1861
Portal history | Portal Biographies | Current events | Annual calendar | Daily item
◄ |
18th century |
19th century
| 20th century
| ►
◄ |
1830s |
1840s |
1850s |
1860s
| 1870s
| 1880s
| 1890s
| ►
◄◄ |
◄ |
1857 |
1858 |
1859 |
1860 |
1861
| 1862
| 1863
| 1864
| 1865
| ►
|►►
Heads of State · Nekrolog · Art Year · Literature Year · Music Year · Sports Year
| 1861 | |
|---|---|
 Jefferson Davis is elected President of the Confederate States of America . Jefferson Davis is elected President of the Confederate States of America .
|
 Franz Joseph I issued the February patent for the Austrian Empire . Franz Joseph I issued the February patent for the Austrian Empire .
|
 The American Civil War begins with the attack on Fort Sumter by the Confederate States Army . The American Civil War begins with the attack on Fort Sumter by the Confederate States Army .
|
|
| 1861 in other calendars | |
| Armenian calendar | 1309/10 (turn of the year July) |
| Ethiopian calendar | 1853/54 (September 10-11) |
| Baha'i calendar | 17/18 (March 20/21) |
| Bengali solar calendar | 1266/67 (beginning of April 14th or 15th) |
| Buddhist calendar | 2404/05 (southern Buddhism); 2403/04 (alternative calculation according to Buddha's Parinirvana ) |
| Chinese calendar | 75th (76th) cycle
Year of the metal rooster辛酉 ( at the beginning of the year metal monkey 庚申) |
| Chula Sakarat (Siam, Myanmar) / Dai calendar (Vietnam) | 1223/24 (turn of the year April) |
| Dangun era (Korea) | 4194/95 (October 2/3) |
| Iranian calendar | 1239/40 (around March 21) |
| Islamic calendar | 1277/78 (July 8/9) |
| Jewish calendar | 5621/22 (September 4th / 5th) |
| Coptic Calendar | 1577/78 (September 10-11) |
| Malayalam calendar | 1036/37 |
| Rumi Calendar (Ottoman Empire) | 1276/77 (March 1) |
| Seleucid era | Babylon: 2171/72 (turn of the year April)
Syria: 2172/73 (turn of the year October) |
| Vikram Sambat (Nepalese Calendar) | 1917/18 (April) |
In 1861 After: the global political attention shifts the Americas to election of Abraham Lincoln to the United States President several earlier this year in November last year to explain southern their withdrawal from the Union and establish a little later, the Confederate States of America . Jefferson Davis is elected President of the Confederation. With the attack on Fort Sumter , the American Civil War finally began on April 12, and both sides expect it to end soon within a year.
In Mexico , the civil war in favor of the constitutionally elected President Benito Juárez came to an end. But the war has brought the country to the brink of economic ruin. The declaration that the payment of national debts abroad will be stopped calls the European powers Great Britain, Spain and France on the scene. In December, a Spanish expeditionary force lands in Veracruz, the vanguard of the European invasion of Mexico.
In Europe, Wilhelm I becomes the new King of Prussia , Emperor Franz Joseph I of Austria issues the February patent and the Protestant patent and Tsar Alexander II cancels serfdom in the Russian Empire . After the successful unification struggle , the Kingdom of Italy is proclaimed under Victor Emanuel II and Prince Alexandru Ioan Cuza proclaims the new Principality of Romania .
events
Politics and world events
| chronology | |
|---|---|
| January 1st |
Switzerland : Josef Martin Knüsel becomes Federal President . |
| January 2nd | |
| January 9th |
United States : Mississippi is the second of the southern states to declare its exit from the Union . |
| 10. January |
United States: Florida declares its exit from the Union. |
| 11th January |
United States: Georgia declares its exit from the Union. |
| January 14th |
Bolivia : José María Achá overthrows President José María Linares . |
| January 19th |
United States: Alabama withdraws from the Union. |
| January 26th |
United States: Louisiana withdraws from the Union. |
| January 29th |
United States: Kansas joins the Union as a state. |
| February 1st |
United States: Texas adopts its declaration of exit from the Union. |
| February 4th |
Establishment of the Confederate States of America . |
| 13th February |
Italy : Francis II of Naples and Sicily surrenders to the troops of the Kingdom of Sardinia . |
| February 18 |
Jefferson Davis is sworn in as President of the Confederate States of America . |
| February 26th |
Austrian Empire : Franz Joseph I issues the February patent . |
| February 28 |
United States : The Colorado Territory is established. |
| 2nd March |
United States : Dakota Territory and Nevada Territory are established. |
| 4th of March |
Abraham Lincoln is sworn in as President of the United States of America . |
| March 11 |
The Constitution of the Confederate States is adopted. |
| 17. March |
Victor Emmanuel II proclaims the Kingdom of Italy . |
| 2nd of April |
Gabriel García Moreno becomes President of Ecuador . |
| April 8th |
Austrian Empire : Franz Joseph I issues the Protestant patent . |
| 12./13. April |
Attack on Fort Sumter , the Civil War begins. |
| 17th April |
United States: Virginia adopts its declaration of exit from the Union. |
| May 3rd |
Winfield Scott puts forward his anaconda plan against the Confederation. |
| May 6th |
United States: Arkansas and Tennessee declare their exit from the Union. |
| May 7th |
Virginia joins the Confederate States. |
| May 16 |
Tennessee joins the Confederate States. |
| May 18 |
Arkansas joins the Confederate States. |
| May 20th |
United States: North Carolina withdraws from the Union and joins the Confederation. |
| June |
Tomás Cipriano de Mosquera conquers Santa Fé de Bogotá and becomes President of the Granada Confederation . |
| 3rd of June |
Civil War: Battle of Philippi |
| 8th June |
United States: Tennessee's exit from the Union is confirmed by referendum. |
| the 10th of June |
Civil War: Battle at Big Bethel |
| 25th June |
Abdülaziz becomes Sultan of the Ottoman Empire . |
| 2nd July |
Civil War: Battle at Hoke Run |
| 17th of September | |
| September 18 |
José Joaquín Pérez becomes President of Chile . |
| November 1st |
George B. McClellan replaces Winfield Scott as Commander-in-Chief of Union Forces. |
| December 8th |
Mexico : A Spanish expeditionary force lands in Veracruz. |
| Ongoing events | |
| Federal War in Venezuela (since 1859) | |
| Civil War in Colombia (since 1860) | |
| Prussian constitutional conflict (since 1860) during the New Era (since 1858) | |
| Rotativismo in Portugal (since 1856) | |
| Nian Uprising (since 1853) and Taiping Uprising (since 1850) against the Qing Dynasty in China (since 1644) | |
| Bakumatsu (since 1853) of the Edo period in Japan (since 1603) | |
| Second French Empire in France (since 1852) | |
| Founding days in Germany and Austria (since around 1840) | |
| Tanzimat reforms in the Ottoman Empire (since 1839) | |
| Victorian Age in Great Britain (since 1837) | |
North America
Civil War
prehistory
After Abraham Lincoln , who is known for his strict principles on the slave issue, was elected President of the United States last year , the state of South Carolina declared its withdrawal from the Union on December 20 . Although Lincoln, whose hands were tied until his inauguration on March 4th, urged his predecessor James Buchanan to act, he remained inactive with the argument that, from his point of view, the secession was illegal, but that he had no constitutional power. to intervene militarily. Encouraged by this inaction, more southern states turn their backs on the United States at the beginning of the year .
Within a few days, Mississippi (January 9th), Florida (January 10th), Alabama (January 11th) and Georgia (January 19th) declared their exit from the United States, followed by Louisiana on January 26th. On February 4 , a Provisional Congress is constituted in Montgomery , Alabama, made up of representatives of the states that have resigned until then and which are now forming the Confederate States of America . Congress, which is to draft a constitution and elect a president, elects Robert Woodward Barnwell of South Carolina as interim chairman on the proposal of William Parish Chilton , who however passes the office on to Howell Cobb of Georgia that same day .
A provisional constitution is passed on February 8th, on the basis of which Jefferson Davis is elected provisional president of the Confederate States of America the next day . Davis is sworn in on February 18. During February, Congress decided to set up a Confederate States Navy and a Confederate States Army , and at the end of March a Confederate States Marine Corps .
Texas , whose resignation declaration decided on February 1 at a convention in Austin , will be approved by referendum on February 23 and will therefore come into effect on March 2, is the last state that existed before Abraham Lincoln took office on March 4 and Start of the war of secession from the Union and join the Confederate States. However, Governor Sam Houston , hero of the Texas War of Independence, refuses to take the oath of allegiance to the Confederation and resigns. He will be succeeded on March 18 by Edward Clark .
On March 4, Abraham Lincoln took office as the 16th President of the United States with Vice President Hannibal Hamlin . In his inauguration speech, Lincoln adopted a conciliatory tone. He promises not to be the first to resort to violent measures, but at the same time makes it clear that his oath of office obliges him to definitely oppose a split in the Union.
Exactly on the day of Lincoln's inauguration, The Stars and Bars will be introduced in the south as the first flag of the Confederate States of America , and on March 11th the Provisional Confederate Congress will adopt the final version of the Confederate States Constitution , which will become the February 8th Provisional Constitution replaces. The new constitution is essentially the same as that of the United States . Significant differences between the two constitutional texts exist only with regard to the view of slavery, the rights of the member states and parliamentary budget and taxation controls.
On April 12th, Fort Sumter was attacked . The front Charleston location Fort is also after the secession of South Carolina remained under the control of pro-Union troops. When supply ships from the north appear in Charleston Bay, Jefferson Davis orders the capture of the fort, which Commander Robert Anderson finally hands over to Southern General Pierre Gustave Toutant Beauregard after a day of bombardment . There are no victims in the attack on the fort, but the Union artilleryman Daniel Hough is killed when the Union flag is saluted, one of the conditions of surrender. He is considered to be the first to die in the American Civil War .
Further political and strategic development

In this looming conflict, the north is far superior to the south in terms of population and economic strength. Above all, however, the Union cannot immediately take advantage of its numerical military superiority: At the beginning of the war, the US army consisted of around 16,000 men and most of the garrisons are in the west and along the Canadian border.
The south has the strategic advantage that the upper class of the southern states has a more pronounced military tradition than that of the north, which means that the Confederation has a relatively larger number of capable military personnel at its disposal. Above all, however, it does not have to wage a war of conquest to achieve its war goals , but can rely on the Union's exhaustion from war and on possible economic intervention by other powers if the war drags on.
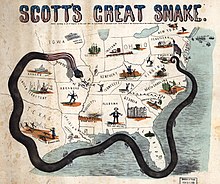
Both sides expect the war to last for a short time. The militiamen called up by Abraham Lincoln to reinforce the active units are only hired for three months, the militiamen of the South for a year. The campaign plan against the Confederation, presented in two versions by George B. McClellan to the Union's Commander-in-Chief, Lieutenant General Winfield Scott , assumes such a short duration of the war. Scott himself presented a plan to the Lincoln Cabinet on May 3rd, designed for a long-term war. The campaign plan , later known as the Anaconda Plan , immediately met with severe criticism and on November 1, Scott resigned as Commander-in-Chief in favor of McClellan. The Anaconda Plan, however, will prove to be decisive for the war in its later implementation. On July 22nd, the Congress finally approved a volunteer army of 500,000 men for the Union Army .
While a certain war mood is slowly emerging in the north, the beginning of the war moves four other southern states , Virginia , Tennessee , Arkansas and North Carolina to declare their exit from the Union and to join the confederation, in some cases this is also accompanied by referendums. Other slave-holding states such as Maryland , on the other hand, opt to remain in the Union. Shortly after Virginia's accession, the Confederation capital moves from Montgomery , Alabama, to Richmond , Virginia. In spite of this revaluation it comes in this state of all things to the "secession from secession": Several western counties split off on April 27th and declare their re-entry into the Union and in Wheeling on June 11th the Restored Government of Virginia meets and declares the Virginia's exit from the Union is invalid.
