Australasian Mediterranean
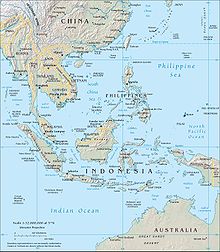
The Australasian Mediterranean, which is up to 7440 m deep, is a western Mediterranean of the Pacific Ocean . With an area of 9.08 million km² , the Australasian Mediterranean is the world 's largest sea that is not an ocean .
geography
The Australasian Mediterranean, which is part of the intercontinental Mediterranean , is located in the Australasian region between Southeast Asia and Australia .
In contrast to the American Mediterranean - but above all to the European Mediterranean - the Australasian Mediterranean is the least separated from the ocean by continents . While it is well separated from the Indic by the Malay Peninsula and the dense Sunda Islands , the archipelagos and chains that separate the Mediterranean from the Pacific are much wider.
It consists among others in the Arafura Sea , to which the Gulf of Carpentaria heard the Banda Sea , the Celebes Sea , the Java Sea , the Molukka , the Ceram Sea , the South China Sea when the Gulf of Thailand and the Gulf of Tonkin include the Sulu Sea and the Timor Sea , to which the Joseph Bonaparte Gulf belongs; Arafura and Timor Seas , the latter Gulf and the previously mentioned Gulf of Carpentaria are the southernmost areas of the Australasian Mediterranean Sea.
The Australasian Mediterranean borders or includes these states: Brunei , the People's Republic of China , Indonesia , Cambodia , Malaysia , the Philippines , Thailand and Vietnam ; these are all countries that come into contact with the South China Sea (a tributary of the Pacific that is integrated into the Australasian Mediterranean ) and its marginal seas . It also borders northern Australia and the extreme southwest of Papua New Guinea . Furthermore, Singapore and East Timor lie within this Mediterranean Sea.
In addition to the numerous large and small islands and island groups / chains as well as islets of the Malay Archipelago (e.g. Great Sunda Islands , Lesser Sunda Islands , Moluccas and Philippines Islands), Groote also belongs to this extensive Mediterranean Sea, which is counted among the oceanic tributaries Eylandt , Melville Island, and Taiwan .
Between these islands, island groups and chains the Australasian Mediterranean is among others on the Lombok- and Malacca Straits or via the Singapore Strait to the Indian Ocean , respectively. The Luzon Strait and Formosa Strait and other straits connect to the Pacific .
Data
The Australasian Mediterranean Sea covered with numerous part seas 9,080,000 sq km area . Its deepest point is 7,440 m below sea level (for this and for further data, see below under sea floor).
Seabed
Within the Australasian Mediterranean Sea or on its sea floor there are thresholds , deep-sea basins and a sea depression :
To the deep sea basins includes the to 3,680 m deep Arubecken that in the Arafura is that up to 4,972 m deep Bacanbecken, the South East of the Molukka represents that to 5,801 m deep Banda pool, the in Banda is that up to 5,318 m deep Burubecken in the Ceram sea , which until 6218 m deep Celebesbecken in the Celebes sea , which until 6961 m deep Flore pool in the Flores sea , which until 3497 m deep Sawubecken in the Savu sea , which until 5559 m deep South China basin in the South China sea and to 7,022 meters deep Sulu Basin in the Sulu Sea . The sea depth is 7,440 m deep Weber depth , which lies in the far eastern part of the Banda Sea and is the lowest point in the Australasian Mediterranean.
Back seas, golfs and straits
Side or partial seas , golfs and / or major straits of the Australasian Mediterranean are:
- Arafura lake
- Bali Sea
- Banda Lake
- Celebes Sea
- Lake Flores
- Java lake
- Halmahera Lake
- Johorstrasse
- Lombok Street
- Luzonstrasse
- Makassar Street
- Malakka Street
- Moluccan Sea
- Sawusee (Savusee)
- Seramsee
- South China Sea
- Singapore Strait
- Formosa Street
- Sawu Lake
- Sulu Lake
- Sunda Street
- Timor Sea
Archipelagos and islands
The largest archipelagos , islands and peninsulas in the Australasian Mediterranean are:
- Bathurst Island
- Dongsha Islands
- Groote Eylandt
- Hainan
- Indochinese Peninsula ; u. a .:
-
Malay Peninsula ; u. a .:
- Samui Archipelago; u. a .:
- Tioman
- Melville Island
-
Moluccas :
- Northern Moluccas ; u. a .:
- Southern Moluccas ; u. a .:
- New Guinea (the south and west of the island)
- Paracel Islands
- Philippines ; u. a .:
- Riau Islands ; u. a .:
- Sangihe Islands
- Spratly Islands
- Sunda Islands :
- Taiwan
- Talaud Islands
States and Dependent Territories
States delimiting or lying within the Australasian Mediterranean Sea and areas dependent on other states are: