Anjou
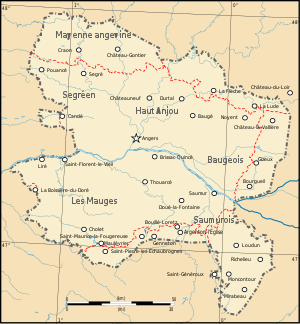
Anjou is the name of a historical province in France with the capital Angers . The region is located in the lower Loire Valley and is now primarily known as a wine-growing region . In terms of its extent, it corresponds essentially to the present-day Maine-et-Loire department and the northern part of the Vienne department (8975 km²).
The coat of arms of the province corresponds to that of the Dukes of Anjou from the House of Anjou-Valois .
history
coat of arms
Description: Blue with red board three golden lilies .
Ancient and early Middle Ages
The region of the later Anjou was originally inhabited by the Celtic tribe of the Andecavers , who were subjected to the Roman Empire during the Gallic War (58 to 50 BC) of the Roman politician Gaius Iulius Caesar . After the division of Gaul by Emperor Augustus in 17 AD, Anjou belonged to the province of Gallia Lugdunensis .
After the fall of the Roman Empire during the Migration Period , the area of Anjous, north of the Loire, was under the rule of Syagrius , while the area on the south bank belonged to the Visigothic Empire . The Frankish king Clovis I successively defeated Syagrius in the Battle of Soissons (486) and the Visigoths in the Battle of Vouillé (507), after which the Anjou was incorporated into the Frankish Empire . Due to the frequent division of rule of the Merovingians , it belonged to the part of Neustria and, after the division of the empire under the Carolingian dynasty in the Treaty of Verdun (843), to western France .
High Middle Ages
The county of Anjou
After Angers had been plundered by the Normans in 845 and 852 , King Charles II the Bald set up the Neustrian mark and subordinated this to Robert the Strong, the progenitor of the Robertines . Robert fell in the Battle of Brissarthe in 866 and his sons Odo and Robert ascended to the West Frankish throne in the following years, in competition with the Carolingians. Robert's son, Duke Hugo the Great , appointed vice counts as deputies to better manage his territories, for example in Angers Ingelger , who became the founder of the first house of Anjou . His son Fulko I the Red took on the title of Count on his own initiative, which was recognized by Duke Hugo around 930.
Spatially was the Anjou in the west of the counties of Nantes and Rennes which the Duchy of Brittany were, in the north of the county of Maine , in the east of the county Tours ( Touraine ) and in the south of the county Poitou , which a part of Duchy of Aquitaine was , surround.
After the central power of the kings was pushed back more and more to the Île-de-France after the ascension to the throne in 987 of the first Capetian Hugo Capet , whom the Counts of Anjou supported, the House of Anjou rose to a dominant power in western France. Count Fulko III. Nerra defeated the Bretons in the second Battle of Conquereuil in 992 and extended his influence through extensive castle building to Brittany, Touraine and Maine. All castles were made of stone, which was a special feature at the time. In the Battle of Pontlevoy in 1016 he was able to repel an advance of the rival House of Blois . Gottfried II Martel expanded the county in 1033 after defeating the Duke of Aquitaine to include Montcontour , Mirebeau and Loudun . He gained a foothold in the Saintonge and defeated the Counts of Blois again in 1044 in the Battle of Nouy , whereby the County of Tours could be won for Anjou.
With Count Gottfried III. the bearded man was followed in 1060 by the second house ( house Château-Landon ) in the county of Anjou. Gottfried III. was ousted in 1068 by his brother Fulko IV the grouchy . His son Fulk V the Younger won the conflict over control of Maine against the Dukes of Normandy in 1109 . In his later years Fulk V moved to the holy land, where he rose to King of Jerusalem by marriage and founded an Anjou dynasty there, which ruled until 1205.
The "Angevin Empire"
Fulko left his estates to his eldest son Gottfried V the fair . This had the habit of wearing a branch of gorse (Latin: planta genesta ) as a crest , and was therefore called Plantagenêt . This designation continued under his descendants as a dynasty name, who moved under these names into the center of medieval history in Europe.
