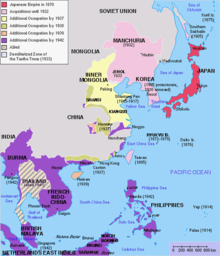
Japanese colonies
Japan has had two periods in the course of its history when it acted as a colonial power. However, the meaning and purpose of the colonies was different in each period.
Antiquity
According to interpretations of the Nihonshoki , there is said to have been an outpost of Japan from the Yamato era called Mimana on the Korean Peninsula from around 370 to 562 AD . However, its existence is controversial. Possibly it was the state of Gaya , which was under the strong influence of Japan and exported iron . The Chinese Chronicle Song Shu also names a colony of the Wa (Japan) in the south of the Korean Peninsula. According to Rurarz (2009), Mimana is also mentioned in the original version of the Korean Samguk Sagi and in two Korean epigraphs . Korean historians, most notably the nationalist Gim Seokhyeong, are strictly against the claim that Japan had a colony on Korean territory. Gim counters that Japan was a Korean colony, but had to take criticism even from Korean historians.
Until the 12th century there was Tamna (Japanese: Kingdom Tanimora) on Jeju Island . It is believed that Old Japanese was spoken in Jeju until the year 700, which was gradually supplanted by Korean immigrants from Silla and Baekje. Even today there are some loan words from Japanese. It is also assumed that Gaya's language was related to Japanese.
Modern times
Due to its self-imposed isolation of almost 250 years, Japan did not open up to the West until military pressure from the United States took place in 1854. After that, it quickly grew into an efficient and modern industrial nation based on the Western model; the Japanese Empire became the first Asian industrial state .
The prevailing European opinion during the 17th and 18th centuries was that Japan itself would sooner or later fall as a colony to a major Western power. Japan wanted to prevent this and, according to the words of the Meiji oligarch Inoue Kaoru , "found an empire like the European countries" and have colonies in order to become equal and not to become dependent. Therefore it strove to increase its economic power and its political importance to an expansion of its sphere of influence, especially in East Asia and the Pacific area . This led to the occupation of extensive colonial areas by Japan in the period from 1895 to 1945. The imperial claims of the Japanese Empire culminated with the propagation of a Greater East Asian sphere of prosperity in 1940 with the establishment of colonies and Japanese satellite states . After the defeat in World War II , Japan gave up any claim to its colonial territories by ratifying the San Francisco Peace Treaty . With the entry into force of the peace treaty, Japanese colonial history ended on April 28, 1952.
The colonies
- In 1895, Formosa (now Taiwan) and the pescadors came under Japanese rule after the First Sino-Japanese War . The independence of Korea from Imperial China is recognized by that.
- After the victory in the Russo-Japanese War in 1905 , Japan received South Sakhalin and the patronage of Korea.
- In 1910 , Korea was incorporated as a Japanese colony through annexation .
- During and after the First World War ( Versailles Treaty ), the former German colonies of Kiautschou and the archipelagos of the Palau Islands , Carolines , Marshall Islands and the Northern Marianas fell to Japan. However, Kiautschou had to be returned to China in 1922.
- In 1931 , Japan occupied Manchuria during the Manchurian Crisis and established the Manchukuo state.
- In 1937 the Second Sino-Japanese War broke out , which continued in World War II .
- During the Second World War, Japan conquered extensive areas in East and Southeast Asia, including French Indochina , Dutch East Indies , Malaysia , the Philippines and a large number of archipelagos in the Pacific. However, these are torn from Japan by the United States in the course of the Pacific War .
Course of the expansion policy
The actual beginning of the Japanese colonial policy is difficult to assess; early on ( 1873 - 1875 ) uninhabited, small islands such as the Bonin Islands , the Marcus Island and the Kuril Islands were acquired peacefully.