- November 6th: The people elect Jefferson Davis as President of the Confederate States of America .
- November: The Trent affair almost leads Britain to join the war on the Confederate side.
Eastern theater of war
Blockade of Chesapeake Bay
- Between May 7th and June 5th there were several small skirmishes, none of which resulted in a clear decision.
- June 10: In the roughly one hour battle at Big Bethel , the attacking Union troops under Benjamin Franklin Butler are thrown back by the Confederates under John Bankhead Magruder .
- June 27: The battle at Mathias Point ends with a Confederation victory.
Operations in western Virginia
- May 14: George B. McClellan becomes commander of the Ohio Defense Forces of the Union.
- June 3: The Union's victory in the battle at Philippi is an important prerequisite for the establishment of West Virginia .
- July 11: Union forces under McClellan and William S. Rosecrans win the Battle of Rich Mountain .
- July 28: Robert Edward Lee takes command of the Confederate forces in northwestern Virginia.
- August 26th: In the battle at Kessler's Cross Lanes , the Confederates defeat the Union forces.
- September 10: In the Battle of Carnifex Ferry , the Union troops under William Starke Rosecrans defeat the Confederates and regain control of the Kanawha Valley .
- 12-15 September: After three days of fighting, Union forces repel the Confederate attack on Cheat Mountain .
- October 3: The battle on the Greenbrier River ends without a decision.
- December 13: The battle at Camp Allegheny ends in a draw, but Union troops succeed in driving the Confederates out of the territory of West Virginia for good.
Manassas campaign
- July 2: Union wins in battle at Hoke Run .
- JULY 18: The Confederate Army of the Potomac wins the Battle of Blackburn's Ford on the Army of Northeastern Virginia Union.
- July 21: The Confederates win the First Battle of Bull Run and destroy the hopes of the north to march quickly on the Confederate capital Richmond and thus put a quick end to the war. General Irvin McDowell was subsequently deposed as Commander in Chief of the Army of Northeastern Virginia and replaced by Major General George B. McClellan , who increased the strength of the army to 150,000 men and had it trained well.
McClellan's operations in Northern Virginia
- October 21: The southern states defeat the northern states in the battle at Balls Bluff .
- October 22nd: North Virginia Confederate Defense Area established under the command of General Joseph E. Johnston .
- December 20: The Battle of Dranesville ends with a Union victory.
Western theater of war
- May 20: Kentucky , home state of both Abraham Lincoln and Jefferson Davis, initially tries to remain neutral in the conflict. However, neutrality is not observed by any of the warring parties.
- September 3: Confederates under Leonidas Polk invade southern Kentucky, whereupon Union troops under Ulysses S. Grant march in. There were several smaller skirmishes, including at Barbourville .
- September: The congress in Frankfort declares - against the will of the governor sympathizing with the confederation - the state to belong to the Union. On November 20, there is a declaration of independence by supporters of the Confederation in Bowling Green and a Confederate government of Kentucky is established . As a result, the state remains divided.
- November 3rd: Construction of Fort Knox begins under the name of Fort Duffield and will be completed in two months.
Trans Mississippi
- January 29: The eastern part of the Kansas Territory is admitted as a Free State under the name Kansas . It is officially the 34th state in the United States .
- July 5: In the battle near Carthage , Missouri, the southern states under Governor Claiborne Fox Jackson achieve an insignificant victory.
- July 27: Following the conquest of Jefferson City , union loyal Hamilton Rowan Gamble is elected governor of Missouri to replace Claiborne Fox Jackson .
- August 1: After a victory at Mesilla , the Confederation declares the southern half of New Mexico Territory as Arizona Territory as Confederate Territory. The plan to conquer the territory came from Henry Hopkins Sibley .
- August 10: The Battle of Wilson's Creek , Missouri, is the first major battle across the Mississippi River . It is won by the Confederates.
Western United States Territories
With the admission of the eastern part of the previous Kansas Territory under the name of Kansas as a federal state on January 29, the federal government of the United States de facto recognized the eastern border of the Jefferson Territory, which was founded in 1859 and has been independently organized since then . At the time of admission, no information is given about what to do with the western half of the Kansas Territory, which amounts to recognition of the entire Jefferson Territory that has claimed that part of the Territory. However, the federal government bypasses formal recognition by organizing the Colorado Territory within the boundaries of the Jefferson Territory on February 28 . William Gilpin becomes governor, the newly established Colorado City is raised to the place of the previous capital Golden , the territory motto is Nil sine numine . Ten days earlier, the Arapaho and Cheyenne peoples ceded most of their territories to the United States. However, the Pike's Peak Gold Rush is slowly subsiding, not least because many gold seekers continue to move to British Columbia, where a new gold rush has broken out.
From parts of the Minnesota Territory and the Nebraska Territory , the Dakota Territory will be merged as the Territory of the United States on March 2 . The territorial capital of the area, which in addition to the present-day US states South and North Dakota also includes large parts of Montana and Wyoming , is Yankton , and William Jayne is appointed as the first governor .
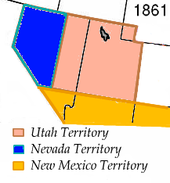
On the same day, the western part of the Utah Territory is also separated and reorganized as the Nevada Territory . Governor is James W. Nye appointed. The capital, originally in Genoa , will soon be relocated to Carson City . The separation of the territory takes place, among other things, because of the strong tensions between the Mormons in the east of the previous Utah Territory and members of other Christian currents in the west.
- As a result of the Bascom affair , a ten-year guerrilla war between Chiricahua - Apache chief Cochise and the US Army begins .
British North America
Than is known that in the last two years in the Cariboo region in British Columbia has come to gold finds that begins Cariboo Gold Rush . In order to get the flow of gold prospectors under control, which is made up of disappointments from the Fraser Canyon gold rush that has just subsided , but which also includes many newcomers from Europe, the Royal Engineers begin building the Cariboo Road , which will be completed in 1865 .
Mexico
The liberal troops of the elected President Benito Juárez conquer Mexico City , the capital of the Conservatives, in January and win the Mexican Civil War, which has been going on since 1858 . The elected liberal government will then move from Veracruz to Mexico City and Juárez will be able to take up his constitutional term as president.
But the civil war has drained the country financially. On July 17th, the government decided to stop paying Mexico's foreign debt for two years. The national bankruptcy calls Mexico's main creditors France , Great Britain and Spain on the scene. These three countries sign the London Treaty on October 31st , which stipulates that the signing nations will collectively collect the outstanding debts by whatever means necessary. On December 8th, Spanish troops landed in Veracruz as the first expeditionary force for a European intervention . Among the allied great powers, the French Emperor Napoleon III persecuted . however own plans.
South America
In a coup on January 14th, Minister of War José María Achá overthrew the Bolivian president and “dictator for life” José María Linares , who had come to power in a coup four years earlier. Linares goes into exile in Chile, where he dies that same year. Bolivia receives a new constitution on August 5th.
The conservative Gabriel García Moreno , who took power in Ecuador with the support of Juan José Flores last year , is calling a national assembly in the capital Quito in January . He is elected almost unanimously as the new President and takes up his official term on April 2nd. He restitutes and initially strengthens the rights of the Catholic Church in Ecuador. In addition, he reached a compromise with Peru after relations had suffered over the past few years, among other things because Peru took in President Guillermo Franco Herrero , who was overthrown by Moreno , and who is said to have signed a treaty annexing the province of Guayaquil to Peru, to gain support.
The constitutional term of office of President Mariano Ospina Rodríguez , who has hardly any control of the country due to the civil war between conservatives and liberals , ends in the Granada Confederation , which later became Colombia , which emerged from the Republic of New Granada in 1858 . Since it is impossible for this reason to hold presidential elections, the previous General Procurator Bartolomé Calvo will take over the presidency on an interim basis from April 1st. In the presidential elections in June, Julio Arboleda Pombo was elected as the new president. But just a few days later, the capital Santa Fé de Bogotá was taken by the liberal General Tomás Cipriano de Mosquera , who captured Calvo and Pombo and took over the office of President himself. During his tenure, a new constitution was drafted that led to the establishment of the United States of Colombia in 1863 .
The 60-year-old diplomat José Joaquín Pérez was proclaimed by influential circles in Chile as a candidate “by all and for all” for the upcoming presidential elections and subsequently won all 216 electoral votes. According to the constitution, he took office on September 18 and tried right from the start to separate his reign from the years under his predecessor Manuel Montt Torres . His first official act is an amnesty for political prisoners, a little later he also restores freedom of assembly and the freedom of the press.
Bartolomé Miter , governor of the province of Buenos Aires , which was forcibly incorporated into the Argentine Federation in 1859 , defeated the Argentine army under the former president Justo José de Urquiza in the battle of Pavón on September 17th . The constitutional President Santiago Derqui then resigns and will be replaced on 5 November by the previous Vice President Juan Esteban Pedernera , who is holding presidential elections for the coming year. General Urquiza retires as governor in the province of Entre Ríos .
Caribbean
Due to ongoing military attacks by neighboring Haiti , the President of the Dominican Republic , Pedro Santana , asks Spain for military intervention and renewed administration of the Caribbean state . However, Spain , which sees an opportunity to reclaim its former colony , goes beyond taking over management. On March 18, the annexation is proclaimed, which leads to nationwide unrest. Pedro Santana, who is appointed governor general and captain general in Santo Domingo , soon realizes that important decisions are only made in Spain.
Prussia
- January 2: After lying in a coma for almost two months, King Friedrich Wilhelm IV of Prussia dies of a stroke at Sanssouci Palace in Potsdam . His successor will be his brother Wilhelm I. In the appeal to my people on January 8th, he affirmed his loyalty to the oath on the constitution, which he had already taken in 1858 as Prince Regent.
- June 6: Liberal MPs around Max von Forckenbeck found the German Progressive Party , the first modern political party in Germany, which also claims to be an all-German party. The faction of the old liberals around Georg von Vincke is clearly weakened. In its founding program, the DFP primarily advocates reforms to the rule of law. She calls for independent judges and equal access for all citizens to the courts, as well as the reintroduction of jury courts . Further demands include the responsibility of the government towards parliament, the strengthening of local self-government and equal rights for all religious communities while at the same time separating church and state.
- July 14th: In Baden-Baden , King Wilhelm I of Prussia is slightly injured in an assassination attempt by the student Oskar Becker . Becker's shot grazes the king on the neck, but causes only an insignificant bruise there. The assassin allows himself to be arrested without resistance by the Prussian diplomat Albert von Flemming , who accompanied the king on his walk.

- October 18: The magnificent coronation meeting of Wilhelm I takes place in the castle church in Königsberg . Wilhelm puts the crown on himself and takes the scepter, the imperial orb and the imperial sword from the altar, then he crowns his wife Augusta as queen. The coronation represents a compromise between the hereditary homage preferred by Wilhelm and the oath of the king in parliament, as required by the constitution.
- December 12th: In the election to the Prussian House of Representatives , carried out according to the three-class suffrage , the German Progressive Party immediately becomes the strongest parliamentary group.
- Prussian constitutional conflict : The Prussian House of Representatives again provisionally approves 5 million Reichstaler for the army reform of War Minister Albrecht von Roon .
Empire of Austria
The February patent
Archduke Rainer Ferdinand Maria Johann Evangelist Franz Ignaz of Austria replaces Anton von Schmerling as Prime Minister in the Austrian Empire . However, Schmerling was appointed Minister of State by Emperor Franz Joseph I and remained the most influential politician in the empire. On February 26, Emperor Franz Joseph I issued the February patent designed by Schmerling for the entire monarchy . The October diploma from the previous year, which met fierce resistance from both the German liberals and the Magyars in the Reichsrat , is thus canceled. The law creates, among other things, the state of Vorarlberg with its own state parliament and state committee, but as an administrative unit with the Fürsteten Grafschaft Tirol .