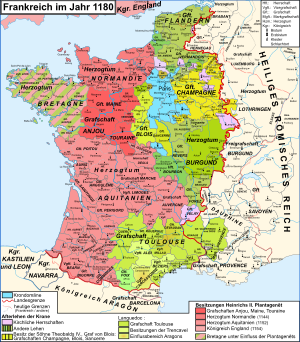
Gottfried stood by his marriage to the heir to the Anglo-Norman kingdom Mathilde at the beginning of as in modern research " Angevin Empire " ( Empire of Anjou ) designated countries accumulation of this dynasty, which became a major power in the Western Europe. In the fight against Mathilde's opponent Stephan von Blois , Gottfried subjugated Normandy in 1144. Both son Heinrich expanded the property of his family in 1152 by marrying the Duchess Eleanor of Aquitaine , who brought the duchies of Aquitaine and Gascony into the marriage. After the death of Stephen of Blois in 1154, he succeeded Henry II as King of England , with which the Plantagenets' sphere of influence extended from the Pyrenees to the southern border of Scotland .
It should be noted that this “Angevin Empire” was neither an English Empire nor a self-contained state structure. The continental possessions of the Plantagenets were fiefs of the French kingdom, hence the Plantagenets vassals of the French king for these areas . So worshiped as Henry II. In 1156. King Louis VII. , The ex-husband of his wife, for the areas concerned. Still, the aim of the French kings was to limit the power of the Plantagenets. King Philip II knew how to take advantage of their internal family conflict, in which the sons rose up against their father Henry II several times, sometimes encouraged and supported by their mother Eleanor of Aquitaine. When their son Richard, at the instigation of his mother, also paid homage to King Philip II for Anjou in November 1188, he triggered another conflict with his father Heinrich II. In the Treaty of Azay-le-Rideau (July 1189), the beleaguered Heinrich had to recognize the French king as feudal lord again and cede several areas to him.
In May 1194, King Philip II opened a war against Richard (I) "Lionheart", who had meanwhile become king, aiming to seize its territories, but Richard was able to repel this offensive with victories at Fréteval (1194) and Gisors (1198) and force Philip to a humiliating peace. However, Richard's death in April 1199 was to herald the end of the "Angevin Empire".
Richard's successor, Johann Ohneland , was able to prevent King Philip II from re-accessing the Plantagenet empire by taking the feudal oath for all continental holdings of the Plantagenets on the French king in May 1200. But a few months later Johann married the Aquitaine noblewoman Isabella of Angoulême . Their first fiancé Hugo X. von Lusignan sued the English king with his liege lord, the French king, of kidnapping the bride and thus gave King Philip the opportunity to initiate a court case against Johann. After Johann failed to comply with several subpoenas before this tribunal, a default judgment was passed on him, in which he was declared forfeited all of his land holdings. In June 1202, King Philip began to execute the sentence and marched with an army into the Touraine and then into the Anjou. His protege, Duke Arthur I of Brittany, besieged his own grandmother Eleanor of Aquitaine in the castle of Mirebeau in July of that year, Johann freed his mother by defeating the siege army and being able to imprison his nephew. When Arthur died in captivity a year later, most of John's vassals fell away from him and submitted to King Philip. In October 1206 Johann renounced all areas north of the Loire in an armistice.
The struggle was to continue when the German King Philip of Swabia was murdered in 1208 . Then Johann's nephew Otto von Braunschweig was able to assert himself as sole king, from 1209 emperor, in Germany. Both then entered into an alliance against France. In the spring of 1214 Johann invaded the Anjou with an army with the aim of retaking it from his home. The royal seneschal of Anjou Guillaume des Roches , who was once a follower of Richard the Lionheart, holed up in the castle of Roche-aux-Moines (now Savennières ), which Johann immediately besieged. On July 2nd, Prince Ludwig VIII appeared with an army in front of the castle and after a brief skirmish put Johann to flight, a few days later Ludwig's father defeated the emperor's army in the battle of Bouvines . Johann Ohneland then renounced the Loire regions again in a contract concluded on Chinon . The “Angevin Empire” came to an end. The Plantagenets remained in the possession of the English crown until 1485 and should also hold some areas in France, but the Anjou was incorporated into the crown domain .
