Wingst
| coat of arms | Germany map | |
|---|---|---|

|
Coordinates: 53 ° 43 ' N , 9 ° 4' E |
|
| Basic data | ||
| State : | Lower Saxony | |
| County : | Cuxhaven | |
| Joint municipality : | Land Hadeln | |
| Height : | 33 m above sea level NHN | |
| Area : | 55.62 km 2 | |
| Residents: | 3320 (Dec. 31, 2019) | |
| Population density : | 60 inhabitants per km 2 | |
| Postal code : | 21789 | |
| Primaries : | 04778, 04754 | |
| License plate : | CUX | |
| Community key : | 03 3 52 056 | |
| LOCODE : | DE 75M | |
| Community structure: | 16 districts | |
| Address of the municipal administration: |
Marktstrasse 21, 21762 Otterndorf |
|
| Website : | ||
| Mayor : | Patrick Pawlowski ( CDU ) | |
| Location of the community Wingst in the district of Cuxhaven | ||
Wingst ( Low German Wingst ) is a municipality in the municipality of Land Hadeln in the district of Cuxhaven in Lower Saxony .
geography
location
The community of Wingst is located around 35 km east of the mouth of the Elbe in the North Sea and just a little west of the lower reaches of the Oste . The districts of the community are located around the Wingst ridge . They are located northwest of Hemmoor on the federal highway B 73 and on the Green Coastal Road .
The Balksee is located in the southwest of the municipality of Wingst . In Altkehdingen there is a former nature reserve, the Altkehdingen forest .
Community structure
|
|
Neighboring communities
| Cadenberg | ||
| Bülkau |

|
Oberndorf |
| Near center | Hemmoor |
history
Incorporations
On June 1, 1970, the community Voigtding was incorporated. Opole was added on July 1, 1972.
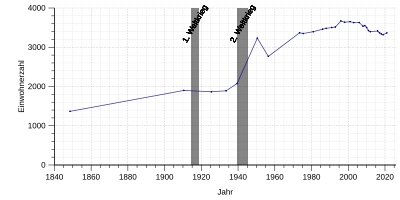
Population development
|
|
¹ as of December 31st
politics
Municipal council
The Wingst community council consists of 14 councilors and councilors. This is the specified number for the member municipality of an integrated municipality with a population between 3001 and 5000 inhabitants. The council members are elected for a five-year term by local elections. The current term of office began on November 1, 2016 and ends on October 31, 2021.
The honorary mayor is also entitled to vote and sit on the council of the municipality.
The last local election on September 11, 2016 resulted in the following:
| Political party | Proportional votes | Number of seats |
|---|---|---|
| CDU | 50.43% | 8th |
| SPD | 41.15% | 6th |
| Single applicant Lamke | 5.92% | 1 |
| FDP | 2.48% | 0 |
- The turnout in the 2016 local elections was 66.24%, above the Lower Saxony average of 55.5%.
- CDU and EWL form the CDU / Lamke group: 9 seats
mayor
The local council elected local council member Patrick Pawlowski (CDU) as honorary mayor for the current electoral term. His deputies are Martin Lamke (EWL), Stephan Reyelt (SPD) and Swen Vinup (CDU).
Chronicle of the mayor
- 2016 – date: Patrick Pawlowski (CDU)
- 2011–2016: Michael Schlobohm
- 2008–2011: Reinhard Poppe (CDU)
- 2001–2008: Klaus Föge (the younger; not related), (CDU)
- 1964–2001: Klaus Föge (the elder), (CDU)
- 1952–1964: Claus Glüsing
- 1946–1952: Ernst-August von der Wense ( DP )
- 1934–1945: Gustav Offermann, watermill
- 1927–1934: Hinrich Gooß, Dobrock
- 1907-1927: JA Meyer
- 1873–1907: A. Kröncke
coat of arms
| Blazon : "In green on a silver mountain, a silver fir tree , left and right by a golden ear of corn ." | |
| Justification for the coat of arms: The fir tree symbolizes the ancient Wingster forest. The ears of wheat indicate the agriculture that feeds the residents. |
Culture and sights
Buildings
- Bugenhagen House, named after the Bugenhagen Bible from 1533/34 ; the previous owner August Winter from Altkehdingen gave the church community the Bible of the reformer from Pomerania. Bugenhagen gave his sermons in Low German: that is why in June the parish festival is preached on flat.
