Michigan Territory
The Michigan Territory was a territory of the United States that existed from June 30, 1805 through January 26, 1837. After that, the territory was accepted into the union as the 26th state named Michigan . The capital was Detroit .
history
prehistory
After the arrival of the Europeans, the area that later became the Michigan Territory was first under French and then British control. After the American Revolutionary War , several states had competing claims to land in the region. In 1779, Virginia established Illinois County , which encompassed all of the land east of the Mississippi River , north of the Ohio River and west of the Appalachians . However, the county government never actually had full control over the entire area, only over a few old French settlements along the main streams. Other states also claimed portions of what would later become Michigan, including the states of New York , Connecticut, and Massachusetts .
The states then ceded their claims in 1787 and the Continental Congress enacted the Northwest Ordinance , which created the Northwest Territory . The region that would later become Michigan was initially disorganized territory. On June 20, 1790, Knox County was established, which comprised the western half of the Lower Peninsula and most of the Upper Peninsula of Michigan. In 1792, Hamilton County was expanded to include the eastern portion of Michigan that was not part of Knox County. On August 15, 1796, Wayne County was established from parts of Knox and Hamilton Counties and comprised most of what was later to become Michigan Territory and parts of what is now Ohio , Indiana , Illinois and Wisconsin .
When a separate government was established in the Northwest Territory in 1800, the western half of Michigan was added to the Indiana Territory . Wayne County was reduced to the eastern part of Michigan and remained part of the Northwest Territory. Knox County became the Indiana Territory and its borders were expanded in 1801 to include most of the western part of the "Lower Peninsula" and a small piece of the "Upper Peninsula". The St. Clair County , another county of Indiana Territory, has been extended to the western part of the "Upper Peninsula" and a small piece of "Lower Peninsula" along the shore of Lake Michigan.
When Ohio became the 17th state to join the Union in 1803, the eastern half of Michigan was annexed to the Indiana Territory. At that time, old Wayne County practically ceased to exist. Then Wayne County was recreated a second time, from parts of Knox and St. Clair Counties, which included the entire "Lower Peninsula", much of the "Upper Peninsula" and parts of what is now Illinois, Indiana and Wisconsin.
organization
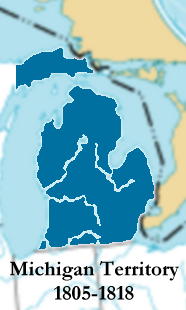
The Michigan Territory was created by a law passed in the US Congress on January 11, 1805 , but it did not actually take effect until June 30, 1805. The law defined the territory as "the entire area in the Indiana Territory lying north of a line drawn eastward from the southern bend or extreme of Lake Michigan and then intersected by Lake Erie and east of a drawn line drawn from the aforesaid south bend through the middle of the lake to its north end and thence due north to the northern border of the United States . ”A historical roadside marker about three miles east of the Naubinway at 46 ° 5 ′ 50 ″ N , 85 ° 23 ′ 51 ″ W , commemorates the northernmost point on Lake Michigan, which is a mile west of the point.
The first Territory Governor William Hull abolished Wayne County and established new districts according to his own ideas, which were short-lived, however. Lewis Cass became governor in 1813 and resigned from Hull's work. He resurrected Wayne County for the third time, including all of the land within Michigan that was ceded by the indigenous peoples under the Detroit Treaty of 1807.
During the British-American War , General Isaac Brock captured Detroit on August 16, 1812, making the Michigan Territory at least nominally a part of Upper Canada . On August 24, 1812, Colonel Henry Procter proclaimed the continuation of civil government with existing law, with Procter as acting governor and Chief Justice Augustus B. Woodward as acting secretary . On February 4, 1813, Procter suspended the civil government and imposed martial law .
When Indiana (1816) and Illinois (1818) joined the union, the rest of their territories were added to the Michigan Territory. An area that included 30 parishes was transferred from the Michigan Territory to Indiana to allow access to Lake Michigan. Soon after, the federal government began signing treaties with local Indian tribes and purchasing their land.
In 1824, the Michigan Territory received its second degree of territorial status, and powers passed from the governor and a handful of judges to the people. These elected 18 men to the Legislative Council , nine of whom were confirmed by the President ; the first meeting took place on June 7, 1824. In 1825 the council was expanded from nine to 13 representatives, the 13 being chosen by the President from 26 candidates.
The Erie Canal was opened in 1825 and now allowed settlers from New England and New York to reach Michigan by sea through Albany .
