Geography of africa
The geography of Africa is the description of the physical structure of the continent Africa and the resulting interaction between this habitat and its inhabitants.
physical geography
Topographical description
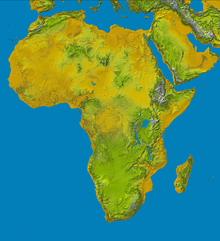
With an area of 30.3 million km² (22% of the total land area of the earth), Africa is the second largest continent after Asia and about three times the size of Europe. The following subdivision of Africa into regions is used, among others, by the UN statistical agency UNSD :
- North Africa : Egypt , Algeria , Libya , Morocco , Sudan , Tunisia , Western Sahara
- West Africa : Benin , Burkina Faso , Ivory Coast , Gambia , Ghana , Guinea , Guinea-Bissau , Cape Verde , Liberia , Mali , Mauritania , Niger , Nigeria , Senegal , Sierra Leone , Togo
- Central Africa : Angola , Equatorial Guinea , Democratic Republic of the Congo , Gabon , Cameroon , Republic of the Congo , São Tomé and Príncipe , Chad , Central African Republic
- East Africa : Ethiopia , Burundi , Djibouti , Eritrea , Kenya , Comoros , Madagascar , Malawi , Mauritius , Mozambique , Rwanda , Zambia , Seychelles , Zimbabwe , Somalia , Somaliland , Tanzania , Uganda
- Southern Africa : Botswana , Lesotho , Namibia , South Africa , Swaziland
Other classifications are sometimes used.
At the height of Central Africa is the Equator , the Tropic of Cancer runs through North Africa and the southern tropic through Southern Africa.
North africa
North Africa refers to the area that includes the Maghreb , the Sahara desert , the Nile valley and other parts of the Nile river system .
In the Maghreb lies the Atlas Mountains , which are around 2300 kilometers wide , the highest peak of which is the 4165 meter high Toubkal in southern Morocco.
The Sahara stretches from the African Atlantic coast in the west to the Red Sea in the east. It consists in the east of the Libyan desert west of the Nile and the Arabian desert and the Nubian desert east of the Nile. The Ténéré desert is located in the south of the Sahara. The Sahel zone lies south of the Sahara .
There are large mountain ranges in the Sahara, such as the Ahaggar , the Aïr , the Tibesti , the Ennedi massif and the extinct volcano Marra . The highest point is the Emi Koussi in the Tibesti with 3415 meters.
The Nile flows through the Sahara and forms the approximately 24,000 km² Nile Delta on the coast of the Mediterranean Sea . The river delta consists of loose sediments that have been deposited over the millennia.
West Africa
West Africa lies south of the Sahara, east and north of the Atlantic . It includes the western part of the greater Sahel and Sudan landscapes , as well as the rainforests of Upper Guinea .
The region consists of flat coastal areas and mountains such as the Upper Guinea Swell and the Adamaua highlands with the Cameroon Mountain .
The largest lake is the Volta Reservoir , the largest rivers the Niger , Senegal and the Gambia .
Central Africa
Central Africa lies south of the Sahara, east of West Africa and west of the Great Rift Valley . The area is determined by the Congo River, the river with the most water in Africa.
The mountain ranges are the Lower Guinea Sill on the coast and to the east of it the North Equatorial Sill , the Congo Basin and the Lunda Sill . Even further to the east lies the Central African Threshold , which East Africa follows.
The second largest tropical jungle in the world is located in the Congo Basin .
Great lakes are Lake Tanganyika and Lake Mweru , near the Central African threshold. The Lake Chad is located on the southern edge of the Sahara, he was several thousand years, he is more than ten times as large as today.
The rivers are the Congo and its tributaries such as the Lualaba , Kasai and Aruwimi .
East Africa
East Africa lies east of the Nile and east of the East African Rift Valley . There is the desert region of Danakil-Somalia .
Mountains are the highlands of Abyssinia , which extends to the Red Sea and on the coast of the Indian Ocean the East African lake highlands , where the Kilimanjaro massif and the Mount Kenya massif are located.
In East Africa there are large lakes such as Lake Victoria , Lake Turkana , Lake Tana and Lake Malawi . Major rivers are the Zambezi , the Juba , the Shabelle and the Blue Nile .
The island of Madagascar in the Indian Ocean is also part of East Africa, but the island is quite independent because of its isolated location.
Southern Africa
The Southern Africa is dominated by the Mozambique up along the coast extending from Angola Great Escarpment and the enclosed by this inland highlands. Important mountains are the Drakensberg and the Brandbergmassiv . There are forests and grasslands as well as the Namib desert and the Kalahari savannah .
Big rivers are the Limpopo and the Oranje .
Geological description
The continent lies on the African lithospheric plate and has moved with it for the past 100 million years at a low speed of only a few centimeters per year to the north.
