1940
Portal history | Portal Biographies | Current events | Annual calendar
◄ |
19th century |
20th century
| 21st century
◄ |
1910s |
1920s |
1930s |
1940s
| 1950s
| 1960s
| 1970s
| ►
◄◄ |
◄ |
1936 |
1937 |
1938 |
1939 |
1940
| 1941
| 1942
| 1943
| 1944
| ►
| ►►
Heads of State · Elections · necrology · Art Year · Literature Year · Music Year · Movie Year · broadcast year · sports year
Calendar overview 1940
| 1940 | |
|---|---|
| The German Empire begins with the Battle of Britain . | |
| German troops occupy Paris in the western campaign . The Third French Republic ends. |
The Soviet Union commits in the occupied eastern Poland the Katyn massacre . |
| 1940 in other calendars | |
| Armenian calendar | 1388/89 (turn of the year July) |
| Ethiopian calendar | 1932/33 (September 10-11) |
| Baha'i calendar | 96/97 (March 20/21) |
| Bengali solar calendar | 1344/45 (beginning of April 14th or 15th) |
| Buddhist calendar | 2483/84 (southern Buddhism); 2482/83 (alternative calculation according to Buddhas Parinirvana ) |
| Chinese calendar | 77th (78th) cycle
Year of the Metal Dragon庚辰 ( since February 8th , before that Earth Rabbit己卯) |
| Chuch'e ideology (North Korea) | Chuch'e 29 |
| Chula Sakarat (Siam, Myanmar) / Dai calendar (Vietnam) | 1302/03 (turn of the year April) |
| Dangun era (Korea) | 4273/74 (October 2/3) |
| Iranian calendar | 1318/19 (around March 21) |
| Islamic calendar | 1358/59 (February 9/10) |
| Japanese calendar | 昭和Shōwa 15; Kōki 2600 |
| Jewish calendar | 5700/5701 (October 1-2) |
| Coptic calendar | 1656/57 (September 10-11) |
| Malayalam calendar | 1115/16 |
| Minguo calendar (China) | Year 29 of the republic |
| Seleucid era | Babylon: 2250/51 (turn of the year April)
Syria: 2251/52 (turn of the year October) |
| Suriyakati Calendar (Thai Solar Calendar) | 2482/83 (April 1) |
| Tibetan calendar | 1686 |
| Vikram Sambat (Nepalese Calendar) | 1996/97 (April) |
Events
Politics and world events
Second World War
Winter War between the Soviet Union and Finland
- January 7 : Stalin appoints Semyon Konstantinovich Tymoshenko as Commander-in-Chief of the Northwest Front .
- January 8 : The Battle of Suomussalmi in the Winter War ends with a success for the Finnish troops . They succeed in thwarting the Soviet attempt to interrupt Finland's transport links to Sweden.
- January 15 : The Soviet Union begins continuous artillery bombardment of the Finnish lines.
- January 28 : Finland begins a counter-offensive at the Battle of Kuhmo . The Finnish army under Hjalmar Siilasvuo succeeds in encircling a Soviet division, but a final victory fails due to a lack of ammunition.
- February 1 : Semyon Konstantinowitsch Tymoshenko conducts the first trial attacks against the Finnish defensive lines using contract tactics.
- February 12 : Soviet troops conquer the "million dollar bunker" in the Mannerheim line. On February 15, the major attack on the Mannerheim Line begins .
- February 17th : After two months of fighting, the Red Army succeeds in breaking through the Mannerheim Line with the conquest of the "Poppius Bunker".
- March 1st : The city of Viipuri is surrounded by Soviet troops from both land and sea.
- March 13 : Finland waived in the Treaty of Moscow to Karelia , which the Socialist Karelian Bear Soviet republic is transformed. Around 420,000 people are fleeing the lost territories. Numerous strategically important islands in the Gulf of Finland and the fishing peninsula on the North Sea must also be ceded . Hanko in south-west Finland is leased to the Soviet Union as a naval base for thirty years. Finland also has to agree to a rail link between the Swedish border at Tornio and Murmanskto build and operate. In contrast to 1939, the Soviet negotiators no longer demand a military alliance.
- Despite the victory, the poor performance of the Red Army in the winter war is perceived by other great powers and subsequently underestimated.
Poland / Baltic States
- February 8 : German occupation of Poland 1939–1945 : The Łódź Ghetto (later Litzmannstadt), one of the largest Jewish ghettos of the Nazi era, is set up by SS Brigade Leader Johannes Schäfer on the orders of District President Friedrich Uebelhoer .
- March 5 : At Lavrenti Beria's suggestion, the Politburo of the CPSU orders the execution of “nationalists and counter-revolutionary activists” in Soviet-occupied Poland - the Katyn massacre .
- March 8th : With the Poland decrees , Polish forced laborers are subjected to discriminatory regulations by police ordinance.
- March 27 : Heinrich Himmler , the Reichsführer SS , orders the construction of the Auschwitz concentration camp .
- April 3 to May 11 : Units of the Soviet secret service NKVD murder several thousand Polish officers and civilians in the Katyn massacre near Smolensk .
- May 16 : The General starts AB action of the Nazis . With the targeted killing hidden behind it , possible Polish resistance leaders are executed in the stand trial .
- May 20 : The first transport of prisoners arrives at the Auschwitz concentration camp accompanied by SS-Hauptscharführer Gerhard Palitzsch from Sachsenhausen concentration camp . The second transport follows on June 14th .
- May 31 : German authorities blow up the Chopin monument in Warsaw to damage Polish national sentiment.
- June 15 , 16 and 17 : The Soviet Union occupies the Baltic states of Lithuania , Estonia and Latvia .
- 14 / July 15 : The Estonian parliamentary election, 1940 is a sham election under Soviet direction.
- July 30th : In the course of extensive deportations from Estonia to the Soviet Union, among others, President Konstantin Päts and his family are deported to Ufa .
- August 3 : The Lithuanian Soviet Socialist Republic becomes part of the Soviet Union.
- August 5 : The Latvian Soviet Socialist Republic becomes part of the Soviet Union.
- August 6 : Estonia, the Estonian Soviet Socialist Republic, is forced to join the Soviet Union .
- September 19 : Witold Pilecki , co-founder of the Tajna Armia Polska and a member of the Polish Home Army against the German occupation of Poland , is arrested in order to organize the resistance in Auschwitz .
- October 2 : The German occupation authorities in Warsaw orders that all 400,000 Jews living in Warsaw must live in a ghetto .
- November 15 : The Warsaw Ghetto is sealed off from the “Aryan” part of the city by building a three meter high wall .
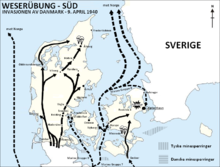
The attack on Denmark and Norway
- February 16 : The German cargo ship Altmark is attacked and boarded in Norwegian territorial waters with 303 Allied sailors captured on board by the British destroyer HMS Cossack . The so-called Altmark incident arouses doubts about Norway's neutrality and on February 19 Adolf Hitler decides to intensify the planning of the “ Weser Exercise Company ”, the occupation of Denmark and Norway .
- April 7th : A German naval association sets off from the Columbus quay and the destroyer quay at the Bremerhaven naval base for Narvik and Trondheim .
- April 8 : As part of Operation Wilfred , British units begin paving the waters between mainland Norway and its islands with sea mines to prevent German transport of iron ore from Sweden through Norwegian waters. In the event of a German reaction, Plan R 4 should come into force, which provided for the Allied invasion of neutral Norway.
- April 9th : German troops start the Weser Exercise South operation with the invasion of Denmark. The Danish army only offers partial resistance. In the evening, the country is completely occupied.
- April 9 : German units under Eduard Dietl occupy the Norwegian port of Narvik without resistance. Trondheim and other port cities are also occupied as planned. Only in Oslo are there delays until the following day, which gives the royal family the opportunity to escape towards Tromsø with the country's entire gold reserves .
- April 10th : The British Navy carries out its first attack on German invading forces in the Battle of Narvik . The German Navy suffers heavy losses. On April 13th there was another battle, which again ended in defeat for the German ships.
- April 12 : British troops occupy to Denmark belonging Faroe Islands .
- April 14th : Allied troops begin landing near Narvik.
- April 24th : Josef Terboven is appointed Reich Commissioner for Norway. On the same day, Norwegian troops begin to attack the German units in Narvik, which are faced with a five-fold superiority of the Allies in the following weeks.
- April 25 : The flag of the Faroe Islands is internationally recognized by Great Britain. Since then, April 25 has been a public holiday in the Faroe Islands.
- 7 / 8 May : During the Norway debate in the British House of Commons of be conservative government strategic failures blamed. The debate leads to the overthrow of Neville Chamberlain's administration and the formation of a coalition government under Winston Churchill on May 10th .
- May 24th : The Allies begin to withdraw from Norway to reinforce the troops in France, where the western campaign began on May 10th.
- May 28 : The Germans have to evacuate Narvik, but can hold the Luleå – Narvik railway , which is important for ore transport .
- June 7th : The Norwegian King Haakon VII , together with his family and the Norwegian government, is evacuated from Tromsø by the British heavy cruiser HMS Devonshire and taken out of the country.
- June 8th : The Wehrmacht occupies Narvik again.
- June 8th : During a sea battle in the European Arctic Ocean , the British ships HMS Glorious , HMS Acasta and HMS Ardent are sunk by the German battleships Scharnhorst and Gneisenau . 1519 people are killed. However, through their fight, the Glorious carrier group saved the weakly secured evacuation convoy from Narvik, which was only 100 nautical miles to the north, from a disaster.
- June 10 : Norway's army surrenders to the German armed forces .
Western campaign and war against England
- January 10th : The German major Helmut Reinberger, contrary to orders, transports the plans drawn up by Hitler for the case of Gelb , planned for January 17th, by plane. When the pilot flies and has to make an emergency landing near Maasmechelen in Belgium, the plans fall into the hands of the Belgian General Staff. As a result of the Mechelen incident , the date for the invasion of France was postponed for several months, and the previous strategy, corresponding to the Schlieffen Plan from the First World War , in favor of a so-called sickle - cut plan later developed by Erich von Mansteinto create a focus of attack in the Ardennes is abandoned.
- March 18 : Adolf Hitler and Benito Mussolini meet at the Brenner Pass in the Alps and agree on an alliance against France and Great Britain .
- April: British and French aircraft begin to be stationed for Operation Pike , the planned but not executed bombing of Russian oil fields.
- May 10 : With the start of the German campaign in the west , the so-called " Sitzkrieg " ends : the German Wehrmacht occupies the neutral countries of the Netherlands , Belgium and Luxembourg in order to bypass the Maginot Line . The governments of the three countries flee to Great Britain. The resistance of the Dutch army is low, only the fortress Holland around the cities of Leiden, The Hague, Rotterdam, Dordrecht and Utrecht is doggedly defended.
- May 10 : The Chamberlain government resigns: a war coalition cabinet under Churchill takes over the leadership of Great Britain. On the same day, the Royal Air Force began attacking German cities. 35 bombers attack Mönchengladbach .
- May 12 : The German Wehrmacht crosses the French border.
- May 13 : British Prime Minister Winston Churchill gives his famous blood-sweat-and-tears speech in front of the British Parliament. The Dutch Queen Wilhelmina goes into British exile with her family.
- 13. bis 15. May : In the Battle of Sedan German armored troops of the breakthrough in the strategic depth of the Allied units. The campaign in the west surprisingly developed into a blitzkrieg for all involved . On May 20th, German tanks were parked near Abbeville on the English Channel.
- May 14 : The bombing of Rotterdam kills 814 people, destroys the entire old town and immediately leads to the surrender of the Netherlands the next day.
- May 15 : The first Dutch resistance group is formed.
- May 17th : The Volksdeutsche movement is founded in Luxembourg City . Her superior is Damian Kratzenberg and her main task is to use propaganda to bring the Luxembourgers to a Germany-friendly attitude in order to lead them “ home to the Reich ”.
- May 26th : The Battle of Dunkirk begins. The northern French city of Dunkirk is the last evacuation port of the British Expeditionary Force . The British and French succeed in defending the bridgehead until almost 340,000 Allied soldiers have been evacuated to England by the Germans in Operation Dynamo before the city was captured on June 4th . Immediately after the battle, Fall Rot begins , the "Battle for France."
- May 27 : 97 British prisoners of war are executed by Germans in the Le Paradis massacre .
- May 28 : Leopold III. , the King of the Belgians , surrenders with his troops to the German Reich without having any political powers. He cites the inability to act of Hubert Pierlot's government, which fled to London .
- May 28 : The French passenger ship Brazza is sunk on the west coast of Portugal by the German submarine U 37 . Of the 576 passengers and crew members, 379 perished.
- June 4 : Prime Minister Winston Churchill gives a speech to the House of Commons and then on the radio under the motto We Shall Fight on the Beaches . In it he strengthens the British will to defend against the Nazi regime .
- June 10 : Italy declares war on France and Great Britain. The Italian dictator Mussolini speculates on being granted land (e.g. a French colony) in peace negotiations.
- June 10 : The French government - Paul Reynaud has been Prime Minister since March 21 - leaves Paris for Bordeaux and declares Paris an open city .
- June 12th : After German troops broke the Maginot Line, French units evacuate Lorraine .
- June 14th : German troops occupy Paris .
- June 16 : Paul Reynaud resigns as Prime Minister after being in the minority in Parliament voting on continuing the war and completing the Franco-British union proposed by Winston Churchill . The French President Albert Lebrun then entrusts his deputy, the popular Henri Philippe Pétain , the "hero of Verdun ", with the formation of a government and the initiation of armistice negotiations . which a little later sealed the end of the Third Republic .
- June 17 : German bombers sink the passenger steamer Lancastria with 6,000 to 9,000 people on board, which was used to evacuate British troops from France, off the French coast near Saint-Nazaire . 2,477 will be saved; the rest die. It is the loss-making shipwreck in British history; it is kept secret by orders of Winston Churchill .
