Laaber
| coat of arms | Germany map | |
|---|---|---|

|
Coordinates: 49 ° 4 ' N , 11 ° 53' E |
|
| Basic data | ||
| State : | Bavaria | |
| Administrative region : | Upper Palatinate | |
| County : | regensburg | |
| Management Community : | Laaber | |
| Height : | 402 m above sea level NHN | |
| Area : | 29.66 km 2 | |
| Residents: | 5286 (Dec. 31, 2019) | |
| Population density : | 178 inhabitants per km 2 | |
| Postal code : | 93164 | |
| Area code : | 09498 | |
| License plate : | R. | |
| Community key : | 09 3 75 162 | |
| LOCODE : | DE LA3 | |
| Market structure: | 33 districts | |
Market administration address : |
Jakobstrasse 9 93164 Laaber |
|
| Website : | ||
| Mayor : | Hans Schmid ( CSU ) | |
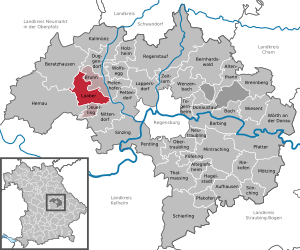
| Location of the Laaber market in the Regensburg district | ||
Laaber is a market in the Upper Palatinate district of Regensburg in Bavaria and the seat of the Laaber administrative community .
The place has had market rights since the end of the 14th century and is now the location of numerous commercial enterprises. The castle ruins are a well-known landmark in the Labertal.
geography
Geographical location
The market is located west of Regensburg in the eastern foothills of the Franconian Jura on the Schwarzen Laber .
Community structure
There are 33 districts: (residents in brackets, as of December 31, 2010)
|
|
|
|
history
Until the church is planted
The history of the Laaber market was determined for centuries by the fortunes and personalities of the noble family of the same name. Today the old remains of Laaber Castle and some documents are still witnesses of this famous noble family.
see also Burgstall Martinsberg , Burgstall Durchelenburg , Burgstall Eselsburg
In connection with the founding of the Reichenbach Monastery , the Lords of Laaber are mentioned for the first time in a document in 1118. Previously they called themselves after Brunn and most likely descend directly from the Regensburg burgrave Babo. Thus they are related to the Riedenburgers . They have been related by marriage to the neighboring Abensbergers several times since the middle of the 12th century.
Their participation in public life in the empire and country in the 11th, 12th and 13th centuries was significant and has been continuously documented in documents and archives since 1181. In the period from 1334 to 1337, for example, Hadmar von Laaber was the mayor of Regensburg, and in 1366 Ulrich von Laaber was mayor of Nuremberg. Hadmar IV, whose tombstone was laid in the parish church in Laaber, was in Berlin in 1374 with Emperor Karl IV and a few years later was also mayor of Regensburg.
The knightly race of the von Laaber family also excelled in the field of poetry and song of minnesia. Probably the most famous work is "The Hunt" by minstrel Hadmar III . At the beginning of the 15th century, the von Laaber family were considered very rich. They had properties all over the area from Nuremberg to Regensburg. But with the passing of Hadmar IV in 1420, during whose lifetime Laaber had been granted market rights, the change, the distribution of property, sale and thus the destruction of the property began.
It remained in the hands of the descendants until 1465, but when the last of the von Laaber family, Hadmar VII, died ten years later, the rights over the castle and the place, the rule between the dukes and administrators were divided. Laaber then came into the possession of the Duke of Bavaria-Landshut , who had a court and care office set up here. When from 1503 to 1505 Georg the Rich of Bavaria-Landshut formed a separate duchy of Palatinate-Neuburg from the land share of Georg the Rich , Laaber was also added. In the 1530s, Ottheinrich introduced Lutheranism in Neuburg - including Laaber. Until 1618 the pastors of Laaber and the surrounding area were Lutheran. Laaber remained a maintenance office of the Duchy of Palatinate-Neuburg in the following centuries and shared the fate of this area. In 1778 it was returned to Bavaria together with the Palatinate regions. Laaber has had its market rights since 1393 after a license was granted. In 1818 the political municipality was established.
The lords of Prunn, Laber, Breitenegg and their rule from 1080 to 1475
The family tree of Messrs. Von Laaber was created by Hund and Aventinus. Franz Xaver Scheuerer presented the work as a revision in autumn 1980. Both spellings appear, Herren von Laaber and Laber. They were strictly Catholic.
