German Confederation became a unified customs and trading area. Areas that are actually attached to the Zollverein (implemented by federal law in 1868):
- Mecklenburg-Strelitz
- Mecklenburg-Schwerin
- Schleswig-Holstein, now part of Prussia
- the Principality of Lübeck, which belongs to Oldenburg
Customs connection areas (with the status of customs connection areas, the following areas were economically connected to Germany):
- the Austrian community of Jungholz (with the customs treaty of May 3, 1868)
- the Austrian Kleinwalsertal (with the customs treaty of 1891, which was valid until modern times.)
The following remained outside the customs area:
- the Hanseatic city of Hamburg
- the Hanseatic city of Bremen
- the Hanseatic city of Lübeck
- Liechtenstein
- Austria (with the exception of the Austrian municipality of Jungholz and the Austrian Kleinwalsertal )
By Article 6 of the Customs Union Treaty of July 8, 1867, the provisions in Articles 3, 4 and 5, as well as in Articles 10 to 20 and 22 of the Customs Union Treaty of July 8, 1867 (provisionally) did not apply to:
- the following states and territories of the North German Confederation, namely:
- in Prussia - the locality Drenikow , the locality Porep , the locality Suckow , the Colonie and the leasehold Vorwerk Groß-Menow , the manors and villages Zettemin (with Peenwerder ), Duckow , Rottmannshagen , Rützenfelde , Karlsruh , Pinnow , the port of Geestemünde , the Fort William in Bremerhaven , the Elbinsel Altenwerder that Elbinsel Krusenbusch , the Elbe island of Finkenwerder , the Elbe island of Finkenwerder flowers sand that Elbinsel Kattwieck that Elbinsel High Schaar , the Elbinsel Over hoes that Elbinsel Neuhof , the Elbe island Wilhelmsburg that Voigtei Kirchwerder , the village community Aumund
- the Grand Duchy of Mecklenburg-Schwerin , with the exception of its areas enclosed by Prussia - Rossow , Netzeband , Schönberg
- the Grand Duchy of Mecklenburg-Strelitz
- in Oldenburg the port of Brake
- the Duchy of Lauenburg
- the Hanseatic City of Lübeck with a district of its or the surrounding area corresponding to the purpose
- the Hanseatic City of Bremen with a district of its or the surrounding area corresponding to the purpose
- the Hanseatic City of Hamburg with a district of its or the surrounding area with Altona, corresponding to the purpose
- the following parts of Baden , namely the island of Reichenau , the place Büsingen , the Büttenharter Hof , the places and courtyards Jestetten (with Flachshof , Gunzenrieder-Hof , Reutehof ), Lottstetten (with Balm, Dietenberg , Nack , Locherhof , Volkenbach ), Dettighofen (with a courtyard , Altenburg (Jestetten) , Baltersweil , Berwangen , Albführerhof near Weisweil )
See also
Web links
- Deutscher Zollverein on HGIS Germany
- Customs Union Agreement (with information on territorial development)
Individual evidence
- ^ Cf. Hahn, Hans-Werner: History of the German Customs Union. Göttingen 1984. p. 195.