Ulyanovsk
| city
Ulyanovsk
Ульяновск
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| List of cities in Russia | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Ulyanovsk ( Russian Улья́новск ; until 1924 Simbirsk , Russian Симби́рск ) is a major Russian city on the Volga with 614,786 inhabitants (as of October 14, 2010) and the capital of the Ulyanovsk region .
geography
Ulyanovsk is located in the central part of European Russia and extends on both sides of the Kuibyshev reservoir of the Volga, with the greater part of the population in terms of population on the right bank. The distance to Moscow is almost 700 kilometers to the west. The nearest town is Novouljanowsk (literally "New Ulyanovsk") about 20 km south of Ulyanovsk.
City structure
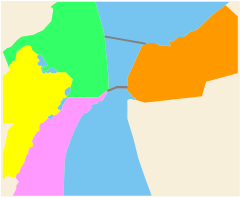
Ulyanovsk is administratively divided into four districts (so-called Rajons ) (population figures as of 2009):
- Leninsky (Ленинский, "Lenin Raion") - 100,942 inhabitants
- Saswijaschski (Засвияжский, "behind the Swijaga") - 213,193 inhabitants
- Zavolzhsky (Заволжский, "behind the Volga") - 214,406 inhabitants
- Zheleznodorozhny (Железнодорожный, "Railway Rajon") - 75,241 inhabitants
climate
| Ulyanovsk | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Climate diagram | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
Average monthly temperatures and rainfall for Ulyanovsk
Source: Roshydromet
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
history

Today's Ulyanovsk was founded in 1648. Originally the place was called Simbirsk (initially Sinbirsk , according to some hypotheses derived from a Tatar fortress called Sinbar that existed at the time of the Golden Horde ) and served as a military base for the Russian tsarism on its eastern borders. At that time, Simbirsk was laid out as a fortress modeled on the old Russian Kremlin . In 1670 the fortress was able to withstand an attack by the rebellious farmers around Stenka Razin . However, it later lost this importance and developed as a normal provincial settlement. In the 18th century Simbirsk was subordinate to the governorates of Kazan and Astrakhan until it was given city status in 1796 and became the center of the new Simbirsk governorate .
In the course of the 19th century, the city developed into an important trading metropolis and one of the richest cities in the Russian Empire , thanks in part to its location on the Volga . During this period, numerous public facilities and architecturally sophisticated buildings were built here, a number of which have survived to this day. In 1898 Simbirsk received a railway connection for the first time and in 1913 a power station. The Volga Bridge was completed in 1916, which in the following decades led to the expansion of the city to the left bank of the river.
This was followed by the October Revolution in 1917 and the civil war in which communists occupied the city. On July 21, 1918, the city was conquered by the White Guards with the support of the Czechoslovak legions . It was not until September 12, 1918 that the Red Army, under the leadership of G. Gai , succeeded in regaining power over the city.
In 1924 Simbirsk was renamed Ulyanovsk in honor of the recently deceased revolutionary leader Vladimir Ilyich Ulyanov ( Lenin ), who was born here in 1870 . The city kept this name even after the end of the Soviet era . In the city there was a POW camp 215 for German POWs of the Second World War .
Population development
| year | Residents |
|---|---|
| 1897 | 41,684 |
| 1939 | 103.779 |
| 1959 | 205,942 |
| 1970 | 351.085 |
| 1979 | 463.964 |
| 1989 | 625.155 |
| 2002 | 635.947 |
| 2010 | 613.786 |
Note: census data
economy
Ulyanovsk is now an important industrial center, especially with the UAZ automobile plant , the aircraft manufacturer Aviastar-SP (known, among other things, for the Antonov An-124 transport aircraft , which are built in 532 m long and 36 m wide final assembly halls) and the armaments factory Ulyanovsky Mechanichesky Sawod . There are also other machine and equipment manufacturing companies in the city. In addition, Ulyanovsk is the headquarters of the airline Volga-Dnepr Airlines .
In 2014, the Schaeffler Group opened a production plant in Ulyanovsk, where, among other things, couplings, components for engines and tapered roller bearing units are manufactured. In 2015 DMG Mori Aktiengesellschaft opened a factory for turning and milling machines that works extensively with local suppliers.
traffic
The two banks of the Volga are connected in Ulyanovsk by the bridge, which was completed in 1916, but which is now considered to be congested. A new bridge for automobile and rail traffic has been built and is open to traffic. The construction of the bridge was interrupted for ten years due to lack of funds. The unfinished bridge, which did not come close to either of the two Volgaufers, was the backdrop for the 2003 music video for the song Nitschja by the singing duo Nitschja of the same name . Urban public transport in Ulyanovsk is relatively well developed with its own tram (on the western bank of the Volga) and trolleybus network (on the eastern bank). There are also plans for a light rail system that will also connect the two sides of the Volga.