Until the end of the First World War
The first sign of Japan's development into a serious colonial power can be seen in 1876 - 1879, the act of conquering the Ryukyu Islands with Okinawa at the expense of the Chinese Empire . Also in 1876, Japan forces the opening of Korea and the first trade agreements with it by sending three gunboats to the Imperial Japanese Navy . Korea interests Japan because of its geographical proximity and some mineral resources such as coal.
During the First Sino-Japanese War Japan achieved in 1895 , the island of Formosa (today Taiwan ) and the nearby Pescadores islands of China as colonies. Korea itself, which Japan is mainly concerned with in this conflict, gains independence from China and falls under the Japanese sphere of influence. For the first time, Japan is becoming a serious colonial power in the eyes of the western world .
Japan also maintained numerous concessions in China between 1895 and 1945, where the equality with other imperialist powers was additionally underlined:
- Concession in Shanghai (1895-1943)
- Concession in Tientsin (1898–1943)
- Concession in Hankou (1898-1943)
- Concession in Chongqing (1897–1943)
- Suzhou Concession (1897-1943)
- Concession in Hangzhou (1897-1943)
- Concession in Shashi (1897-1943)
Japan comes into conflict with the Russian Empire over the rule of Manchuria . As a result of the conflict, the Russo-Japanese War broke out in 1904 , which Japan won. The decisive factor was a surprise attack on the Russian military port of Port Arthur . In modern times, this represents the first successful military confrontation between an Asian country and a major European power and its importance for the later self-image and the approach of the Japanese should not be underestimated.
Japan acquires the Liaodong peninsula (in the south of Manchuria) and the southern half of the Sakhalin Island , which thus receives the Japanese name Karafuto , and on which the Karafuto prefecture was established in 1907 , as well as the diplomatic assignment of Korea to the Japanese Empire. In 1905 Korea becomes a protectorate of Japan; in 1910 it is officially annexed as the Chosen Colony .
Russia has to pull out of Manchuria and Japan is building the South Manchurian Railway to bring raw materials from Manchuria to Korea, from where they are shipped to Japan. To protect this railway, the Kwantung Army is founded, which is stationed in the Chinese colonies and areas of influence of Japan.
In the First World War , Japan participated on the side of the Allies ( Entente ) and after the end of the war was awarded some formerly German colonies by the Treaty of Versailles : The Mariana Islands , the Carolines , Palau and the Marshall Islands became Japanese colonies, as well as during the war (on 7. November 1914 ) the former German colony of Kiautschou , which was returned to China on December 10, 1922 at the urging of American diplomacy.
Interwar period
Even before the global economic crisis in 1929, the voice of the expansionists heard (1927 with the election is in the leadership of Japan Tanaka Giichis the Prime Minister ), argue the other for the establishment of a weiträumigeren influence area, new markets for the domestic industries and thus the conquest of colonies. However, after Black Thursday and the Great Depression, which severely damaged the country and many small farmers (due to the collapse of the American silk markets, etc.), the domestic pressure after drastic foreign policy steps increased enormously, and the reputation grew especially in the high-ranking circles of the military after actions loudly. Similar to the radical nationalist circles in the Weimar Republic , various secret societies and conspiracies such as the Cherry Blossom Association are formed here , which see it as their goal to free Japanese politics from the supposed weakness of the democratic parties and parliament To lead the empire to new fame and great international influence.
After a group of such conspirators from circles of the Japanese army in Manchuria in September 1931 provoked the intervention of the military through a staged act of sabotage on the South Manchurian Railway Company (the so-called Mukden incident ) ( Manchurian crisis ), the troops stationed in Guangdong took part in one For half a year, the entire Manchuria, weakened by the Chinese civil war , took possession of the whole of Manchuria , without a declaration of war . The administration of Manchuria falls into Japanese hands, the puppet state of Manchukuo is established under the “leadership” of Puyi , the last Chinese emperor of the Qing dynasty . The League of Nations condemns the Japanese actions and on October 24, 1931, calls for a Japanese troop withdrawal and an investigation into the incidents in Manchuria. Japanese politicians meanwhile deny having given the order to occupy Manchuria and claim that the army is operating on its own, which is likely to have been true to a certain extent.