- June 18 : The French general Charles de Gaulle calls for resistance from London (“ Appeal of June 18 ”) and forms the Comité national français as a provisional government in exile.
- June 18 : Prime Minister Winston Churchill delivers his speech This Was Their Finest Hour in the British House of Commons to strengthen the motivation of the British to resist after the German successes in the western campaign of World War II .
- June 21 : Mussolini lets the Italian army start an offensive in the Alps in order to strengthen its own negotiating position, but can only achieve minimal gains in territory.
- June 22nd : The armistice between France and Germany is signed in Compiègne in the same place and in the same railway carriage as 1918 The de facto surrender brings among other things the division of France into a northern and western part under German military administration under the command of Alexander von Falkenhausen and an unoccupied southern part (about 40% of the land area) with Vichy as the seat of the French government.
- July 3 : To prevent the feared surrender of French warships to the Germans, British units attacked naval units in Operation Catapult in the French naval port of Mers-el-Kébir in Algeria. Militarily, the operation, in which around 1,300 French seamen are killed, is only partially a success. Two ships can be sunk, but the rest of the fleet escapes towards the ports of southern France.
- July 10th : The Battle of Britain begins with attacks by the German Air Force on convoys in the English Channel and British naval facilities near the coast. With these attacks, the German Reich wants to force Great Britain to surrender.
- July 11th : Philippe Pétain founds the État français in Vichy . The day before the National Assembly in Vichy authorized him to do so. This ends the Third French Republic .
- July 12 : Philippe Pétain announces the first three constitutional acts, in which he declares himself Chef d'État with the right to give instructions to the executive, legislative and judiciary. With constitutional act number 4, he also declared Pierre Laval to be his deputy.
- July 16 : Adolf Hitler orders preparations for Operation Sea Lion , the invasion of Great Britain.
- July 19 : In a speech in the Reichstag, Adolf Hitler appeals to the British government for peace.
- August 2nd : The Luxembourg CdZ is founded. The previous Grand Duchy is subordinated to a German civil administration and thus practically equated with German Reich territory. The use of the French language was banned shortly afterwards. On October 22nd, the Luxembourg Chamber of Deputies and the Luxembourg State Council, which remained in office as the national administration, are dissolved.
- August 2 : The German part of Lorraine is also given a civil administration through a Führer decree. Josef Bürckel becomes the head of the civil administration based in Saarbrücken .
- August 11th : Operation Razzle begins to destroy the German harvest by mass dropping fire tokens
- August 13 : The German Air Force begins a series of large-scale attacks on facilities of the British Royal Air Force in the Battle of Britain .
- September 7th : The London Blitz begins in the Battle of Britain , a 57-day Air Force bombing of London .
- September 17 : Hitler postpones Operation Sea Lion against Great Britain "until further notice".
- September 18 : The British ocean liner City of Benares is torpedoed and sunk by the German submarine U 48 in front of the Rockall sandbank without warning. Of the 248 fatalities, 77 are children from a UK child rescue program.
- October 22 : Deportation of around 6,500 Jewish citizens from Baden, the Palatinate and Saarland to Gurs in the south of France ( Camp de Gurs )
- October 24 : At a meeting with Hitler in Montoire , Philippe Pétain refuses to enter the war on the Axis powers and declares France's neutrality. However, he considers a collaboration with the German Reich to be necessary to ensure the supply of the population, to keep the type and extent of the material, personal and industrial exploitation of the country within limits and to achieve the repatriation of the almost two million French soldiers from German captivity .
- October 28 : The Canadian ocean liner Empress of Britain sinks off the Irish north-west coast after being bombed by a German maritime patrol aircraft and torpedoed by a German submarine; 45 people die.
- October 29 : Major daytime attacks on London cease, but night attacks continue.
- November 14 : The first air raid on Coventry by the Air Force 3 and the scout units of the battle group 100 during The Blitz is the heaviest air raid of the war. At least 568 people are killed and Coventry Cathedral is destroyed.
- On the night of December 29th to 30th, one of the most devastating German air raids on the City of London resulted in a firestorm dubbed the “second great fire of London”.
Balkans and " Operation Barbarossa "
- June 26 : The Soviet Union sends an ultimatum to the Kingdom of Romania demanding that they cede Bessarabia , northern Bukovina and the Herza area .
- June 28th : After the ultimatum expires, the Red Army occupies the aforementioned Romanian areas. The German Reich tolerates the intention expressed in the secret additional protocol to the German-Soviet non-aggression pact to reclaim the area.
- July 31st : Hitler declares his decision to the top of the Wehrmacht to wage a campaign against the Soviet Union by spring 1941 at the latest .
- August 30 : In the Second Vienna Arbitration Award , Germany and Italy award parts of Romania (northern Transylvania ) to the Kingdom of Hungary . They also guarantee Romania's new borders.
- September 6th : Carol II , King of Romania, abdicates. His son Michael I is the successor.
- October 12 : First parts of the German Army Mission in Romania ( Staff R ) move into Romania.
- October 28 : Greek President Ioannis Metaxas rejects the Italian ultimatum to grant bases with the famous word όχι ( No ). Thereupon begins with the invasion of Italian troops from Albania from the Greco-Italian war .
- December 13 : Adolf Hitler issues “Directive No. 20” on preparations for the occupation of Greece next spring.
- December 18 : Hitler issues directive No. 21 in preparation for the attack on the Soviet Union ( Operation Barbarossa ).
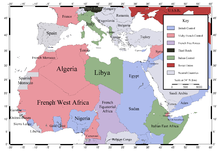
The war in Africa
- June 28 : Italo Balbo , Governor-General of Italian Libya , is killed by self- fire when his aircraft approaches Tobruk . Benito Mussolini replaced him with Rodolfo Graziani , whom he immediately commissioned with a large-scale offensive against Egypt until August 8 , with the aim of conquering the Suez Canal .
- July 9 : The sea battle at Punta Stilo during the siege of Malta between the British Mediterranean Fleet under Andrew Cunningham and the Italian Regia Marina under Inigo Campioni ends in a draw.
- August 26 : As the first governor of a French colony subordinated to Félix Éboué to Chad the Free French under Charles de Gaulle. Cameroun and French Equatorial Africa will join this move this autumn.
- September 9th : The Italian invasion of Egypt is prepared with a series of air strikes on British border posts .
- September 13 : With the Italian invasion of Egypt by the 10th Italian Army under Mario Berti , fighting begins in North Africa .
- September 16 : Italian troops capture Sidi Barrani . The Italian invasion of Egypt ends without major fighting with the Allies. The result falls far short of Mussolini's expectations. In the next few weeks, Rodolfo Graziani ignored all requests to continue the invasion.
- 23. bis 25. September British and Free French associations try in the: operation Menace vain, the port of Dakar in French West Africa to bring the ships and the Vichy fleet there at anchor under their control.
- 11 / November 12 : The British attack on Taranto loses the Italian Regia Marina at a stroke around half of its battleships.
- December 8 : Operation Compass , a British counter-offensive against the Italians in Egypt, begins with a series of air strikes, led by Richard O'Connor . The Western Desert Force advances over the Halfaya Pass until December 15 and can finally take Sollum and Fort Capuzzo. The rapid advance across the Libyan border is being slowed down, however, because large troops are being withdrawn for the fight in Italian East Africa .
Second Sino-Japanese War
- March 30 : A pro-Japanese puppet government under Wang Jingwei is set up in the Chinese city of Nanking , which was occupied by Japan in the Second Sino -Japanese War.
- July: Konoe Fumimaro becomes Japanese Prime Minister again.
- August 1 : Foreign Minister Matsuoka Yōsuke announces the concept of a Greater East Asian sphere of prosperity to the exclusion of “Western influences”.
- August 20 to December 5 : The Chinese Red Army leads the Hundred Regiments Offensive against the Japanese Army .
- September 27th : Japan concludes the three-power pact with the German Reich and Italy and thus forms the Berlin-Rome-Tokyo axis .
- October 12 : Prime Minister Konoe Fumimaro founds the Japanese collective movement Taisei Yokusankai . All other parties are banned.
- October 16 : The United States embargo oil and metal scrap on Japan.
Further acts of war in Asia and Oceania
- December 1 : The Franco-Thai war between the France of the Vichy government in Indochina and the Kingdom of Thailand begins after a few minor clashes. The French Navy sends three ships to attack the coastal town of Trat .
- 6. bis 8. December / December 27 : German auxiliary cruiser conduct a raid on Nauru . They sink five Allied merchant ships and severely damage the phosphate loading stations on the island. Although the loading stations and the delivery of fertilizer are of great importance to the economy for Australia and New Zealand on Nauru and Ocean Island , the islands are militarily unprotected and the attacking Germans can carry out their attacks without losses. The two attacks on Nauru are during World War IIthe most effective attacks by German auxiliary cruisers in the Pacific. Phosphate shipments to Australia, New Zealand and Japan have to be halted for a period of ten weeks after the attack.
Alliance policy
- March 18 : Adolf Hitler and Benito Mussolini have a hastily arranged meeting on the Brenner Pass . Mussolini gives a vague promise that Italy will enter the war at an "appropriate time".
- September 2 : Great Britain and the USA sign destroyer-by-base agreement . For the provision of bases for a period of 99 years in the Bahamas , Bermuda , Jamaica , St. Lucia , Trinidad , Antigua as well as on Newfoundland and in British Guyana , the USA handed over seven ships from the Royal Navy 43 and the Royal Canadian Navy Time of the First World War.
- August 17 : In the Ogdensburg Agreement signed by American President Franklin D. Roosevelt and Canadian Prime Minister Mackenzie King near the city of Ogdensburg , New York , the USA and Canada agree to jointly defend the American continent in the event of an invasion by the British Islands through Germany.
- September 27 : With the signing of the three-power pact between Germany , Italy and Japan in the Great Hall of the New Reich Chancellery , the Berlin-Rome-Tokyo axis is created .
- October 4th : Hitler and Mussolini meet again at the Brenner Pass.
- November 12th / 13th : The state visit of the Soviet Foreign Commissioner Molotov to Germany serves to examine a balance of interests between the countries of the Tripartite Pact and the Soviet Union .
- November 20 to 24 : Hungary (20th), Romania (23rd) and Slovakia (24th) join the Tripartite Pact .
- December 12th : The "Eternal" Hungarian - Yugoslav friendship treaty is concluded. It was broken by Hungary on April 3, 1941 .
Switzerland
- January 1st : Marcel Pilet-Golaz becomes Federal President of Switzerland for the second time .
- July 25 : The Commander-in-Chief of the Swiss Army , General Henri Guisan , summons all senior officers to report to Rütli . As a precaution, you will receive orders for national defense in the event of a feared German-Italian invasion.
- November 15 : In submitting the two hundred to the Swiss Federal Council, petitioners from the right-wing camp demand the disempowerment of editors-in-chief of bourgeois newspapers and the expulsion of the League of Nations from Switzerland.
Other events in Europe
- January 1 : The student service comes into force in the German Reich , which must be completed during the first three semesters of the course in the comradeships of the National Socialist German Student Union or the service groups of the German student body.
- March 13 : The revolutionary Sikh Udham Singh shot and killed Sir Michael O'Dwyer , the former governor of the Punjab , in London . Dwyer was responsible for the Amritsar massacre committed by the British military on February 13, 1919 .
- December 24th : First Christmas ring broadcast by “ Großdeutscher Rundfunk ” to “connect the front and home”.
Other events worldwide
- January 6th : From Simonstown , an English naval base in South Africa, the US cruiser Louisville picks up gold worth around 150 million dollars as collateral for goods and arms credits to England.
- February 27 : During a flight over Antarctica , Richard E. Byrd discovers an unknown island, which he gets the name Thurston Island .
- March 23 : The All India Muslim League , led by Ali Jinnah , adopts the Lahore resolution in Lahore , British India . It calls for a separate state for the Indian Muslims on the basis of the two-nation theory . It will then be seven years before the founding of Pakistan .
- August 20 : Stalin's agent Ramón Mercader assassinated the Russian revolutionary leader Leon Trotsky in Mexico City . He died the following day of his injury.
- September 16 : In the United States, which is conscription introduced.
- October 10th in Cuba , one of the most progressive constitutions of the time comes into force. However, it is practically never put into practice.
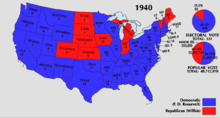
- November 5 : Republican Wendell Willkie is defeated by Democratic incumbent Franklin D. Roosevelt in the US presidential election . He is the only President of the United States to be elected for a third term.
economy
- March 3rd : The RMS Queen Elizabeth is secretly sailing from Liverpool on her maiden voyage because of the war. The world's largest passenger ship at the time was heading for New York City.
- May 15 : The chemical company DuPont starts selling five million pairs of nylon stockings in selected stores in major US cities ( N-Day ).
- May 15 : The first McDonald’s restaurant is opened by the brothers Richard and Maurice McDonald in San Bernardino, California on Route 66 .
- May 26th : The weekly newspaper Das Reich , created by the National Socialists to influence German intellectuals, appears with the first edition.
- June 5 : The German newspaper appears for the first time in the Netherlands in German-occupied Amsterdam .
- June 7th : The Spanish airline Iberia (Líneas Aéreas de España), founded in 1927 , is nationalized.
- September 7th : In Vienna the Vugesta , an institution for the redistribution of stolen private property of Jewish Austrians during the time of National Socialism, starts its activities.
- Since the war-related shortage of raw materials made the production of Coca-Cola difficult in Germany, the German Coca-Cola chief chemist Wolfgang Schetelig in Essen developed Fanta as a substitute product, so that Coca-Cola does not have to do without business in Germany. The drink initially consists mainly of whey and apple scraps, as well as various fruit juice concentrates sourced from Italy.
science and technology
Development of the atomic bomb
- March: The emigrated physicists Otto Frisch and Rudolf Peierls write the Frisch-Peierls-Memorandum at the University of Birmingham on the possibility of building a "super bomb" by using the energy released by nuclear fission. Frisch and Peierls hand the memorandum, in which they express their concern that such a weapon could be developed in Nazi Germany, under the seal of strict secrecy to their Australian colleague Mark Oliphant , who in turn forwards it to Henry Tizard , a senior air force officer .