The February constitution regulates legislation between the emperor and the two chambers of the Imperial Council. The Reichsrat, which meets for the first time on April 29, thus becomes a real parliament, which, along with the emperor, who has the right of veto, is also responsible for deciding on imperial legislation. The House of Representatives of the Reichsrat is to be elected by the state parliaments. This regulation is also criticized mainly by the Hungarian MPs because of its centralized orientation.
Hungary
In Pest , the Hungarian state parliament meets on April 6th on the basis of the February patent, which soon splits into two parties. The address party under Ferenc Deák , which wants to address the Hungarian position on the February constitution in an address to the monarch and thus enter the path of negotiations, finally, after long debates, sat down on June 5 with 155 votes to 152 against the decision- making party under Kálmán Tisza who wants to declare the legal validity of the 1848 laws by simple resolution. The demand to reduce the Austrian influence on Hungary to a personal union with Austria is answered by the emperor on July 8th with the demand to revise the March laws from the Hungarian Revolution beforehand .
When the Hungarian state parliament then referred to the pragmatic sanction and the laws of 1848 as the only acceptable basis that made Franz Joseph's coronation dependent on the reunification of the neighboring countries with Hungary, rejected the appointment of the Reichsrat in Vienna and against any resolution of the same protests, the Vienna government under Minister of State Anton von Schmerling breaks off all further negotiations and dissolves the state parliament on August 21.
Further regional political developments
The Kingdom of Dalmatia is separated from the Kingdom of Croatia and Slavonia and has its own parliament . This regulation will also be laid down in the February constitution after a lengthy discussion . Lazarus Baron von Mamula becomes imperial governor in the crown land of Dalmatia . On October 9, the Slav National Party unsuccessfully demands the restoration of the Triune Kingdom of Croatia, Dalmatia and Slavonia in Sabor .
With the February patent, the previously centrally ruled crown land of Austrian Silesia will also have its own parliament , which will meet for the first time on April 3rd. One of the MPs is the later Conservative Minister of State Richard Graf Belcredi .
Ante Starčević and Eugen Kvaternik found the Hrvatska stranka prava ( Croatian Legal Party ). The aim of the new party is the extensive political independence of Croatia , which is to become a constitutional monarchy linked only through a personal union with the Austrian Empire .
The lawyer and previous Vice-President of the City Council Andreas Zelinka becomes the new Mayor of Vienna after the re-election of Johann Kaspar Freiherr von Seiller , who has ruled since 1851, has refused. In the first elections after the end of neo-absolutism , the liberals win.
Switzerland / France
- January 1: The previous Vice President Josef Martin Knüsel , a partisan Jakob Stämpflis during the Savoy trade , takes over the office of Swiss Federal President .
In a contract with the French Emperor Napoleon III. resigns Prince Charles III. from Monaco on February 2nd to the cities of Menton and Roquebrune . For the loss of 80% of his national territory, he received four million francs from France. At the same time, France recognizes the independence of the principality under the sole sovereignty of the prince. For the first time in its history, the principality is no longer tied to a protective power . France and Monaco also agree to establish a customs union , and France agrees to build a coastal road between Menton and Nice , and on the Nice-Genoa railway , jointly operated by the Compagnie des chemins de fer de Paris à Lyon et à la Méditerranée to be built with Italian railway companies to set up a train station in Monaco.
- May 31: As part of the Basel City Expansion Act of 1859, the Aeschentor is demolished.
- The French Emperor Napoleon III. lets troops march into the Swiss Dappental .
Risorgimento in Italy
Francis II , King of Naples and Sicily , who retired to the fortress of Gaeta after the lost battle on Volturno last year , signed the surrender there on February 13th to the army of King Victor Emanuel . He hands his kingdom so that the Kingdom of Sardinia-Piedmont and goes into exile in the Papal States to Rome.
The previous King of Sardinia, Victor Emmanuel II, proclaimed the Kingdom of Italy with the capital Turin a month later, on March 17th . Camillo Benso von Cavour is appointed Prime Minister of the new state , an activity he carried out until his death on June 6th. He is succeeded by Bettino Ricasoli .
The Risorgimento , which was so successful last year , was replaced in the following years by irredentism , the call for the liberation of the “still unredeemed Italian territories”. Especially in the south of the country, however, so-called briganti such as Carmine Crocco , Giuseppe Garibaldi's former campaigner , who are disappointed with the new state of Italy and with promises, are still fighting for a re-establishment of the rule of the Bourbons .
Russian Empire
- 25./27. February: On the occasion of the 30th anniversary of the Battle of Grochów it comes in the Russian part of Poland to mass demonstrations . Five people were shot dead by the Cossacks . This aggravates the situation and leads to further demonstrations.
- March 3: Tsar Alexander II lifts serfdom in the Russian Empire . Most of the design for the Emancipation Manifesto came from Nikolai Alexejewitsch Milyutin .
- April 8th: Over 100 people are killed in a large demonstration in Poland.
- October 5: The Archbishop of Warsaw, Antoni Melchior Fijałkowski , dies. His funeral, attended by more than 1,000 people, is turned into a political rally.
Other events in Europe
- November 11th: The sudden death of Peter V of Portugal and two of his brothers gives rise to rumors that the king has been murdered. This leads to uprisings that are particularly directed against Prime Minister Nuno José Severo de Mendoça Rolim de Moura Barreto . Peter's younger brother Ludwig I ascends the throne.
- December 14th: The British Prince Consort Albert of Saxe-Coburg and Gotha dies. Queen Victoria will never get over his death.
Ottoman Empire

The 31-year-old Abdülaziz succeeds his brother Abdülmecid I , who died on June 25, as the 32nd Sultan on the throne of the Ottoman Empire . Under the influence of the Grand Viziers Mehmed Emin Ali Pascha and Mehmed Fuad Pascha, he continued the course of domestic reform and rapprochement with Europe. On his accession to the throne, he donated the Osmanje Order and commissioned the Armenian architect Sarkis Balyan to build the Beylerbeyi Palace on the Asian side of Istanbul . The building, which replaces a 16th century wooden palace located there, was completed in 1865.
After the two Danube principalities of Moldavia and Wallachia elected him prince of their respective states in 1859, Alexandru Ioan Cuza proclaimed the new united principality of Romania under Ottoman suzerainty on December 24th . Iași will be the capital for the time being .
Arabian Peninsula
- Bahrain becomes a British protectorate under pressure from British diplomat Lewis Pelly , who is initiating a military expedition .
- Turki ibn Said tries in vain to overthrow his brother Thuwaini ibn Said as ruler of Oman .
Empire of China
Almost a year after China's devastating defeat in the Second Opium War against the European powers, the thirty-year-old Emperor Xianfeng dies on August 22nd in the Imperial Summer Palace in Chengde , where he has retired. As his successor, his five-year-old son Tongzhi ascended the imperial throne on November 11th .
His mother Cixi , one of the concubines of the previous emperor, took over the reign of the minor as the "empress widow " against the initial resistance of a Regency Council. Together with officer Zeng Guofan , she will initiate the Tongzhi Restoration over the next few years . Citing China's superiority over the West in ideological and moral matters, it calls for a return to its Confucian traditions, but recognizes the country's need to catch up in economic, military and technological areas. Cixi becomes the most powerful person in the country for the next half century. For now, however, the Qing Dynasty continues to struggle with two dangerous revolutions, the Taiping Uprising and the Nian Uprising .
Prussian East Asia Expedition

- January 14th: Hendrick Heusken , interpreter for the American Consulate in Japan, who supports the Prussian East Asia Expedition in its negotiations with the Shogun, is attacked by anti-Western Rōnin des Satsuma - han on his way home in the evening and wounded despite the protection given to him. He succumbs to his injuries the following day.
- January 24th: German-Japanese relations : Shogun Tokugawa Iemochi concludes the Prussian-Japanese friendship, trade and shipping treaty in Edo after five months of negotiations with the Prussian East Asia Expedition under Friedrich zu Eulenburg . His indulgence towards foreign countries leads to resistance in the ranks of the samurai and promotes the Bakumatsu , the end of the shogunate in Japan . The Eulenburg expedition then makes its way to China, where it also signs a contract on September 2nd. While the first contract is only valid between Japan and Prussia, the contract with China applies to the entire German Customs Union . The expedition arrives in Bangkok on September 22nd.
Philippines
- After the Spaniards conquered most of the Cotabato region , the Sultan of Maguindanao accepted Spanish sovereignty in exchange for an annual pension of 1000 pesos.
Portuguese Timor
- The pulling of the population to do forced labor on public projects in Portuguese Timor triggers independent rebellions in the spring in the Mambai empire of Laclo and in the Tetum empire of Ulmera . Governor Afonso de Castro returns from his vacation in Java on April 6 and begins to suppress the uprising.
- June 10: Governor Castro declares a state of emergency and distributes weapons to civilians and the Chinese population of Dilis .
- August 26th: The Laclo rebellion is put down.
- September 18: The uprising in Ulmera is put down, the chief taken prisoner.
Australia
Burke and Wills' expedition
- February 9: Burke and Wills' expedition reaches the Little Bynoe River , a tributary in the Flinders River delta , where they find that they cannot reach the sea because the mangrove swamps in front of them are impassable. After another unsuccessful attempt, they make their way back to Cooper Creek . On the way back, the expedition ends in a catastrophe. Only one member of the expedition returns to Melbourne alive.
- April 17th: The expedition member Charles Gray dies in the Polygonum Swamp on the Ruhr.
- April 21: The three remaining members of the expedition reach the depot on Cooper Creek and find it abandoned. William Brahé's team left the site just a few hours earlier.
- June 26: The Victorian Contingent Party , led by Alfred Howitt, is the first to search for Burke and Wills.
- June 28th: Robert O'Hara Burke and William John Wills die on Cooper Creek .
- August 24: The Queensland Relief Expedition under William Landsborough departs from Brisbane . Starting in November, she will primarily search the area around the Gulf of Carpentaria .
- September 15: Alfred Howitt finds John King , the only survivor of the expedition, with an Aboriginal tribe . Then he also finds the bodies of Burke and Wills and buries them.
- October: The South Australian Burke Relief Expedition under John McKinlay finds several bodies in the Polygonum Swamp and therefore assumes a massacre of Burkes and Wills expedition.
- December 4th: The Victorian Burke and Wills Relief Expedition under Frederick Walker, which set out on September 7th, massacres a group of Aborigines.
- December 9: The Victorian Exploring Party , led by Alfred Howitt, sets out to recover the bodies of Burke and Wills and bring them to Melbourne for an honorable funeral.
Other events
- September: John McDouall Stuart returns to inhabited areas from his expedition. In October he goes on another research trip.
- The Lambing Flat Riot continues and culminates on June 14th. The Australian government subsequently enacts the Chinese Immigration Act .
New Zealand
- May 25: With his gold discovery near Dunedin , Thomas Gabriel Read triggers the gold rush in Otago , which changed the Otago region lastingly until 1863.
After a successful motion of censure against Edward Stafford , William Fox will become Prime Minister of New Zealand for the second time on July 12th . In the same year Thomas Gore Browne is replaced by George Edward Gray as Governor of New Zealand .
Africa
- March 10: With the capture of the capital Ségou by Muslim fighters from the ranks of the Tukulör and subsequent pressures against the population to convert to Islam , the African empire Bambara in the area of today's Mali ends after around 150 years .
- August 6th: Britain annexes Lagos .
