COVID-19 vaccination in Germany

In the fight against the COVID-19 pandemic (for the situation in Germany, see COVID-19 pandemic in Germany ), vaccines against the pathogen SARS-CoV-2 are being developed around the world . As of January 2021, according to the World Health Organization (WHO), more than 150 vaccines were already in preclinical development .
In November 2020, the federal and state governments decided on a national vaccination strategy to enable vaccinations in Germany. The federal government finances the procurement of vaccines, the federal states organize the distribution and set up a total of 60 vaccination centers. In order to ensure sufficient availability of vaccines, the federal government uses a central procurement mechanism via the European Commission . The vaccine approval for all EU member states is carried out by the European Medicines Agency (EMA).
The organization and logistics of vaccinations are more difficult than routine vaccinations, because the first available vaccines are difficult to transport, store and have to be cooled to varying degrees.
The first of the received RNA vaccine Tozinameran of BioNTech and Pfizer on 21 December 2020, the conditional marketing authorization in the EU . The first vaccinations took place on December 26, 2020. On January 6, 2021, the vaccine was given mRNA in 1273 by Moderna marketing approval with conditions. Vaxzevria, originally AZD1222 , from AstraZeneca followed on January 29, and Ad26.COV2.S from Johnson & Johnson on March 11 .
In Germany, the COVID-19 vaccination measures were prioritized until June 6, 2021 in accordance with the Coronavirus Vaccination Ordinance issued by the Federal Ministry of Health on the basis of the Infection Protection Act . This came into force on December 15, 2020 and stipulated that people over 80 years of age, who work in the healthcare or nursing profession and who are therefore exposed to a higher risk of infection, should be vaccinated first. The vaccination ordinance was changed with effect from March 8, 2021.
By May 31, 2021, over 55.4 million vaccine doses had been delivered to Germany. Of these, 90.0 percent had been vaccinated up to this point.
With effect from June 7, 2021, the vaccination prioritization expired. Those who were prioritized on the waiting list of the vaccination centers that day kept their place on the waiting list. At the beginning of June 2021, the state of Lower Saxony assumed that the release of the waiting lists for all state residents over 12 years would lead to the rapid replenishment of the lists. On June 29, 2021, however, it announced that the country's waiting list would be processed a week later.
Vaccination goals
At the press conference of Chancellor Angela Merkel , the Governing Mayor of Berlin Michael Müller and the Bavarian Prime Minister Markus Söder on February 1, 2021, the Chancellor stated that the aim of the vaccination campaign against COVID-19 was that every person willing to vaccinate by the end of summer Receive a vaccination offer in 2021. This commitment was reaffirmed several times in the course of 2021. Therefore, vaccines had to be produced quickly, delivered to the vaccination centers and inoculated. On June 25, 2021, Chancellery Minister Helge Braun estimated that it will probably be possible to vaccinate anyone who is ready to be vaccinated for the first time by the end of July / beginning of August 2021.
The Robert Koch Institute defines the point in time at which all people in Germany who have no medical concerns about their vaccination and who are willing to be vaccinated can be considered fully vaccinated (see below under #refresh vaccinations ) as the "end of the vaccination series" . It is important here that the status of a recovered person is limited to six months from the first positive test for SARS-CoV-2. This group of people also belongs to those who have to be vaccinated (albeit at different times) and thus delay the end of the vaccination series.
The hope that the SARS-CoV-2 virus would be less and less available to potential hosts and that ultimately “ herd immunity ” could develop in Germany was combined with rapid mass vaccination . In June 2021, doubts arose about the reachability of the destination.
On June 22, 2021, the virologist Christian Drosten expressed the assumption that the COVID-19 pandemic would end with the occurrence of “herd immunity”. The formula: "70 percent will become immune - regardless of whether through vaccination or infection - and the remaining 30 percent will then no longer have any contact with the virus" is, however, wrong. It is also wrong if the assumed quota is increased (as a reaction to the fact that new virus variants that displace their predecessors “on average infect more people than those infected with previous variants”). The virus will always find ways to infect people who have not been vaccinated, and new virus variants will manage to infect at least those who have not been completely vaccinated, although in most cases not with as serious consequences as in the case of non-vaccinated people. Nevertheless, it makes sense to stick to the goal of vaccinating as high a percentage of the population as possible in Germany (and other countries too).
Organization and logistics of vaccinations
Vaccination centers and mobile facilities
Around 430 vaccination centers and mobile vaccination teams had been set up by the beginning of April 2021. The federal states chose different approaches, for example:
- Initially, nine central vaccination centers were created in Baden-Württemberg. Since January 22, 2021, a week later than initially planned, additional vaccinations have been carried out at around 50 decentralized locations in the districts.
- Since mid-December 2020, Bavaria has set up a vaccination center in every district and every independent city with the exception of Aschaffenburg, 100 in total. The facilities are different, for example in a trade fair, barracks or a bath.
- Six vaccination centers were planned in Berlin.
- In Brandenburg, eleven vaccination centers were initially planned.
- Two vaccination centers were planned in Bremen.
- Vaccinations take place in Hall A3 in Hamburg. With a 12-hour operation, up to 7,000 people could be vaccinated per day.
- Initially 28 vaccination centers were to be set up in Hessen.
- Initially, 12 vaccination centers and 40 mobile vaccination teams were to be set up in Mecklenburg-Western Pomerania.
- Around 60 vaccination centers were initially planned in Lower Saxony.
- In North Rhine-Westphalia, 53 vaccination centers were initially planned in districts and urban districts.
- Rhineland-Palatinate: A vaccination structure was created by December 15, 2020, which consists of 31 vaccination centers and mobile vaccination teams for people in need of care, flanked by the possibility of vaccinating their own staff.
- In Saarland, three vaccination centers were initially set up (in Saarbrücken , Saarlouis and Neunkirchen ), as well as mobile vaccination teams. On March 1, 2021, a fourth vaccination center started operations in Lebach . It is operated by the Bundeswehr in the Graf Haeseler barracks .
- In Saxony, a central vaccination center and a total of 26 mobile vaccination teams were set up in each district by December 15, 2020. Further facilities were planned.
- In Saxony-Anhalt, vaccination centers have been set up in all eleven rural districts and the three independent cities. Mobile vaccination teams are also used.
- In Schleswig-Holstein 28 locations for vaccination centers were initially planned.
Resident doctors
In mid-March 2021, the base load of the vaccination centers for the following month of April was set at 2.25 million vaccinations per week. However, there was no telling how many vaccines would actually be delivered this month. This also left open in March 2021 how much vaccine family doctors could receive. The vaccinations in general practitioners began on April 6, 2021. 35,000 general practitioners had ordered 1.4 million doses for this. Around one million cans were delivered in each of the first two weeks of April, and a tripling of this was expected by the end of April. At the beginning of June, over 70,000 practices took part.
In a first step, general practitioners in private practice should vaccinate in the statutory health insurance system , later also specialists and private doctors should be included. Similar to flu vaccines, the federal government wants to supply wholesalers with vaccines, which they supply to general practitioners via pharmacies. As a side effect, the number of vaccinations reported should be reduced. In the first two weeks of April, general practitioners will only inject the vaccine from Biontech, after intermediate stages the vaccines from AstraZeneca and Johnson & Johnson. This is made possible not least by new findings on the stability of the Biontech / Pfizer vaccine outside of ultra-low temperature refrigeration.
prioritization
The vaccinations were initially linked to a prioritization. The vaccination itself is voluntary. Risk groups should be considered first. The vaccination regulations of the Federal Ministry of Health were based on the recommendations of the Standing Vaccination Commission at the Robert Koch Institute (RKI), the German Ethics Council and the National Academy of Sciences Leopoldina on the right to vaccination against the SARS-CoV-2 coronavirus.
While the assignment of people to priority groups was regulated by federal ordinance, each federal state initially decided for itself who was to be prioritized within a group. People in care facilities could be vaccinated directly on site by mobile vaccination teams. Each federal state determined for itself how the various groups were informed and the appointments were made. In most countries, people with the right to vaccinate were written to and were able to make appointments by phone or online. In some countries vaccination of hospital staff took place in parallel, in others the residents of nursing homes were preferred.