Incorporations
Before the municipal reform, all the places in today's municipality belonged to the Parsberg district . On January 1, 1971, the previously independent community of Endorf was incorporated. On July 1, 1971, Bergstetten and Großetzenberg were added. A small part of the dissolved municipality of Haag with fewer than ten inhabitants was added on May 1, 1978. The Parsberg district was dissolved in 1972, Laaber came to the Regensburg district. On January 1, 2014, a part of the dissolved community-free area Pielenhofer Wald was incorporated on the right of the Naab .
Population development
Between 1988 and 2018 the market grew from 4,595 to 5,222 by 627 inhabitants or by 13.7%.
Culture and sights
Castles and Palaces
Churches
- Catholic parish church of St. James
- Catholic side church of the Visitation of the Virgin Mary in Anger
- Catholic branch church St. Laurentius in Bergstetten
- Catholic branch church of the Birth of Mary in Endorf
- Catholic branch church of St. John the Baptist in Großetzenberg
- Catholic side church St. Joseph in Weißenkirchen
- Waldetzenberg Church
All architectural monuments
politics
Market council
The local council has 20 members and has been composed as follows since the local elections on March 15, 2020:
| Political party | Seats |
|---|---|
| CSU | 7th |
| FW / FWGL | 5 |
| SPD | 3 |
| Green | 2 |
| CWLU | 2 |
| FDP | 1 |
Of the 4,279 residents who are entitled to vote in the Laaber market, 3,040 exercised their right to vote, bringing the turnout to 71.04 percent.
mayor
Hans Schmid ( CSU ) was re-elected in the local elections on March 15, 2020 with 53.80% of the vote.
coat of arms
| Blazon : "In black a crowned and red-tongued golden lion head , above which three diamonds are floatingnext to each other, the middle blue, the side silver." | |
Economy and Infrastructure
traffic
Laaber has a junction on the A 3 Nuremberg - Regensburg and a train station on the Regensburg-Nuremberg railway line .
education
- Laaber primary school
- Laaber Middle School
Personalities
- Hadamar von Laber (around 1300 – around 1360), important medieval poet
- Ludwig Auer (1839–1914), elementary school teacher, writer, publisher and entrepreneur, was born in Laaber
- Henning Müller-Buscher (* 1944), German musicologist and publisher ( Laaber-Verlag )
- Maria Scharfenberg (* 1952), Bavarian state politician ( Bündnis 90 / Die Grünen ), lives in Laaber
- Albert Schmid (* 1945), former federal politician ( SPD ), was born in Laaber and lives there
literature
- Franz X. Bogner: In the valley of the Schwarzen Laber. Pustet, Regensburg 1999, ISBN 3-7917-1673-5 .
- Franz X. Bogner: The black talk from the air . Schwarze Laber Foundation, Parsberg 2014, ISBN 978-3-00-047433-0 .
Individual evidence
- ↑ "Data 2" sheet, Statistical Report A1200C 202041 Population of the municipalities, districts and administrative districts 1st quarter 2020 (population based on the 2011 census) ( help ).
- ↑ Markt Laaber in the local database of the Bayerische Landesbibliothek Online . Bavarian State Library, accessed on November 28, 2017.
- ^ Wilhelm Volkert (ed.): Handbook of Bavarian offices, communities and courts 1799–1980 . CH Beck, Munich 1983, ISBN 3-406-09669-7 , p. 546 .
- ^ Federal Statistical Office (ed.): Historical municipality directory for the Federal Republic of Germany. Name, border and key number changes in municipalities, counties and administrative districts from May 27, 1970 to December 31, 1982 . W. Kohlhammer GmbH, Stuttgart / Mainz 1983, ISBN 3-17-003263-1 , p. 658 .
- ↑ www.regierung.oberpfalz.bayern.de
- ↑ https://wahlen.landkreis-regensburg.de/kommunal2020/20200315/09375162/html5/Gemeinderatswahl_Bayern_66_Gemeinde_Markt_Laaber.html
- ↑ https://wahlen.landkreis-regensburg.de/kommunal2020/20200315/09375162/html5/Buergermeisterwahl_Bayern_67_Gemeinde_Markt_Laaber.html
- ↑ Entry on Laaber's coat of arms in the database of the House of Bavarian History , accessed on August 6, 2020 .
Web links
- Entry on the coat of arms of Laaber in the database of the House of Bavarian History