- April 10th : The British MAUD commission consisting of six scientists meets for the first time to discuss the possible production of an atomic bomb . At this constituent meeting, a research program on isotope separation and nuclear fission is decided.
archeology
- April 16 : The French Egyptologist Pierre Montet opens the tomb of Pharaoh Amenemope in Tanis in the tomb of Pharaoh Psusennes I, which was discovered intact by the researcher .
- September 12th : Marcel Ravidat, Jacques Marsal, Georges Agnel and Simon Coencas discover the Lascaux cave in the French department of Dordogne with its Neolithic cave paintings, which can be attributed to Franco-Cantabrian cave art . The priest and prehistorian Henri Breuil arrives on September 21 and publishes a first scientific description that same year. He sees the works of art as belonging to the Périgordien .
architecture
- The Linz Nibelungen Bridge for the “ Führerstadt Linz ” is completed.
aviation
- April 27 : With the dismantling of LZ 127 "Graf Zeppelin" and LZ 130 "Graf Zeppelin II" , the large airship era ends .
- May 6th : The airship hangar at the "Rhein-Main" airfield was blown up
- May 13 : Russian-born Igor Iwanowitsch Sikorski takes off in the United States for the first free flight with the Sikorsky VS-300 , a helicopter with a tail rotor configuration , the most widely used design to this day.
- October 11th : The German test pilot Erich Klöckner reached a height of 11,460 meters and thus the edge of the stratosphere with a glider, a crane from the German Research Institute for Gliding . The flight was finally canceled due to the cold, and Klöckner suffered frostbite on his fingers and earlobes.
- October 12 : The attack aircraft Ilyushin Il-2 completes its first flight after a conversion under the designation ZKB-57 . The Soviet machine will develop into one of the most built aircraft (36,163 units).
- October 26 : The US American fighter aircraft North American P-51 “Mustang” successfully completes its maiden flight .
- November 25 : The British multipurpose aircraft de Havilland DH.98 Mosquito is tested in its first flight.
- November 25 : The medium-range bomber Martin B-26 takes off on its maiden flight in the USA.
Teaching and Research
- January 29 : Using Guide adoption receives Alfred Rosenberg of Adolf Hitler commissioned the High School of the Nazi party to establish as Nazi elite university.
Culture
Visual arts
- The American painter Edward Hopper paints his painting Gas in oil on canvas .
Movie
- January 24 : John Ford's film The Fruits of Wrath, based on the novel of the same name by John Steinbeck, premieres in New York . The leading role is played by Henry Fonda . Jane Darwell will receive an Oscar for her supporting role as Ma Joad.
- February 7 : Walt Disney's second full-length cartoon Pinocchio premieres in the United States.
- March 27 : Alfred Hitchcock's first Hollywood film, Rebecca, based on the novel by Daphne du Maurier with Laurence Olivier and Joan Fontaine in the leading roles, premieres in Los Angeles . It was received with enthusiasm by critics and audiences alike and was subsequently the only Hitchcock film to receive an Oscar for Best Picture.
- April 25 : The feature film The Postmaster by Gustav Ucicky, loosely based on the story of the same name by Alexander Pushkin , premieres in Vienna. In autumn he receives the Coppa Mussolini for the best foreign film at the Venice Film Festival .
- July 17 : The anti-Semitic and anti-British propaganda film The Rothschilds of Erich Waschneck has in Berlin its premiere . The film does not prove to be very successful and is held back by the Reich Ministry for Public Enlightenment and Propaganda immediately after the premiere .
- July 27 : In the United States the animated short film has A Wild Hare ( The rabbits case ) by Tex Avery premiere. It is the first animation appearance by Bugs Bunny , who is voiced by Mel Blanc .
- September 5 : The Film Festival of Venice, the German propaganda film Jud Suess of Veit Harlan premiered. The work commissioned by the National Socialist government is freely based on the novella of the same name by Wilhelm Hauff and is enthusiastically received by the public. Main actor Ferdinand Marian accepted the title role on the orders of Joseph Goebbels after several other actors had already refused. The German premiere will take place on September 24th in Berlin.
- October 15 : Charlie Chaplin's famous film satire on Adolf Hitler, The Great Dictator , starts with the world premiere in New York .
- November 13 : The good two-hour animated film by Walt Disney , titled Fantasia has on Broadway in New York City premiere.
- November 29 : The Eternal Jew from Fritz Hippler is the third anti-Semitic German propaganda film of the year in the Ufa-Palast am Zoo premiered.
- December 26 : The film version of The Philadelphia Story with Katharine Hepburn , Cary Grant , James Stewart and Ruth Hussey has premiere at the Radio City Music Hall in New York City .
- December 30th : The Nazi propaganda film request concert by Eduard von Borsody with Ilse Werner and Carl Raddatz premieres in Berlin's Ufa-Palast am Zoo . After The Great Love , it becomes the third Reich's most commercially successful film.
literature
- March: Agatha Christie publishes the Hercule Poirot novel Sad Cypress ( morphine ).
- In the United States appears Carson McCullers ' first novel, The Heart Is a Lonely Hunter ( The Heart Is a Lonely Hunter ).
- Ernest Hemingway published his novel For Whom the Bell Tolls ( Whom the Bell Tolls ).
Music and theater
- April 13 : at the Semper Opera in Dresden has opera Romeo and Juliet by Henry Suter champion its premiere .
- April 16 : The opera Maryša by Emil František Burian is premiered in Brno. The libretto is based on a piece by Alois and Vilém Mrštík .
- May 18 : The world premiere of the opera Volo di notte by Luigi Dallapiccola based on Antoine de Saint-Exupéry's second novel Vol de nuit takes place at the Teatro della Pergola in Florence.
Disasters
- January 21 : An uncontrollable fire breaks out off the French Mediterranean coast after an explosion on board the Italian passenger ship Orazio . The ship burns out and sinks; 106 people are killed, although help is quickly on the spot.
- August 13 : Three Australian cabinet members and Chief of Staff Brudenell White are killed in a plane crash in Canberra , Australia . A total of 10 people die.
- August 31 : The Lovettsville air disaster kills 25 people. US Senator from Minnesota , Ernest Lundeen, was among the dead .
- October 22nd : After the collision with a cargo ship, the Canadian destroyer "Margaree" sinks in the North Atlantic . 140 dead
- October 23 : The Hurtigruten passenger steamer Prinsesse Ragnhild is shaken by an explosion shortly after casting off in Bodø off the island of Landegode and sinks. The cause is still unclear, 299 people died.
- November 10 : earthquake of magnitude 7.3 in Romania , around 1,000 dead
- December 12th : Accident during the construction of the later Theodor-Heuss-Bridge , 30 dead
Minor accidents are listed in the sub-articles of Catastrophe .
Sports
- The Summer Olympics are just like the Winter Olympics not held because of the war.
Nobel Prizes
Nobel Prizes are not awarded.
Born
January
- January 1 : Ercan Aktuna , Turkish football player, coach, official and columnist († 2013 )
- January 1 : Genya Ravan , American rock singer
- January 1st : Ludwig Reich , Austrian mathematician and university professor
- January 2 : Nanni Galli , Italian racing driver († 2019 )
- January 2nd : Horst Rankl , German writer and actor
- January 3 : Tsutomu Hanahara , Japanese wrestler, Olympic champion
- January 3 : Thelma Schoonmaker , American film editor
- January 4th : Gao Xingjian , Chinese storyteller, translator, playwright, director, critic and artist
- January 4th : Helmut Jahn , German-American architect
- January 4th : Brian David Josephson , British physicist
- January 4th : Pavel Smetáček , Czech jazz clarinet, saxophonist and composer
- January 5th : Athol Guy , Australian musician
- January 5th : Phil Trim , Spanish musician of African-American descent
- January 6 : Van McCoy , American musician and producer († 1979 )
- January 7th : Armin Abmeier , German bookseller and editor († 2012 )
- January 7th : Helga Schubert , German psychologist and author
- January 8 : Miriam Ariza , Dominican pianist
- January 9 : Dario Antiseri , Italian philosopher
- January 9 : Barbara Buczek , Polish composer, pianist and music teacher († 1993 )
- January 9 : Günter Deckert , right-wing extremist politician
- January 9th : Ruth Dreifuss , Swiss politician
- January 9 : Dieter Mertens , German historian († 2014 )
- January 11th : Franco Balmamion , Italian cyclist
- January 11 : Eike Ebert , German politician
- January 11 : Apollo Lynge , Greenland cross-country skier († 2002 )
- January 12 : Matthias Habich , German actor
- January 12 : Ronald Shannon Jackson , American jazz drummer († 2013 )
- January 13th : Detlef Engel , German pop singer
- January 13 : Dieter Schulte , German trade unionist
- January 13 : Tadaoki Ishihara , Japanese composer and professor
- January 13 : Edmund White , American writer
- January 14th : Roland Benz , German soccer player
- January 14th : John Castle , British actor
- January 14th : Siegmund Nimsgern , German opera and concert singer
- January 15 : Martha Jungwirth , Austrian painter
- January 16 : Willi Paul Adams , German Americanist and historian († 2002 )
- January 16 : Reinhart Ahlrichs , German chemist († 2016 )
- January 16 : Franz Müntefering , German politician
- January 17 : Hans-Jürgen Ambrosius , German trade union official († 2011 )
- January 17th : Frieder Birzele , German politician and Member of the State Parliament
- January 17th : Hans-Werner Hector , German entrepreneur, co-founder of the software company SAP AG
- January 17th : Kipchoge Keino , Kenyan athlete
- January 17th : Mircea Ion Snegur , Moldovan politician
- January 17th : Tabaré Vázquez , Uruguayan politician († 2020 )
- January 18 : Martin Kayenburg , German politician and Member of the State Parliament
- January 18 : Pedro Rodríguez , Mexican Formula 1 and sports car racing driver († 1971 )
- January 19 : Paolo Borsellino , Italian judge and mafia hunter († 1992 )
- January 19 : John Siegfried Mehnert , German whistleblower and actor
- January 19 : Bernhard Sinkel , German director, writer and producer
- January 20 : Jana Brejchová , Czech actress
- January 20th : Klaus the violinist , German musician and songwriter
- January 21 : Peter Lauster , German psychologist and author
- January 21 : Jack Nicklaus , American golfer
- January 21 : Peter Stopper , German soccer player
- January 22nd : Karin Anselm , German film and theater actress
- January 22nd : Rolf Attenhofer , Swiss small artist
- January 22nd : John Hurt , British actor († 2017 )
- January 22 : George Seifert , American football coach
- January 22nd : Eberhard Weber , German bass player and composer
- January 23 : Jürgen Grasmück , German author of science fiction novels († 2007 )
- January 23 : Werner Krämer , German football player († 2010 )
- January 23 : Armin Maiwald , German journalist, television director and presenter
- January 23 : Joanna Miles , American actress
- January 23 : Egon Oehri : Liechtenstein middle-distance runner
- January 23 : Johnny Russell , American country musician and songwriter († 2001 )
- January 24 : Vito Acconci , American architect, landscape architect and installation artist († 2017 )
- January 24th : Joachim Gauck , German politician and journalist, eleventh Federal President of Germany and first federal commissioner for the Stasi files
- January 24th : Alois Glück , German politician and MdL
- January 25 : Gonzalo Aguirre Ramírez , Uruguayan politician, lawyer and journalist
- January 25 : Brent McCall , American composer († 2019 )
- January 25 : Wolfgang Paul , German soccer player
- January 26 : Rafael Martínez , Colombian singer, composer and poet
- January 27 : Ahmet Kurtcebe Alptemoçin , Turkish politician and Foreign Minister of Turkey
- January 27 : James Cromwell , American actor
- January 28 : Guido Bachmann , Swiss writer and actor († 2003 )
- January 28 : Miguel Barnet , Cuban writer and ethnologist
- January 28th : Helma Gautier , Austrian actress
- January 28th : Carlos Slim Helú , Mexican entrepreneur
- January 29 : Katharine Ross , American actress and children's book author
- January 29th : Kunimitsu Takahashi , Japanese racing car driver
- January 31 : Peter John Andrews , British paleoanthropologist
- January 31 : Helmut Hunger , German soccer player
February
- February 1st : Erik Freitag , Austrian composer and violinist
- February 1 : Henning Kaul , German politician
- February 2 : Thomas M. Disch , American writer († 2008 )
- February 4th : Martin Jones , English pianist
- February 4 : George A. Romero , American director, producer († 2017 )
- February 5 : HR Giger , Swiss visual artist, painter and Oscar winner († 2014 )
- February 6th : Peter Baumeister , German jazz drummer and banker
- February 6 : Tom Brokaw , American journalist
- February 6 : Helga Thiede , German singer (soprano)
- February 6th : Hannsjörg Voth , German artist.