Violations of the vaccination ordinance usually had no consequences. In some cases it was suggested that this should be classified as an administrative offense .
Federal Minister of Health Jens Spahn announced at the beginning of January 2021 that if at least one or two other vaccines were approved as expected (in particular from AstraZeneca , Johnson & Johnson and / or Curevac ), a vaccination offer could be made to all those willing to vaccinate in the summer. With the vaccines from Biontech / Pfizer and Moderna alone , this could be the case by the end of 2021. Chancellor Angela Merkel stated that the federal government intends that all citizens should have the opportunity to receive a (first) vaccination by September 21, 2021.
On the occasion of the start of vaccinations with the AstraZeneca vaccine, the vaccination ordinance was amended on February 8, 2021. Initially, it should only be vaccinated in people between the ages of 18 and 65. On February 24, 2021, a change came into force according to which people who work in childcare facilities, day care and in elementary schools, special schools or special needs schools are assigned to the second highest priority group.
The third vaccination ordinance came into force on March 8, 2021. According to this, family carers , among others, are now entitled to vaccinate with the highest priority. Testing personnel can move up to priority group 2. The previous vaccination sequence can also be deviated from if this is necessary for an efficient organization of the vaccinations or the prompt use of existing vaccines, as well as if this results in a dynamic spread of infections in highly polluted border regions (so-called ring vaccination) as well as in or from high-incidence areas (so-called . Bar vaccination) can be prevented. The requirement to only give AstraZeneca's vaccine to people between the ages of 18 and 65 should no longer apply. The times of the follow-up vaccinations for the previously approved vaccines can no longer be extended. In the future, the federal states will be able to recognize written information from statutory or private health insurances about a prioritized right to vaccination as such. Medical practices and company doctors are now also allowed to give vaccinations. The vaccination centers and mobile vaccination teams are to remain unchanged.
On May 10, 2021, Federal Minister of Health Jens Spahn announced that the prioritization for the Johnson & Johnson vaccine had been lifted. This will proceed in the same way as that of AstraZeneca, which means that Ad26.COV2.S from Johnson & Johnson (for which one vaccination dose is sufficient) can not only be vaccinated in people over 60. The same requirements also apply to medical information.
On May 17, 2021, it was reported that, following a resolution by the federal and state health ministers, vaccination prioritization should be completely lifted from June 7, 2021. This would mean that the previous classification according to age, previous illnesses and occupation would no longer apply in regional vaccination centers, medical practices and company doctors.
Combined vaccinations and booster vaccinations
One way to increase protection against infections with and illnesses from COVID-19 is to have the second vaccination with a vaccine from a different group of active substances than the first vaccination. This procedure is called combination vaccination or cross vaccination and can also be used with a second vaccination in people who were originally vaccinated only once with the Johnson & Johnson vaccine. This procedure should be distinguished from booster vaccinations , in which a third vaccination is carried out at the earliest six months after the second vaccination, and if possible with a further developed variant of the vaccine used for the first vaccination and / or the second vaccination
The Robert Koch Institute (RKI) said on June 25, 2021 formulated his own question: "Could after a completed vaccination series later boosted with another carried COVID-19 vaccine?" That nothing speak against revaccination. In the question itself the premise can be found that the completion of the vaccination series (ie the first and second vaccinations of all persons who are allowed to be vaccinated against COVID-19 and who agree to such a vaccination) have priority over booster vaccinations. In May 2021, the RKI mainly used the term “booster vaccination” to describe the change from people who had been vaccinated with AstraZeneca to Biontech or Moderna for a further vaccination, i.e. in the sense of a combined vaccination.
It is not yet known exactly how long the vaccination protection will last after a double vaccination against COVID-19. The head of the Standing Vaccination Commission, Thomas Mertens , assumed in May 2021 that a booster vaccination would probably be necessary by 2022 at the latest. However, since some studies show that immunity only lasts for around six months after a vaccination, a booster vaccination will be due as early as autumn 2021 for some. Pfizer boss Albert Bourla even believes that a third dose could possibly be necessary earlier than six months after the second vaccination.
In May 2021, the Federal Association of Medical Officials urged politicians to come up with a concept. Ute Teichert , the chairwoman of the Federal Association of Doctors in the Public Health Service, warned in the Rheinische Post : “On the part of politics, I don't hear any suggestions on how this should be organized, it rather seems as if politics were running haphazardly such a situation. ”Other countries such as Great Britain are already preparing for the booster vaccinations.
According to a study published on June 28, 2021 in the magazine " nature ", the vaccines from Biontech and Moderna trigger a long-lasting immune reaction. Booster vaccinations of people who have received this vaccine could therefore be unnecessary for years. In this case, the aforementioned recommendations would be particularly important for people who received vaccines from AstraZeneca and Johnson & Johnson as of December 2020.
Leif Erik Sander , infection immunologist at the Berlin Charité , recommended on June 25, 2021 senior citizens and people with immune deficiencies to be vaccinated a third time in autumn 2021. Such vaccinations are possible in parallel to the annual flu vaccination.
Vaccination in children and adolescents
In April 2021, Biontech / Pfizer applied to the European Medicines Agency for approval of their mRNA vaccine tozinameran for children and adolescents aged 12 to 15 years. On May 26, 2021, Federal Health Minister Jens Spahn declared on vaccination for older children and adolescents that parents, their children and their doctors should make the vaccination decision themselves on the basis of a recommendation from the Standing Vaccination Commission (STIKO). The STIKO does not expect that there will be a general vaccination recommendation for all children. After approval by the European Medicines Agency, children and adolescents over the age of 12 would gradually be offered vaccinations. However , Spahn rejected a vaccination as a prerequisite for attending classroom lessons : "I don't see that we will have a mandatory vaccination for school attendance."
The day before, virologist Alexander Kekulé said that a complete elimination of the coronavirus and its mutants was an illusion. Only a “control state” can be achieved, in which a certain number of new infections is accepted, “and then we don't have to simply vaccinate all children up to the age of zero”. So far one has no empirical values. Vaccination has never ended a pandemic and a new vaccine has been used globally in all age groups: "This is a world experiment since the emergence of Homo sapiens ."
The chairman of the board of directors of the World Medical Association , Frank-Ulrich Montgomery , spoke out against recommending vaccination to minors on May 26, 2021. There is currently too little data to allow statements about the risk in children. However, it is known that the course of the disease in children is significantly less and less dangerous than in adults or the elderly. Alena Buyx , the chairwoman of the German Ethics Council , believes that a vaccination offer for 12 to 15-year-olds is correct, "because they naturally want protection themselves". There are also severe courses and Long Covid Syndrome in adolescents . There are also reasons for group protection so that the school becomes safer.
Biontech / Pfizer provided the first information about the effectiveness of their vaccine before the US manufacturer Moderna in early May 2021. In the age group from 12 to 15 years of age, it had shown an effectiveness of 100 percent in the USA and was well tolerated. The side effects would have corresponded to those in the age group from 16 to 25 years. In parallel, a clinical study on the effectiveness and safety in children between six months and eleven years is ongoing. Reliable data on this should be available by September 2021.
Moderna announced on May 25, 2021 that its mRNA-1273 vaccine had shown 100 percent effectiveness in children and adolescents aged twelve and over in an as yet unpublished clinical study with more than 3,700 participants. None of the subjects developed COVID-19 disease after being fully vaccinated and the vaccine was well tolerated. At the beginning of June, Moderna wanted to submit applications for approval to the Food and Drug Administration and authorities around the world. Moderna is aiming for European approval for children and adolescents aged 12 to 17 years.
On May 24, 2021, following a recommendation by the European Medicines Agency, the European Commission approved vaccinations with the Biontech / Pfizer vaccine for adolescents aged 12 and over. On May 27, 2021, Chancellor Angela Merkel emphasized in a conversation with the country leaders that parents should not be forced to have their child vaccinated. There is no compulsory vaccination.