The Great Rift Valley runs through the east of Africa and will lead to the separation of the Horn of Africa from Africa. The resulting volcanism has led to the formation of high mountains in East Africa.
Another area that has been changed by plate tectonic processes is the Atlas Mountains in North Africa. When the land masses of Europe and Africa at the southern end of the Iberian Peninsula pressed against each other 65 million years ago to around 1.8 million years ago, these mountains unfolded.
climate
The West African monsoons last from June to September and arise from the temperature difference between the colder Atlantic Ocean and the hotter continent. The influence also extends into the western and central Sahel zone, where almost all of the annual rain falls during these months. The highest precipitation values are around 2000 mm precipitation per year.
In Central Africa one experiences the zenith precipitation , a rain that occurs depending on the season where the sun is exactly at the zenith . In such a place the precipitation occurs there every day.
Off the west coast of Southern Africa, the Benguela Current flows with comparatively cold seawater from the Antarctic. Together with the steady wind in the region, Southern Africa is in the area of the west wind zone , this leads to the condensation of the moisture contained in the air on the coast and since when the air is warmed up, the relative humidity also drops to the formation of the Namib desert.
nature
Tropical rainforests are found in Africa in the regions of Upper Guinea and the Congo Basin. This landscape changes into the wet savannah (1000–1500 mm rain per year), the dry savannah (500–1000 mm rain per year) and then into the thorn bush savannah (250–500 mm rain per year). The savannah consists of open grassland , the height of which depends on the amount of rain, and trees that are some distance apart. Since the precipitation areas migrate depending on the season, the plants of the savannah must be able to survive the dry season and the animals must follow the rain.
The thorn bush savannah is found in the Sahel zone , which forms the transition to the Sahara desert, but also in East Africa and Southern Africa.
The African deserts are characterized by rare rains, so that many plants are concentrated in oases where underground watercourses come to the surface. Other plants are found where the subterranean watercourses come so close to the surface that deep-rooted plants can reach them. Another possibility is that plants only begin to grow after a rain, and so the desert occasionally "blooms". The subterranean water of the Sahara is also pumped out on a large scale, for example through the Great Man Made River project , so that large-scale agriculture can be carried out near the population centers in otherwise arid regions. However, there is a threat of salinisation of the soil.
A special area is the Okavango Delta in southern Africa. There is an inland delta of the Okavango River , which in the middle of the semi-arid Kalahari creates a wetland area of around 12,000 square kilometers depending on the annual flood. Since the tide arrives at the end of the Okavango Delta at the height of the dry season, large numbers of animals gather there.
Since the Namib desert is geologically very old, animals that specialize in the climate, such as the mist-drinker beetle, have developed and other animals have adapted their way of life to the constantly dry region.
Human geography
Traffic geography
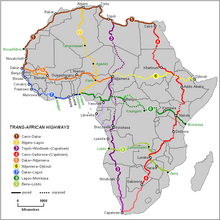
Africa is developed in terms of traffic through the Trans-African Highways , a system of transcontinental road projects. The total length of all nine Trans-African Highways is 56,683 kilometers.
Population density
In 2008 North Africa is expected to have a population of 197 million people. The most densely populated region is the area on the River Nile. A similar pattern can be seen in West Africa, where 291 million people live, 110 million of them alone on the Niger River. 122 million people live in Central Africa, and it is largely a sparsely populated area. About 301 million people live in East Africa, with the highest population density in the states east of the Central African threshold in the neighboring states of Burundi , Rwanda and Uganda . Uganda is one of the headwaters of the Nile and since large parts of the country are at an altitude of 1,000 m above sea level, the climate right at the equator is also pleasantly tempered. Rwanda and Burundi are also located on a high plateau at an average height of around 1500 m. Another area with a high population is on Lake Malawi. 55 million people live in southern Africa, although the population density here is rather low. In total there are probably 967 million people in Africa in 2008.
Spatial distribution of language families
In Africa there are different language families .
- Afro-Asian languages (blue color) with around 350 million speakers in North Africa and Northern East Africa.
- Niger-Congo languages (the two red colors) with around 370 million speakers in West Africa, Central Africa, southern East Africa and southern Africa.
- Nilo-Saharan languages (yellow color) with around 35 million speakers from Sudan to Mali
- Khoisan languages (green color) with 355 thousand speakers, mainly in western southern Africa.
- Austronesian languages (purple color) with 19 million speakers on the island of Madagascar .
See also
- African coral reefs
- Deserts of Africa
- List of rivers in Africa
- List of mountains or elevations in Africa
- List of lakes in Africa
- Natural parks in Africa
- List of the largest cities in Africa
- Discovery history of Africa
Individual evidence
- ↑ Regional breakdowns
- ↑ Deutscher Wetterdienst, AH Fink: Climate and Weather of the Tropics (PDF; 1.2 MB)
- ↑ a b c d e f 2008 WORLD POPULATION Data Sheet (PDF; 728 kB)