- February 7 : Christopher J. Arthur , philosopher and author
- February 7th : Helmut Ruge , German cabaret artist († 2014 )
- February 8 : Jörg Rüdiger Siewert , German physician
- February 9 : Brian Lawrence Bennett , English musician
- February 9 : Hubert Burda , German art historian and publisher
- February 9 : JM Coetzee , South African writer
- February 10 : Cornell Green , American football player
- February 10 : Rainer Holbe , German journalist, television presenter and author
- February 10 : Tibor Kovács , Hungarian archaeologist († 2013 )
- February 11 : Dennis Gaubatz , American football player
- February 11 : Jūrō Kara , Japanese writer
- February 11 : Werner Mauss , German private investigator and agent
- February 12 : Bashir Ahmad , Scottish politician († 2009 )
- February 12 : Rufin Anthony , Pakistani Bishop († 2016 )
- February 12 : Hank Brown , American politician
- February 12 : Wolfgang Solz , German soccer player († 2017 )
- February 12 : Pastor Vega , Cuban director († 2005 )
- February 13 : Maximilian Ardelt , German entrepreneur
- February 13 : Winfried Heurich , German organist, choir director and composer
- February 13 : Charles O. Cecil , American diplomat
- February 13 : Werner Pirchner , Austrian composer († 2001 )
- February 14 : Abdelwahab Abdallah , Tunisian diplomat and politician
- February 14 : Arno Anzenbacher , Austrian anthropologist and social ethicist
- February 14 : Roland Baader , German economist and publicist († 2012 )
- February 14 : Eberhard Blum , German flautist († 2013 )
- February 14th : Mary Rand , British athlete and Olympic champion
- February 15 : İsmail Cem , Turkish journalist and politician († 2007 )
- February 15th : Ursula Krinzinger , Austrian gallery owner and art dealer
- February 15 : Francesco Valle , Italian boxer († 2003 )
- February 16 : Uwe Bremer , German painter and graphic artist
- February 17th : Karl Hermann Haack , German politician
- February 17 : Winfried Hassemer , German Vice President of the Federal Constitutional Court († 2014 )
- February 17 : Willi Holdorf , German athlete (decathlon) and football coach († 2020 )
- February 17 : Gene Pitney , American singer and songwriter († 2006 )
- February 17th : Eckart Werthebach , German politician
- February 18 : Fabrizio De André , Italian songwriter († 1999 )
- February 18 : Anna Oppermann , German visual artist († 1993 )
- February 19 : Tewolde Berhan Gebre Egziabher , Ethiopian professor of biology and environmental protection
- February 19 : Saparmyrat Nyýazow , Head of State and Government of Turkmenistan († 2006 )
- February 19 : Smokey Robinson , American singer
- February 20 : Ido Abram , Dutch educationalist († 2019 )
- February 20 : Rudolf Edlinger , Austrian politician
- February 20 : Christoph Eschenbach , German pianist and conductor
- February 21 : Gaston Caperton , American politician
- February 22nd : Jacques Andrieux , French soccer player
- February 22nd : Ugo Colombo , Italian cyclist († 2019 )
- February 22nd : Judy Cornwell , British actress
- February 22nd : Jon Elster , Norwegian-American sociologist
- February 22nd : Billy Name , American photographer and filmmaker († 2016 )
- February 22 : Ülo Tuulik , Estonian writer
- February 22nd : Chet Walker , American basketball player
- February 23 : Peter Fonda , American actor and film director († 2019 )
- February 23 : Werner Salevsky , German enduro athlete († 1991 )
- February 23 : American football player Jackie Smith
- February 24th : Denis Law , Scottish football player
- February 24 : Bruno Nicolè , Italian football player († 2019 )
- February 24 : Yüksel Pazarkaya , Turkish-German writer
- February 24th : Guy Périllat , French ski racer
- February 24th : Reinhold Thode , judge at the German Federal Court of Justice
- February 25 : Béchara Pierre Raï , Maronite patriarch of Antioch
- February 25 : Sigmar Wittig , German mechanical engineer and university professor
- February 26 : Whitney Smith , American vexillologist († 2016 )
- February 27 : Troels Andersen , Danish art historian
- February 27 : Vartán Waldir Boghossian , Armenian-Brazilian Bishop
- February 27 : Barbara Collier , Canadian soprano
- February 27 : Arafa Hussein Mustafa , German Semiticist and university professor († 2019 )
- February 27 : Friedel Rausch , German soccer player and coach († 2017 )
- February 28 : Aldo Andretti , American racing car driver
- February 28 : Mario Andretti , American racing car driver
- February 28 : Jürgen Chrobog , German lawyer and diplomat
- February 28 : Joe South , American singer and songwriter († 2012 )
- February 29th : Bartholomeos I , Patriarch of Constantinople
- February 29 : Klaus-Jürgen Jacob , German biologist, director of the Cottbus Zoo († 2013 )
- February 29 : Klaus-Dieter Lehmann , German cultural manager
- February 29th : Hideo Ochi , Japanese-German karateka
March
- March 1st : David Broome , British show jumper
- March 1st : Gene Perla , American jazz bassist
- March 1st : Erich Schleyer , German-Austrian actor and author
- March 1 : Lothar Schruff , German economist
- March 1 : Ralph Towner , American jazz musician
- March 2 : Juraj Beneš , Slovak composer, teacher and pianist († 2004 )
- March 2 : Joyce Green , American rockabilly musician
- March 2 : Lothar de Maizière , German politician, Minister-President of the GDR in 1990
- March 3rd : Walter Renneisen , German actor
- March 3rd : Horst Schmidbauer , German politician and Member of the Bundestag
- March 3 : Angelika Waldis , Swiss writer and journalist
- March 4th : Fernando Casado , Dominican singer, actor and entertainer
- March 4 : Wolfgang Hoffmann-Riem , judge at the Federal Constitutional Court
- March 4th : Franz Löschnak , Austrian lawyer, politician
- March 5 : John W. Carlin , American politician, governor of Kansas
- March 5th : Graham McRae , New Zealand racing car driver
- March 5 : Werner Petzold , German painter and graphic artist
- March 5th : Josef Piontek , German soccer coach and player
- March 6 : Billy Adams , American rockabilly musician († 2019 )
- March 6 : Philippe Amaury , French publisher († 2006 )
- March 6 : Miguel José Asurmendi Aramendia , Spanish religious and bishop († 2016 )
- March 7 : Rudi Dutschke , German student leader, dissident († 1979 )
- March 8 : Peter Baumbach , German architect and professor at the Berlin-Weißensee School of Art
- March 8 : Manfred Manglitz , German soccer player
- March 8 : Barry Smith , Australian motorcycle racer
- March 8 : Johnny Ventura , Dominican singer
- March 8 : Richard Williamson , British ancient ritualist bishop
- March 9th : Jean-Jacques Debout , French chansonnier, lyricist, composer and theater promoter
- March 9 : Gerold Meraner , Italian politician (South Tyrol)
- March 9 : Reijo Taipale , Finnish tango and pop singer († 2019 )
- March 10 : Chuck Norris , American actor and karate world champion
- March 10 : Francis Schwartz , American composer
- March 11 : Alberto Cortez , Argentine singer-songwriter († 2019 )
- March 11 : Fanny Morweiser , German writer († 2014 )
- March 12 : Al Jarreau , American jazz, pop and R&B singer and songwriter († 2017 )
- March 12th : Mauri Antero Numminen , Finnish singer, composer, author and filmmaker
- March 12 : Sheila Och , Czech children's book author († 1999 )
- March 13 : Herbert Schui , German economist and politician († 2016 )
- March 14th : Hans-Olaf Henkel , German manager, President of the Federation of German Industries. V.
- March 14 : Julian Hunte , diplomat, President of the 58th UN General Assembly
- March 14 : Armin A. Steinkamm , German legal scholar
- March 15 : Jacques Hustin , Belgian singer and painter († 2009 )
- March 15 : Roland Schmider , German football official
- March 16 : Wolf-Dietrich Arnold , German orthopedist and university professor
- March 16 : Rainer Jork , German politician († 2020 )
- March 16 : Vaqif Mustafazadə , Azerbaijani composer and pianist († 1979 )
- March 16 : Claus Offe , German political scientist
- March 16 : Jan Pronk , Dutch politician, UN special envoy for the Sudanese crisis region of Darfur
- March 16 : Keith Rowe , British guitarist and artist
- March 16 : Barbara Stolterfoht , German social politician
- March 17th : Anni Biechl , German athlete
- March 17th : Gottfried Munzenberg , German physicist
- March 17th : Jim Telfer , Scottish rugby player and coach
- March 18 : Hartmut Graßl , German climate researcher
- March 19 : Norbert Eimer , German politician (FDP)
- March 19 : Barbara Franklin , American politician
- March 19 : Michael Geyer , German journalist, moderator and editor-in-chief († 2003 )
- March 19 : Pete Smith , American baseball player
- March 20 : Cornelis Christiaan Jacob Andriessen , Dutch painter, sculptor and printmaker
- March 20 : Giampiero Moretti , Italian racing driver and entrepreneur († 2012 )
- March 21 : Walter Andreas Angerer , German painter and composer
- March 21 : Solomon Burke , American soul / R&B singer († 2010 )
- March 21 : Paul Friedrichs , German enduro athlete († 2012 )
- March 21 : Herbert Joos , German jazz trumpeter or flugelhornist and graphic artist († 2019 )
- March 21 : Wilhelm Kaiser-Lindemann , contemporary German composer and horn player († 2010 )
- March 21 : Gerd Kohlhepp , German economic geographer and Brazilian researcher
- March 21 : Maria Frumentia Maier OSF , German Catholic nun, social pedagogue and psychologist
- March 21 : Gerhard Zemann , Austrian actor († 2010 )
- March 22 : Fausto Bertinotti , Italian politician (communist)
- March 22nd : Hans Geisler , Saxon politician
- March 22nd : Gayle Griffith , American country and rockabilly musician
- March 22nd : Fritz Indra , Austrian graduate engineer and honorary professor for combustion engines
- March 22nd : Konrad R. Müller , German portrait photographer
- March 22 : Jim Simon , American football player
- March 22nd : Masahiko Togashi , Japanese jazz drummer († 2007 )
- March 23 : Alan Blaikley , British pop music writer
- March 24th : Diane von Orléans , married Duchess of Württemberg, German painter and artist
- March 25 : Rodolfo Mederos , Argentine tango bandoneonist
- March 25th : Mina , Italian singer
- March 26 : Peter Adler , German politician († 2010 )
- March 26 : James Caan , American actor
- March 26 : Christina Odenberg , Swedish bishop
- March 26 : Nancy Pelosi , American politician
- March 27th : Silvano Bertini , Italian boxer
- March 27 : Derrick Morgan , Jamaican singer
- March 27 : Sandro Munari , Italian rally driver
- March 27th : Klaus Peter , German hammer thrower
- March 28th : Giuseppe Andrich , Italian bishop
- March 28 : Ben d'Armagnac , Dutch performance artist († 1978 )
- March 28 : Russell Banks , American writer
- March 29 : Heinz Ludwig Arnold , German publicist († 2011 )
- March 29 : Eden Kane , British singer
- March 29 : Octavian Nemescu , Romanian composer († 2020 )
- March 29 : Godfrey Reggio , American director
- March 30 : David Askevold , American-Canadian artist († 2008 )
- March 30th : Astrud Gilberto , American singer and composer
- March 30th : Wilhelm von Gottberg , German politician
- March 30 : Jerry Lucas , American basketball player
- March 30th : Uwe Timm , German writer
- March 31 : Brian Ackland-Snow , British art director and production designer († 2013 )
- March 31 : Erwin Marschewski , German politician
- March 31 : Timm Ulrichs , German artist
April
- April 1 : Wangari Muta Maathai , Kenyan environmental activist, Nobel Peace Prize laureate († 2011 )
- April 1 : Graciela Paraskevaídis , Argentine composer († 2017 )
- April 2 : Michael Garleff , German historian
- April 2 : Mike Hailwood , British motorcycle racer and Formula 1 driver († 1981 )
- April 2 : Donald Jackson , Canadian figure skater
- April 2nd : Karl-Heinz Thielen , German soccer player
- April 3 : Wolf Kahler , German actor
- April 3 : Takeki Manabe , non-party Japanese politician
- April 3 : Vygandas Kazimieras Paulikas , Lithuanian veterinarian and helmet intologist
- April 4th : Richard Attwood , British racing car driver
- April 4th : Jochen Gerz , German artist
- April 4 : Robby Müller , Dutch cameraman († 2018 )
- April 4 : Michael Ruetz , German photographer
- April 4 : Gustav-Adolf Stange , German lawyer and politician
- April 5 : Tommy Cash , American country singer
- April 5 : Klaus Detter , German judge, judge at the Federal Court of Justice from 1985 to 2005
- April 5 : Manfred Strahl , German journalist, editor and writer († 2000 )
- April 6 : Pedro Armendáriz junior , Mexican actor († 2011 )
- April 6 : Marie Anne Fliegel , German actress
- April 6th : Gernot Mittler , German politician
- April 7th : Jan W. Morthenson , Swedish composer and musician
- April 8 : John Havlicek , American basketball player († 2019 )
- April 9 : Hans Bankl , Austrian professor of pathological anatomy († 2004 )
- April 9th : Hans-Joachim Reske , German athlete
- April 10 : Clark Blaise , Canadian writer
- April 11 : Władysław Komar , Polish athlete († 1998 )
- April 12 : Herbie Hancock , American jazz pianist and composer
- April 12 : Jack Hibberd , Australian playwright and author
- April 13 : Friedemann Berger , German writer († 2009 )
- April 13 : Vladimir Cosma , Romanian film composer and conductor
- April 13 : Umberto Grano , Italian racing driver
- April 13 : Jean-Marie Gustave Le Clézio , Franco-Mauritian writer and Nobel Prize for Literature
- April 13 : Max Mosley , British sports official
- April 14th : Julie Christie , British film actress