On June 24, 2021, the RKI announced that the Standing Vaccination Commission recommended vaccinating those children and adolescents aged 12 to 17 who
- have certain previous illnesses mentioned by name,
- live in the vicinity of endangered people who cannot protect themselves or
- are exposed to an increased risk of infection due to their work.
Children from 12 years of age and adolescents who do not meet these conditions could, however, be vaccinated after medical advice and if the child or adolescent or the custodian or guardians individually wish and accept the risk. Markus Knuf, chief physician at the children's clinic at the Worms Clinic , points out that - even if children are much less severely ill with COVID-19 - there is a risk of morbidity . According to a survey in which 178 German centers took part, 1,603 children and adolescents were reported to be hospitalized due to COVID-19 by June 6, 2021. Five percent of them had to receive intensive medical care.
One of the main reasons for restricting the recommendation by the Standing Vaccination Commission was the lack of data on the safety of vaccination in children and adolescents: The only approval so far for the age group from 12 to 17 years, the vaccine from Biontech / Pfizer, is only that Data from a phase II / III study with 2,260 children and adolescents. However, according to Knuf, good immunogenicity , satisfactory tolerability and safety could be documented for a relatively small group, although rare and undesirable effects cannot be predicted with sufficient certainty.
Nadav Davidovitch from Ben Gurion University recommends vaccinating the age group of 12 to 15 year olds only once with Biontech. A study that has not yet been published has shown that a vaccination already leads to 100 percent effectiveness after three weeks. A second vaccination, however, hardly increases protection, but could lead to more side effects.
Vaccination statistics
Federation
The first vaccination took place on December 26, 2020 in Halberstadt . As later became known, the Wittenberg district administrator Jürgen Dannenberg was vaccinated on the same day after doses were left over from a test run for employees of a vaccination center.
Nationwide, at least 44,886,784 people have now received the first vaccination (as of June 29, 2021). This corresponds to 53.97 percent of the German population. On January 14, 2021, the first 115 people received their second dose of vaccine. A total of 29,803,258 second vaccinations (complete vaccination rate: 35.84 percent) have taken place since then.
→ For a comparison with other countries, see SARS-CoV-2 vaccine # vaccination statistics .
The Robert Koch Institute (RKI) has been publishing vaccination statistics on working days since December 28, 2020 .
Number of vaccinations
The following diagram shows the development of the number of people who received the first and second vaccination:
|
|
||||||
| As of June 29, 2021 1 | ||||||
Vaccinations per day
|
|
||||||
| Status: June 29, 2021 (Source: RKI vaccination dashboard) | ||||||
Federal states
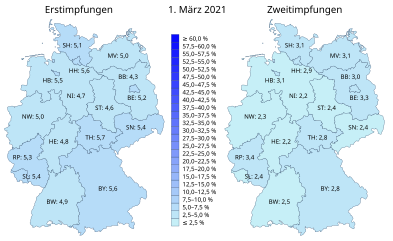
| country | Vaccinated people | Share in the total population | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| first vaccination | complete vaccination | first vaccination | complete vaccination | |||
|
|
5,917,320 | 3,846,748 | 53.31% | 34.65% | ||
|
|
6,677,770 | 4,619,310 | 50.88% | 35.20% | ||
|
|
1,975,842 | 1,238,574 | 53.85% | 33.75% | ||
|
|
1,300,620 | 818.157 | 51.57% | 32.44% | ||
|
|
419,521 | 241,653 | 61.59% | 35.47% | ||
|
|
945.612 | 632,437 | 49.79% | 33.30% | ||
|
|
3,326,605 | 2,114,978 | 52.90% | 33.63% | ||
|
|
870,663 | 597.105 | 54.14% | 37.13% | ||
|
|
4,376,081 | 2,757,010 | 54.74% | 34.49% | ||
|
|
10,026,816 | 6,770,093 | 55.87% | 37.72% | ||
|
|
2,226,753 | 1,384,041 | 54.39% | 33.81% | ||
|
|
562.714 | 412,361 | 57.02% | 41.78% | ||
|
|
1,937,096 | 1,398,970 | 47.57% | 34.36% | ||
|
|
1,121,727 | 743.050 | 51.11% | 33.86% | ||
|
|
1,670,991 | 1,040,156 | 57.55% | 35.82% | ||
|
|
1,090,117 | 700.251 | 51.10% | 32.82% | ||
| Bundeswehr / Federal Police | 162,376 | 88,444 | ||||
| 44,608,624 | 29,403,338 | 53.64% | 35.35% | |||
| Total contaminated cans | 74,011,962 | |||||
| As of June 28, 2021 1 | ||||||
- course
Status of the COVID-19 vaccinations over time:
Procurement and availability of vaccines
Orders
The European Commission agreed with the pharmaceutical companies Biontech and Pfizer to purchase 200 to 300 million single doses of their RNA vaccine tozinameran . If no vaccine doses were lost and each person to be vaccinated received two single doses, this would cover vaccination for up to a third of the EU population. Germany is to receive 38 million vaccine doses from the contingent ordered. In total, by November 2020 the EU Commission will have up to 405 million cans from the Tübingen-based manufacturer Curevac , 400 million each from AstraZeneca and Johnson & Johnson , up to 300 million each from Biontech / Pfizer and Sanofi / GlaxoSmithKline and 160 million Ordered cans from Moderna . At this point in time, the vaccines were still pending approval.
Warehousing
The Standing Vaccination Commission (STIKO), the Federal Ministry of Health and the federal states agreed in December 2020 to initially only vaccinate half of the doses delivered and to reserve the other half for the second vaccination. In the event of a calculable increase in quantity, the reserved quantities could also have been used as the first doses. According to North Rhine-Westphalian information, leading federal states in the vaccination statistics initially vaccinated up to 70 percent, but not all second doses. Mecklenburg-Western Pomerania, Rhineland-Palatinate and Schleswig-Holstein put back fewer doses than the other federal states in January 2021. Bavaria announced in January 2021 that it would no longer keep the doses for the second vaccination due to more predictable vaccine deliveries.
Deliveries
planning
According to the Federal Ministry of Health dated January 4, 2021 - subject to pending approvals - the delivery of 20.5 million vaccine doses for the first quarter of 2021 was agreed with four manufacturers. 69.5 million cans from five manufacturers are to follow in the second quarter of 2021. 127.0 million cans are to be delivered in the third quarter of 2021 and 97.5 million in the fourth quarter of 2021. 45.0 million cans are planned for the first quarter of 2022. A total of 361.1 million cans should be available.