Anjou-Capet
The Anjou was now ruled directly by the crown until King Louis IX. enfeoffed his younger brother Prince Karl I with the county in 1246. Louis IX thus complied with the will of his father, King Ludwig VIII. Charles I of Anjou was considered a ruthless power man and was one of the most powerful men in Europe of his time. In 1266 he ended the rule of the Hohenstaufen in southern Italy, whose kingdom of Sicily he took over. There, Charles founded the Capetian sidelines of the Anjou , which ruled Naples until 1435 . Furthermore, the Hungarian kings descended from him from 1301 to 1386. The county of Anjou itself was not to remain with the dynasty for long.
Late Middle Ages
Anjou-Valois
On the occasion of the wedding of Marguerite d'Anjou , the daughter of Charles II of Naples , to the French prince Charles of Valois in 1290, the Anjou was given to her as a dowry in the marriage. In 1297 the county was given the dignity of a pair . Both son climbed in 1328 as Philip VI. the French royal throne and founded the Valois dynasty . The Anjou was also reunited with the crown domain. King Johann II apanaged his second son Ludwig I with the Anjou in 1360 , which he also upgraded to a duchy. Just like the previous Anjous, the Valois sideline of Anjou , founded by Ludwig, was involved in southern Italy after it was adopted by Queen Joan I of Naples in 1380 and recognized as their overall heir. Of Ludwig's descendants, however, only "the good king" ( le bon roi ) René briefly ascended the royal throne of Naples. After the death of the last Duke Charles IV. In 1481, King Ludwig XI. the Anjou returned to the crown domain as a settled fiefdom. The title of Duke of Anjou was bestowed on various royal princes in the further course of the French monarchy.
Anjou was the scene of the Hundred Years' War during the Valois Dukes . After the invasion of northern France by Henry V of England , the army of Dauphin Charles VII defeated the English in March 1421, together with Scottish troops in the Battle of Baugé . The Anjou was spared a longer English occupation.
Modern times
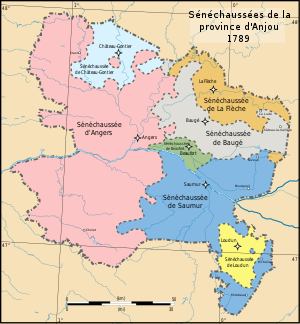
When King Philip II, after his victory over the Plantagenets, who added Anjou to the crown domain for the first time, the royal authority in this region was represented by a Seneschal ( Sénéchal ) who had his seat in Angers. Over time, several sub - seneschallates ( Sénéchaussées secondaires ) in Baugé , Beaufort , Château-Gontier and La Flèche were subordinated to the Seneschal in Angers, who now assumed the function of senior seneschall ( Sénéchaussée principales ). King Francis I also set up seneschallates in Loudun and Saumur around 1544 . The three administrative units were grouped together with the Seneschalates of Touraine and Maine in the Généralité of Tours since 1542.
During the wars of religion in the 16th century, the Anjou belonged mainly to the Catholic League. The Duke of Anjou (later King Henry III ) conquered Loudun, which was held by the Protestant Huguenots , in 1568 and defeated them, under the Amiral de Coligny , in October 1569 in the battle of Montcontour . Two days after St. Bartholomew's Night in Paris (August 24, 1572), several Huguenots fell victim to the massacres in Angers. In the Edict of Nantes issued in 1598, King Henry IV assigned the Huguenots the city of Saumur as a safety place ( places de sûreté ), where they founded one of their most important academies.
During the Estates General convened in 1789 , the Anjou was represented by 24 deputies, 16 for Angers and 4 each for Saumur and Loudun. After the outbreak of the French Revolution (July 1789), the provinces of France were replaced by départements by resolution of the National Assembly in 1790. Most of the Anjou was incorporated into the Mayenne-et-Loire department, which was later renamed the Maine-et-Loire department . The Seneschalate of Loudun and the land around Mirebeau and Montcontour were assigned to the Vienne department, where this area has since formed the western half of the Châtellerault arrondissement . The city of Richelieu came to the Indre-et-Loire department , Craon and Château-Gontier to the Mayenne department and La Flèche to the Sarthe department .
additional
- The Lorraine cross is also called the Croix d'Anjou in France . This symbol was the seal of the Valois Dukes of Anjou, who ruled Lorraine from 1431 to 1473 .