- April 14 : Ernest Lieb , founder of the American Karate System († 2006 )
- April 15 : Jeffrey Archer , Conservative British politician and bestseller writer
- April 15 : Wilfried Erdmann , German single-handed sailor
- April 16 : Rolf Dieter Brinkmann , German poet and narrator († 1975 )
- April 16 : Margrethe II , Queen of Denmark
- April 16 : Waltraud Meißner , Palatinate dialect poet
- April 16 : Erika Simm , German politician and Member of the Bundestag († 2015 )
- April 17th : Billy Fury , English rock musician († 1983 )
- April 17th : Siegfried Jerusalem , German singer (tenor)
- April 17th : Walter Klaiber , Methodist Bishop
- April 17th : Anja Silja , German soprano
- April 17th : Cardinal Agostino Vallini , Cardinal of the Italian Curia
- April 18 : Ira von Fürstenberg , European actress and jewelry designer
- April 18 : Joseph Leonard Goldstein , American geneticist
- April 18 : Gordon Spice , British racing driver and racing car designer
- April 19 : Kurt Ahrens , German racing car driver
- April 19 : Werner Anzill , German soccer player
- April 19 : Frank Davey , Canadian poet, writer and former university professor
- April 19 : Otto Emersleben , German writer
- April 19 : José Luis Gómez , Spanish actor
- April 19 : Bernd Heinrich , German-American biologist
- April 19 : Erwin Kaldarasch , German handball player and coach
- April 19 : Sydney Possuelo , Brazilian Indian protection activist
- April 20 : Susy Andersen , Italian actress
- April 20 : George Andrie , American football player († 2018 )
- April 20 : Johannes von Buttlar , German non-fiction author
- April 20 : Antonio Mattiazzo , Italian Roman Catholic Bishop
- April 20 : Alberto Vázquez , Mexican actor and singer
- April 21 : Souleymane Cissé , Malian filmmaker
- April 21 : Claire Marienfeld , German politician
- April 21 : Elke Müller , German politician († 2014 )
- April 21 : Peter Schneider , German writer
- April 21 : Knut Terjung , German journalist
- April 21 : Wolfgang Uhrig , German sports journalist, editor-in-chief at Kicker
- April 22nd : Berndt Seite , Prime Minister of Mecklenburg-Western Pomerania
- April 23 : Konrad Kleinknecht , German physicist
- April 23 : Dietrich Schwanitz , German English scholar and writer († 2004 )
- April 23 : Klaus Willimczik , German sports scientist
- April 24th : Sue Grafton , American crime novelist († 2017 )
- April 25 : Ethel Afamado , Uruguayan singer and writer
- April 25 : Henrik Arildskov , Danish gardener, vocational school teacher and TV presenter
- April 25 : Jochen Borchert , German politician
- April 25 : Al Pacino , American actor, director and film producer
- April 26 : Dietmar Hopp , German entrepreneur (SAP AG)
- April 26 : Giorgio Moroder , Italian producer and composer
- April 28 : Manfred Liebel , German professor
- April 29 : George Rufus Adams , American jazz musician († 1992 )
- April 29 : Jürgen Schumann , captain of the Lufthansa plane Landshut († 1977 )
- April 30th : Jeroen Brouwers , Dutch writer
- April 30 : John Grew , Canadian organist, harpsichordist and music educator
- April 30 : Darrell McCall , American musician
- April 30th : Ermindo Angel Onega , Argentinian football player († 1979 )
- April 30 : Ekkehard Weber , Austrian ancient historian, epigraphist and classical philologist
- April 30 : Burt Young , American actor
May
- May 1st : Fakhruddin Ahmed , Bengali economist
- May 1st : Felipe Arizmendi Esquivel , Mexican Bishop and Cardinal
- May 3rd : Margita Bert , German medic
- May 3 : Garth Fagan , Jamaican dancer and choreographer
- May 3 : David H. Koch , American entrepreneur, philanthropist and politician († 2019 )
- May 4th : José Luis Astigarraga Lizarralde , Spanish religious chaplain († 2017 )
- May 4th : Víctor Farías , Chilean Germanist and journalist
- May 4th : Peter Gregg , American racing driver († 1980 )
- May 5th : Lars Gunnar Åberg , Swedish actor, director, musician and artist
- May 5th : Jürgen Anbuhl , German politician
- May 6 : Lutz Stavenhagen , German politician († 1992 )
- May 6 : Vito Taccone , Italian cyclist († 2007 )
- May 6 : Mario Wallenda , American high wire artist († 2015 )
- May 7th : Ingvild Birkhan , Austrian philosopher and women's researcher
- May 7 : Angela Carter , British writer († 1992 )
- May 7th : István Kiss , former Hungarian long-distance runner
- May 7th : Dorit Zinn , German writer
- May 8 : Ricky Nelson , teenage star in the United States († 1985 )
- May 9th : Klaus Aeffke , German rower
- May 9 : James L. Brooks , American film director and screenwriter
- May 9 : Richard Edwin Morrissey , British jazz musician († 2000 )
- May 11 : Anthony Kwami Adanuty , Ghanaian Bishop
- May 11 : Niklaus Meienberg , Swiss writer and journalist († 1993 )
- May 11 : Herbert Müller , Swiss racing driver († 1981 )
- May 11 : Volker Röhricht , judge at the German Federal Court of Justice
- May 12 : Peter Huckauf , German writer
- May 13 : Immo Appenzeller , German astronomer
- May 13 : Bruce Chatwin , British writer († 1989 )
- May 14 : Troy Shondell , American pop and country singer († 2016 )
- May 15 : Roger Eugene Ailes , American television producer († 2017 )
- May 15th : Carlos Bielicki , Argentine chess master
- May 15 : Yoshimi Katayama , Japanese motorcycle and car racer († 2016 )
- May 15 : Hanne Vack , German activist
- May 16 : Robert Corbett , British officer
- May 17 : Hartwig Ebersbach , German painter
- May 17th : Valie Export , Austrian media artist
- May 17 : Peter Gerety , American actor
- May 17 : Alan Kay , American computer scientist
- May 17th : Ingrid Turković-Wendl , Austrian figure skater and TV presenter
- May 18 : Anita Kupsch , German actress and voice actress
- May 19th : Jan Janssen , Dutch cyclist
- May 19 : Frank Lorenzo , American manager
- May 20 : Moisés Nogueira Avelino , Brazilian doctor, businessman and politician
- May 20 : Stan Mikita , Slovak-Canadian ice hockey player († 2018 )
- May 20 : Dominique Nguyên Chu Trinh , Bishop of the Vietnamese Diocese of Xuan Loc
- May 20 : Frode Thingnæs , Norwegian jazz musician and composer († 2012 )
- May 20 : Norbert Werbs , German theologian and auxiliary bishop in the Archdiocese of Hamburg
- May 21 : Martin Carthy , British folk singer, guitarist and mandolin player
- May 21 : Tony Sheridan , co-founder of beat music († 2013 )
- May 21 : Peter Uhlig , German enduro athlete († 1971 )
- May 22nd : Carlos Galván , Argentinian bandoneonist and tango musician († 2014 )
- May 22nd : Helga Labs , chairwoman of the pioneering organization "Ernst Thälmann"
- May 22 : Michael Sarrazin , Canadian actor († 2011 )
- May 22nd : Klaus Schlappner , German soccer coach
- May 22 : Rita Waschbüsch , German politician
- May 24 : Joseph Brodsky , Russian-American poet and Nobel Prize for Literature († 1996 )
- May 25 : Marianne Ahrne , Swedish director, screenwriter and writer
- May 25 : Nobuyoshi Araki , Japanese photographer
- May 25 : Luis Lintner , South Tyrolean missionary in Brazil († 2002 )
- May 26 : Levon Helm , American musician († 2012 )
- May 27 : Gillian Barge , British actress († 2003 )
- May 27 : Jan Bruins , Dutch motorcycle racer († 1997 )
- May 27 : Stig Hoffmeyer , Danish actor
- May 28 : John Bergamo , American drummer and composer († 2013 )
- May 28th : Hans Dulfer , Dutch jazz musician
- May 29 : Curtis Anthony Anderson , American philosopher
- May 29 : Taihō Kōki , Japanese sumo wrestler († 2013 )
- May 31 : Augie Meyers , American musician
- May 31 : Theobald Schurte , Liechtenstein sports shooter
- May 31 : Dino Zandegù , Italian cyclist
June
- June 1 : René Auberjonois , American actor († 2019 )
- June 1 : Barbara Lass , Polish-German film actress († 1995 )
- June 1 : Kip Thorne , American physicist
- June 2 : Bernd Giese , German chemist
- June 2nd : Constantine II , last king of Greece
- June 4th : Veronika Bayer , German actress († 2008 )
- June 4th : Josefina Miniño , Dominican ballet dancer and choreographer
- June 4th : Ludwig Schwarz , Austrian bishop
- June 4th : Klaus Urbanczyk , German soccer player
- June 5th : Gerlinde Hämmerle , Baden-Württemberg politician
- June 5th : Peter Nidetzky , Austrian TV presenter
- June 5 : Hans-Otto Wilhelm , German CDU politician († 2019 )
- June 6th : Willie John McBride , Irish rugby player
- June 6th : Hugo Walser , Liechtenstein athlete
- June 7 : Helmut Bieler , German composer, pianist and music teacher († 2019 )
- June 7th : Tom Jones , Welsh pop singer
- June 7th : Samuel Little , American serial killer
- June 7 : Ronald Pickup , British actor
- June 8th : Françoise Levie , Belgian film producer, director and writer
- June 8 : Nancy Sinatra , American singer and actress
- June 9th : Inge Harst , German table tennis player
- June 10th : Arnaldo Coen , Mexican painter, sculptor, illustrator and set designer
- June 10 : Helga Neuner , German actress
- June 10 : Peter Ryan , Canadian racing car driver († 1962 )
- June 11 : Adelgunde Mertensacker , German politician and university lecturer († 2013 )
- June 11th : Volkmar Sigusch , German sex researcher and doctor
- June 13 : Hans-Dieter Dechent , German entrepreneur, racing team owner and racing car driver († 2014 )
- June 13 : Dallas Long , American athlete, dentist, doctor
- June 13 : Gojko Mitić , Serbian actor and director
- June 14th : Francesco Guccini , Italian Cantautore, writer and actor
- June 14th : Janis Hansen , American actress
- June 14th : Horst Teltschik , German politician and business manager
- June 15th : Parent Akay , Turkish shot putter and volleyball coach
- June 16 : Neil Goldschmidt , American politician
- June 16 : Petr Kaplan , Czech rock singer and guitarist († 2007 )
- June 17 : George A. Akerlof , Professor of Economics
- June 17th : Marcel Aubour , French football player
- June 17 : Bobby Bell , American football player
- June 17th : Dieter Farwick , German Brigadier General and publicist
- June 18 : Mirjam Pressler , German writer and translator († 2019 )
- June 19 : Rainer Langhans , German author and actor
- June 19 : Ursula Lietz , German politician († 2018 )
- June 20 : Kozō Andō , Japanese Kendōka († 2003 )
- June 20 : Eugen Drewermann , Catholic theologian and psychotherapist
- June 21 : Mariette Hartley , American actress
- June 22nd : Raimund Gensel , German actor († 2002 )
- June 22nd : Abbas Kiarostami , Iranian film director († 2016 )
- June 22nd : Daniel Gray Quillen , American mathematician († 2011 )
- June 22nd : Ursula Schäppi , Swiss actress and comedian
- June 23 : Wilma Rudolph , Afro-American athlete and exceptional athlete († 1994 )
- June 23 : Stuart Sutcliffe , painter and musician, early member of the Beatles († 1962 )
- June 23 : Dieter Thomae , German politician († 2020 )
- June 23 : Joachim Wenzel , Vice President of the German Federal Court of Justice († 2009 )
- June 25 : Peer Augustinski , German actor and voice actor († 2014 )
- June 25th : Thomas Köhler , German luge rider
- June 25th : Judy Pollock , Australian sprinter and middle distance runner
- June 26th : Manon , Zurich artist
- June 26th : Gerhard Widder , German politician
- June 27 : Gianluigi Aponte , Italian entrepreneur and shipowner
- June 29th : Vyacheslav Petrovich Artyomov , Russian composer
- June 29 : John Dawes , Welsh rugby player
- June 30 : Heinrich Gillis Görtz , German painter and graphic artist († 2010 )
- June 30th : François Xavier Le Van Hong , Auxiliary Bishop of the Archdiocese of Huê in Vietnam
July
- July 2 : Irving Martin Abella , Canadian writer and historian
- July 2nd : Georgi Ivanov , the first Bulgarian cosmonaut
- July 2 : Tony Liscio , American football player († 2017 )
- July 3 : Mihai Adam , Romanian football player († 2015 )
- July 3 : Lamar Alexander , American politician, governor of Tennessee
- July 3 : Jerzy Buzek , Polish politician, Prime Minister
- July 3 : Peer Raben , German composer († 2007 )
- July 4th : Rupert von Plottnitz , German lawyer and politician
- July 6 : Viktor Grigoryevich Kuskin , Soviet ice hockey player († 2008 )
- July 6 : Nursultan Nazarbayev , Kazakh politician and president
- July 6 : Jeannie Seely , American country singer and songwriter
- July 7 : Richard Keith Armey , American politician and economist
- July 7 : Wolfgang Clement , German politician, Federal Minister for Economic Affairs and Labor († 2020 )
- July 7 : Ringo Starr , British musician (The Beatles)
- July 7th : Rosel Zech , German theater and film actress († 2011 )
- July 8 : Peter Danckert , German politician and Member of the Bundestag
- July 9 : Jair da Costa , Brazilian soccer player
- July 10 : Helen Donath , American soprano
- July 10 : Rolf Herings , German football coach († 2017 )
- July 10 : Erich Iltgen , German politician, President of the Saxon State Parliament († 2019 )
- July 10 : Bernd Struck , German physicist and handball player
- July 11th : Artur Hennings , German chess player in the GDR († 2003 )
- July 11th : Gunnar Prokop , Austrian handball coach
- July 11 : Tommy Vance , British radio presenter († 2005 )
- July 12th : Hans-Friedrich von Ploetz , German diplomat and politician
- July 13 : Patrick Stewart , English actor
- July 14 : Kwame Addo-Kufuor , Ghanaian politician and Minister of Defense
- July 15 : Ian Charles Athfield , New Zealand architect († 2015 )
- July 15 : Chris Cord , American racing car driver
- July 17th : Otmar Alt , German painter, graphic artist, designer and sculptor
- July 17th : Mickey Hawks , American rock and roll musician († 1989 )