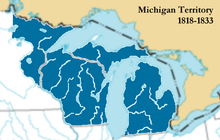
In 1834 the undistributed land from the Louisiana Purchase , east of the Missouri ( South Dakota , North Dakota , Iowa, and western Minnesota ), was added to the Michigan Territory, an area officially known as "Northern Missouri and the eastern part of the Missouri and White Earth Rivers ”. At that point, the Michigan Territory comprised what is now the states of Michigan, Wisconsin, Iowa, Minnesota, and much of Dakota.
In 1835 the Toledo War broke out between Ohio and the Michigan Territory because the Michigan Territory wanted to keep the controversial "Toledo Strip". The Toledo area of Ohio was eventually traded in exchange for the western section of the "Upper Peninsula" of Michigan.
The slavery was in the territory under the Northwest Ordinance prohibited but English and French residents were allowed to keep slaves they already had at the time of the design of the territory. According to censuses, the slave population was 24 in 1810 and 32 in 1830. Today it is believed that the slaves counted were, in many cases, enslaved Native Americans and non-enslaved African Americans . With the creation of the Wisconsin Territory in 1836, the Michigan Territory shrank. The Wisconsin Territory was created in 1836 with the current border in the "Upper Peninsula".
On July 3, 1836, in preparation for the admission of Michigan into the Union, the Wisconsin Territory was spun off from the Michigan Territory, which consisted of the current states of Wisconsin, Minnesota, Iowa and the eastern part of the Dakotas. Michigan became a state on January 26, 1837 , which encompassed the "Upper Peninsula" as far west as the Montreal River as part of the decision in the conflict over the Toledo Strip, and blocked Michigan's sovereignty for several years. Detroit remained the state's capital until March 17, 1847, before moving to Lansing . At the time of Michigan sovereignty, the population is estimated to be approximately 200,000, which was above the Northwest Ordinance's Minimum of 60,000.
Acquisition of territory
What would later become Michigan was British territory and was not ceded to the United States until 1783. At that time, however, the area was owned by the indigenous people. The majority of these could be won through assignment, coercion or other means. Before Michigan was colonized by American settlers, the Ottawa , Potawatomi , Anishinabe, and Wyandot lived there . The treaties for the cession of the land were signed between 1795 (the Treaty of Greenville ) and 1842 (the Treaty of La Pointe ). Other significant treaties were the Treaty of Governor Hull of 1808, the Treaty of Saginaw of 1819, the two Treaties of Chicago of 1821 and 1833, the Carey Mission of 1828 and the Treaty of Washington of 1836, and the subsequent Treaty of January 4, 1837.
Subdivisions of territory
Wayne County, Michigan was originally part of the vast Northwest Territory that was eventually shaped into its present size by separating it into several parts: Monroe in 1817, Michilimackinac County, Michigan (later called Mackinac and subdivided seven more times), and Macomb County in 1818 , St. Clair Counties and St. Joseph Counties in 1820, and Washtenaw Counties in 1822. ( Chippewa County was created from Mackinac in 1826, and four other counties in Michigan, with other parts going to Minnesota.) The first church created was that of Detroit in Wayne County 1802.
Showano County, Michigan was also created in 1818 and later renamed Crawford County , which originally covered much of what is now Minnesota. The following year Oakland County was created, which was later divided or part of Genesee , Lapeer , Sanilac , Shiawassee, and Saginaw . Saginaw was then further divided into eight separate counties, three of which, Isabella , Arenac and Midland , were created during the Territorial Period. The Lenawee County was in 1822 from what had once been Indian land created. Seven years later, Hillsdale County was separated from this. Other parts of Lenawee became Cass and Berrien . Branch was created entirely from the Michigan Territory in 1829. The Kalamazoo County was created in 1829 from the St. Joseph County, where the majority of the West Michigan was and was divided into many other counties: Allegan , Barry , Calhoun , Eaton , Ionia , Montcalm , Kent , Ottawa and Clinton (some were during created during the territorial period, others later). Jackson and Ingham were created from Washtenaw in 1829. Isabella was created from parts of Saginaw and Midland in 1831 . The Gratiot County was created in the same year from parts of Saginaw and Clinton. Seven of the 12 counties created in 1829 were named for President Andrew Jackson's Cabinet members and one for Jackson himself. Iowa County, which later became part of the state of Wisconsin, was also created in 1831 and was part of what was later returned to Michigan as Keweenaw in the "Upper Peninsula". Brown County, created in the Michigan Territory in 1818, was a very large area that covered much of what is now Wisconsin. West of the Mississippi River and south of Rock Island , the Dubuque and Des Moines Counties were created in the Territory of Michigan in 1834, which became part of the Territory of Wisconsin in 1836. These areas later became part of Iowa. Milwaukee County was created in 1834 and passed to Wisconsin in 1836.
