Álava
|
Álava Basque Country Autonomous Community , Spain |
|
|---|---|
 coat of arms |
 flag |
| Designations | |
| Spanish name : | Álava |
| Basque name : | Araba |
| Basic data | |
| Autonomous Community : | Basque Country Autonomous Community |
| Capital : | Vitoria-Gasteiz |
| Official languages : | Spanish , Basque |
| Area : | 3,032 km² |
| Residents : | 331,549 (Jan 1, 2019) |
| Population density : | 109.35 inhabitants / km² |
| ISO 3166-2 : | ES-VI |
| Website : | www.alava.net |
| Location of the province of Álava | |

Álava ( Basque Araba ) is the southernmost of the three provinces of the autonomous community of the Basque Country in Spain . Álava has an area of 3,032.4 km² and 331,549 inhabitants (as of 2019). The capital is Vitoria-Gasteiz . In the center of the province is the approx. 260 km² Burgalesian exclave Condado de Treviño .
geography
Álava borders the Basque provinces of Vizcaya and Guipúzcoa in the north, the province of Burgos ( Castile-León ) in the west, the Rioja region in the south and Navarre in the east .
Álava stretches from the Cantabrian Mountains in the north to the Ebro Valley in the south. The province's rainy climate (between 850 and 1300 mm / year) represents a transition from the maritime climate of the Atlantic coast in the north to the continental climate of the Castilian plateau in the south. Within Álava, therefore, very different ecosystems can be found in a small area . The northern valleys (e.g. the Nervión Valley or the Aramaio Valley ) are characterized by green pastures and deciduous forests (especially beech ), the central areas of the Llanada Alavesa (plateau of Álava) and Treviño are already much drier The climate of the Ebro Basin with the neighboring province of La Rioja is already continental throughout.
Álava is traversed by the foothills of the Cantabrian Mountains , the mountain ranges of which usually run from east to west and often represent weather divisions . The highest point in the province is Mount Gorbea at 1.48 m . The area is generally hilly to mountainous, the official register of the Basque Mountains counts 127 peaks between 600 m and 1,480 m for Álava. The central area in Álava is the Llanada Alavesa plateau , which is about 550 m above sea level.
The main river in the province is the Ebro , which forms the southern border of the Basque Country. The Zadorra river crosses the Álava plateau, grazes the capital Vitoria and flows into the Ebro at Miranda de Ebro. Other important rivers in the province are the Nervión and the Bayas .
history
One of the main connections between the Iberian Peninsula and the rest of the European continent has run through Álava since the Stone Age . The Alava dolmens are evidence of the early settlement of the area . In ancient times , the Romans settled the area of today's province, the evidence of which is the settlement Iruña-Veleia in the Llanada Alavesa around 8 km southwest of today's city of Vitoria. With the fall of the Roman Empire, the Suebi , Alans , Vandals and Visigoths left their mark on Álava during the Great Migration .
From the 8th to the 10th century, the Moors temporarily ruled the Basque province. The Muslim historian Ibn al-Athir reports that Alava and the fortresses there were conquered, sacked and partially depopulated by the Moors under Abd ar-Rahman II , Lord of Andalusia , in 838 . From the 9th century the princes of Castile and Navarre gained influence and eventually ousted the Moors ( reconquista ) . From the 10th century on, Álava belonged alternately to the kingdoms of Castile and Navarre , but Navarre lost strength over time, so that the province finally fell to Castile in 1332.
Despite belonging to Castile and thus later to Spain , Álava was able to maintain a number of special rights ( span. Fueros ) until the 19th century . These special rights continue to exist to this day in the rights of the autonomous regions of the Basque Country and Navarre .
In the years 870 to 1088 Alava, where the Mozarabic rite was predominant, was the seat of a bishop. The Mozarabic rite was banned by Pope Gregory VII in 1074 and at a council in Burgos (1080) the Roman rite was declared binding for all of Spain.
population
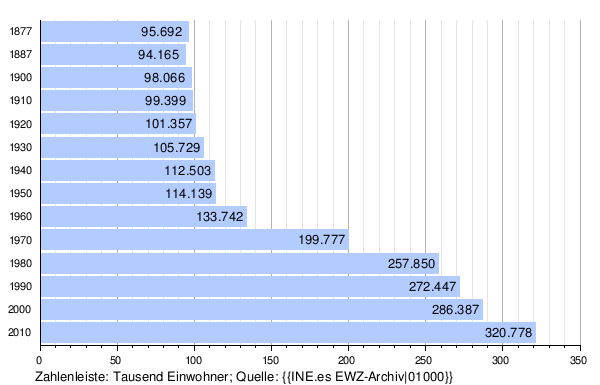
Population development of the province
Places and communities
The capital and only major city of the province with 251,774 inhabitants (as of 2019) is Vitoria-Gasteiz , where over 75% of the population of Álava is based. Vitoria is also the capital of the Basque Country . In addition to Vitoria, the places Llodio , Amurrio and Salvatierra are important in Álava .
- Largest communities
| local community | Spanish name | Residents (January 1, 2019) |
|---|---|---|
| Gasteiz | Vitoria | 251,774 |
| Laudio | Llodio | 18.102 |
| Amurrio | Amurrio | 10,350 |
| Agurain | Salvatierra | 5,062 |
| Oion | Oyón | 3,386 |
| Iruña-Oka | Iruña de Oca | 3,411 |
| Aiara | Ayala | 2,974 |
| Dulantzi | Alegría | 2,876 |
| Zuia | Zuya | 2,302 |
language
In contrast to the two Basque provinces of Vizcaya and Guipúzcoa, the population of Álava is largely Spanish-speaking. Basque is spoken mainly in the Aramaio valley and occasionally in Legutiano , but also in the capital Vitoria by some immigrants, due to the Basque government and the university. In 2001, 93.6% of the population of Álava reported Spanish as their first language, 1.9% Basque and 3.5% Spanish and Basque.
Administrative division
The administrative districts of Álava, otherwise known as comarcas in Spain , are called in Álava Cuadrillas . Álava is divided into seven cuadrillas :
Enclave of the Condado de Treviño
In addition to the aforementioned Cuadrillas , the enclave Condado de Treviño is located in the middle of the province of Álava , which for historical reasons belongs to the Castilian province of Burgos . The Condado de Treviño is the object of a political dispute between the autonomous regions of Castile-León and Basque Country , both of which claim the enclave for themselves. Many residents of the Condado de Treviño are more inclined to belong to the Basque Country, albeit largely for practical reasons because of the close proximity to the city of Vitoria.
Web links
- Alavanet ( Memento of December 18, 2008 in the Internet Archive ) (Spanish, Basque, English)
Individual evidence
- ↑ Cifras oficiales de población resultantes de la revisión del Padrón municipal a 1 de enero . Population statistics from the Instituto Nacional de Estadística (population update).
- ↑ Cifras oficiales de población resultantes de la revisión del Padrón municipal a 1 de enero . Population statistics from the Instituto Nacional de Estadística (population update).
- ↑ Eustat (Basque Institute for Statistics): Euskadi en cifras - Cultura y Euskera ( Memento of October 1, 2006 in the Internet Archive )