The Chinese reaction to this is trade boycotts; Japanese ships are no longer loaded and unloaded in the major Chinese port cities. Japanese exports are down to a sixth of the usual level. The mood continued to heat up, and so in January 1932 Japan responded to a seemingly insignificant incident in Shanghai (five Japanese monks were ambushed and beaten on the street, one of them died of his injuries), which led to storms of protest in the Japanese media and the public: Among other things, on January 29th the first area bombing of civilians in history by Japanese land and ship artillery and bombers stationed on aircraft carriers; around 18,000 Chinese civilians are killed and around 240,000 lose their homes. The trade boycotts will eventually be dropped and a demilitarized zone will be built around Shanghai. The League of Nations verbally condemns the Japanese actions, but still does not take any concrete measures against the aggressive actions of the Japanese. In May 1933, in view of the internal instability on the one hand ( civil war between the Kuomintang and communists) and on the other hand the open threat of a Japanese invasion of Beijing , the Chinese leadership concludes an armistice and recognizes the Japanese claims to Manchuria in it, despite the fact that Japan has already made them atrocities, including the there later war crimes and human experiments of unit 731 will follow.
After a coup d'état on May 15, 1932 that was unsuccessful in the first instance (martial law is not imposed), but in the end an extremely bloody coup d'état, which completely shook the confidence of the Japanese in their parliamentarians, the military and with it the expansionists took over the political leadership in Japan.
Japan leaves the League of Nations completely in 1933 because of harsh criticism and the Hoover-Stimson Doctrine , which called for the ceasefire as a treaty obtained through illegal actions under international law to be ignored internationally. The foreign policy position of Japan shifted completely towards an aggressive, totalitarian expansionism. The first treaties were concluded with National Socialist Germany and Fascist Italy (including the Anti-Comintern Pact ).
Until the end of the Second World War
As a product of the incident at the Marco Polo Bridge between Japanese and Chinese troops on July 7, 1937 , the Second Sino-Japanese War broke out , which (primarily Chinese) historians also regard as the actual beginning of the Second World War . In the course of this, the Japanese armed forces conquer the entire Chinese coast including the cities of Shanghai , Nanjing , Canton , Suzhou and Tsingtau (the former German colony of Kiautschou ), as well as the island of Hainan . This leads to a large number of war crimes , above all the events that went down in history as the Nanking massacre in what was then the Chinese capital .
In September 1940 Japan signed the tripartite pact with Nazi Germany and Mussolini's Italy; With the consent of the Vichy regime, it took over the colonies in French Indochina ( Vietnam , Laos , Cambodia ) and made efforts to gain a foothold in the Dutch East Indies , today's Indonesia . The ideology of the Greater East Asian Prosperity Sphere is spreading.
The Japanese expansionist efforts are met with strong criticism from the USA , which reacts with oil embargoes against Japan and the strengthening of the American military presence in the Pacific . Japan sees itself as economically pushed to the wall, and the newly elected Prime Minister Tōjō Hideki launched the Japanese attack on Pearl Harbor on December 7, 1941 , while the peace efforts were still ongoing , which ultimately resulted in the United States entering the so-called Pacific War (historical model on this: Russo-Japanese War , attack on Port Arthur ). The intention behind it was to gain a free hand in conquering further colonies in the Pacific by eliminating the American Pacific fleet.
In December 1941 , Japan forces Thailand to enter a military alliance by marching in troops . The Japanese troops occupy Burma , British Malaya , Singapore , Borneo , Hong Kong and also the Dutch East Indies . By May 1942 , the Philippines , which were under American rule , the Solomon Islands and the north of the island of New Guinea fell into Japanese hands. The oil fields of Sumatra and Borneo were of the greatest interest to the Japanese armed forces . With the defeat in the bloody and drawn-out Battle of Guadalcanal , the triumphant advance of the Americans in the Pacific War begins . Japan gradually loses more territories, the Americans practice the tactic of " island hopping " (island jumping).