- July 17 : Francisco Toledo , Mexican painter († 2019 )
- July 18 : Lillian Faderman , American professor of literature
- July 20 : Karl-Heinz Appelt , German sculptor, sculptor and graphic artist († 2013 )
- July 22 : Thomas Wayne , American rockabilly and pop singer († 1971 )
- July 23 : Gunter Halm , Minister for Light Industry of the GDR
- July 23 : Friedrich Graf von Westphalen , German lawyer
- July 24 : Dieter Bellmann , German actor and director († 2017 )
- July 24 : Stanley Hauerwas , Methodist theologian and pacifist
- July 26 : Brigitte Hamann , German historian and author († 2016 )
- July 26 : Jürgen Kurbjuhn , German football player († 2014 )
- July 27 : Pina Bausch , German dancer, choreographer, dance teacher and ballet director († 2009 )
- July 27 : Johannes Rogalla von Bieberstein , German librarian
- July 27 : Manfred Haas , German football official
- July 27 : Lothar Herbst , Polish poet and leading opposition activist († 2000 )
- July 27 : Jonny Hill , Austrian musician, lyricist, producer and entertainer
- July 27 : Gary Kurtz , American film producer († 2018 )
- July 27 : Troy Perry , theologian and founder of the Metropolitan Community Church
- July 28th : Gianpaolo Ambrosi , Italian luge rider
- July 28 : Judy Grahn , American writer
- July 29th : Gernulf Garbe , German sports medicine specialist, orthopedic surgeon and chirotherapist as well as bodybuilder
- July 29th : Wolfgang Grzyb , German soccer player († 2004 )
- July 29 : Bernhard Jagoda , German politician; President of the Federal Labor Office († 2015 )
- July 31 : James Anderson , American cognitive scientist
- July 31 : Frido Mann , German-speaking psychologist and writer
August
- August 1 : Mahmoud Dowlatabadi , Iranian writer
- August 1 : Horst Herrmann , German university professor and church critic († 2017 )
- August 3 : Lance Alworth , American football player
- August 3 : Joseph Dorfman , Israeli composer and music teacher († 2006 )
- August 3rd : Raymond Allen "Ray" Draper , American jazz tuba player († 1982 )
- August 3 : Roscoe Mitchell , American jazz saxophonist
- August 3 : Martin Sheen , American actor
- August 4th : Coriún Aharonián , Uruguayan composer and musician († 2017 )
- August 4th : Herwig Nachtmann , Austrian publisher
- August 4 : Abdurrahman Wahid , Indonesian politician, President († 2009 )
- August 5th : Franco Cardini , Italian historian
- August 5th : Christian Clemens , German chess player
- August 5 : Roman Gabriel , American football player
- August 5th : Norbert Gansel , German politician
- August 5th : Sigi Schwab , German guitarist and composer
- August 5 : Natalie Trundy , American actress († 2019 )
- August 6th : Peter Ehlebracht , German music comedian
- August 6 : Egil Kapstad , Norwegian jazz pianist († 2017 )
- August 7 : Jean-Luc Dehaene , Belgian politician, Prime Minister († 2014 )
- August 7th : Hans Eisele , German soccer player († 2002 )
- August 7th : Martin Heisenberg , German neurobiologist and geneticist
- August 8 : Just Jaeckin , French director and photographer
- August 8th : Hans-Georg Specht , Lord Mayor of Mülheim an der Ruhr
- August 8 : Dennis Tito , American entrepreneur and first space tourist
- August 9th : Volker Hauff , German politician
- August 9 : Marie-Luise Marjan , German actress
- August 10 : Peter William Atkins , British chemist and physical chemist
- August 10 : Weniamin Smechow , Russian actor and theater director
- August 10 : Marie Versini , French actress
- August 10 : Sid Waddell , British television commentator († 2012 )
- August 11th : Malena Kuss , Argentine musicologist
- August 11 : Lennie Pond , American racing driver († 2016 )
- August 12 : Tony Oladipo Allen , Nigerian drummer, composer and songwriter († 2020 )
- August 12 : Aleksandar Jossifow , Bulgarian composer († 2016 )
- August 13 : Jean-Claude Andruet , French rally driver
- August 13 : Allen Blairman , American modern jazz drummer
- August 13 : Paul Eßling , German assassin († 1982 )
- August 13 : Wolfgang Luh , German university professor for mathematics
- August 13 : Dirk Sager , German journalist († 2014 )
- August 14 : Arthur B. Laffer , American economist
- August 14th : Aristides Royo , 36th President of Panama
- August 14 : Max Schautzer , Austrian TV presenter
- August 15 : Gudrun Ensslin , German terrorist, member and co-founder of the RAF († 1977 )
- August 15 : Willi Jäger , German mathematician
- August 15 : Helmut Kuhlmann , German CDU politician
- August 16 : Bruce Beresford , Australian film director, writer, producer and actor
- August 19 : Johnny Nash , American pop and reggae musician († 2020 )
- August 20 : Gary Collins , American football player
- August 21 : Günter Helmchen , German chemist
- August 22 : Karl-Ernst Apfelbacher , German theologian († 2015 )
- August 22nd : Lynne Bowen , Canadian historian
- August 22 : Heinrich Kuhn , German doctor and politician
- August 23 : Vicki Brown , British singer († 1991 )
- August 23 : André Laberge , Canadian organist and harpsichordist
- August 25 : Norbert Grupe , German professional boxer and actor († 2004 )
- August 25 : Thomas Kakuska , Austrian musician, professor of music and performing arts in Vienna († 2005 )
- August 27 : Enrico Feroci , Italian Archbishop and Cardinal
- August 27 : Dieter Senghaas , German political scientist and peace researcher
- August 27 : Sonny Sharrock , American jazz guitarist († 1994 )
- August 28 : Christian Ludwig Attersee , Austrian Pop Art painter
- August 28 : William Cohen , US politician and Secretary of Defense
- August 28 : Heinz Klevenow , German actor and theater director
- August 28 : Dyson Lovell , British actor and film producer
- August 28 : Roger Pingeon , French cyclist († 2017 )
- August 29 : Bennie Maupin , American jazz musician
- August 29 : Rotraud Schindler , German actress and comedian
- August 31 : Jack Thompson , Australian actor
- August 31 : Dorrit Willumsen , Danish writer
September
- September 1st : Franco Bitossi , Italian cyclist
- September 1st : Anatoly Donchenko , German chess player
- September 1 : Annie Ernaux , French writer
- September 1 : János Galambos , Hungarian mathematician († 2019 )
- September 2nd : Rudolph Angermüller , German musicologist
- September 2nd : Régis Debray , French philosopher
- September 2nd : Jack White , German music producer
- September 3rd : Pauline Collins , British actress
- September 3 : Eduardo Galeano , Uruguayan journalist, essayist and writer († 2015 )
- September 4th : Mona Kelly , Canadian singer
- September 5 : Billy Adler , American film director
- September 5 : Raquel Welch , American actress
- September 6 : Udo Arnold , German historian and university professor
- September 6 : Rudolf Bindig , German politician and Member of the Bundestag
- September 6th : Hans Christian Knuth , Bishop of the Schleswig District of the North Elbian Evangelical Lutheran Church
- September 7th : Dario Argento , Italian film director and screenwriter
- September 9 : Vicente Segrelles , Spanish cartoonist and author
- September 9 : Lothar Ulsaß , German football player († 1999 )
- September 10 : Dave Burrell , American jazz pianist
- September 11 : Klaus Gerwien , German football player († 2018 )
- September 11th : John David Hawkins , British Hittite scientist
- September 11th : Brian De Palma , American film director
- September 12 : Joachim Frank , German-American biophysicist and Nobel Prize winner
- September 12 : Linda Gray , American actress
- September 13 : Óscar Arias Sánchez , President of Costa Rica, Nobel Peace Prize Laureate
- September 13 : Kurt Faltlhauser , German politician
- September 14th : Manfred Ach , German politician
- September 14 : James Morsley Anderson , American physician and chemist
- September 14 : Larry Brown , American basketball coach
- September 14 : Wenceslav Konstantinow , Bulgarian writer and translator († 2019 )
- September 15th : Chris Menges , British cinematographer and film director
- September 15 : Jürgen Schröder , German MEP
- September 15 : Norman Spinrad , American science fiction writer
- September 16 : Lisle Arthur Atkinson , American jazz bassist († 2019 )
- September 16 : Hamiet Bluiett , American jazz musician († 2018 )
- September 16 : Jutta Heine , German athlete and Olympian
- September 17th : Jan Eliasson , Swedish diplomat
- September 17 : Cynthia Flood , Canadian writer
- September 17th : Klaus Küng , Roman Catholic Bishop of the diocese of St. Pölten
- September 17th : Karin Reschke , German writer
- September 17th : Heidelinde Weis , Austrian actress
- September 18 : Frankie Avalon , American musician and actor
- September 18 : Abbas al-Fassi , Moroccan politician
- September 19 : Karin Baal , German theater, film and television actress
- September 19 : Bill Medley , American singer
- September 20 : Tarō Asō , Japanese politician
- September 20 : Joseph J. DioGuardi , American politician
- September 21 : Lowell Lee Andrews , American murderer († 1962 )
- September 21 : Rudolf Jaggi , Swiss composer († 2015 )
- September 21 : Hermann Knoflacher , Austrian civil engineer, planner, Univ.-Prof. at the TU Wien, President of the Club of Vienna
- September 22nd : Edward Bogusławski , Polish composer and music teacher († 2003 )
- September 22 : Anna Karina , Danish actress († 2019 )
- September 23 : Gerhard Hennige , German athlete
- September 23 : Hans Siemensmeyer , soccer player
- September 23 : Michel Temer , Brazilian politician
- September 24th : Amelita Baltar , Argentine tango and folk singer
- September 24 : Don Brash , New Zealand opposition leader
- September 24 : Yves Navarre , French writer († 1994 )
- September 24 : José Ramírez Conde , Dominican painter († 1987 )
- September 25 : Brigitte Burmeister , German literary scholar and writer
- September 26 : Gary Bartz , American jazz saxophonist
- September 26 : Klaus Grehn , German politician († 2017 )
- September 26 : Heinz Jacobsen , German handball official
- September 27 : Reiner Dick , Professor of Business Administration († 1974 )
- September 27 : Rudolph Moshammer , German fashion designer († 2005 )
- September 28th : Guido De Rosso , Italian cyclist
- September 30th : Harry Jerome , Canadian athlete and Olympian († 1982 )
October
- October 1 : Phyllis Chesler , American writer
- October 1st : Fredi M. Murer , Swiss filmmaker
- October 1 : Steve O'Rourke , British music manager, racing team owner and racing car driver († 2003 )
- October 1 : Marc Savoy , American accordion player and maker
- October 2 : Hans-Jürgen Audehm , German textbook author
- October 2 : Werner Dörflinger , German politician, Member of the Bundestag
- October 2 : Gheorghe Gruia , Romanian handball player († 2015 )
- October 2 : Herbert Riehl-Heyse , German journalist and author († 2003 )
- October 3 : Alan O'Day , American singer and songwriter († 2013 )
- October 4 : Barbara Henneberger , German ski racer († 1964 )
- October 4th : Silvio Marzolini , Argentine footballer († 2020 )
- October 4th : Steve Swallow , American jazz musician
- October 5 : Rein Aun , Soviet athlete († 1995 )
- October 5 : Manfred Bissinger , German publicist
- October 5th : Giacomo Caliri , Italian racing car designer and aerodynamicist
- October 6 : Boris Dmitrijewitsch Andrejew , Soviet cosmonaut
- October 6 : Manfred Bietak , Austrian Egyptologist
- October 6 : Wyche Fowler , American politician
- October 6 : Eberhard Zeidler , German mathematician († 2016 )
- October 7 : Larry Young , American jazz musician (organist, composer) († 1978 )
- October 9 : Hans Ulrich Humpert , German composer († 2010 )
- October 9 : John Lennon , British musician (The Beatles) († 1980 )
- October 9 : Bernd Wulffen , German diplomat
- October 10 : Helge Adolphsen , German theologian
- October 10 : Erling von Mende , German sinologist
- October 10 : Kiyoshi Tanabe , Japanese boxer
- October 11 : Christoph Blocher , Swiss entrepreneur and politician (SVP)
- October 11th : Reiner Frieske , German handball goalkeeper
- October 12 : Anton Fischhaber , German racing car driver
- October 12 : Woldetensaé Ghebreghiorghis , Ethiopian Bishop
- October 12 : Fares Maakaroun , Lebanese clergyman and bishop of the Melkites in Brazil
- October 12th : Silvano Tomasi , Italian Archbishop and Cardinal
- October 13 : Peter Eckardt , German politician and Member of the Bundestag
- October 13 : Chris Farlowe , English rhythm and blues singer
- October 14th : Cliff Richard , British pop star
- October 15 : Isabella Ackerl , Austrian historian, Germanist and author
- October 15 : Peter Doherty , Australian veterinarian and immunologist
- October 15 : Benno Ohnesorg , student who was shot at a demonstration in Berlin († 1967 )
- October 15 : Edwin Skinner , athlete and Olympian from Trinidad and Tobago
- October 16 : Dave DeBusschere , American basketball player († 2003 )
- October 17th : Jürgen Abraham , German entrepreneur
- October 17th : Marion Michael , German actress († 2007 )
- October 18 : Uzi Even , Israeli university professor
- October 18 : Ruth Wagner , German politician
- October 18 : Cynthia Weil , American composer
- October 19 : Bettina von Arnim , German painter, draftsman and graphic artist
- October 19 : Michael Gambon , Irish actor
- October 20 : Yossi Mar-Chaim , Israeli composer
- October 21 : Peter Maurice Arnison , Australian officer and politician
- October 21 : Rainer Christlein , German prehistorian († 1983 )
- October 21 : Natalia Makarova , Russian ballet dancer
- October 21 : Manfred Mann , South African-British rock musician