| Biontech / Pfizer |
Moderna | AstraZeneca | Curevac | Johnson & Johnson |
Sanofi / GSK |
to hum | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 4th quarter 2020 | 1.3 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1.3 |
| 1st quarter 2021 | 9 | 1.8 * | 6 * | 4 * | 0 | 0 | 20.8 |
| 2nd quarter 2021 | 25th | 6.5 * | 17 * | 11 * | 10 * | 0 | 69.5 |
| 3rd quarter 2021 | 40 | 17 * | 33 * | 14 * | 23 * | 0 | 127.0 |
| 4th quarter 2021 | 25th | 23.5 * | 0 | 17 * | 4 * | 28 * | 97.5 |
| 1st quarter 2022 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 17 * | 0 | 28 * | 45.0 |
| to hum | 100.3 | 48.8 * | 56 * | 63 * | 37 * | 56 * | 361.1 |
| * No approval in the EU at the time of installation | |||||||
| Biontech / Pfizer |
Moderna | AstraZeneca | Curevac | Johnson & Johnson |
Sanofi / GSK |
to hum | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 4th quarter 2020 | 1.3 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1.3 |
| 1st quarter 2021 | 10.3 | 1.8 | 5.6 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 17.7 |
| 2nd quarter 2021 | 31.5 + 8.7 |
6.4 | 16.9 | 3.5 * | 10.1 * | 0 | 68.4 + 8.7 |
| 3rd quarter 2021 | 17.6 + 17.1 |
17.6 + at least 9.1 |
33.8 | 9.4 * | 22 * | 0 | 100.4 + at least 26.7 |
| 4th quarter 2021 | 2.7 + 10.8 |
24.6 + 18.3 |
0 | 11.7 * | 4.6 * | at least 27.5 * | at least 71.1 + 29.1 |
| to hum | 63.4 + 36.6 |
50.4 + at least 27.4 |
56.3 | 24.6 * | 36.7 * | at least 27.5 * | at least 258.9 + at least 64 |
|
* No approval in the EU at the time of listing in italics: from an additional contract, "Conclusion of contract by EU in final implementation" |
|||||||
| Biontech / Pfizer |
Moderna | AstraZeneca | Curevac | Johnson & Johnson |
Sanofi / GSK |
to hum | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 4th quarter 2020 | 1.3 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1.3 |
| 1st quarter 2021 | 10.7 | 1.8 | 5.6 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 18.1 |
| 2nd quarter 2021 | 40.2 | 6.4 | 16.9 | 3.5 * | 10.2 * | 0 | 77.2 |
| 3rd quarter 2021 | 34.7 | 26.7 | 33.8 | 9.4 * | 22 * | 0 | 126.6 |
| 4th quarter 2021 | 13.5 | 42.9 | 0 | 11.7 * | 4.6 * | 27.5 * | 100.2 |
| to hum | 100.4 | 77.8 | 56.3 | 24.6 * | 36.8 * | 27.5 * | 323.4 |
| * No approval in the EU at the time of installation | |||||||
| Biontech / Pfizer |
Moderna | AstraZeneca | Curevac | Johnson & Johnson |
Sanofi / GSK |
to hum | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Delivered 4th quarter 2020 | 1.33 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1.33 |
| Delivered in the 1st quarter of 2021 | 11.03 | 1.76 | 5.58 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 18.37 |
| 2nd quarter planned for 2021 | 50.3 | 6.4 | 12.4 to 15.4 | 1.4 * | 10.1 | 0 | 80.6 to 83.6 |
| 3rd quarter planned for 2021 | 34.7 | 26.8 | 35.3 to 38.3 | 10.5 * | 22nd | 0 | 129.3 to 132.3 |
| 4th quarter planned for 2021 | 13.5 | 42 | 0 | 12.6 * | 4.6 | 27.5 * | 101.2 |
| to hum | 110.9 | 78 | 56.3 | 24.5 * | 36.7 | 27.5 * | 333.9 |
| * No approval in the EU at the time of installation | |||||||
For the period up to the end of the first quarter of 2021, a total of 12 million doses from Biontech / Pfizer and Moderna were expected at the end of January, excluding promised production increases. According to an updated list of a federal-state conversation on February 1, 2021, delivery of at least 258.9 million vaccine doses is expected in 2021. In addition to the planned figures for the quarters, no figures were initially available for individual months.
In April 2021, 15 million doses should be made available.
Curevac was hoping for approval of its vaccine within the next two months in April 2021. According to a report dated May 26, 2021, approval of the vaccine has been delayed because phase 2b / 3 has not yet provided enough data. On May 28, 2021, Curevac reported that there were no safety concerns after an initial interim analysis and that the HERALD study would continue to collect enough data to conduct a statistically significant effectiveness analysis , especially as the study was affected by the spread of multiple Covid-19 -Virus strains are coined.
For the full year 2021, around 324 million doses are expected (100.7 million from Biontech / Pfizer, at least 78 million from Moderna, 56.3 million from AstraZeneca, 36.7 million from Johnson & Johnson and - in each case subject to Approval - 24.5 million from Curevac and 27.5 million from Sanofi / GSK).
It also run negotiations on the purchase of the Russian vaccine Sputnik V . According to the Federal Ministry of Health, this would be possible if the vaccine receives European approval and can definitely be delivered in the second or third quarter of 2021. The states of Bavaria and Mecklenburg-Western Pomerania signed preliminary contracts for the delivery of 2.5 million and 1 million vaccine doses respectively in April 2021. In the state of Berlin this failed due to the resistance of Bündnis 90 / Die Grünen . Instead, Senator for Economic Affairs Ramona Pop called for the emergency approval of Curevac's vaccine at the end of April 2021. At the end of May 2021, Bavaria's Prime Minister Markus Söder urged a swift decision on the approval of the Sputnik V vaccine.
The use of the vaccine Ad26.COV2.S from Johnson & Johnson was delayed in mid-April 2021 due to observed sinus vein thrombosis .
Forecasts
The delivery forecast of the Federal Ministry of Health dated May 12, 2021 (based on an update due to the delay in CVnCoV ) expects the following vaccine doses by the end of the 2nd quarter or by the end of 2021:
- BioNTech / Pfizer: 50.2 million / 119 million
- Moderna: 6.4 million / at least 78 million
- AstraZeneca: 12.4-15.4 million / 56.3 million
- Johnson & Johnson: 10.1 million / 36.7 million (doubtful, see below)
The forecast points out that there are uncertainties and that deviations are not unusual.
On June 12, 2021, it was announced that Johnson & Johnson would have to destroy 60 million vaccine doses due to quality defects, as the Food and Drug Administration (FDA) has not given clearance. Germany in particular has planned many vaccination doses from the manufacturer. It is feared that up to 9 million doses could be missing by July 2021. Since the Johnson & Johnson vaccine only requires one dose, this would correspond to 18 million vaccine doses from the other manufacturers.
On June 28, 2021, the FAZ reported that the vaccine from the US manufacturer Moderna can be delivered more quickly because the vaccination campaign in the USA is stalling. Every person willing to vaccinate can thus be guaranteed the first vaccination by the end of July 2021, maybe even earlier. The EU has secured two 80 million doses of the Moderna vaccine. Federal Minister of Health Jens Spahn has confirmed the significant increase in delivery at Moderna (almost doubling the previous forecast to 1.33 million vaccination doses per week for the beginning of July 2021). In August 2021, Moderna wants to deliver around 2.6 million vaccine doses per week and almost 3 million in the following month. In total, Germany will receive 5.3 million vaccine doses from the two overlapping Moderna contracts in July 2021, then 10.3 million in August and 14.5 million in September. Biontech is expected to deliver 3.2 million cans a week in July 2021. AstraZeneca plans to deliver 5 million vaccine doses in the first week of July and Johnson & Johnson another million.
Actual deliveries
Delivery problems were already reported by Biontech / Pfizer, Moderna and AstraZeneca in mid-January 2021.
By the end of calendar week 25 on June 27, 2021, 82,024,303 doses of vaccine had been delivered. Of this, 57,619,463 cans are from Biontech / Pfizer, 13,869,863 from AstraZeneca, 7,641,280 from Moderna and 2,893,697 from Johnson & Johnson.
| Status: June 27, 2021 1 | ||||||
| country | Delivered cans | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Biontech / Pfizer |
Moderna | AstraZeneca | Johnson & Johnson | total | Proportion of mRNA |
||
|
|
5,100,669 | 722,400 | 1,258,600 | 129,514 | 7,211,183 | 80.75% | |
|
|
6,146,524 | 735,600 | 1,713,108 | 149,829 | 8,745,061 | 78.70% | |
|
|
1,702,854 | 264,000 | 436.334 | 42,973 | 2,446,161 | 80.41% | |
|
|
1,137,566 | 145,200 | 297.945 | 28,338 | 1,609,049 | 79.72% | |
|
|
312.935 | 32,400 | 98,467 | 11,613 | 455.415 | 75.83% | |
|
|
844.052 | 127,200 | 193.137 | 21,568 | 1,185,957 | 81.90% | |
|
|
2,863,986 | 326,400 | 826,408 | 71,938 | 4,088,732 | 78.03% | |
|
|
793,577 | 103,200 | 192.069 | 20,018 | 1,108,864 | 80.87% | |
|
|
3,647,256 | 399,600 | 1,111,416 | 92,587 | 5,250,859 | 77.07% | |
|
|
8,384,336 | 1,148,400 | 2,221,085 | 205.072 | 11,958,893 | 79.71% | |
|
|
1,888,815 | 270,000 | 457.267 | 48.123 | 2,664,205 | 81.03% | |
|
|
559,698 | 63,600 | 106.039 | 11,194 | 740.531 | 84.17% | |
|
|
1,949,503 | 274,800 | 411.478 | 47,980 | 2,683,761 | 82.88% | |
|
|
1,030,354 | 152,400 | 228.917 | 26,219 | 1,437,890 | 82.26% | |
|
|
1,378,152 | 188,400 | 348.384 | 33,212 | 1,948,148 | 80.41% | |
|
|
1,021,234 | 141,600 | 230,646 | 23,421 | 1,416,901 | 82.07% | |
|
|
200,070 | 230,500 | 68,050 | 48,600 | 547.220 | 78.68% | |
| As of May 31, 2021 1 | |||||||
Causes of the vaccine shortage in the 1st half of 2021
Contrary to what was expected in spring 2020, three vaccine developments (Biontech / Pfizer, Moderna and AstraZeneca), including their technical production, were successfully completed by the end of 2020 and used in the EU at the beginning of 2021, and others a few months later. However, the great success in research and development at the level of politics and business policy was partly clouded. The criticism of the lack of vaccine focuses on the fact that it could have been produced more quickly.