- St. Michaelishaus from 1989, inaugurated on Michaelmas day
- 23 m high observation tower Deutscher Olymp on the hill of the same name (53 m high). The accessible tower was renovated in 2014.
- Grand stone grave Wingst
- Waterworks
Museums
The forest museum from 1966 in Wassermühle presents flora and fauna of the Wingster forest. 2013: new interactive concept to explain, especially to children, the connections between the forest habitat and the threat posed by humans. The listed adobe half-timbered house from 1739, which was documented as a school, had a classroom and the teacher's official residence. Museum visits only after registration.
Zoo in the Wingst
In the summer of 1972, today's zoo in Wingst was founded as a baby zoo by the animal trading company Ruhe. It was intended for the admission of baby animals from other zoos , in which often too many baby animals were born or who were not adopted by their parents. The animals often belonged to the "second generation" of zoo animals and had gotten used to humans while their parents were still caught in the wild . From around 2000 a new concept with new enclosures was implemented for the zoo. Today there are more groups of animals in more naturally designed enclosures in the Wingster Zoo. In 2006/07 the zoo was expanded to include a wolf and bear forest. The core zone of the zoo, the contact area, was redesigned in 2009 and based on a farm in Lower Saxony. Since 2018 the animal population has been changed to worldwide forest animals.
sport and freetime
- Wingst play park with 50,000 m², with a leisure center and 60 play and sports facilities, 500 m long summer toboggan run with drag lift, tree rope path / high ropes course, water fun track and interactive playground.
- Wingst indoor and outdoor pool with 100 m giant slide, indoor pool (16 m long), multi-purpose pool, mother-child area, outdoor pool , diving pool with diving boards (1, 3, 5 m) and sunbathing lawn.
- Five signposted hiking trails about 6 to 20 km in length; since 2011 the 30 km circular route, which also opens up the Neuhaus-Bülkau Canal. In 2013 the network of trails was expanded to include a circular hiking trail around Cadenberge.
- Family adventure trail from 2011, an educational forest trail with interactive stations with the Wingster forest playground and the Wingst spa gardens.
- In 2010 and 2011, nine year-round fitness machines were set up in the Kurpark Wingst under the heading “Fitness for everyone”.
- Various local cycle routes and the North Sea Cycle Route
- International Dobrock horse show
- The Giants Run will take place in Wingst for the first time in April 2017. It is an extreme obstacle course race that makes use of the advantages of the landscape.
- In 2018 the first Camp Canies (dog-man race) was established, which, like the Giants Run, makes use of the advantages of the landscape. The event has taken place annually since then.
- In 2019, after a 23-year break, a sled dog race took place again. A continuation is planned.
Camellia breeding
The world-famous camellia paradise of Peter Fischer Wingst existed for many years until 2014. After Fischer's death, some specimens were saved for the zoo in Wingst. The perennial nursery Klingel and Luckart with Malte Fischer organize camellia days every March.