Territorial population
These censuses do not include most Native Americans, as they were defined as Indians not taxed in the U.S. Constitution (Article 1, paragraph 2). In 1800 there were 43,365 residents throughout the Northwest Territory. Under the Northwest Ordinance , the territory could only get statehood if the population exceeded 60,000.
| year | population |
|---|---|
| 1810 | 4,762 |
| 1820 | 8,896 |
| 1830 | 31,639 |
| 1834 | 87.273 |
| 1840 | 212.267 |
Territorial offices
Governors
| governor | Term of office |
|---|---|
| William Hull | March 1, 1805 - October 29, 1813 |
| Lewis Cass | October 29, 1813 - August 6, 1831 |
| George B. Porter | August 6, 1831 - July 6, 1835 |
| Stevens T. Mason | July 6, 1835 - September 15, 1835 |
| John S. Horner | September 15, 1835 - July 3, 1836 |
Secretaries
| Secretary | Term of office |
|---|---|
| Stanley Griswold | March 1, 1805 - March 18, 1808 |
| Reuben Atwater | March 18, 1808 - October 15, 1814 |
| William Woodbridge | October 15, 1814 - January 15, 1828 |
| James Witherell | January 15, 1828 - May 20, 1830 |
| John T. Mason | May 20, 1830 - July 12, 1831 |
| Stevens T. Mason | July 12, 1831 - September 15, 1835 |
| John S. Horner | September 15, 1835 - July 3, 1836 |
Supreme Court
From 1805 to 1823 the Territorial Supreme Court Justices were appointed by the President, who was then confirmed by the US Senate . Their terms of office were not limited. In 1823, the US Congress passed a law establishing a territorial government and established a four-year term for judges.
| Supreme Court Justices | period of service |
|---|---|
| Augustus B. Woodward | March 2, 1805 - February 1, 1824 |
| Frederick Bates | March 3, 1805 - November 1808 |
| John Griffin | December 23, 1805 - February 1, 1824 |
| James Witherell | April 23, 1808 - January 15, 1828 |
| Solomon Sibley | February 2, 1824 - July 17, 1836 |
| John Hunt | February 20, 1824 - June 15, 1827 |
| Henry C. Chipman | July 18, 1817 - April 25, 1832 |
| William Woodbridge | January 15, 1828 - April 25, 1832 |
| Ross Wilkins | April 26, 1832 - July 17, 1836 |
| George Morrell | April 26, 1832 - July 17, 1843 |
Congress delegate
In 1819 the Michigan Territory was given authority to elect a congressional delegate.
| Delegate | period of service | Political party |
|---|---|---|
| William Woodbridge | 1819-1820 | Whig |
| Solomon Sibley | 1820-1823 | |
| Gabriel Richard | 1823-1825 | |
| Austin Eli Wing | 1825-1829 | |
| John Biddle | 1829-1831 | |
| Austin Eli Wing | 1831-1833 | |
| Lucius Lyon | 1833-1835 | democrat |
| George W. Jones | 1835-1837 | democrat |
See also
literature
- Alec R. Gilpin: The Territory of Michigan (1805-1837). Michigan State University Press, East Lansing 2002, ISBN 978-0-87013-151-6 .
Individual evidence
- ^ Paul Finkelman, Martin J. Hershock, Clifford W. Taylor: The History of Michigan Law. Ohio University Press, 2006, ISBN 0-8214-1661-8 , p. 13.
- ↑ Naubinway Rest Area in the Geographic Names Information System of the United States Geological Survey
- ↑ Northernmost Point of Lake Michigan ( Memento of the original from November 14, 2007 in the Internet Archive ) Info: The archive link was automatically inserted and not yet checked. Please check the original and archive link according to the instructions and then remove this notice. , Michigan Historical Markers
- ^ Treaty Between the Ottawa, Chippewa, Wyandot, and Potawatomi Indians. World Digital Library , November 17, 1807, accessed August 3, 2013 .
- ↑ George Washington Williams: History of the Negro Race in America from 1619 to 1880. Vol. II, GP Putnam's Sons, New York 1883, p. 9.
- ^ Simeon D. Fess: The History of Political Theory and Party Organization in the United States. Ginn and Company, Boston 1910, p. 272.