Order deficits in the EU
Karl Lauterbach , epidemiologist and health expert of the SPD , feared as early as August 2020 that even if an effective vaccine was available at the beginning of 2021, vaccination of the entire population of Germany could drag on until 2022. Unlike US-American politicians for the USA, German politicians would only have secured a rather small selection of vaccines and only a rather modest delivery volume through contracts. Lauterbach's fear that by mid-2021 it would only be possible to vaccinate 20 percent of the population in Germany turned out to be too pessimistic.
The main negotiating partners of the vaccine providers were not the nation states within the EU, but the EU itself. In November 2020, Biontech / Pfizer offered the EU 500 million doses of their mRNA vaccine BNT162b2 . However, the EU initially only wanted to lose 200 million - with an option for a further 100 million - although the phase 3 study already showed a high level of effectiveness. With CureVac, on the other hand, the EU ordered up to 405 million doses (180 million optional, 225 million fixed) of the mRNA vaccine CVnCoV in November 2020, i.e. before the start of the phase 3 study .
At the beginning of January 2021, Frauke Zipp , a member of the Leopoldina , criticized the federal government and accused those in charge of failing to order vaccines: "If you were already promising companies like Biontech, Curevac, Moderna and AstraZeneca for 60 percent of the time in the summer If the population had ordered, it would have cost around ten billion euros. ”This is nothing compared to the sums that have to be spent to support the economy.
Due to the lack of vaccines at the time, the Federal Ministry of Health considered at the beginning of January 2021 to exceed the maximum interval of 42 days for the vaccine from Biontech / Pfizer. Such a stretch has also been considered in the UK . However, this was associated with the risk that the effectiveness of the overall vaccination would suffer and that people who had already been vaccinated could also become infected. In addition, it was feared that the coronavirus could adapt to the vaccine, see section SARS-CoV-2 vaccine # negligence in multi-dose vaccines .
At the beginning of 2021 there was also no alternative to the RNA vaccines. Biontech promised to work with the EU to further expand production capacities and provide additional doses of vaccine.
Contracts with vaccine manufacturers
AstraZeneca's vaccine received EU approval at the end of January 2021. However, the first deliveries fell well short of expectations. After AstraZeneca announced in January 2021 that it would deliver fewer vaccines to the EU due to production difficulties, there was a dispute with the EU Commission. This insisted that there were binding orders, while AstraZeneca argued that only “Best Reasonable Efforts” had to be undertaken. In addition, the EU ordered three months later than the UK. On January 29, 2021, the contract was published with redactions, later without such. The treaty with the UK was signed a day later and is largely the same as that with the EU, including the phrase "Best Reasonable Efforts".
Around the same time, the EU Commission published the contract with Curevac , also with blackouts . The Wirtschaftswoche wrote on 23 January 2021 that Curevac to confess to the liability that Pfizer did not want to take over. The negotiations with Biontech / Pfizer were delayed because of the liability issue .
In February 2021, the EU Commission published the third of six contracts in a partially blackened version, which was concluded with Sanofi / GlaxoSmithKline .
After AstraZeneca failed to meet its delivery commitments, the European Commission filed a lawsuit against the company at the end of April 2021. According to reports from June 18, 2021, a Brussels court issued an interim judgment on the same day in an urgent procedure, according to which the manufacturer, which promised 300 million vaccine doses, was obliged to deliver 50 million vaccine doses to the EU in stages by September 2021.
Since January 30, 2021, vaccine exports from the European Union have to be reported. This is intended to provide more clarity about vaccine production in the EU and exports. Exports to developing countries and partner countries such as Switzerland, Israel or Ukraine are exempt from this rule, but not to the United Kingdom. Canada, which (as of February 2021) receives all vaccines from Biontech / Pfizer and Moderna from Europe, has been assured by the EU Commission that the deliveries will not be affected.
Delays also occurred with the vaccine from Johnson & Johnson due to the de facto US export ban. In March 2021, the USA refused the request of the EU Commission to give Europe some of the 30 million vaccine doses from AstraZeneca , which could not be used in the USA due to the lack of approval. The United States received full shipments despite a 15 million doses outage of Johnson & Johnson's vaccine production at an American plant in April 2021, while shipments for the EU were cut.
In addition to the vaccines themselves, basic materials for vaccine production are also affected by the US export ban. The legal basis for this is the Defense Production Act , which both Donald Trump and Joe Biden activated to impose strict export restrictions up to and including an export ban on goods relevant to the crisis. According to the company's board of directors, the manufacturer Curevac is also affected by the lack of raw materials . According to information from government circles, there is no official US export ban. Rather, US production should be pushed first before exporting.
United States Export Restrictions
In the United States , according to Executive Order 13962 of then President Trump, which was continued by his successor Biden, vaccine manufacturers are required to initially deliver the vaccine for supply in the United States. As a result, Pfizer's European production facilities, which have less capacity than the US facilities, must produce the vaccine for the rest of the world (including Canada). In early February 2021, Chancellor Angela Merkel criticized the US exporting “next to nothing” of the Pfizer vaccine.
Measures to remedy the shortage of vaccines
More doses per ampoule
On December 27, 2020, the Federal Ministry of Health recommended state authorities and vaccination centers to draw six instead of the previous five doses from a Biontech / Pfizer vaccination ampoule under suitable conditions. Doctors had previously been able to take more doses at their own discretion. The European Medicines Agency granted the relevant approval on January 8, 2021.
Demand for crisis production
In order to accelerate the vaccine supply, some German politicians, including Christian Lindner , called for a "crisis production" in December 2020 and January 2021 . The proposals ranged from free-market incentives for licensing to the issuing of compulsory licenses .
Revocation of vaccination patents
US President Biden decided in May 2021 to revoke the patents for COVID-19 vaccines. This was advocated by Robert Habeck , while Chancellor Angela Merkel and Federal Health Minister Jens Spahn are skeptical about it and also see it as a possible risk to the safety of vaccine production. The know-how about the development of new vaccines is insufficient. In order to be able to bring them to market quickly, a corresponding infrastructure and logistics as well as a high capital base are required. Effective protection of intellectual property is also important. The Chancellor suggested that the US contribute to increased production of vaccines instead of repealing patents.
Vaccine Safety and Risk Factors
The vaccines that have been used so far have previously been tested in phase III studies on tens of thousands of patients without any serious side effects . After a scientific review of the study data, they were approved by the European Medicines Agency and the Standing Vaccination Commission (STIKO) at the Robert Koch Institute .
The Paul Ehrlich Institute (PEI) is responsible for monitoring vaccine safety in Germany. In order to identify rare side effects, the tolerability of the vaccines is subject to ongoing testing. The institute also developed the SafeVac 2.0 smartphone app. Vaccinated persons can thus provide digital information on how they tolerated the vaccination. According to a safety report by the PEI, a total of 11,915 suspected side effects were recorded by February 26, 2021 after 5.9 million vaccinations, of which 2,003 were classified as serious. Suspected cases are all cases in which changes in health are found after the vaccination, regardless of the cause. The most commonly observed side effects are headache and vaccination site pain. The suspected cases of severe reactions include 330 deaths of people with a median age of 85 years who, as far as can be determined, either suffered from COVID-19 or multiple previous illnesses or died from or with COVID-19 before full vaccination protection was established. According to calculations by the PEI, the reported deaths are no more frequent than the number of deaths that can be expected even without vaccination, given the age of the vaccinated.