Regular events
- First quarter: Plattdeutsche Theatertage
- Indoor equestrian tournament of the Lower Elbian Racing, Riding and Driving Club, end of April
- Low German church service, in the Wingster forest on Ascension Day
- May, Children's Day at the Wingst Zoo
- June to August “Summer Nights in the Kurpark”: free spa concerts in the Kurpark Wingst, i. d. R. Friday evening
- Giants Run: extreme obstacle course, beginning of June
- Shooting festival Wingst-Westerhamm, second weekend in June
- Shooting festival in Wingst-Weißenmoor, last weekend in June
- Schützenfest Wingst-Zollbaum, the first Sunday in July and the Saturday before
- Shooting festival Wingst-Dobrock, second weekend in July
- Wingst-Grift shooting festival, first weekend in August
- International riding tournament, the Dobrocker riding tournament is one of the largest tournaments in northern Germany at the end of July / beginning of August
- "Schlager Arena" - Schlager Festival, end of August
- Tropical night at the zoo, always the third Friday in July
- Camp Canis, dog-human race, September
- North German water polo mini-cup of the U11 in the indoor pool / November
- Autumn / Winter: Cooking courses at Hotel Peter
- Autumn / winter: dog sled races
- Olympic flame at the end of December on and around the German Olympus observation tower
Economy and Infrastructure
The Wingst lives mainly from tourism , which can be seen in the many holiday homes , hotels and hostels and the camping park. The calm and comparatively untouched landscape is the cause of recreational tourism .
traffic
In Wingst there is a train station (formerly “Höftgrube”, today “Wingst”) on the Niederelbebahn from Hamburg to Cuxhaven ( Verkehrsgesellschaft Start Unterelbe mbH ). The community is connected to the trunk road network through the federal highway B 73 via Stade and the federal highway B 27 via Cuxhaven. There is a good network of cycle paths around the Wingst. Local passenger transport is handled by collective call taxes.
education
- Primary School Am Wingster Wald
- Secondary schools in the neighboring Cadenberge
research
The German Research Center for Geosciences (GFZ) in Potsdam operates one of four German geomagnetic observatories in Wingst .
Personalities
Sons and daughters of the church
- Luise Cooper (actually: Adolphine Luise Cooper) (1849–1931), development worker and author, born in Wingst-Oppeln
- Rolf Geffken (* 1949), lawyer specializing in labor law and author, born in Wingst-Höden
People connected to the community
- Richard Graf von Schwerin (1892–1951), officer, most recently lieutenant general in World War II and u. a. Commander of the 79th Infantry Division, died in Wingst-Dobrock
- Ernst-August von der Wense (1899–1966), politician ( DP ), district administrator in the Hadeln district and member of the Lower Saxony state parliament, died in Wingst-Ellerbruch
Myths and legends
- Remper the giant
- From the giant Wingis
- How the Wingst got its name
- The knight of the Remperburg
- The Balksee
- The city of Balk
- The treasure from Silberberg
- The bull from the Balksee
- How the Silberberg and the Gretenberg got their name:
- Long ago a family of giants is said to have lived in Wingst. The mother of the family was called Grete and she loved a beautiful wooded hill, which was named after it. Like his father Wingis, his son Bolik wanted to find a silver treasure, so on his mother's advice he went to the Harz Mountains and brought home a sack full of stones. He had mistaken the shine of frozen stones for lumps of silver and only noticed the mistake at home. The hill where he scattered the stones is now called Silberberg and is the largest elevation in the region. He is said to have thrown three of the giant stones out of anger into the forest in front of Lamstedt, where they still lie today.
literature
- Willi Klenck: home book of the former district Neuhaus an der Oste . 1957.
- Walter Umland: Wingster Chronicle . Ed .: Municipality of Wingst. Niederelbe Druck, Otterndorf 1995, ISBN 3-924239-33-9 .
- Eberhard Michael Iba (Ed.): Hake Betken siene Duven. The saga of the Elbe and Weser estuaries (= special publications by the men from Morgenstern , Heimatbund at the Elbe and Weser estuaries . Volume 16 ). 3. Edition. Men from Morgenstern Verlag, Bremerhaven 1999, ISBN 3-931771-16-4 .
Web links
Individual evidence
- ↑ State Office for Statistics Lower Saxony, LSN-Online regional database, Table 12411: Update of the population, as of December 31, 2019 ( help ).
- ^ Federal Statistical Office (ed.): Historical municipality directory for the Federal Republic of Germany. Name, border and key number changes in municipalities, counties and administrative districts from May 27, 1970 to December 31, 1982 . W. Kohlhammer, Stuttgart / Mainz 1983, ISBN 3-17-003263-1 , p. 243 .
