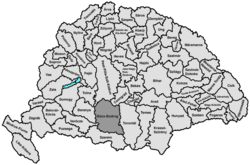
Bács-Bodrog county
|
Bács-Bodrog County (Batsch-Bodrog) (1910) |
|
|---|---|

|
|
| Administrative headquarters : | Zombor |
| Area : | 10,362 km² |
| Population : | 812.385 |
| Ethnic groups : | 45% Hungarians 23% Germans 18% Serbs , 4% Slovaks , 1% Ruthenians , 9% others (especially Bunjewatzen , Schokatzen and Gypsies ) |
|
|
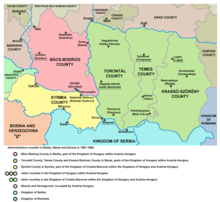
Bács-Bodrog [ ˈbaːʧ ˈbodroɡ ] (German seldom also Batsch-Bodrog County ; Hungarian Bács-Bodrog vármegye , Serbian Bačko-Bodroška županija , Latin comitatus Bacsiensis et Bodrogiensis ) was a county in southern Hungary , between the Danube and the lowest Tisza , that existed until 1920 bounded to the north by Pest-Pilis-Solt-Kiskun and Csongrád counties . In 1881 it covered 11,080 square kilometers in the Batschka , with around 638,000 inhabitants, mainly Hungarians , Serbs , Germans , other Slavs and Raizen .
location
The land is lowland , full of swamps and lakes, extremely fertile in wheat that was widely exported, wine, tobacco, and rich in livestock, game and fish. There was a lack of wood. The miles-long Römerschanzen are strange . The capital of the county, which was crossed by the Alföld-Fiumaner and Budapest-Semliner railways as well as the Franzenskanal , also known as Bácser Kanal, was Zombor .
In the north the county was made up of Pest-Pilis-Solt-Kiskun counties and Csongrád counties , in the east by Torontál counties , in the south by Syrmia counties (Szerém) and in the west for a short stretch in the south-west by Wirowititz counties (Verőce) and the Baranya county .
history
Bács and Bodrog counties were established in the 11th century, with Bács county in the southeastern part of what was later to become Bács-Bodrog county and Bodrog county in the northwestern part. After the occupation by the Ottomans , the area became part of the Sanjak Segedin in the 16th century , after the reconquest in 1699 the old state was restored and the two counties were finally united in 1802. In 1848/49 it was added to the Voivodeship of Serbia and then from 1849 to 1860 it was incorporated into the Serbian Voivodeship and the Temesian Banat .
After the end of the First World War in 1918, Serbian troops occupied the area. Until the Treaty of Trianon , it was administered by the Kingdom of Serbs, Croats and Slovenes and then divided between Hungary and the Kingdom. While Yugoslavia received the largest part in the south, about 15 percent of the county area in the north remained with Hungary. The part that remained with Hungary with the capital Baja remained within its borders until the major county reform in 1950 and then formed the new Bács-Kiskun county with the southern parts of Pest-Pilis-Solt-Kiskun county .
District subdivision
In the early 20th century the following chair districts existed (mostly named after the name of the administrative seat):
| Chair districts (járások) | |
|---|---|
| Chair district | Administrative headquarters |
| Apatin | Apatin |
| Bácsalmás | Bácsalmás |
| Baja | Baja |
| Hódság | Hódság, today Оџаци / Odžaci |
| Kula | Kula, today Кула / Kula |
| Óbecse | Óbecse, today Бечеј / Bečej |
| Palánka | Palánka, today Бачка Паланка / Bačka Palanka |
| title | title |
| Topolya | Topolya, today Бачка Топола / Bačka Topola |
| Újvidék | Újvidék, today Нови Сад / Novi Sad |
| Zenta | Zenta |
| Zombor | Zombor, today Сомбор / Sombor |
| Zsablya (Józseffalva) | Zsablya, today Жабаљ / Žabalj |
| City districts (törvényhatósági jogú városok) | |
| Baja | |
| Szabadka, today Суботица / Subotica | |
| Újvidék, today Нови Сад / Novi Sad | |
| Zombor, today Сомбор / Sombor | |
| City district (rendezett tanácsú város) | |
| Zenta, today Сента / Senta | |
The cities of Baja and Bácsalmás are in today's Hungary , the remaining cities in today's Serbia .
Web links
- Entry on the county in Meyers Konversationslexikon from 1888
- Entry in the Pallas Lexicon (Hungarian)
See also
- József Podmaniczky from Aszód and Podmanin , county chief
- List of historical counties of Hungary
- Batschka
Individual evidence
- ↑ A magyar szent corona országainak 1910. évi népszámlálása . Budapest 1912, p. 12 ff.
- ↑ A magyar szent corona országainak 1910. évi népszámlálása . Budapest 1912, p. 22 ff. (1910 census)