- August 16: Radama II succeeds his late mother Ranavalona I to the throne of Madagascar . He begins to reopen the island and to establish contacts with foreign countries.
- August 18: After Jonker Afrikaner's death , his son Christian Afrikaner becomes Kaptein der Orlam -Afrikaner and thus comes into conflict with his half-brother Jan Jonker Afrikaner . Around the same time, Maharero becomes chief of another Herero tribe through the death of his father Tjamuaha , who know how to use this conflict for themselves.
business
Money economy and taxes
- February 27: Law passed in the United States allowing privately printed cards to be mailed, the first state authorization to use postcards . On December 17th, John P. Charlton took advantage of the new US postcard law and had the postcard protected by copyright. He sells his idea to Hyman L. Lipman, who produces cards labeled “Lipman's Postal Card”. A patent on the idea, however, is not allowed.
- April: The Confederate States of America introduce a new currency , the CSA dollar . Already in the first year of the war it loses a third of its value.
- August 5: Abraham Lincoln signs the Revenue Act of 1861 , introducing income tax in the United States.
- In England the paper tax will be abolished.
- The Sardinian lira will be replaced by the Italian lira .
trade
- February 11th: The Stuttgart Stock Exchange is founded after a local "Industrie-Börseverein" had already been founded in the previous year.
- May 13: The “General German Trade Day”, the forerunner of the German Chamber of Commerce and Industry, meets for the first time in Heidelberg .
- May 31: The Federal Assembly of the German Confederation adopts the General German Commercial Code ( ADHGB ).
- October 25: The Toronto Stock Exchange opens in Canada .
traffic

- The AG of the Bavarian Eastern Railways establishes an initial connection with the Austrian rail network by connecting to the Kaiserin-Elisabeth-Bahn . The Wels – Passau branch line with the Kaiserin-Elisabeth-Brücke built by Joseph Anton von Maffei goes into operation on September 1st. The connection from Schwandorf via Cham will already be in place on January 7, and will be extended to Furth im Wald on September 20 and to the border with the Bohemian Western Railway to Pilsen on October 15 . With this, the 446-kilometer-long railway network approved in the founding license of 1856 was created within five years.
- February 5th: The Thai King Mongkut orders the construction of Thanon Charoen Krung , the first cobbled street in Bangkok .
- February 20: The General Directorate of the Bavarian Transport Authority opens operations on the Hochstadt-Marktzeuln – Kronach – Gundelsdorf route . The owners are the city of Kronach and the Nuremberg manufacturer v. Cramer Velcro.
- February 21: The Kingdom of Württemberg and the Kingdom of Bavaria sign a state treaty for the construction of the Remsbahn from Stuttgart to Nördlingen by the Royal Württemberg State Railways with a connection to the Bavarian rail network. This includes the so-called Brenzbahn clause . Württemberg must submit to the condition that no rail connection between it and the Cannstatt – Ulmer Bahn will be established for a period of twelve years from the day the railway opens.
- March 2nd: Due to the looming American Civil War, it is decided to discontinue the Butterfield Overland Mail . The last stagecoach will be on the route between St. Louis and San Francisco on March 21st .
- May 11th: The Kehl Rhine bridge between the Grand Duchy of Baden and the French Empire , built on behalf of the French Eastern Railway and the Baden State Railways , goes into operation. At this point in time, the double-track railway bridge is the only permanent bridge on the Upper Rhine .
- May: The Centralbahnhof in Basel goes into full operation.
- June: History of the Railroad in North America : The Central Pacific Railroad is founded.
- July 25: The first section of the Remsbahn from Cannstatt via Waiblingen, Schorndorf, Gmünd and Aalen to Wasseralfingen, built by the Royal Württemberg State Railways , is opened. The Schwäbische Hüttenwerke are on the route , an important state-owned steelworks that supplied all of the rails laid on the Remsbahn until the mid-1860s.
- AUGUST 29: The Wilhelm-Luxembourg Railway Company opened in Luxembourg , the railway line Luxembourg-Wasserbillig .
- October 15 : The second section of the Plochingen – Immendingen railway , Reutlingen Hbf - Rottenburg am Neckar , is completed.
Business start-ups
- January 12: The Sparkasse Caixa Econômica e Monte de Socorro is founded in Rio de Janeiro .
- May 25: In Christchurch on New Zealand's South Island, the future daily newspaper The Press appears - for the time being still as a weekly magazine .
- November 15: Julius Vogel founds the Otago Daily Times , New Zealand's oldest daily newspaper , as part of the Otago Gold Rush .
- The Saalbau AG in Frankfurt am Main is founded.
- The watch manufacturer Junghans is founded in Schramberg in the Black Forest.
- The button maker and trimmings master Ludwig Beck founds his own company in Munich .
- The shipping company Compagnie Générale Maritime , founded in 1855, received a contract from the French state to transport mail across the Atlantic, creating the Compagnie Générale Transatlantique .
- Franz Rudolph Wurlitzer starts producing musical instruments .
media
The Danish geologist and Greenland researcher Hinrich Johannes Rink founds Atuagagdliutit ( Readable ), the first Greenland newspaper. It has had a major impact on the development of the modern Greenlandic written language and the promotion of Greenlandic culture and identity. In addition to practical advice on seal hunting and fishing, the contents of this period include, above all, political reports, which are intended to motivate Greenlanders to participate in politics. The newspaper provides children with suitable literature in their language for the first time. The Atuagagdliutit also contains illustrations by local artists such as Aron von Kangeq and thus contributes significantly to the support of Greenlandic art. In line with its goal of political education and the emancipation of Greenlanders, the newspaper is free for Greenlanders, only Danes have to pay for it. Due to the difficult transport routes, the Atuagagdliutit initially only appears twice a year.
The Národní listy ( People's Papers ) was launched on the initiative of František Ladislav Rieger . The organ of the Czech national party Národní strana with its publisher Julius Grégr developed into the most influential political daily newspaper in the Kingdom of Bohemia over the next few years .
- Ottokar Franz Ebersberg founds the satirical magazine Kikeriki in Vienna .
Others
- May 17th: Thomas Cook organizes the first foreign package tour with accommodation and meals. British workers travel to Paris by ship and rail.
- August 10: The United States Treasury Department issues demand notes , a form of fiat money . Due to their specific green color, they will soon be colloquially known as “greenbacks”.
- September 17th: The Strasbourg bookseller Oscar Berger-Levrault publishes the world's first stamp catalog with an edition of a few dozen .
- The American company Western Union completed the first transcontinental telegraph line based on the Pacific Telegraph Act of 1860 .
- October 22nd: The Pony Express is replaced by a transcontinental telegraph line.
science and technology
Africa research
Thomas Baines , together with James Chapman , undertakes an expedition through the area of today's Botswana and Namibia and paints a group of baobabs that still exist today and are called Baines Baobabs in the area of today's Nxai-Pan National Park .
Theodor von Heuglin is continuing the expedition he started the previous year , which aims to clarify the fate of the African explorer Eduard Vogel , who has been missing since 1855 . On June 17th the expedition reached Massaua and stayed in the high Bogos countries during the rainy season , but then did not go directly to Khartoum , but made a long detour through Abyssinia to beyond Gonder , whereupon Werner Munzinger and Gottlob Kinzelbach , on July 1st encountered in Massawa to the expedition to part on 11 November of Heuglin and make the futile attempt on Darfur in Wadai penetrate.
Together with the geologist Richard Thornton, Karl Klaus von der Betten is the second European to reach Kilimanjaro , confirming the discovery of Johannes Rebmann 13 years earlier , whose reports of ice and snow near the equator have found no faith for years. The two of them explore the mountain on this expedition up to a height of around 1,580 m.
Based on an extended hunting trip to Egypt and the Sudan, the Briton takes Samuel Baker his first expedition to Central Africa , the source of the Nile to discover, in the hope of a meeting with the East African expedition under Captains Speke and Grant somewhere on Victoria -See .
The adventurer Alexandrine Tinné travels via Syria and Palestine to Cairo, where she settles. From here she made her way south in early 1862.
Richard Francis Burton and Gustav Mann are the first Europeans to climb the Cameroon Mountain .
archeology
- The French archaeologist Léon Heuzey begins excavations in the ancient Macedonian city of Aigai .
- The Kummerhy barrow near Süderbrarup is being excavated.
- Excavations are taking place for the first time at the megalithic site of Maes Howe in Scotland .
astronomy
Observatories
The foundation stone for the observatory founded by King Pedro V will be laid in Lisbon on March 11th . The blueprints designed by the French architect Jean Colson are inspired by the construction of the observatory in Pulkovo , Russia. Friedrich Georg Wilhelm Struve , Director of the Pulkowo Observatory , offers his services to the Portuguese government and will become the most important and influential advisor over the next few years. The first astronomical observations begin in 1867.
In Leipzig, after around a year of construction, the new observatory planned by Director Karl Christian Bruhns will open in Johannistal on November 8th , and a new observatory will also be built in Leiden under the direction of Director Frederik Kaiser .
The Great Comet of 1861
Australian astronomer John Tebbutt discovered the Great Comet of 1861 on May 13 from New South Wales , now cataloged as C / 1861 J1 . The perihelion of the comet is on June 11th, and from June 29th it is also visible in the northern hemisphere . It is visible to the naked eye until mid-August. The brightness of the comet is so great that objects cast shadows in its light at night and the comet remains visible in the daytime sky .
Further astronomical research
- 30 September: The German-Danish astronomer Heinrich Louis d'Arrest discovered in the constellation Pegasus later than NGC 1 called Galaxy .
- October 8: Heinrich Louis d'Arrest finds the galaxy later known as NGC 109 in the constellation Andromeda .
- Heinrich Louis d'Arrest begins with systematic observations of the Coma galaxy cluster , which lasted until 1867.
List of asteroids discovered in 1861
| No. and name |
Diameter (km) |
Date of discovery | Explorer |
|---|---|---|---|
| (63) Ausonia | 103.1 | February 10th | Annibale de Gasparis |
| (64) Angelina | 98 | 4th of March | Ernst Wilhelm Leberecht Temple |
| (65) Cybele | 237.3 | 8th of March | Ernst Wilhelm Leberecht Temple |
| (66) Maya | 71.8 | 9th April | Horace Parnell Tuttle |
| (67) Asia | 58.1 | 17th April | Norman Robert Pogson |
| (68) Leto | 122.6 | April 29 | Karl Theodor Robert Luther |
| (69) Hesperia | 138.1 | 26th of April | Giovanni Schiaparelli |
| (70) Panopaea | 122.2 | 5th of May | Hermann Mayer Salomon Goldschmidt |
| (71) Niobe | 83.4 | 13 August | Karl Theodor Robert Luther |
| (72) Feronia | 85.9 | May 29th | Christian Heinrich Friedrich Peters |
Biology and paleobiology
Human biology
The French anthropologist and doctor Paul Broca discovered the Broca area , a region in the cerebral cortex that is probably primarily responsible for the grammatical aspects of languages. Children up to around three years of age train their language in this center. Second languages learned later are stored separately in neighboring brain areas near Broca's area. Recent studies have shown that the Broca Center is responsible for speech motor skills, sound formation, sound analysis, articulation and the formation of abstract words.
paleontology
The imprint of a feather found in the Solnhofen limestone in the previous year serves the paleontologist Hermann von Meyer as the basis for his first description of the "primeval bird" referred to by the generic name Archeopteryx ( old feather ). In the meantime, an almost complete skeleton of the Archaeopterix lithographica has been found in Langenaltheim near Solnhofen, although it is only mentioned briefly in Meyer's work. Whether the two finds actually belong to the same genus is controversial today. The second example is sold to the British Museum in London a few months after its discovery . The driving force behind the purchase is the British naturalist Richard Owen , head of the natural history collection at the British Museum and a declared opponent of Charles Darwin's theory of evolution . Richard Owen also wrote the first description of the "London copy", meticulously avoiding any reference to the possible interpretation as a mediating link between reptiles and birds.
zoology
The German entomologist Hermann August Hagen describes for the first time numerous dragonflies - genera such as Celithemis , Erythemis , Orthemis , Pantala , Perithemis and Tramea as well as the species Erythrodiplax funerea , Sympetrum madidum .
