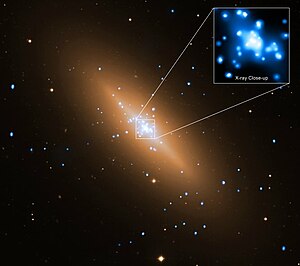
NGC 3115
| Galaxy NGC 3115 |
|
|---|---|
|
|
| Superimposition of an image in the optical spectral range of the Very Large Telescope with an image in the X-ray range of the Chandra Space Telescope | |
| AladinLite | |
| Constellation | sextant |
|
Position equinox : J2000.0 , epoch : J2000.0 |
|
| Right ascension | 10 h 05 m 14.0 s |
| declination | -07 ° 43 ′ 07 ″ |
| Appearance | |
| Morphological type | S0- / PAS |
| Brightness (visual) | 9.1 mag |
| Brightness (B-band) | 10.1 mag |
| Angular expansion | 7.2 ′ × 3.2 ′ |
| Position angle | 43 ° |
| Surface brightness | 12.3 mag / arcmin² |
| Physical data | |
| Affiliation | NGC 3115 group |
| Redshift | 0.002212 ± 0.000013 |
| Radial velocity | 6 (63 ± 4) km / s |
|
Stroke distance v rad / H 0 |
(22 ± 2) x 10 6 ly (6.75 ± 0.48) Mpc |
| history | |
| discovery | Wilhelm Herschel |
| Discovery date | February 22, 1787 |
| Catalog names | |
| NGC 3115 • UGC A 199 • PGC 29265 • MCG -01-26-018 • 2MASX J10051397-0743068 • GC 2008 • H I 163 • h 3223 • USGC S146 NED02 • GIN 775 | |
NGC 3115 is a lenticular galaxy of the Hubble type S0 in the constellation Sextant south of the ecliptic . It is an estimated 22 million light years away from the Milky Way and has a diameter of about 60,000 ly. The center of the galaxy is home to an extremely massive black hole of about two billion solar masses, with a total mass between 300 and 400 billion solar masses.
NGC 3115 is sometimes called the spindle galaxy , not to be confused with Messier 102, which is also called.
The object was discovered on February 22, 1787 by the German-British astronomer Wilhelm Herschel .
Web links
Commons : NGC 3115 - collection of images, videos, and audio files