The Robert Koch Institute sees the hierarchy of risk factors that can lead to a severe course of COVID-19 as a simple, uncomplicated and effective basis for the vaccination priority in outpatient medical care. It has compiled these in its Epidemiological Bulletin 19/2021 after evaluating around 94,000 cases of illness. Accordingly, the five largest risk factors for a severe course are haemato-oncological diseases (31.5%), metastatic solid tumor diseases with therapy (28.2%), dementia (24.3%), metastatic solid tumor diseases without therapy (23.3%) and heart failure (21.7%).
According to a report dated June 14, 2021, in recent weeks the PEI has received increasing reports of suspected myocarditis or perimyocarditis in the context of a vaccination. Since the start of vaccinations at the end of December 2020, there have been 92 cases according to the data as of May 31, 2021. Of these, 69 cases concern Biontech / Pfizer, seven Moderna and 14 AstraZeneca cases, but so far only two unconfirmed Johnson & Johnson cases. 61 people developed isolated myocarditis that only affects the heart muscle , five developed pericarditis and 24 people developed a mixed form with perimyocarditis. 52 cases in young men aged 16 and over were compared to 38 cases in women affected.
Recommendations on vaccine use
The Standing Vaccination Commission pointed out at the beginning of January 2021 that the vaccines from Biontech / Pfizer and Moderna are considered to be equivalent in terms of effectiveness and safety, but that it is not possible to give a person the vaccine of the other manufacturer for the second vaccination, even if it is based on the same principle of action. So far there is no data on this.
Controversy
Handling the AstraZeneca vaccine
In mid-February 2021, 54 percent of the 200 registered people did not show up for a special vaccination for medical staff in Saarland . At the time, there were reservations about the AstraZeneca vaccine due to lack of data, lower efficacy and more common side effects.
Science journalist Mai Thi Nguyen-Kim described the criticism of AstraZeneca's vaccine as a particularly worrying example of the unclean and misleading presentation of scientific results in the media: "Here, the media promote reservations that harm health and society." Virologist Christian Drosten explained at AZD1222 In contrast to other vaccines, new research results would be published particularly transparently and quickly. This leads to the fact that negative partial results are continuously discussed in public, which leads to a falsified perception. If you look at the whole picture rather than just individual results, the vaccine is highly effective and safe.
In view of the large number of unused doses, Bavaria's Prime Minister Markus Söder pleaded at the end of February 2021 for the AstraZeneca vaccine to be released for everyone on a voluntary basis.
On March 3, 2021, the Standing Vaccination Commission recommended that AstraZeneca's vaccine be used in all age groups. The interval between the first and second vaccination should be 12 weeks if possible. The recommendation is based on an analysis and evaluation of new study data.
In connection with a vaccination with AZD1222, sinus vein thrombosis and thrombocytopenia were observed in seven vaccinated persons in Germany up to March 15, 2021 . Until it was clarified whether there could be a connection with the vaccinations, several European countries, including Germany on March 16, 2021, temporarily suspended the vaccinations. By April 29, 2021, around 60 cases of sinus and cerebral vein thrombosis had occurred in Germany after vaccination with the AstraZeneca vaccine. Seven women and six men died.
After the European Medicines Agency declared on March 18, 2021 that the benefits of the vaccine outweigh the risks, the vaccinations were resumed, supplemented by an additional note.
On March 30, 2021, the federal and state health ministers decided that in future vaccinations with the AstraZeneca vaccine should only be given to people aged 60 and over. On April 1, 2021, the Standing Vaccination Commission recommended that people under the age of 60 who had already received their first AstraZeneca vaccination should be given an RNA vaccine twelve weeks later. However, the use of the AstraZeneca vaccine below this age threshold remains possible, provided a vaccine candidate is aware of the possible risks, with an individual risk analysis and after careful medical advice.
On April 21, 2021 it was reported that due to the concern of many doctors that they would have to assume liability for any vaccine damage , the recommendation of the Standing Vaccination Committee was changed. After this, AstraZeneca may give the vaccine to those under 60 after medical advice. The change corresponds to a request of the National Association of Statutory Health Insurance Physicians and is intended to create legal certainty . The new information sheet was published on April 23, 2021. At the beginning of May 2021, the Saarland Ministry of Health announced that the state would accept liability for an AstraZeneca vaccination even for people under the age of 60 if the vaccination was properly carried out after prior medical advice. According to the "Draft of a Second Act to Change the Infection Protection Act and other laws" of May 4, 2021, the Federal Infection Protection Act is to be amended to the effect that “the right to care in the event of vaccination damage also in the event of health damage caused by vaccinations against the coronavirus SARS-CoV- 2 applies ". According to the National Association of Statutory Health Insurance Physicians (KBV), this would mean that doctors no longer bear any liability risk when vaccinating with the vaccine from AstraZeneca, because the vaccinated would have a claim to health care against the state.
In order to increase the incentive to vaccinate with AZD1222, the federal and state governments made it possible in May 2021 to shorten the vaccination interval at AstraZeneca to four weeks. This was often criticized because of the reduced effectiveness of the vaccination - according to previous studies. Researchers at the University of Greifswald who discovered the mechanism of vaccine-induced thrombocytopenia (VITT) see a certain risk in this. Because there is a possibility that after the first vaccination, people will develop special PF4 antibodies unnoticed without them having activated platelets during the first vaccination. If the second vaccination was given too early, the affected person might still have such PF4 antibodies in their bloodstream.
Investigation of the composition of AZD1222
At the end of May 2021, researchers at Ulm University Medical Center published an analysis of the composition of batches ABV4678, ABV5811 and ABV7764 of the AZD1222 vaccine from AstraZeneca . In addition to proteins from the vector virus that makes up the vaccine, the researchers also found quantities of human proteins and regulatory viral proteins that are not part of the (actual) vaccine. In the case of batch ABV5811, for example, about two thirds of the amount of protein consisted of impurities, and about half of the other two batches. The heat shock proteins found , which could intensify inflammatory reactions and may also be associated with autoimmune reactions, are particularly worrying. The researchers called for the purity of the vaccine to be improved by revising the manufacturing process and quality control. The criticism was rejected from circles of the pharmaceutical company and declared that they work to the highest possible standards.
Curevac vaccine
On June 7, 2021, Federal Health Minister Jens Spahn stated that the European Medicines Agency (EMA) did not expect the approval of the vaccine CVnCoV from Curevac before August 2021. Already from the phase 1 study, which was published on November 9, 2020 on medRxiv without peer review, it was already clear that the vaccine already had such strong side effects at a dose of 12 µg that the dose no longer exceeded this can be increased. The head of the vaccination study, Peter Kremsner, confirmed this on June 17, 2021: “Twelve micrograms was already quite intolerable. For me this is the number one explanation, which causes the efficacy data, which are now just below 50 percent. ”At the same time, the antibody response was only in the range as with a survived natural infection and thus by a factor of 2 to 5 lower than with mRNA-1273 from Moderna and Tozinameran from Biontech.
On June 16, 2021, Curevac announced in a mandatory stock exchange announcement that the interim analysis of the phase 2b / 3 study had not met the specified goals. There is only a "preliminary effectiveness of 47 percent against Covid 19 disease of any severity".
Distance between first and second vaccination
While the German Society for Immunology and the United Kingdom are aiming to postpone second vaccinations if necessary, the US FDA rejected this, citing possible resistance . The European Medicines Agency also insisted on observing the maximum interval of 42 days between the two doses necessary for complete vaccination protection. The Standing Vaccination Commission also made it clear at the beginning of January 2021 that it did not support a deviation in the vaccination interval. In doing so, she primarily considered the question of when it is certain, how long the vaccination protection will last and what consequences mutations of the coronavirus could be associated with. She recommended that both vaccinations should be carried out with a minimum interval of 21/28 and 42 days, based on approval studies. By mid-March 2021, almost all federal states had switched to the maximum vaccination interval of six weeks ( Biontech / Pfizer and Moderna ) or twelve weeks ( AstraZeneca ).