The German ornithologist Jean Cabanis wrote the first description of the bird species Sooty Thrush ( Turdus nigrescens ), Fiery-Billed Aracari ( Pteroglossus frantzii ), fire-warbler ( Parula gutturalis ) and monochrome hooked beak ( Diglossa plumbea ).
The German zoologist Albert Günther describes several fish species for the first time, including the circular thorn surgeonfish , the moonlight threadfish and several types of wrasse .
chemistry
When examining Dürkheimer mineral water by means of spectral analysis at the Ruprecht-Karls-Universität Heidelberg , Robert Wilhelm Bunsen and Gustav Robert Kirchhoff discover two previously unknown lines in the blue spectral range . As a result, they succeed in isolating the newly found alkali metals cesium and rubidium in the form of cesium and rubidium chloride . At the meeting on May 10th, the Imperial Academy of Sciences in Vienna will be informed of this discovery. These studies also make it possible to explain the Fraunhofer lines in the solar spectrum and thus lay an essential basis for modern astronomy .
medicine
Ignaz Semmelweis , Professor of Obstetrics at the University of Pest , publishes the work The Etiology, the Concept and Prophylaxis of Childbed Fever , in which he describes the death of many women who have recently given birth to iatrogenic infections due to poor cleanliness , based on a study he carried out in 1847/48 and disinfection . His theses meet with incomprehension and resistance from the majority of his colleagues, as hygiene in particular is viewed as a waste of time. His behavior in defending his work, in which he repeatedly called colleagues “murderers”, did nothing to diminish their reaction , which was called the Semmelweis reflex almost a hundred years later .
Philosophy / Political Science
The English philosopher John Stuart Mill publishes the democratic theoretical work Considerations on Representative Government .
Research and Teaching
After the English natural scientist Michael Faraday held a six-part series of lectures on the natural history of a candle at the turn of the year , the first edition of the popular scientific work will appear in April under the full title A Course of Six Lectures on the Chemical History of a Candle: To Which is Added a Lecture on Platinum by Griffin, Bohn & Co. in press.
Following the example of German- and French-speaking polytechnic universities, the Massachusetts Institute of Technology in Cambridge, USA, is set up on April 10 as a tripartite institution consisting of “a society of arts, a museum of arts [industrial arts], and a school of industrial science “was founded. Founder William Barton Rogers , a well-known naturalist, wants to create an independent university geared towards the needs of an increasingly industrialized America. However, due to the civil war, the first students could not be accepted until 1865.
In Seattle in the Washington Territory , after overcoming numerous obstacles, the University of Washington begins teaching on November 4th . The establishment of a university was originally planned in Lewis County , but no suitable property could be found there. Finally, the politician Arthur A. Denny and two fellow pioneers provide a suitable piece of land in what is now the center of Seattle. The new university has been struggling with problems such as the lack of students and lack of money from the start.
Halil Bey , Ottoman Ambassador to Saint Petersburg, and Mehmet Tahir Münif , who later became Minister of Education, found the Ottoman Scientific Society . Members of the learned society are civil servants, dignitaries and scholars. One of her goals is to organize public lectures and courses in rooms made available to her by the Ottoman government, the Sublime Porte . The company publishes the first Turkish scientific journal Mecmūʿa-yi Fünūn /مجموعه فنون / 'Journal of the [secular] sciences'.
Technical achievements
- MAY 17: The Scottish physicist James Clerk Maxwell performs as part of a lecture on the on the three-color theory of Hermann von Helmholtz and Thomas Young -based additive color mixing at the Royal Institution, the first color photograph , a tartan band before. The presentation takes place with three slides , which have been photographed with a reflex camera constructed by Thomas Sutton at the beginning of the year through three color filters ( red, green and blue ) and projected congruently through the appropriate filters .
- September 16: The largest steam-powered forging hammer in Germany starts work in Essen at the Krupp company under the direction of Alfred Krupp . With reference to the company founder Friedrich Krupp , he was given the name "Fritz". The forging hammer has a drop weight of 50 tons . In the same year Krupp founds its own photography department.
- October 24: The HMS Warrior , the first ocean-going armored ship with an iron hull, is put into service.
- OCTOBER 26: invention of the telephone : Johann Philipp Reis leads his invention, the telephone Frankfurt Physics Association ago.
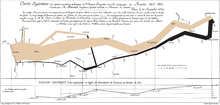
- The French civil engineer Charles Joseph Minard published a graphic on the losses of the French army during Napoleon's Russian campaign in 1812 , the Carte figurative des pertes successives en hommes de l'Armée Française dans la campagne de Russie 1812–1813 . This form of representation becomes known as the Sankey diagram about half a century later .
- The Gatling Gun is invented by Richard Gatling .
- In the construction of the Mont-Cenis-Tunnel , drilling machines with compressed air drive ( pneumatic hammer ) are used for the first time .
- The former British naval officer Robert FitzRoy issued storm warnings and simple weather forecasts from 1861 on, but these were mostly wrong and earned him a lot of ridicule. Nevertheless, FitzRoy is considered to be one of the first meteorologists .
Surveying
- The Franziszeischer Cadastre , the first Austrian real estate cadastre , is completed. The surveying work for the plots in the Austrian Empire began in 1817.
Culture
| Culture | |
|---|---|
Visual arts
The Hogarth Club of the Pre-Raphaelites held from February to May in 6 Waterloo Place , London, his last exhibition. In September - after a discussion as to whether the demand for entrance fees is admissible - the dissolution of the non-profit association is decided by the members due to financial problems and carried out in December.
In Cologne, the new Wallraf-Richartz-Museum , donated by Johann Heinrich Richartz for Ferdinand Franz Wallraf's art collections and built according to plans by Josef Felten and Julius Carl Raschdorff in the English-Neo-Gothic style , opens on July 1st after a five-year construction period.
Paul Cézanne is coming to Paris from his hometown of Aix-en-Provence in April . After being rejected from the École des Beaux-Arts , he enrolls at the Académie Suisse . There he meets, among others, Armand Guillaumin , Achille Emperaire and Camille Pissarro, who is ten years his senior . However, he does not feel at home in Paris and is returning to Aix-en-Provence in September to work in his father's bank.
- Pierre-Auguste Renoir begins studying painting in the class of the Swiss painter Charles Gleyre .
- October 1 to November 24: General German Art Exhibition in Cologne: Arnold Ferdinand Ewald , Ferdinand Georg Waldmüller , Marie Wiegmann and Reinhard Sebastian Zimmermann, among others, are exhibiting here .
- When the banker JHW Wagener left his collection in his will, the National Gallery was created in Berlin.
literature
- February 9: Charles Baudelaire publishes a second censored version of his volume of poetry Les Fleurs du Mal .
- After April 19th: James Ryder Randall writes the poem Maryland, My Maryland .
- December 25th: The first part of Théophile Gautier's novel Le Capitaine Fracasse appears in Revue nationale . The last part appears on June 10, 1863.
- Fyodor Michailowitsch Dostojewski publishes the novel Humiliated and Offended in the magazine Vremja in St. Petersburg .
- George Eliot publishes the novel Silas Marner .
- Former slave Harriet Jacobs publishes her autobiography Incidents in the Life of a Slave Girl in Boston . The foreword comes from Lydia Maria Child after Harriet Beecher rejected Stowe .
Music and theater
- January 5th: The world premiere of the 50-minute operetta Le Chanson de Fortunio by Jacques Offenbach based on a libretto by Hector Crémieux and Ludovic Halévy at the Théâtre des Bouffes-Parisiens in Paris is so successful that the audience applauds a complete repetition enforces.
- January 16: More than a decade after its appearance in the magazine Moskvitjanin , the comedy It stays in the family ( Свои люди - сочтёмся ) by Alexander Nikolayevich Ostrowski premiered at the Alexandrinsky Theater in Saint Petersburg.
- March 23rd: The first version of the operetta Le pont des soupirs by Jacques Offenbach with the libretto by Hector Crémieux and Ludovic Halévy is successfully premiered at the Théâtre des Bouffes-Parisiens .
- March: The first performance of the Paris version of Richard Wagner's opera Tannhäuser and the Sängerkrieg on Wartburg , which is directed by Pierre-Louis Dietsch as conductor, turns into such a fiasco that the production has to be canceled after only three performances. The main reason for this is that Wagner incorporated a ballet interlude into the arrangement of his opera as a concession to the taste of the French audience, but atypically right at the beginning of the opera, and not, as was usual in French operas at this time, in the second act During the performance there were arguments between Wagner and the conductor.
- 4th to 8th August: The second Tonkünstler meeting takes place in Weimar. In the session on August 7th, the General German Music Association is founded. Founding members include Louis Köhler , Franz Brendel and Franz Liszt , who left Weimar a little later.
- August 29: After a concert premiere by the Wiener Singverein on March 1, the staged world premiere of the Singspiel The Conspirators or The Domestic War by Franz Schubert takes place almost 33 years after the composer's death in Frankfurt am Main. The libretto is by Ignaz Franz Castelli . Schubert decided not to perform the work from 1823 after the Berlin composer Georg Abraham Schneider celebrated a success with the same material.
- September 1st: The last performance of Mozart's Magic Flute takes place at the opera house on Hagenmarkt in Braunschweig . The new venue on Steinweg will be inaugurated on October 1st .
- September: Johannes Brahms composes Variations and Fugue on a theme by Handel .
- October 2nd: The Hlahol men's choir is officially founded in Prague, although it has been in existence since June.
Others
- March 22nd: The Photographische Gesellschaft , the first association of photographers in Austria, is founded in a hall of the Imperial Academy of Sciences in Vienna .
- April 2: After more than 20 years of construction, Napoleon Bonaparte's coffin is reburied from the side chapel to the sarcophagus in the basement of the completed crypt of the Invalides .
- May 9: After a two-year construction period, the Dresden Zoo, designed by architects Carl Adolph Canzler and Peter Joseph Lenné at the suggestion of the Dresden Chicken Breeding Association , is one of the oldest zoos in Germany. Albin Schoepf becomes the first director .
- In Hamburg , the Museum Godeffroy , founded by Cesar Godeffroy (1813–1885) , and the first publicly accessible aquarium in German-speaking countries are opened in the Hamburg Zoo.
- End of the year: Construction of the New Court Opera on Vienna's Ringstrasse begins.
society
- March 2nd: An association for the rescue of people at sea is founded in Emden , which four years later is incorporated into the newly formed German Society for the Rescue of Shipwrecked People .
- July 11th: The all-German shooting association is founded in Gotha . Two days later, the Thuringian Schützenbund was founded in the same city under the protectorate of Duke Ernst II of Saxe-Coburg and Gotha .
- July 12: James Butler Hickok kills gang leader David McCanles and two other men in a shootout at Rock Creek Station on the Oregon Trail and is subsequently named Wild Bill .
- September 17th: The Strasbourg bookseller Oscar Berger-Levrault develops the first still faulty stamp directory , which will be revised and improved by the French state official and philatelist Alfred Potiquet by the end of the year.
- November 1: With the Offences against the Person Act 1861 , England changes the penalty for homosexuality , anal intercourse and sodomy from the death penalty to life imprisonment.
- Alfred Krupp begins building masters' houses for his senior employees in Essen . That is the beginning of Krupp housing construction.