- ^ Ulrich Schubert: Community directory Germany 1900 - Neuhaus an der Oste district. Information from December 1, 1910. In: gemeindeververzeichnis.de. February 3, 2019, accessed June 7, 2019 .
- ^ A b c Michael Rademacher: German administrative history from the unification of the empire in 1871 to the reunification in 1990. Landkreis Land Hadeln ( see under: No. 56 ). (Online material for the dissertation, Osnabrück 2006).
- ↑ a b Statistisches Bundesamt Wiesbaden (ed.): Official municipality register for the Federal Republic of Germany - 1957 edition (population and territorial status September 25, 1956, for Saarland December 31, 1956) . W. Kohlhammer, Stuttgart 1958, p. 188 ( digitized version ).
- ↑ Lower Saxony State Administration Office (ed.): Municipal directory for Lower Saxony . Municipalities and municipality-free areas. Self-published, Hanover January 1, 1973, p. 44 , Landkreis Land Hadeln ( digitized version ( memento from August 7, 2019 in the Internet Archive ) [PDF; 21.3 MB ; accessed on June 10, 2020]).
- ↑ a b c d e f g h i j community directory - archive - regional structure - annual editions - Lower Saxony. (All politically independent municipalities in EXCEL format). In: Destatis website. Federal Statistical Office, accessed on January 29, 2020 .
- ↑ a b Wingst municipal council. In: Website of the municipality of Land Hadeln. Retrieved December 18, 2017 .
- ^ Lower Saxony Municipal Constitutional Law (NKomVG); Section 46 - Number of Deputies. In: Lower Saxony Regulations Information System (NI-VORIS). December 17, 2010, accessed February 12, 2017 .
- ↑ a b Municipality of Wingst - overall results of the municipal council election 2016. In: Website Zweckverband Kommunale Datenverarbeitung Oldenburg (KDO). Retrieved February 12, 2017 .
- ↑ The CDU gets the most votes nationwide. In: Website Norddeutscher Rundfunk . September 12, 2016. Retrieved February 12, 2017 .
- ↑ a b Councilor Mayor Patrick Pawlowski. In: Website of the municipality of Land Hadeln. Retrieved December 18, 2017 .
- ↑ Former mayor: Michael Schlobohm. (No longer available online.) In: Website Samtgemeinde am Dobrock. Archived from the original on January 23, 2015 ; Retrieved December 27, 2011 .
- ↑ a b The new mayor is Reinhard Poppe. In: Website Cuxhavener Nachrichten. March 5, 2008, archived from the original on March 2, 2014 ; Retrieved December 26, 2011 .
- ↑ a b c d e f g Walter Umland: Wingster Chronicle . Ed .: Municipality of Wingst. Niederelbe Druck, Otterndorf 1995, ISBN 3-924239-33-9 , p. 38-39 .
- ^ History and coat of arms of Wingst. In: Website of the municipality of Land Hadeln. Retrieved May 19, 2017 .
- ↑ Who we are. In: Website Waldmuseum Wingst. Retrieved June 24, 2013 .
- ↑ Zoo in Wingst. In: Official website Wingst. Retrieved June 24, 2013 .
- ↑ Wingst Play Park. In: Official website Wingst. Retrieved June 24, 2013 .
- ↑ Wingst indoor and outdoor swimming pool. (No longer available online.) In: Official website Wingst. Archived from the original on June 30, 2013 ; Retrieved June 24, 2013 .
- ↑ The Wandering Wingst in Cuxland between the Elbe, the Oste and the North Sea! In: Official website Wingst. Retrieved June 24, 2013 .
- ^ Dobrock tournament. In: dobrock-turnier.de. Retrieved March 25, 2018 .
- ^ Geomagnetic Observatories. Retrieved July 18, 2020 .
- ↑ List of IMOs and Responsible GINs. Retrieved July 18, 2020 .