Karl Lauterbach advocated extending the vaccination interval to 12 weeks for the vaccines from Biontech and Moderna in order to vaccinate more people at least once. Even with the first vaccination, severe courses could be avoided and the number of super vectors could be reduced significantly. The German Society for Immunology also repeated its appeal to extend the vaccination interval. The chairman of the Standing Vaccination Commission, Thomas Mertens , however, was not convinced due to insufficient data.
Against the virus variant B.1.617 .2, which prevailed over the other variants in India in May 2021, a single vaccination is less effective than variant B.1.1.7, which was still predominant in Europe at the same time . This led the UK and Northern Ireland to shorten the vaccination interval for those over 50 from 12 weeks to 8 weeks. Above all, the Chancellor's promise that it would be possible to offer vaccinations to all those willing to vaccinate in Germany by the end of the summer was viewed critically. Early second vaccinations could prove to be a "luxury" in this situation.
Vaccine choice after initial vaccination with AstraZeneca
The heterologous vaccination (so-called cross vaccination) of AstraZeneca and Biontech has proven to be safe and very effective in terms of the amount of antibodies, according to a study by the Berlin Charité , sometimes even more effective than twice Biontech and significantly more effective than twice AstraZeneca. The study CombivaxS from Spain with 663 subjects, also showed that by the second vaccination with one dose Tozinameran increased much more of BioNTech the amount of antibody is used as a second dose of AZD1222 from AstraZeneca and the antibody response, the level of homologous vaccination with Tozinameran or mRNA in 1273 reached . If the vaccination interval is only 28 days, however, cross- vaccination leads to stronger vaccination reactions .
Since April 1, 2021, the Standing Vaccination Commission has recommended an mRNA vaccine as a second vaccination for people under 60 years of age because of the risk of sinus thrombosis. Those vaccinated for the first time with AstraZeneca can decide for themselves whether they will be vaccinated with AstraZeneca or an mRNA vaccine for the second vaccination. According to the President of the European Medicines Agency's team of vaccines experts, Marco Cavaleri, there have been no sinus thromboses in Great Britain with a second vaccination. However, the database is currently (as of mid-June 2021) still low. On the other hand, he explained that it would have been better not to use AstraZeneca at all, and also pointed out that the effectiveness is better after the first dose, but worse after the second dose, especially in its effectiveness against the beta variant and those in the UK increasing delta variant .
On July 1, 2021, the Standing Vaccination Commission changed its recommendation for those vaccinated for the first time with the AstraZeneca vaccine. Regardless of age, all people who have been vaccinated once should now receive a second vaccination with an mRNA vaccine. The interval between the first and second vaccination no longer needs to be 9 to 12 weeks, but only "at least four weeks".
Reaction to "escape mutations"
As early as February 2021, it was feared that mutations in the SARS-CoV-2 spike gene could reduce the effectiveness of the vaccines against new variants, that reinfections would become more likely and that there would be a third corona wave. The federal government designated the Czech Republic and the Austrian state of Tyrol as virus mutation areas and issued entry restrictions.
Compulsory vaccination: legal situation and political intentions
Vaccinations against SARS-CoV-2 are considered voluntary in Germany. Vaccination opponents and vaccination skeptics who decide against vaccination cannot be forced to vaccinate according to the current legal situation. Whether compulsory vaccination could still be ordered, possibly on the basis of the Infection Protection Act or its modification ( Third Civil Protection Act ), which came into force on November 19, 2020, has not yet been conclusively clarified. However, the European Court of Human Rights ruled on April 8, 2021 that it may be permissible for a state in Europe to order an obligation to vaccinate against certain diseases. A fine in the event that a person subject to vaccination does not fulfill his duty would also be lawful in such cases.
The Infection Protection Act already provides for a restriction of the basic right to physical integrity in the event of compulsory vaccination . In June 2020, individual scientists called for compulsory vaccination to be considered, as otherwise not enough people could be vaccinated to build up herd immunity due to the relatively low willingness to vaccinate at the time . The Bavarian Prime Minister Markus Söder spoke out in favor of compulsory vaccination for nursing staff as early as the beginning of 2021, especially if the willingness to vaccinate among them does not increase.
The German Ethics Council , through its chairman Alena Buyx , made it clear on January 12, 2021 that it rejects a general mandatory vaccination, but pointed out that under certain circumstances an "area-related mandatory vaccination" should be considered. It is about people who cannot be protected in any other way than that the people who care for them are vaccinated themselves. Regarding the Bavarian Prime Minister's request to increase the corresponding vaccination quota, Buyx said that it should be carefully checked whether a situation arises in which there is actually no other option than such a mandatory vaccination. Federal Minister of Health Jens Spahn announced again in mid-January 2021 that there would be no compulsory vaccination. Rather, the federal government relies on arguments, information and trust.
An exception has always been soldiers who have to tolerate vaccination against communicable diseases. The Ministry of Defense wants to check whether this can also be considered for a vaccination against SARS-CoV-2.
Further legal and socio-psychological aspects
Decision on vaccinations for children and adolescents
For all vaccinations of children and adolescents, the wishes of the parents of the child or adolescent to be vaccinated must be observed. Young people aged 16 and over can decide for themselves whether they want to be vaccinated. If the parents cannot agree on whether their child should be vaccinated, the recommendations of the Standing Vaccination Commission apply according to a ruling by the Frankfurt am Main Higher Regional Court of March 8, 2021 (AZ 6 UF3 / 21).
Freedom of choice in the vaccine
On January 11, 2021, it was said that there would be no nationwide choice between vaccines from Biontech / Pfizer and Moderna. In Berlin, on the other hand, there was freedom of choice for prioritized people under 65 years of age in winter 2021. Since thousands of doses of the AstraZeneca vaccine were left behind in the Tegel vaccination center, Health Senator Dilek Kalayci admitted on February 17, 2021, “that freedom of choice may have been a mistake”. Berlin's Governing Mayor Michael Müller made it clear that someone who rejects the AstraZeneca vaccine “has for the time being wasted his chance”. This is then offered to others.
On April 16, 2021, Oliver Funken, chairman of the General Practitioner Association of North Rhine-Westphalia, stated that around 30 percent of patients in North Rhine-Westphalian medical practices rejected the AstraZeneca vaccine. At this point in time, epidemiologists warned that withdrawing from a vaccination at short notice or missing the vaccination appointment without notice would reduce the rate of vaccination and deprive younger people of the opportunity to vaccinate early. The probability of being able to achieve “ herd immunity ” is also reduced . Doctors started promoting vaccinations with AstraZeneca. Some demanded that those who refuse AstraZeneca be placed at the bottom of the waiting list.
Restrictions on freedom and their partial lifting
Initially, the question of whether restrictions of freedom that affect all citizens, such as the ban on going to restaurants and events, should be refrained from was also controversial. The return of these basic rights to those who have been fully vaccinated and recovered has often been referred to as “privileges”.
The general practitioner and specialist lawyer for medical law Alexander Ehlers and other lawyers pleaded for people who have been completely vaccinated and recovered not to be further restricted in their constitutional freedoms , since the reason for their limitation, the risk of infection in contact with other people, no longer exists for them. The Bochum lawyer Andrea Kießling, who researches public health law, said that if basic rights are returned to those who have been vaccinated and recovered, enforcement problems could arise, for example with the control and enforcement of the mask requirement. But that does not change the legal assessment that a restriction of the fundamental rights of non- disruptors would be disproportionate . For Steffen Augsberg , Professor of Public Law at the University of Göttingen , the term “privileges” is wrong. From a legal point of view, it is a question of the restitution of fundamental freedoms, ie the "normal state". But Augsberg also emphasized that this only applies if it is certain that completely vaccinated people are no longer contagious.
At the beginning of the discussion, the legal situation appeared largely blurred. Federal Foreign Minister Heiko Maas was one of the first politicians in Germany to recommend that people who have been vaccinated be given back their basic rights, for example by allowing them to visit restaurants or events earlier than the rest of the population. Chancellor Angela Merkel thought this discussion was premature. At that time (mid-January 2021) less than two percent of the population had been vaccinated at least once. This particularly affected people in nursing homes.