- October 21 : Marita Petersen , first female head of government of the Faroe Islands († 2001 )
- October 21 : Roy Woods , American car racing driver and racing team owner († 2004 )
- October 22 : José Colángelo , Argentine tango pianist and composer
- October 23 : Adolf Fehr , Liechtenstein ski racer
- October 23 : Ellie Greenwich , American singer, songwriter and music producer († 2009 )
- October 23 : Edson Arantes do Nascimento, known as Pelé , Brazilian soccer player
- October 24 : Giacomo Bulgarelli , Italian soccer player († 2009 )
- October 24 : Jörg-Dietrich Hoppe , German medical representative († 2011 )
- October 25 : Bobby Knight , American basketball coach
- October 26 : Domna Adamopoulou , Greek actress
- October 26 : Tilo Prückner , German actor († 2020 )
- October 26th : Wolfgang Digit , German actor and voice actor
- October 27 : John Gotti , American Mafioso († 2002 )
- October 28 : Karl Arnold , German weightlifter († 2012 )
- October 28 : Richard Kriesche , Austrian object and media artist
- October 29th : Frida Boccara , French singer († 1996 )
- October 29 : Connie Mack , American politician
- October 29th : Heinrich Mussinghoff , German bishop
- October 31 : Reimer von Essen , German jazz clarinetist and bandleader
- October 31 : Uwe-Karsten Heye , German journalist, diplomat and author
November
- November 1 : Larry Kusche , American pilot, flight instructor, librarian and non-fiction author
- November 2 : Vincenzo Cerami , Italian writer and screenwriter († 2013 )
- November 2nd : Phil Minton , British jazz singer and trumpeter
- November 2nd : Carolin Reiber , German journalist, TV announcer and presenter
- November 3 : Dieter Acker , German-speaking composer († 2006 )
- November 4th : Marlène Jobert , French actress
- November 4th : Jonathan Leakey , Kenyan-British businessman
- November 5th : Ivan Angeli , Italian director
- November 5 : Anthony Rolfe Johnson , English tenor († 2010 )
- November 5th : Dmitri Alexandrowitsch Prigow , Russian artist († 2007 )
- November 5th : Elke Sommer , German actress, singer, director and painter
- November 5 : Ted Kulongoski , American politician
- November 6 : Alice Arlen , American screenwriter and biographer († 2016 )
- November 6th : Volker Jacobs , German journalist
- November 6 : Dieter F. Uchtdorf , Apostle of The Church of Jesus Christ of Latter-day Saints
- November 7th : Antonio Skármeta , Chilean writer
- November 8 : Charles Thomas Kowal , American astronomer († 2011 )
- November 10 : Screaming Lord Sutch , British musician and politician († 1999 )
- November 10 : Ralf Weikert , Austrian conductor
- November 11 : Barbara Boxer , US politician
- November 11th : Dennis James Coffey , American studio guitarist
- November 11th : Mario Pavone , American jazz bassist
- November 11th : Jacob Stickelberger , Swiss songwriter and lawyer
- November 12th : Jürgen Todenhöfer , German politician, author and manager
- November 13 : Rudolf Schwarzkogler , Austrian photographer and artist († 1969 )
- November 14 : David Henry Auston , American physicist
- November 15 : Klaus Ampler , German racing cyclist († 2016 )
- November 16 : Manfred Heise , German politician
- November 17th : Jurgis Aušra , Lithuanian manager and politician
- November 17th : Rudolf Dreßler , German politician
- November 17 : Luke Kelly , Irish singer and banjo player († 1984 )
- November 17 : Gunnar Uldall , German politician († 2017 )
- November 18 : Adriano Aprà , Italian author and film critic
- November 18 : Rainer Funke , German politician
- November 18 : Qaboos ibn Said , Sultan of Oman († 2020 )
- November 20 : Hermann L. Gremliza , German journalist and writer († 2019 )
- November 20 : Chiem van Houweninge , Dutch actor
- November 20 : Helma Sanders-Brahms , German film director († 2014 )
- November 21 : Götz Adriani , German art historian
- November 21 : Alfred Beth , German politician
- November 21 : Alberto Villalpando , Bolivian composer
- November 22nd : Frank Duval , German composer, band leader, singer and arranger
- November 22nd : Terry Gilliam , American director, member of Monty Python
- November 22nd : Andrzej Żuławski , Polish film director († 2016 )
- November 23 : John Gudenus , Austrian politician († 2016 )
- November 23 : Gösta Pettersson , Swedish cyclist
- November 24th : Hermann Otto Solms , German politician
- November 25 : Klaus Berger , German theologian († 2020 )
- November 25 : Reinhard Furrer , German astronaut, physicist, pilot († 1995 )
- November 25th : Jan Jongbloed , Dutch football player
- November 25th : María Teresa Luengo , Argentine composer and music teacher
- November 25th : Karl Offmann , Mauritanian President
- November 25 : Percy Sledge , American R&B and soul singer († 2015 )
- November 27 : Bruce Lee , actor and icon of martial arts film († 1973 )
- November 27 : José Ramón Maranzano , Argentine composer
- November 28th : Wittko Francke , German chemist
- November 28 : Kees Olthuis , Dutch composer, bassoonist and pianist († 2019 )
- November 28 : Claude Rault , French religious priest and bishop of the Algerian diocese of Laghouat
- November 29th : Seán Cannon , Irish singer and guitarist
- November 29 : Óscar Espinosa Chepe , Cuban economist, diplomat and dissident († 2013 )
- November 29 : Billy Hart , American jazz drummer
- November 30th : Peter Gamper , German athlete
December
- December 1 : Mário Fernandes da Graça Machungo , Mozambican Prime Minister († 2020 )
- December 1 : Richard Pryor , American actor († 2005 )
- December 2nd : Gunter Schoß , German actor and presenter
- December 3rd : Jacques Auxiette , French politician
- December 3 : Manuela Ferreira Leite , Portuguese economist and politician
- December 3 : Horst Kunz , German chemist
- December 4th : Gerd Achterberg , German soccer player and soccer coach
- December 4th : Barbara Joan Estelle Amiel , British-Canadian journalist and writer
- December 4th : Freddy Cannon , American rock 'n' roll singer
- December 4th : Ulla Norden , German pop singer and presenter († 2018 )
- December 5 : Horst Hirnschrodt , Austrian football player († 2018 )
- December 5th : Peter Pohl , Swedish author of children's books and mathematics professor
- December 5 : August Wolfinger , former Liechtenstein ski racer
- December 6th : Klaus Ammann , Swiss botanist
- December 7th : Heinfried Birlenbach , German athlete († 2020 )
- December 7th : Klaus Tschira , German entrepreneur († 2015 )
- December 9 : Josef Ambacher , German bank director and President of the German Shooting Association († 2012 )
- December 9 : Clancy Eccles , Jamaican reggae musician and producer († 2005 )
- December 10 : Libertina Inaviposa Appolus-Amathila , Namibian politician
- December 10 : Leonas Apšega , Lithuanian politician
- December 12th : Dionne Warwick , American singer and television presenter
- December 13 : Gabriel Edgardo Aguilera Peralta , Guatemalan Ambassador
- December 13th : Edith Clever , German actress and director
- December 13th : Jutta Wachowiak , German actress
- December 14th : Paco Camino , Spanish torero
- December 15 : Irmgard Karwatzki , German politician and Member of the Bundestag († 2007 )
- December 15 : Barbara Valentin , Austrian actress († 2002 )
- December 15 : Nikol Voigtländer , German actor and director
- December 16 : Hervé Poulain , French entrepreneur and racing car driver
- December 17th : Anna Prucnal , Polish-French actress and singer
- December 18 : Ilario Castagner , Italian football player and coach
- December 18 : Lei Feng , soldier of the Chinese People's Liberation Army († 1962 )
- December 18 : Bram Morrison , Canadian actor, singer and guitarist
- December 18 : Klaus Wennemann , German actor († 2000 )
- December 19 : Slobodan Ćurčić , American art historian and Byzantinist († 2017 )
- December 19 : Till Lufft , track and field athlete and sports official
- December 19 : Abraham Munabi , former Ugandan long and triple jumper
- December 19 : Phil Ochs , American protest singer († 1976 )
- December 20 : Klaus Kada , Austrian architect
- December 21 : Moritz de Hadeln , British director of various film festivals
- December 21 : Frank Zappa , American composer, musician († 1993 )
- December 22nd : Eberhard Schöler , German table tennis player
- December 22nd : Sigrid Semper , German politician
- December 23 : Jorma Kaukonen , American blues, folk and rock guitarist
- December 25th : Wolfgang Stürner , German historian
- December 28th : Arackaparambil Kurien Antony , Indian politician
- December 28 : Peter Göring , GDR wall gunner, shot dead by two West Berlin police officers († 1962 )
- December 29th : Nestor Combin , French football player
- December 29 : Brigitte Kronauer , German writer and essayist († 2019 )
- December 30th : Richard Groß , German civil servant
- December 30th : Renate Jaeger , German judge
- December 31 : Karl Bauer , German landscape architect and architect
- December 31 : José de Anchieta Fontana , Brazilian soccer player († 1980 )
Exact date of birth unknown
- Per Lennart Aae , German politician (NPD)
- Joel Agee , American writer and translator
- Leila Ahmed , Egyptian-American university professor for women's studies
- Jo Akepsimas , Greek-French chansonnier and composer
- Asım Akin , Turkish physician, university professor and book author
- Ahmed ibn Abd al-Aziz Al Saud , Saudi prince
- Enrique Anleu-Díaz , Guatemalan composer, musicologist and ethnomusicologist
- Michael A. Arbib , English neuroscientist, computer scientist and mathematician
- William David Arnett , American theoretical astrophysicist
- Jerry Arnold , American rockabilly musician
- Luciana Arrighi , Italian film architect, costume and production designer
- Dietmar Artzinger-Bolten , German lawyer and politician
- Winfried Aßfalg , German special school principal, local researcher and author
- Rudolf Aumann , German chemist
- Judith Binney , New Zealand historian († 2011 )
- Klaus Eisenmann , German conductor and music teacher
- Joachim Heusinger von Waldegg , German art historian
- Barbara Hobom , German science journalist
- Dogabe Jeremiah , Nauruan politician and member of parliament
- Jürgen Kolbe , German Germanist, writer and local politician († 2008 )
- Angela Luther , German terrorist
- Mohamed Majd , Moroccan actor († 2013)
- Tomasz Michalak , Polish violinist and conductor († 1986 )
- Gemma O'Connor , Irish writer
- Burhānuddin Rabbāni , Afghan politician († 2011 )
- Ulrich Ritzel , German journalist and writer
- Reinhard Schulat-Rademacher , German voice actor, radio play speaker and actor († 2010 )
- Jürgen Schwarz , German high school teacher and textbook author
- Peter Thoms , German drummer and actor
- Klaus Trumpf , German musician and university professor
- Chris Tuerlinx , Belgian racing driver († 1973 )
- Richard Weiner , American percussionist and music educator
- Donald Wheelock , American composer and music educator
- Semir Zeki , British-Lebanese neurobiologist
Died
January February
- January 1 : William Albert Ashbrook , American politician (* 1867 )
- January 1 : Frank Neil , Australian theater entrepreneur (* 1886 )
- January 5 : Charles Nagel , American politician and lawyer (* 1849 )
- January 9 : Josef Jiránek , Czech pianist, composer and music teacher (* 1855 )
- January 10 : Alojzy Adamczyk , Polish resistance fighter (* 1895 )
- January 11th : Michał Marian Siedlecki , Polish marine biologist (* 1873 )
- January 13 : Georg Hermann Emil Friedrich Kautz , German administrative lawyer and ministerial director (* 1860 )
- January 20 : Camilla Mayer , German high wire artist (* 1918 )
- January 23 : Giuseppe Motta , Swiss politician (* 1871 )
- January 27 : Isaak Babel , Russian journalist of Jewish origin (* 1894 )
- January 27 : Clement Heaton , British glass painter and blower (* 1861 )
- January 28 : Rodolphe Plamondon , Canadian singer, cellist and music teacher (* 1876 )
- January 31 : René Schickele , French writer (* 1883 )
- February 1 : Hedwig Bleuler-Waser , Swiss temperance specialist (* 1869 )
- February 2 : Ernst Günther Burggaller , German officer, motorcycle and automobile racing driver (* 1896 )
- February 5 : Charles S. Deneen , American politician (* 1863 )
- February 5 : Maria Gleiss , German doctor (* 1865 )
- February 8 : Hans Ostwald , German journalist and writer (* 1873 )
- February 10 : Karl von Müller , German theologian (* 1852 )
- February 12 : Selwyn Edge , British racing car driver (* 1868 )
- February 15 : Onofre Jarpa Labra , Chilean painter (* 1849 )
- February 15 : Otto Toeplitz , German mathematician (* 1881 )
- February 18 : Rudy Wiedoeft , American saxophonist (* 1893 )
- February 19 : Olli Huttunen , Finnish skier (* 1915 )
- February 20 : Abdullah Abdurahman , South African politician (* 1872 )
- February 20 : Hans Bachmann , Swiss hydrobiologist (* 1866 )
- February 20 : Heinrich Seufferheld , German draftsman, painter and etcher (* 1866 )
- February 23 : Karl Duncker , German psychologist (* 1903 )
- February 23 : Ichikawa Sadanji II , Japanese Kabuki actor (* 1880 )
- February 24th : Ascensión del Corazón de Jesús , Spanish nun and founder of the order (* 1868 )
- February 24 : Ludwig Kessing , German worker poet (* 1869 )
- February 26 : Michael Hainisch , first Federal President of the Republic of Austria (* 1858 )
- February 27 : Peter Behrens , German architect, painter and designer (* 1868 )
- February 28 : Andreas Heusler , Swiss Old Germanist (* 1865 )