- The Bavarian Teachers' Association is being re-established in Regensburg after a long-term ban.
religion
- March 18: In the allocation Iamdudum cernimus to the College of Cardinals , Pope Pius IX condemns . not only the intellectual currents of his time, but also the political efforts to further reduce the power of the Pope. He attacks the Risorgimento in Italy in particular .
- April 8th: The Protestant patent of Emperor Franz Joseph I brings for the first time a relative legal equality of the Evangelical Church AB and the Evangelical Church HB with the Roman Catholic Church in the Austrian Empire .
- May 30th to June 5th: At a church conference in Eisenach , the Eisenach regulation is passed , a catalog of regulations for the design of Protestant church buildings in Germany, with which a fundamental standardization of church buildings in the 19th century is aimed at. It replaces the Dresden regulation from 1856.
L'Osservatore Romano , the official organ of the Vatican, will appear for the first time in Rome on July 1st with the subtitle giornale politico morale ( political-moral newspaper ) . The first issues of the newspaper, launched by the deputy “minister of the interior” of the papal government, Marcantonio Pacelli , are four pages long. At the end of the year the subtitle will be abandoned. The motto still used today appears under the head of the newspaper for the first time: "Unicuique suum - non praevalebunt" ("To each his own - they will not overwhelm you"; cf. Mt. 16, 18). The Papal State under Pope Pius IX. , who feels that his independence is threatened by the Risorgimento in particular , uses the newspaper as a fighting organ against anti-clerical forces.
Disasters
Shipping disasters
In the dark and in heavy snowstorms, the steamer Stadt Zürich collides with the steamer Ludwig on Lake Constance, which sinks within a short time. 13 of the 16 people on board are killed. In the city of Zurich , which soon became known as the “devil's ship” because by 1864 it sank more German ships than the entire Danish navy , the only thing you notice of the events is that the bowsprit has broken off and water is entering the ship.
The Canadian passenger steamer Canadian of Allan Line , which was only put into service last year , leaves Québec on June 1 and sets course for Liverpool. Although she only makes five knots due to the heavy ice accumulation and sometimes stops at all, she runs onto an iceberg on June 4th at 11:50 am in the Belle Isle Strait off Newfoundland and sinks within half an hour. During this time, everyone on board can be accommodated in lifeboats , but one of them capsizes, killing 35 people. The remaining 266 survivors are rescued by four fishing boats and brought ashore in the port city of Quirpon.
The Corvette Amazone of the Prussian Navy , which has been in service since 1843, goes down with its entire crew in a hurricane off the Dutch coast on a training voyage to Portugal on November 14th. The information on the number of victims fluctuates between 114 and 143. After the sinking there are rumors that the Amazon was - possibly deliberately - rammed by another ship.
More disasters
The western Argentine city of Mendoza was largely destroyed in an earthquake on March 21, killing around 6,000 people, around a third of the population.
The fire in Glarus began on May 10 and could only be brought under control the next day. Eight to ten people are killed, around 600 buildings fall victim to the fire, 2257 people, at this point 47% of the city's population, become homeless.
On August 25, 23 people died and 176 were injured in the railway accident in the Clayton Tunnel near Brighton . At the time, it was the worst railway accident in British history.
Minor accidents are listed in the sub-articles of Disaster .
nature and environment

The French Emperor Napoleon III. creates a first nature reserve in the forest of Fontainebleau to preserve the forest. The forest , located around 50 km south of Paris in the vicinity of the municipality of Fontainebleau , is still one of the largest contiguous forest areas in Western Europe.
Sports
| Sports chronology | |
|---|---|
| 22nd of January | The Frankfurt gymnastics community is founded. |
| 19th of February | The Kronach gymnastics club is founded. |
| May 20th | The Trysilgutten ski club is founded in Trysil , Norway . |
| 8-11 July | First all-German shooting festival in Gotha . |
| July 11th | The German Schützenbund is founded in Gotha . |
| July 13th | The Thuringian Schützenbund is founded in Gotha . |
| July 18th | The Montevideo Cricket Club is founded. |
| July 19th | The MTV Eintracht Hildesheim is founded. |
| 10-12 August | The second German Gymnastics Festival will be held in Berlin . |
| 4th of October | The Mont Pourri in the Vanoise massif is climbed by Michel Croz single-handedly for the first time. |
Cricket, soccer, gymnastics, fencing
The boom in gymnastics that began in Germany the previous year continued in 1861 . Numerous gymnastics clubs are founded, including the Frankfurt gymnastics community , the Kronach gymnastics club and the Gifhorn men's gymnastics club . 73 previous members of the MTV von 1848 Hildesheim founded the gymnastics club MTV Eintracht Hildesheim on July 19 , which also includes its own fencing department . The 2nd German Gymnastics and Jubilation Festival will be held in Berlin in August . The reason for this is the establishment of the first German gymnasium 50 years earlier and the laying of the foundation stone for the Jahndenkmal in the Hasenheide .
Outside Europe, there will be ups of sports clubs: On 18 July, in Montevideo from British in Uruguay of Montevideo Cricket Club established with an associated football department. And Boston students found the Oneida Football Club as the first football club in the United States, which only lasted five years but did not lose a single football game during that time .
golf
After The Open Championship in golf was held in Prestwick for the first time last year under his influence , the Scottish greenkeeper Tom Morris wins this event for the first time.
rowing
Oxford wins the 18th Boat Race against Cambridge in a time of 23'03 ".
chess
The first congress of the West German Chess Federation (WDSB) will be held in Düsseldorf. However, no master is played out yet.
Rockclimbing
The following mountains were climbed for the first time in 1861:
| Name of the mountain | Height (m) |
region | Date of first ascent | First climber |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Schreckhorn | 4,078 | Bernese Alps | August 16 | Peter and Christian Michel, Leslie Stephen and Ulrich Kaufmann |
| Weisshorn | 4,505 | Valais Alps | August 19th | John Tyndall , Johann Joseph Brennen and Ulrich Wenger |
| Liskamm | 4,527 | Valais Alps | August 19th | William Edward Hall, Jean-Pierre Cachat, Peter Perren, Josef-Marie Perren and others |
| Castor | 4.223 | Aosta Valley , Valais Alps | 26th of August | FW Jacomb and William Mathews / leaders Michel Croz |
| Northrend | 4,609 | Monte Rosa massif , Valais Alps | 26th of August | TF and Edward N. Buxton and JJ Cowell with Michel Payot |
| Monte Viso | 3,841 | Cottian Alps | August 30th | Michel Croz , Jean Baptiste Croz, William Mathews and Frederik Jacomb |
| Mont Pourri | 3,779 | Vanoise massif , Graian Alps | 4th of October | Michel Croz |
| Albertspitze | 4,095 | Cameroon , Central Africa | ? | Richard Francis Burton and Gustav Mann |
| Grays Peak | 4,350 | Rocky Mountains , Colorado | ? | Charles Christopher Parry |
| Torrey's Peak | 4,349 | Rocky Mountains, Colorado | ? | Charles Christopher Parry |
Born
January February
- January 2: Wilhelm Bölsche , German writer and naturalist († 1939)
- January 2: Sofie Röhr-Brajnin , Polish-German opera singer († 1937)
- January 3: Ernest Renshaw , English tennis player († 1899)
- January 4th: Mehmed VI. , Sultan of the Ottoman Empire († 1926)
- January 6: Victor Horta , Belgian Art Nouveau architect († 1947)
- January 7th: Henry Berthold von Fischer , Swiss architect († 1949)
- January 7th: Wilhelm Hein , Austrian orientalist († 1903)
- January 12: James Mark Baldwin , American psychologist and philosopher († 1934)
- January 13: Max Nonne , German neurologist († 1959)
- January 14: Wilhelm von Polenz , German writer († 1903)
- January 14th: Hans Tappenbeck , German officer and Africa explorer († 1889)
- January 18: Demetrios I. Kadi , Syrian clergyman and Patriarch of Antioch († 1925)
- January 19: George Whitfield Andrews , American composer, organist and music teacher († 1932)
- January 19: Max Bewer , German poet and writer († 1921)
- January 19: Bruno Sauer , German archaeologist († 1919)
- January 23: Angelo Simonetti , Italian clergyman, Bishop of Pescia († 1950)
- January 26: Wassili Wassiljewitsch Andrejew , Russian balalaika virtuoso, orchestra leader and composer († 1918)
- January 26: Louis Anquetin , French painter († 1932)
- January 27: Jean-François-Charles Amet , French Vice Admiral and Allied High Commissioner in Constantinople († 1940)
- January 29: William M. Butler , American politician († 1937)
- January 30: Charles Martin Loeffler , German-American composer, violinist and violist († 1935)
- February 3: Ernst Fromhold-Treu , German-Baltic pastor and Protestant martyr († 1919)
- February 4: Franz Winter , German archaeologist († 1930)
- February 5: Bryant B. Brooks , American politician († 1944)
- February 5: August von Parseval , German airship designer († 1942)
- February 5: Bjarnat Krawc , Sorbian composer († 1948)
- February 6: Nikolai Dmitrijewitsch Selinski , Russian chemist († 1953)
- February 8: Harry Ward Leonard , American electrical engineer († 1915)
- February 9: Hans Bartsch von Sigsfeld , German aviation pioneer († 1902)
- February 11: Friedrich Graf von der Asseburg , Prussian major and chamberlain († 1940)
- February 11: Paul Prüssing , German chemist († 1914)
- February 12: Lou Andreas-Salomé , German writer, narrator and essayist († 1937)
- February 15: Alfred North Whitehead , British philosopher and mathematician († 1947)
- February 15: Charles Édouard Guillaume , Swiss physicist († 1938)
- February 15: Halford Mackinder , English geographer and geopolitician († 1947)
- February 15: Julius Wahle , Austrian literary scholar († 1940)
- February 15: William Adams , American politician († 1954)
- February 16: Antonietta Dell'Era , Italian ballerina († 1945)
- February 17th: Karl Adrian , Austrian homeland researcher († 1949)
- February 18: William Throsby Bridges , Australian artillery officer and division commander († 1915)
- February 21: Carl Christoph Bernoulli , Swiss librarian († 1923)
- February 21: Pierre de Bréville , French composer († 1949)
- February 22: Gustav Lange , Norwegian composer, violinist and music teacher († 1939)
- February 22: Hans Schöttler , German Protestant clergyman († 1945)
- February 22: Marie von Miller , German painter and the wife of Oskar von Miller († 1933)
- February 25: Santiago Rusiñol , Catalan painter, writer, journalist and playwright († 1931)
- February 26: Ferdinand I , Bulgarian prince and tsar († 1948)
- February 27: Rudolf Steiner , Austrian founder of anthroposophy († 1925)
- February 28: Leonhard Angerer , Austrian naturalist († 1934)
- February 28: Julius Bergmann , German painter († 1940)
- February 28: Bertha Kipfmüller , German teacher, women's rights activist, pacifist and private scholar († 1948)
March April
- March 4: Curt von Bardeleben , German chess player († 1924)