Ulyanovsk has a long-distance train station, the international airport Ulyanovsk-Vostochny , the regional airport Zentralny (also called Baratajewka ) and an inland port on the Volga. Ulyanovsk is connected to the Russian capital Moscow via a branch of the federal trunk road M5 . The highways R178 , which connects the city with Saransk , and R241 , which leads to Kazan , end here.
Further educational institutions
- Branch of the International Slavonic University of G.R. Derschawin (of the institute)
- Branch of the military academy for stage and transport
- Branch of the Military University of Telecommunications
- Branch of the A. S. Gribojedow Institute for International Law and Economics
- Higher military engineering school
- Agricultural Academy Ulyanovsk
- Aviation University of Civil Aviation Ulyanovsk
- Ulyanovsk Economic Institute of Samara State Economic Academy
- Ulyanovsk State Pedagogical University
- Ulyanovsk State Technical University
- Ulyanovsk State University
Sports
The 36th World Bandy Championship took place in Ulyanovsk and Dimitrovgrad in 2016 . The bandy club HK Volga Ulyanovsk takes part in the game operations of the Super League .
Ulyanovsk is home to the FK Volga Ulyanovsk football club , which represents the city in the third highest Russian league .
military
The 31st Air Assault Brigade of the Russian Airborne Forces is stationed in Ulyanovsk . The Ulyanovsk Garden Suvorov Military School is located in Ulyanovsk , where boys from 5th to 11th grade study. This school is the only one in Russia that is run by the airborne troops.
Town twinning
Ulyanovsk has maintained a partnership with the North Rhine-Westphalian city of Krefeld since 1993 .
sons and daughters of the town
- Yusuf Akçura (1876–1935), ideologue of Pan-Turkism
- Platon Beketow (1761–1836), publisher
- Lyudmila Belousova (1935-2017), figure skater
- Nikolai Bryukhanov (1878–1938), politician
- Yuri Fyodorov (born 1949), ice hockey player
- Harry Flosser (* 1967), animator
- Sergei Fokin (* 1961), football player
- Nadeschda Gernet (1877–1943), mathematician and university professor
- Boris Gnedenko (1912–1995), mathematician
- Ivan Goncharov (1812-1891), writer
- Nikolai Jasykow (1803–1847), poet
- Alexander Kerensky (1881–1970), politician, 1917 minister and head of government, opponent of Lenin
- Sergei Krutowskich (1928–1981), computer engineer
- Lenin , real name Vladimir Ilyich Ulyanov (1870-1924), revolutionary leader and statesman
- Ivan Myasnikov (around 1710–1780), entrepreneur
- Alexei Ostroumow (1858–1925), zoologist, hydrobiologist and university professor
- Iwan Oschogin (* 1978), opera and musical performer
- Anatoly Prudnikow (1927–1999), mathematician
- Alexander Putschkow (* 1957), hurdler
- Dmitri Sadovnikov (1847-1883), ethnographer
- Stanislaw Schuk (1935–1998), figure skating coach
- Wadim Solotuchin (* 1967), lepidopterist
- Alexei Solowjow (* 1984), lepidopterist
- Alexander Turgenew (1784–1845), historian
- Marija Ulyanova (1878–1937), revolutionary and the youngest sister of Lenin
- Paul Unterberger (1842–1921), Russian lieutenant general and governor
- Simon Unterberger (1848–1928), military doctor
- Rustam Waliullin (* 1976), Belarusian biathlete of Tatar origin
Individual evidence
- ↑ a b Itogi Vserossijskoj perepisi naselenija 2010 goda. Tom 1. Čislennostʹ i razmeščenie naselenija (Results of the All-Russian Census 2010. Volume 1. Number and distribution of the population). Tables 5 , pp. 12-209; 11 , pp. 312–979 (download from the website of the Federal Service for State Statistics of the Russian Federation)
- ↑ Maschke, Erich (Ed.): On the history of the German prisoners of war of the Second World War. Verlag Ernst and Werner Gieseking, Bielefeld 1962–1977.
- ↑ Schaeffler opens first plant in Russia. In: owc.de. October 13, 2014, accessed May 5, 2015 .
- ↑ DMG Mori invests 70 million euros in Russia. In: Westfalen-Blatt, September 30, 2015.
- ↑ Transport on welcometoulyanovsk.com (English). Retrieved November 21, 2013.
- ↑ Association website (Russian)
Web links
- Ulyanovsk City Council (Russian)
- German-language website of the Ulyanovsk Region Economic Committee
- Ulyanovsk on mojgorod.ru (Russian)
- Ulyanovsk Photos (Russian)
- City website (Russian / English)