By the end of the war, the Americans are fighting their way to the island of Okinawa , which belongs to the Ryukyu group of islands and represents one of Japan's earliest colonial conquests. The end of the colonialist aspirations of Japan is one of the Allied war aims ( Cairo Declaration ). After Japan surrendered on August 15, 1945 , the lands and island groups were redistributed; the main figures of the Japanese expansionist efforts from the military and politics were indicted in the so-called Tokyo trials , analogous to the Nuremberg trials against the leadership of Nazi Germany .
Loss of colonies
- After the Yalta Declaration, Korea was divided by the victorious powers into two zones of occupation along the 38th parallel , the Russian-Communist in the north and the south, under the administration of the USA. The Korean War broke out in June 1950 . The split in Korea continues to this day.
- Taiwan is once again under Chinese administration and served as an escape destination for the Kuomintang, which were ultimately defeated in the Chinese civil war . The island forms the remaining main part of the Republic of China founded by the Kuomintang , which leads to major conflicts with the Communist People's Republic of China .
- Cambodia , Laos and Vietnam declared their independence in 1945, but initially fell under French colonial rule again, but then gained their independence as a result of the Indochina War in 1954.
- Hong Kong fell back under British administration, then was returned to China in 1997 as contractually agreed.
- The Manchuria was occupied first by the Soviet Union and 1946 according to the Allied war aims ( Cairo Declaration ) to the Republic of China passed. Today it is part of the People's Republic of China .
- Indonesia initially declared its independence, but was then re-occupied by the Netherlands as a colony, gaining independence in 1949 after violent uprisings and regulatory American intervention.
- Papua New Guinea became Australian Trust Territory and became independent in 1975.
- Malaysia initially returned to Great Britain and became independent in 1957.
- The Ryukyu and Bonin Islands went to the USA , but were later returned to Japan (Ryūkyū- Amami 1953, remaining Ryūkyū Islands 1972, Bonin 1968).
- The Carolines , Marianas and the Marshall Islands fell under American rule; with the exception of the Marianas, they became independent in the 1980s and 1990s.
Aftermath of the colonial aspirations
As demonstrated by anti-Japanese demonstrations in front of Japanese facilities in the People's Republic of China in April 2005 (due to the publication of school books glossing over Japanese colonialism and expansionism), the Japanese side still needs to clarify its own history during this period. Since 1945, such international conflicts have often flared up between Japan and the states that at that time fell victim to its colonial aspirations.
See also
Web links
Individual evidence
- ↑ Peter H. Lee, Yongho Ch'oe, Hugh HW Kang: Sources of Korean Tradition. Volume One: From Early Times Through the Sixteenth Century . Columbia University Press, 2013, ISBN 978-0-231-51531-3 ( limited preview in Google Book Search).
- ^ Pankaj Mohan: The Controversy over the Ancient Korean State of Gaya: A Fresh Look at the Korea – Japan History War . 2016.
- ↑ Dongyi Wa State: Book of Song (Chinese).
- ↑ Rurarz 2009, p. 88.
- ↑ Helen Hardacre: The Postwar Developments of Japanese Studies in the United States . BRILL, 1998, ISBN 978-90-04-10981-0 , pp. 45-47.
- ↑ Alexander Vovin: From Koguryǒ to T'amna: Slowly Riding South with the Speakers of Proto-Korean. Korean Linguistics, 2013, 15.2: 222-40.
- ^ Ki-Moon Lee, S. Robert Ramsey: A History of the Korean Language . Cambridge University Press, 2011, §2.3.4, p. 47.
- ↑ Japanlink : Japanese Militarism , Author: Marc Verfürth, found on: June 14, 2009
- ↑ German model colony Kiautschou ( memento from August 26, 2014 in the Internet Archive ), at www.bundesarchiv.de.