- March 4: Franz Xaver Engelhart , German Catholic priest, church musician and composer († 1924)
- March 6: Friedrich Eckenfelder , German painter († 1938)
- March 8: Francis Lodowick York , American organist, composer and music teacher († 1955)
- March 10: E. Pauline Johnson , Canadian poet and writer († 1913)
- March 11: Carl Ferdinand Friedrich Lehmann-Haupt , German ancient orientalist and ancient historian († 1938)
- March 11: Oscar Seifert , Leipzig original († 1932)
- March 13: Gustave Ramaciotti , Australian theater director and soldier († 1927)
- March 14: Rudolf Krauss , German Germanist and literary historian († 1945)
- March 14: Everett Ellsworth Truette , American organist, composer, music publisher and author († 1933)
- March 16: Clara Weaver Parrish , American painter, designer, printmaker and glass painter († 1925)
- March 21: Zygmunt Ajdukiewicz , Polish painter († 1917)
- March 22: Perry Doolittle , Canadian doctor, inventor, racing cyclist and motorist († 1933)
- March 24th: Richard Weiskirchner , Austrian politician, Mayor of Vienna († 1926)
- March 28: Alfred B. Kittredge , American politician († 1911)
- March 29: August Nattermann , German pharmacologist and entrepreneur († 1923)
- March 31: Cabbar Qaryağdıoğlu , Azerbaijani mugham singer († 1944)
- April 1: Katō Tomosaburō , Japanese Prime Minister († 1923)
- April 2: Richard Reitzenstein , German classical philologist and historian of religion († 1931)
- April 3: George Curry , American politician († 1947)
- April 5: Fritz Encke , German horticultural architect and royal horticultural director († 1931)
- April 6: Louis Angermann , German architect († 1892)
- April 11: Émile Bouichère , French organist († 1895)
- April 13: José Pierson , Mexican music teacher († 1957)
- April 16: William F. Hooley , American singer († 1918)
- April 17: Willard Saulsbury Jr. , American politician († 1927)
- April 20: Hermann Muthesius , German architect, privy councilor in the Prussian Ministry of Commerce († 1927)
- April 22: István Tisza , Austro-Hungarian politician and Prime Minister of Hungary († 1918)
- April 23: Edmund Allenby , British Field Marshal († 1936)
- April 23: Carl Moll , Austrian Art Nouveau painter († 1945)
- April 25: Marco Enrico Bossi , Italian organist and composer († 1925)
- April 25: Rudolf Dittrich , Austrian musician († 1919)
- April 26: Rudolf Freiherr Stöger-Steiner von Steinstätten , Minister of War Austria-Hungary († 1921)
- April 27: Georgi Catoire , Russian composer († 1926)
- April 27: William Arms Fisher , American composer, music historian and publisher († 1948)
- April 27: William Lorimer , American politician († 1934)
- April 30: Eduard Adler , German journalist and local politician († 1938)
May June
- May 2: Johannes Geffcken , German classical philologist († 1935)
- May 6: Motilal Nehru , Indian lawyer and statesman; Co-founder of the Swaraj party († 1931)
- May 7: Julius von Bernuth , German major general († 1957)
- May 7: Frank C. Partridge , American politician († 1943)
- May 7: Rabindranath Thakur , Bengali poet and social reformer († 1941)
- May 9: Anna Pappritz , German writer, women's rights activist and abolitionist († 1939)
- May 12: Hugo von François , German officer († 1904)
- May 13: Wilhelm Hegenscheidt , German iron industrialist in Upper Silesia († 1895)
- May 13: Honoré Jackson , Canadian journalist († 1952)
- May 13: Clemens Thieme , German architect († 1945)
- May 15: Augustin Savard , French composer and music teacher († 1942)
- May 16: Irving Wightman Colburn , American inventor and manufacturer († 1917)
- May 16: Herman Webster Mudgett , American serial killer († 1896)
- May 21: Karl Anrather , Tyrolean painter († 1893)
- May 24: Johannes Gillhoff , German writer († 1930)
- May 25: Arthur Edward Aitken , British military commander († 1924)
- May 28: Siegfried Czapski , German physicist, optician and entrepreneur († 1907)
- May 28: Gustav Tammann , German chemist († 1938)
- May 30: Walter M. Pierce , American politician († 1954)
- June 3: Adolf Kronfeld , Austrian doctor († 1938)
- June 5: Charles M. Floyd , American politician († 1923)
- June 6: Joseph M. Terrell , American lawyer, senator and governor of Georgia († 1912)
- June 7: Malcolm R. Patterson , Americ. Politician, Governor of Tennessee († 1935)
- June 8: Karl Gölsdorf , Austrian engineer and locomotive designer († 1916)
- June 10: Pierre Duhem , French physicist and scientific theorist († 1916)
- June 12: Edmond Missa , French composer († 1910)
- June 13: Johannes Angern , Prussian major general († 1938)
- June 15: Ernestine Schumann-Heink , Austrian opera singer († 1936)
- June 17: Sidney Jones , English composer and conductor († 1946)
- June 17: Wilhelm Robert Nessig , German teacher and geologist († 1932)
- June 17th: Georg von Prittwitz and Gaffron , German officer and Africa explorer († 1936)
- June 19: Douglas Haig, 1st Earl Haig , British Field Marshal General († 1928)
- June 19: José Rizal , Filipino writer, patriot, doctor, Freemason and revolutionary, national hero of the Philippines († 1896)
- June 19: Ludwig Traube , German classical philologist and medievalist († 1907)
- June 20: Frederick Gowland Hopkins , English biochemist († 1947)
- June 22nd: John Lemmoné , Australian flautist, composer and music manager († 1949)
- June 22nd: Maximilian Graf von Spee , German admiral († 1914)
- June 29: Nicolas Cadi , Syrian Archbishop († 1941)
July August
- July 5: Johannes Marinus Simon Baljon , Dutch Reformed theologian († 1908)
- July 8: Oscar Matthiesen , Danish painter († 1957)
- July 10: Paul Asten , German Imperial Judge († 1925)
- July 12: Anton Arensky , Russian composer († 1906)
- July 13: Ludwig Edenhofer junior , German organ builder and cellist († 1940)
- July 15: Hirotsu Ryūrō , Japanese writer († 1928)
- July 16: Franz von Blon , German composer and conductor († 1945)
- July 22: Joseph L. Bristow , American politician († 1944)
- July 23: Alexander Willem Frederik Idenburg , Dutch governor of Suriname († 1935)
- July 24th: Benno von Achenbach , founder of the German art of carriage driving († 1936)
- July 24: Elkan Nathan Adler , British lawyer and academic traveler († 1946)
- July 24th: Maurice Renaud , French singer († 1933)
- July 24th: Maximilian Graf von Wiser , German ophthalmologist († 1938)
- July 26th: Wascha-Pschawela , Georgian writer and natural philosopher († 1915)
- July 28: John Albert Johnson , American politician († 1909)
- July 31: Wilhelm Busch , German instrument maker († 1929)
- August 3: Samuel M. Shortridge , American politician († 1952)
- August 3: Michel Verne , French writer († 1925)
- August 4th: Josef Andergassen , Austrian cabinet maker, altar builder and sculptor († 1929)
- August 4: Daniel E. Howard , Liberian President († 1935)
- August 8: William Bateson , British geneticist († 1926)
- August 9: Paul Ruben Arons , German banker and councilor († 1932)
- August 11: Albert Boehringer , German industrialist († 1939)
- August 11: Emil Zsigmondy , Austrian mountaineer († 1885)
- August 13: Herbert H. Turner , British astronomer and seismologist († 1930)
- August 14: Georg Haberland , German entrepreneur († 1933)
- August 14: Augustus Stephen Vogt , Canadian music teacher, choir director, organist and composer († 1926)
- August 25: Franz Amecke , German pastor († 1933)
- August 31: Alexandre-M. Clerk , Canadian composer and conductor († 1932)
- August 31: Benjamin Jan Kouwer , Dutch gynecologist († 1933)
September October
- September 1: Lazăr Edeleanu , Romanian chemist († 1941)
- September 3: James Hartness , American politician († 1934)
- September 3: Cyrus Woods , American lawyer, politician and diplomat († 1938)
- September 7: Besarion Chelaia , Georgian clergyman († 1927)
- September 11th: Juhani Aho , Finnish writer and journalist († 1921)
- September 11: Erich von Falkenhayn , German officer and military politician († 1922)
- September 13: Frederick Judd Waugh , American painter, illustrator and author († 1940)
- September 15: Henry Appia , Swiss Protestant clergyman († 1901)
- September 16: Franz Matsch , Austrian painter († 1942)
- September 17th: Carlo Minoretti , Italian clergyman, Archbishop of Genoa and Cardinal († 1938)
- September 18: Eduard Riggenbach , Swiss Protestant theologian and university professor († 1927)
- September 18: Walter Schott , German sculptor († 1938)
- September 20: Herbert Putnam , American librarian († 1955)
- September 21: Josef Scheiner , Czech lawyer, journalist and politician and member of the Czech gymnastics movement Sokol († 1932)
- September 21: Alfredo Zayas y Alfonso , President of Cuba 1921–1925 († 1934)
- September 23: Adelheid von Bennigsen , German women's rights activist († 1938)
- September 23: Robert Bosch , German industrialist and philanthropist († 1942)
- September 24: Walter Simons , German lawyer and politician († 1937)
- September 29: Carl Duisberg , chemist and industrialist († 1935)
- September 30: William Wrigley Jr. , American industrialist († 1932)
- October 2: Friedrich Simon Archenhold , German astronomer, designer of the giant telescope of the later Archenhold observatory († 1939)
- October 4: Walter Rauschenbusch , German-American Baptist theologian and founder of Social Gospel († 1918)
- October 4: Frederic Remington , American painter and sculptor († 1909)
- October 7: Carl von Dobschütz , Prussian major general († 1946)
- October 10: Édouard Dujardin , French writer († 1949)
- October 10: Fridtjof Nansen , Norwegian researcher, philanthropist and statesman († 1930)
- October 14: Alois Mrštík , Czech writer and dramaturge († 1925)
- October 15: Eduard Schmid , Lord Mayor of Munich († 1933)
- October 15: Josef Ruederer , German writer († 1915)
- October 16: Ernest Barberolle , French rower († 1948)
- October 16: John B. Bury , English ancient historian and philologist († 1927)
- October 16: Richard Sears , American tennis player († 1943)
- October 17: Woldemar Lippert , German archivist and historian († 1937)
- October 19: Richard Seifert , German chemist († 1919)
- October 20: Maximilian Harden , German publicist, critic and actor († 1927)
- October 23: Rudolf Köselitz , German painter and illustrator († 1948)
- October 23: Wilhelm Wrage , German painter († 1941)
- October 24th: Fritz Drechsler , German architect († 1922)
- October 28: Adam Jende , Latvian clergyman and evangelical martyr († 1918)
- October 30: Antoine Bourdelle , French sculptor and teacher († 1929)
- October 31: Christoph Drollinger , German Protestant clergyman and founder of the Swiss community for early Christianity († 1943)
November December
- November 2: Georgi Evgenjewitsch Lwow , Russian politician († 1925)
- November 2: Maurice Blondel , French philosopher († 1949)
- November 2: Charles W. Waterman , American politician († 1932)
- November 6: Thomas Watt Gregory , American politician († 1933)
- November 6: James Naismith , Canadian inventor of the sport of basketball († 1939)
- November 7th: Lesser Ury , German painter († 1931)
- November 9: James A. Reed , American politician († 1944)
- November 11th: Leopold Adametz , Austrian animal breeding and genetic researcher († 1941)
- November 12: Paul Preuss , German botanist and explorer († 1926)
- November 13: Viktor Weber von Webenau , Austro-Hungarian general († 1932)
- November 14: Frederick Jackson Turner , American historian († 1932)
- November 16: Arvid Järnefelt , Finnish writer († 1932)