- February 29 : Simon Abram , Austrian politician (* 1871 )
March April
- March 8 : Walter Gottfried von Auwers , German lawyer and politician (* 1869 )
- March 10 : Agnes von Krusenstjerna , Swedish writer (* 1894 )
- March 10 : Mikhail A. Bulgakov , Russian writer (* 1891 )
- March 13 : Elise Augustat , German politician (* 1889 )
- March 14 : Heinrich Lübbe , German mechanical engineer and inventor (* 1884 )
- March 15 : Christian Aigens , Danish artist (* 1870 )
- March 15 : Robert Leffler , German singer, actor and director (* 1866 )
- March 16 : Selma Lagerlöf , Swedish writer (* 1858 )
- March 19 : Besim Ömer Akalın , Turkish professor and politician (* 1862 )
- March 20 : Johann Gottlieb von Langen , German industrialist (* 1858 )
- March 20 : Alfred Ploetz , German doctor and racist (* 1860 )
- March 21 : Felice Nazzaro , Italian racing driver (* 1881 )
- March 23 : Minakami Takitarō , Japanese writer (* 1887 )
- March 24th : Édouard Branly , French physicist and pioneer of radio technology (* 1844 )
- March 25 : Ludwig Sauer , German organist (* 1861 )
- March 26 : Wilhelm Robert Karl Anderson , German-Baltic astrophysicist (* 1880 )
- March 26 : Helene Böhlau , German writer (* 1856 )
- March 26 : July Schokalski , Russian-Soviet oceanographer (* 1856 )
- March 29th : Johann Schütte , German airship pioneer (* 1873 )
- April 1 : Friedrich Georg Theodat Graf von der Asseburg , Prussian major and chamberlain (* 1861 )
- April 3 : Walter Eisfeld , camp commandant of Sachsenhausen concentration camp and Neuengamme concentration camp (* 1905 )
- April 3 : Josef Ponten , German architect, art historian and writer (* 1883 )
- April 3 : Peter Wust , Christian existential philosopher (* 1884 )
- April 8 : Andrés Delgado Pardo , Venezuelan pianist, composer and music teacher (* 1870 )
- April 15 : Friedrich Andersen , German Protestant theologian (* 1860 )
- April 17 : Katharina Schratt , Austrian actress (* 1853 )
- April 21 : Paul Arendt , German theater actor (* 1853 )
- April 21 : Margaret Fountaine , British butterfly researcher (* 1862 )
- April 25 : Wilhelm Dörpfeld , German architect and archaeologist (* 1853 )
- April 26 : Carl Bosch , German chemist, technician and industrialist (* 1874 )
- April 27 : Karimeh Abbud , Palestinian-Israeli photographer (* 1893 )
- April 30th : Furnifold McLendel Simmons , American politician (* 1854 )
May June
- May 1 : Leonard Leslie Brooke , British illustrator and author (* 1862 )
- May 2 : Jean-François-Charles Amet , French Vice Admiral and Allied High Commissioner in Constantinople (* 1861 )
- May 3 : Rudolf Arndt , German communist and resistance fighter (* 1909 )
- May 3 : Jan de Vries , Dutch mathematician (* 1858 )
- May 4 : Celine Marier , Canadian singer and vocal teacher (* 1871 )
- May 5th : Willi Schlage , German chess master (* 1888 )
- May 8 : Hedwig Scherrer , Swiss graphic artist and painter of the Arts & Crafts movement (* 1878 )
- May 14 : Emma Goldman , American anarchist and peace activist (* 1869 )
- May 15 : Bruno Asch , German politician (* 1890 )
- May 20 : Verner von Heidenstam , Swedish poet (* 1859 )
- May 24th : Achim Konstantin Rudolf Ferdinand von Arnim , German officer (* 1881 )
- May 26 : Wilhelm Prince of Prussia , eldest son of the Prussian and German Crown Prince (* 1906 )
- May 26th : Silvio Vailati , Italian motorcycle racer (* unknown)
- May 28 : Friedrich Karl of Hesse , Prince and Landgrave of Hesse and as Väinö I. King of Finland (* 1868 )
- May 29 : Mary Antoinette Anderson , American stage actress (* 1859 )
- May 30th : Marie Arnsburg , Austrian painter (* 1853 )
- May 30th : Otto Neururer , Catholic pastor (* 1882 )
- June 9 : Janet Scudder , American sculptor (* 1869 )
- June 10 : Marcus Garvey , Jamaican journalist (* 1887 )
- June 15 : Blumepeter , Mannheim local legend (* 1875 )
- June 16 : Vítězslava Kaprálová , Czech composer (* 1915 )
- June 17th : Arthur Harden , British biochemist and Nobel Prize winner (* 1865 )
- June 19 : Pete Henderson , Canadian racing car driver (* 1895 )
- June 19 : Attilio Marinoni , Italian racing car driver (* 1892 )
- June 20 : Ernest Gibson , American politician (* 1871 )
- June 21 : Walter Hasenclever , expressionist German writer (* 1890 )
- June 21 : Tomasz Stankiewicz , Polish cyclist and victim of National Socialism (* 1902 )
- June 21 : Jean Vuillermoz , French composer (* 1906 )
- June 22nd : Wladimir Peter Köppen , German meteorologist and climatologist (* 1846 )
- June 24 : Joseph Meister , the first person successfully vaccinated against rabies (* 1876 )
- June 25 : John Stuchell Fisher , American politician (* 1867 )
- June 27 : Johannes Kirchner , German classical philologist (* 1859 )
- June 27th : Harry Burton , British photographer (* 1879 )
- June 28 : Ferdinando Minoia , Italian racing car driver (* 1884 )
- June 29 : Paul Klee , Swiss painter of abstract painting (* 1879 )
- June: Willi Münzenberg , German peace activist (* 1889 )
July August
- July 1 : Andor Ákos , Hungarian-German architect, interior designer, painter and graphic artist (* 1893 )
- July 1 : Ben Turpin , American comedian (* 1869 )
- July 2 : John William Abercrombie , American lawyer and politician (* 1866 )
- July 5 : Carl Einstein , German art historian and writer (* 1885 )
- July 5 : Luigi Vanoni , Swiss engineer (* 1854 )
- July 10 : Donald Francis Tovey , English composer, pianist and musicologist (* 1875 )
- July 16 : Alexander Koenig , German zoologist (* 1858 )
- July 16 : Grethe Auer , Swiss-Austrian writer (* 1871 )
- July 16 : Johann Jacob Haßlacher , German politician and member of the Reichstag (* 1869 )
- July 21 : Hans Wagner , father of the Philatelist Days (* 1852 )
- July 23 : Karl Peucker , Austrian geographer and cartographer (* 1859 )
- July 26 : Kurt Kluge , German sculptor, ore caster and writer (* 1886 )
- June 28 : Italo Balbo , Italian air marshal (* 1896 )
- July 31 : Elfriede Lohse-Wächtler , German artist, euthanasia victim in Pirna-Sonnenstein (* 1899 )
- August 4th : Adolf Zauner , Austrian Romance studies and linguist (* 1870 )
- August 7th : Ernst Pfuhl , German archaeologist (* 1876 )
- August 8 : Fritz Büchner , German journalist (* 1895 )
- August 10 : Hans-Caspar von Zobeltitz , German writer and editor (* 1883 )
- August 12 : Ulrich Bigalke , German engineer, racing car driver, filmmaker and fighter pilot (* 1910 )
- August 12 : Johann-Volkmar Fisser , German general (* 1893 )
- August 13 : Henry Somer Gullett , Australian politician (* 1878 )
- August 13 : Brudenell White , Australian general (* 1876 )
- August 16 : William Anderson , Australian theater director (* 1868 )
- August 16 : Henri Desgrange , editor of the French sports newspaper L'Auto, founder of the Tour de France (* 1865 )
- August 18 : Walter Percy Chrysler , American automobile pioneer (* 1875 )
- August 20 : Percy Moreau Ashburn , American medic and military doctor (* 1872 )
- August 21 : Paul Juon , Russian composer (* 1872 )
- August 21 : Hermann Obrecht , Swiss politician (* 1882 )
- August 21 : Leon Trotsky , Russian revolutionary (* 1879 )
- August 22nd : Oliver Lodge , British physicist (* 1851 )
- August 22 : Rudolf Medek , Czech writer and soldier (* 1890 )
- August 24th : Hermann Fischer , German banker and politician (* 1873 )
- August 24th : Paul Nipkow , German technician (* 1860 )
- August 30 : Joseph John Thomson , British physicist and Nobel Prize winner (* 1856 )
September October
- September 1 : Gregorio Labayan Aglipay , Filipino clergyman (* 1860 )
- September 1 : Jonathan Bourne , American politician (* 1855 )
- September 2 : David F. Houston , American politician (* 1866 )
- September 4 : Henri Lavedan , French writer and journalist (* 1859 )
- September 7th : Edmund Rumpler , German designer (* 1872 )
- September 10 : Frederick Judd Waugh , American painter, illustrator and author (* 1861 )
- September 11th : Hermann Stehr , German writer (* 1864 )
- September 14 : Émile Argand , Swiss geologist and mineralogist (* 1879 )
- September 18 : Christian Jensen , German classical philologist and papyrologist (* 1883 )
- September 25 : Damian Buck , Swiss Benedictine priest, naturalist and educator (* 1871 )
- September 26 : Walter Benjamin , German writer, art and literary critic (* 1892 )
- September 27 : Helene Aeckerle , German author and translator (* 1875 )
- September 27 : Julius Wagner-Jauregg , Austrian doctor and psychiatrist (* 1857 )
- September 30 : Walter Kollo , German composer (* 1878 )
- September 30th : Oliver Henry Shoup , American politician (* 1869 )
- October 2nd : Johan August Anker , Norwegian sailor, Olympic champion, yacht designer and shipyard owner (* 1871 )
- October 5 : Camilla Jellinek , Austrian-German women's rights activist and lawyer (* 1860 )
- October 6 : Henry Horner , American politician (* 1879 )
- October 7th : Tim Rose-Richards , British racing car driver and naval aviator (* 1902 )
- October 8 : Walter Rusk , Northern Irish motorcycle racer (* 1910 )
- October 9 : Katherine Mayo , American writer and journalist (* 1867 )
- October 11 : Vito Volterra , Italian mathematician and physicist (* 1860 )
- October 12 : William H. Dieterich , American politician (* 1876 )
- October 12 : Luis Fontés , British racing car driver and aviator (* 1912 )
- October 13 : Friedrich Wilhelm Nohe , Chairman of the German Football Association (* 1864 )
- October 16 : George Sebastian Silzer , American politician (* 1870 )
- October 17 : Franz Joseph Dölger , church historian and religious scholar (* 1879 )
- October 19 : Erich Bethe , German classical philologist (* 1863 )
- October 19 : Umberto Caligaris , Italian football player and coach (* 1901 )
- October 19 : Emilio Comici , Italian alpinist and cave explorer (* 1901 )
- October 19 : Eli Kochański , Polish cellist and music teacher (* 1886 )
- October 20 : Erik Gunnar Asplund , Swedish architect, university professor and designer (* 1885 )
- October 21 : William G. Conley , American politician (* 1866 )
- October 23 : Ignacio Antinori , Italian-American mobster (* 1885 )
- October 23 : Max Askanazy , Swiss pathologist and oncologist (* 1865 )
- October 23 : George B. Cortelyou , American politician (* 1862 )
- October 24 : Victor Hollaender , German composer and conductor (* 1866 )
- October 24 : Hans Kyser , German writer and film director (* 1882 )
- October 24th : Pierre-Ernest Weiss , French physicist (* 1865 )
- October 26 : Julius Caldeen Gunter , American politician (* 1858 )
- October 27 : Fini Valdemar Henriques , Danish composer and violinist (* 1867 )
November December
- November 3 : Manuel Azaña , Spanish politician (* 1880 )
- November 4 : Felix Mach , German agricultural chemist (* 1868 )
- November 6th : Ivar Frithiof Andresen , Norwegian opera singer (* 1896 )
- November 7th : Julius Wahle , Austrian literary scholar (* 1861 )
- November 8 : Anne Siberdinus de Blécourt , Dutch lawyer and legal historian (* 1873 )
- November 9th : Neville Chamberlain , British politician and Prime Minister (* 1869 )
- November 12 : Alejandro García Caturla , Cuban composer (* 1906 )
- November 17 : Raymond Pearl , American biologist and geneticist (* 1879 )
- November 17th : Eric Gill , British sculptor, graphic artist and type designer (* 1882 )
- November 18 : Hermann Aichele , German administrative officer (* 1881 )
- November 18 : Benjamin Auerbach , German doctor (* 1855 )
- November 18 : Ivan Jawachishvili , Georgian scientist, founder of the University of Tbilisi (* 1876 )
- November 19 : Johannes Sassenbach , German trade unionist (* 1866 )
- November 20 : Harriot Eaton Stanton Blatch , American suffragette and publicist (* 1856 )
- November 24 : Gustav Neckel , German Old Germanist (* 1878 )
- November 28 : James Hotchkiss Rogers , American organist and composer (* 1857 )
- December 5 : Sebald Rudolf Steinmetz , Dutch ethno- and sociologist (* 1862 )
- December 6th : Andreas Heinrich Voigt , German mathematician and economist (* 1860 )
- December 8th : Louis Pinck , Catholic clergyman (* 1873 )
- December 11th : Nathaniel B. Dial , American politician (* 1862 )
- December 12th : Ernst Aufseeser , German painter, lithographer, xylograph, graphic designer and university lecturer (* 1880 )
- December 12 : Walter von Saint Paul-Illaire , German colonial administrator (* 1860 )
- December 15 : Clara Southern , Australian painter (* 1860 )
- December 15 : August Fischer , pharmacist, company founder of Uhu (* 1868 )
- December 18 : Georg Freundorfer , German zither player and composer (* 1881 )
- December 21 : F. Scott Fitzgerald , American writer (* 1896 )
- December 21 : Clelia Duel Mosher , American doctor and sex researcher (* 1863 )
- December 22nd : Nathanael West , American writer (* 1903 )
- December 30th : Albert Andreae de Neufville , German banker (* 1854 )
- December 30th : Gjergj Fishta , Albanian Franciscan priest, poet and translator (* 1871 )
- December 31 : Jacques-Arsène d'Arsonval , French physicist (* 1851 )
- December: Theodor Makridi , Ottoman civil servant and museum curator (* 1872 )
Exact date of death unknown
- Louis Allard , French trombonist and music teacher (* 1852 )
- Petre Andrei , Romanian sociologist and politician (* 1891 )
- Pierro Arrigoni , Italian architect (* 1856 )
- Selly Askanazy , German doctor (* 1866 )
- Cesare Bernardo Bellini , Italian composer and singing teacher (* 1853 )
- Paul Jatzow , German architect (* 1896 )
Web links
Commons : 1940 - Collection of Pictures, Videos and Audio Files