- November 17: Archibald Lampman , Canadian poet († 1899)
- November 17: Erich Marcks , German historian († 1938)
- November 20: Camillo Cardinal Laurenti , Italian clergyman, Curia Cardinal of the Roman Catholic Church († 1938)
- November 26: Albert B. Fall , American politician († 1944)
- November 28: Verena Conzett-Knecht , Swiss trade unionist and women's rights activist († 1947)
- November 30th: Ludwig Thuille , Austrian composer († 1907)
- December 1: Carl Legien , German union leader († 1920)
- December 5: Armando Diaz , Italian Chief of Staff († 1928)
- December 8: Rosa Krüger , German flower and interior painter († 1936)
- December 8: Aristide Maillol , French sculptor, painter and graphic artist († 1944)
- December 8: Georges Méliès , French magician and film director († 1938)
- December 10: Daisy Greville, Countess of Warwick , British high society lady and mistress († 1938)
- December 10: Karl Groos , German philosopher and psychologist († 1946)
- December 10: Elisabeth von Heyking , German writer and painter († 1925)
- December 15: Pehr Evind Svinhufvud , Finnish President († 1944)
- December 17: Arthur Edwin Kennelly , British-American electrical engineer († 1939)
- December 18: Elisabeth Schellbach , German illustrator († 1929)
- December 19: Nikolai Ivanovich Andrussow , Russian geologist and paleontologist († 1924)
- December 19: Italo Svevo , Italian writer († 1928)
- December 20: Ludwig Sauer , German organist († 1940)
- December 21: Karl August Lingner , German entrepreneur and philanthropist († 1916)
- December 22: Ochiai Naobumi , Japanese poet and literary scholar († 1903)
- December 26: Friedrich Engel , German mathematician († 1941)
- December 26: Karl Hillebrand , Austrian astronomer († 1939)
- December 26th: Ludolf von Krehl , German medic († 1937)
- December 29: Kurt Hensel , German mathematician († 1941)
- December 31: August Abegg , Swiss textile manufacturer († 1924)
Exact date of birth unknown
- John Frederick Abercromby , British golf architect († 1935)
- Zygmunt Andrychiewicz , Polish painter († 1943)
- Bagher Khan , military leader and freedom fighter of the Constitutional Revolution of Iran († 1916)
- Regino López , Cuban actor, director and singer († 1945)
- Amalia Paoli , Puerto Rican opera singer († 1942)
Died
First quarter
- January 1: Carl Johan Fahlcrantz , Swedish painter (* 1774)
- January 2: Friedrich Wilhelm IV. , King of Prussia (* 1795)
- January 5: Heinrich Alexander von Arnim , Prussian statesman (* 1798)
- January 18: Joachim Heinrich Wilhelm Wagener , German banker and patron (* 1782)
- January 17th: Lola Montez , Irish impostor and dancer (* 1821)
- January 17th: Malla Montgomery-Silfverstolpe , Swedish writer (* 1782)
- January 19: Albert Niemann , German chemist (* 1834)
- January 20: Adolf Theodor Roscher , German industrialist (* 1782)
- January 20: Johann Ludwig Urban Blesson , Prussian military writer (* 1790)
- January 22nd: Friedrich Tiedemann , German anatomist and physiologist (* 1781)
- January 22nd: Giovanni Battista Velluti , Italian opera singer, last of the great castrati (* 1780)
- January 24: Robert Perkins Letcher , American politician (* 1788)
- February 1: Elisha Harris , American politician (* 1791)
- February 5: Pierre Bosquet , French general, Marshal of France (* 1810)
- February 7th: Borys Halpert , Polish theater director, librettist and musician (* 1805)
- February 8: Pierre-Bienvenu Noailles , French priest and founder of an order (* 1793)
- February 9: Karl Otto Ludwig von Arnim , German writer (* 1779)
- February 9: Francis Danby , Irish painter (* 1793)
- February 12: André Hippolyte Chelard , French composer (* 1789)
- February 16: Ernst Casimir II of Ysenburg and Büdingen , Prince of Ysenburg and Büdingen (* 1806)
- February 18: Theodor Mügge , German writer (* 1802)
- February 21: Lars Levi Læstadius , Swedish revival preacher in Lapland (* 1800)
- February 21: Ernst Rietschel , German sculptor of late classicism (* 1804)
- February 26: Jacob Best , German entrepreneur and brewer (* 1786)
- February 27: Prosper Ludwig von Arenberg , Duke of Arenberg, Aarschot and Meppen, Prince of Recklinghausen, Count von der Marck (* 1785)
- March 6th: Conrad Kreuzer , Austrian draftsman and landscape painter (* 1810)
- March 10: Taras Shevchenko , Ukrainian poet (* 1814)
- March 16: Victoire von Sachsen-Coburg-Saalfeld , German noblewoman, mother of the British Queen Victoria (* 1786)
- March 17th: Per Conrad Boman , Swedish composer (* 1804)
- March 18: Paolo Ghiringhelli , Swiss Benedictine and governor (* 1778)
- March 18: Mary Ann Brown Patten , American navigator and sailor (* 1837)
- March 22nd: Miguel Lerdo de Tejada , Mexican politician (* 1812)
- March 29: Adrianus Catharinus Holtius , Dutch legal scholar (* 1786)
Second quarter
- April 4: Michael Aigner , Austrian engraver (* 1805)
- April 4: Franz Anton von Kolowrat-Liebsteinsky , Austrian statesman (* 1778)
- April 8: Elisha Graves Otis , American master mechanic (* 1811)
- April 16: Friedrich Landolin Karl Freiherr von Blittersdorf , Baden civil servant (* 1792)
- April 18: Heinrich August Neithardt , German composer (* 1793)
- April 18: Joseph Augenstein , German local politician (* 1800)
- April 19: Charles Ashe à Court-Repington , British general (* 1785)
- April 26: John Munroe , American officer and politician (* 1796)
- April 29: José María Obando , President of New Granada (* 1795)
- May 9: Ernst von Lasaulx , German classical philologist, philosopher of history and politician (* 1805)
- May 10: Christian Christoph Andreas Lange , Norwegian archivist (* 1810)
- May 18: Friedrich August von Ammon , German ophthalmologist (* 1799)
- May 21: Eugen von Mazenod , French Catholic saint and founder of the order (* 1782)
- May 22: Godehard Braun , German auxiliary bishop (* 1798)
- May 29: Joachim Lelewel , Polish historian and freedom fighter (* 1786)
- May 30th: Mikhail Gortschakow , Russian field marshal (* 1792)
- June 3: Stephen A. Douglas , American politician (* 1813)
- June 6th: Camillo Benso von Cavour , Italian Prime Minister (* 1810)
- June 10: Theodore Winthrop , American author and lawyer, major in the Northern Army in the Civil War (* 1828)
- June 16: Nathanael G. Pendleton , American politician (* 1793)
- June 24th: John Campbell, 1st Baron Campbell , British politician and lawyer (* 1779)
- June 25: Abdülmecid I , Ottoman Sultan (* 1823)
- June 29: Elizabeth Barrett Browning , British poet (* 1806)
- June 30th: Robert O'Hara Burke , Irish-born Australian explorer (* 1821)
Third quarter
- July 2: James Abercrombie , American lawyer and politician (* 1792)
- July 2: Karl Heinrich Adelbert Lipsius , German Evangelical Lutheran theologian and educator (* 1805)
- July 4th: Francisco del Rosario Sánchez , Dominican politician, one of the founding fathers of the Dominican Republic (* 1817)
- July 13: James Hopkins Adams , American politician (* 1812)
- July 13: Jan Ackersdijck , Dutch lawyer, statistician and economist (* 1790)
- July 14th: Nathan Appleton , American politician (* 1779)
- July 15: Adam Jerzy Czartoryski , Polish politician (* 1770)
- July 16: Ludwig Pernice , German legal scholar and curator in Halle (* 1799)
- July 20: Ferdinand Wachter , German historian and university professor (* 1794)
- July 22nd: Gregor Wilhelm Nitzsch German philologist (* 1790)
- July 22: Barnard Elliott Bee , Confederate Brigadier General (* 1824)
- July 25: Jonas Furrer , Swiss Federal President (* 1805)
- August 1: Johann Philipp Abresch , German Democrat (* 1804)
- August 11: Catherine Hayes , Irish opera soprano (* 1818)
- August 13: Thomas Witlam Atkinson , English travel writer (* 1799)
- August 15: Adolphe Dumas , French poet, playwright and Provençalist (* 1805)
- August 16: Ranavalona I , Queen of Madagascar
- August 18: Jonker Afrikaner , captain of Orlam (* 1790)
- August 22: Xianfeng , Chinese Emperor (Qing Dynasty) (* 1831)
- August 26: Johan Fredrik Berwald , Swedish composer (* 1787)
- August 28: William Lyon Mackenzie , Scottish-Canadian politician (* 1795)
- September 3: Christian Heinrich Tramm , German architect (* 1819)
- September 7th: Willie Person Mangum , American politician (* 1792)
- September 11th: Karl Gottlieb Anton , German classical philologist (* 1778)
- September 11th: George N. Briggs , American politician (* 1796)
- September 13: Toussaint Poisson , French composer and music teacher (* 1797)
- September 20: Maximilien Simon , French composer and civil servant (* 1797)
- September 22nd: Rose Chéri , French actress (* 1824)
- September 22nd: Ernst Friedrich Zwirner , German master builder and architect (* 1802)
- September 23: Therese Brunsvik de Korompa , Hungarian nobleman, confidante of Ludwig van Beethoven and founder of the kindergartens in Hungary (* 1775)
- September 24: Abba Bagibo , King of Limmu-Ennarea (* 1802)
Fourth Quarter
- October 11: Elizabeth Conyngham, Marchioness Conyngham , mistress of King George IV of Great Britain (* 1769)
- October 23: Jorge Córdova , President of Bolivia (* 1822)
- October 25: Gotthard Emanuel von Aderkas , German-Baltic diplomat and administrative officer (* 1773)
- October 25: Friedrich Carl von Savigny , German legal scholar (* 1779)
- November 1st: Oldwig Anton Leopold von Natzmer , Prussian general (* 1782)
- November 8: Josiah McNair Anderson , American politician (* 1807)
- November 10th: Henri Mouhot , French scientist and explorer (* 1826)
- November 10: Moritz Schreber , German doctor (Leipzig) (* 1808)
- November 11th: Peter V , King of Portugal (* 1837)
- November 12: Albert Dufour-Féronce , German banker, entrepreneur and railway pioneer (* 1798)
- November 13: Arthur Hugh Clough , English writer (* 1819)
- November 17th: Eduard Herrmann Volkmar Ficker , Saxon Evangelical-Lutheran theologian, clergyman and master's degree (* 1801)
- November 20: Christian Friedrich Brendel , German mining engineer (* 1776)
- November 21: Johannes Horkel , German philologist and headmaster (* 1820)
- November 21: Jean Baptiste Henri Lacordaire , French Dominican, preacher and theologian (* 1802)
- November 23: Wilhelm von Harnier , German traveler to Africa (* 1836)
- November 24th: Ferdinand von Eckstein , Danish writer and French civil servant (* 1790)
- November 26th: Wilhelm Hensel , German painter (* 1794)
- November 27: Anne Bignan , French writer and translator (* 1795)
- November 28: Richard M. Young , American politician (* 1798)
- December 1: Heinrich August Hahn , German Protestant theologian and university professor (* 1821)
- December 4th: José María Bustamante , Mexican composer (* 1777)
- December 8: Iossif Ivanovich Charlemagne , Russian architect (* 1782)
- December 14: Albert von Sachsen-Coburg and Gotha , German nobleman, husband of Victoria of Great Britain (* 1819)
- December 14: Heinrich Marschner , German composer (* 1795)
- December 17th: Ignaz Maria Graf von Attems-Heiligenkreuz , Austrian Privy Councilor and Governor of Styria (* 1774)
- December 18: Ernst Anschütz , German teacher, organist, poet and composer (* 1780)
- December 23: William Clayton Anderson , American politician (* 1826)
- December 24th: Carl Gottlieb Bellmann , German musician (* 1772)
- December 25: Jakob Josef Eeckhout , Belgian painter and lithographer (* 1793)
Web links
- Digitized newspapers from 1861 in the newspaper information system (ZEFYS) of the Berlin State Library
- Austrian newspapers from 1861 in AustriaN Newspaper Online (ANNO) of the Austrian National Library