In an ad hoc statement from February 2021, the German Ethics Council spoke out against ending the restrictions for vaccinated people earlier because it was not yet clear whether they were actually no longer contagious. However, its chairwoman Alena Buyx later made it clear that a withdrawal of fundamental rights could no longer be justified in such a case. The Ethics Council went on to say that once enough people, especially those at risk, had been vaccinated, restrictions would have to be scaled back for all citizens. An early lifting of restrictions for vaccinated persons could, however, be useful in special cases of hardship, for example when visits to nursing homes are banned. The Ethics Council also made it clear that a distinction must be made between government measures and decisions by private companies. The latter would in principle have freedom of contract . As soon as restaurants or theaters are allowed to reopen, for example, they should be able to decide for themselves whether they only serve or let in vaccinated people. This does not result in a “mandatory vaccination through the back door”, especially since it would also be conceivable to offer tests as an alternative. The Ethics Council, on the other hand, was critical of the state allowing earlier opening under such conditions . In addition, from his point of view, there should be no differences when it comes to equal participation in “basic” (basic) social activities.
After the Robert Koch Institute came to the conclusion that those who were fully vaccinated have an even lower risk of passing on the virus than those who tested negative, both groups should be treated equally in the future. People who are either (a) fully vaccinated (two weeks after the 2nd dose), (b) have had COVID-19 within the last six months, or (c) have been diagnosed with COVID-19 more than six months ago and have received at least one dose of vaccine , should no longer be quarantined at home if they have had close contact with an infected person. Furthermore, the obligation to test when traveling could largely be dispensed with and areas in which mandatory tests are planned (e.g. outdoor restaurants, museums) could also be visited without a negative test.
The Infection Protection Act (IfSG) was supplemented by the fourth law for the protection of the population in an epidemic situation of national scope with effect from April 23, 2021. The new version of Section 28c IfSG now contains the power to issue ordinances for special regulations for vaccinated, tested and comparable persons.
Possible reliefs were discussed for the first time at the Prime Minister's Conference on April 26, 2021. On May 4, 2021, the federal government passed the COVID-19 Protective Measures Exceptions Ordinance (SchAusnahmV). The Bundestag approved the ordinance on May 6, 2021, and the Bundesrat on May 7, 2021 . The ordinance was promulgated on May 8, 2021 and came into force on May 9, 2021. It provides that exit and contact restrictions no longer apply to fully vaccinated and convalescent people who are expected to be immunized against the SARS-CoV-2 coronavirus. These groups are now allowed to do the same thing, which is also possible with a negative test under state and federal law ( § 3 and § 7 SchAusnahmV). They are also no longer obliged to be quarantined, unless they are returning travelers from virus variant areas (such as India, South Africa, Brazil, Portugal) or who have come into contact with a virus variant that gives cause for concern Person. For the time being, however, the mask requirement and distance requirements are also maintained for these groups.
Alena Buyx, Chairwoman of the German Ethics Council, also believes it is justifiable not to restrict the freedom of those who have been vaccinated, those who have tested negative or who have been immunized any further than necessary. Waging a mere “envy debate” would not do justice to the social, ethical and legal implications.
Announced and actual vaccination behavior
The first surveys on the willingness of adult residents of Germany to be vaccinated against SARS-CoV-2 were carried out in December 2020. Further surveys took place at the beginning of 2021. However, the question of who will actually not be vaccinated could not yet be conclusively answered in these surveys. In December 2020 there was still no vaccination option. In February 2021, non-prioritized people could not even be put on a waiting list in order to express their willingness to be vaccinated.
Statements about the actual number of people who can be vaccinated without compulsory vaccination are only possible if it is certain
- how many people miss an agreed vaccination appointment. In a survey of health authorities in June 2021, the Tagesspiegel found that there are relatively many “truant vaccinations”, ie people who miss a scheduled vaccination appointment without having to de-register. In a vaccination center in Mecklenburg-Western Pomerania, the rate was even 40 percent. It must be checked in the form of a counter-calculation how many people will make use of the opportunity to spontaneously decide in favor of a vaccination if - after having worked through the waiting lists - they have the opportunity to be vaccinated at short notice;
- how trust develops in scientists and doctors making correct recommendations. The requirement for the “trust” factor set by the COVID-19 Snapshot Monitoring (COSMO) , a project of the University of Erfurt to research the state of mind and the mentality of people in Germany during the COVID-19 pandemic, is: “I have the fullest Trust that the vaccinations against COVID-19 will be safe. ”The rejection of AstraZeneca by many who would actually like to vaccinate shows that this trust can easily be lost. Since survey results on the “trust” aspect always relate to people who have not yet been vaccinated, declining rates for the “trust” factor are not very meaningful;
- whether there will be a decision to include younger children in the vaccination campaign in addition to adolescents and children from the age of twelve. Carsten Watzl, Secretary General of the German Society for Immunology , considers vaccination rates of 85 percent and more to be "difficult to achieve [...] as long as there is no approved vaccine for children under the age of 12 and no general vaccination recommendation for anyone under the age of 18."
According to the COSMO project, willingness to be vaccinated depends on the five factors named "5 C":
- Confidence describes the degree of trust in the effectiveness and safety of vaccinations, the health system and the motives of decision-makers;
- Complacency (risk perception) describes the perception of disease risks and whether vaccinations are considered necessary;
- Constraints (barriers in execution), also: convenience , describes the extent of perceived structural hurdles such as stress, lack of time or effort;
- Calculation records the extent of active search for information and conscious evaluation of the benefits and risks of vaccinations;
- Collective Responsibility .
According to a survey by the opinion research institute YouGov, which shows the status around mid-May 2021, the willingness to vaccinate among citizens over the age of 18 has risen to almost 75 percent. The proportion of undecided fell from 16 to 11 percent. However, this survey took place at a time at which the rejection of the vaccination - due to the rejection of an invitation to a “here and now” vaccination by people directly addressed - could not yet make itself felt.
No need for a second vaccination
A second vaccination is only not necessary for vaccinations with the vector vaccine from Johnson & Johnson . People who have been vaccinated with this vaccine are assigned the status of “fully vaccinated” just two weeks after their single vaccination.
In order to achieve this status in Germany, which in many situations is associated with a (partial) return of basic rights that were restricted during the pandemic, everyone who has been vaccinated with a vaccine other than that of Johnson & Johnson must become one vaccinated a second time. This measure is necessary because a single vaccination does not provide sufficient protection against the SARS-CoV-2 pathogen. However, many (not only) in Germany refrain from attending a second vaccination appointment.
The unannounced non-appearance at an agreed vaccination appointment can lead to serious problems: The planned number of vaccinations on the day in question cannot be kept, the vaccination rate decreases and vaccines that have not been vaccinated can spoil. A system of “vaccination jumpers” (ie people who are immediately available as a substitute if a vaccination center or doctor's office can still be vaccinated before work) can help solve these problems.
Reasons for "skipping the vaccination" may be:
- Forgetfulness;
- Failure to communicate that the person concerned has already taken another vaccination opportunity;
- Perception of “more important” appointments;
- Notification of the vaccination center (or treating doctor) that AstraZeneca should be vaccinated (again);
- Underestimating the risks associated with not having a second vaccination, especially in a phase of declining 7-day incidences , combined with an overestimation of the risks associated with a vaccination.
The last two reasons mentioned lead to the fact that appointments for first vaccinations are not kept and vaccination skeptics are more difficult to win for a first vaccination than in times of rising incidences. Often the belief that the pandemic will end without personal intervention also plays a role: According to the above-mentioned COSMO study, there are people in Germany who believe that herd immunity will soon exist from which they can then benefit.
See also
literature
- Federal Ministry of Health (Ed.): National vaccination strategy COVID-19 . November 6, 2020 ( Online [PDF]).
- STIKO resolution on the 2nd update of the COVID-19 vaccination recommendation and the associated scientific justification . In: Epidemiological Bulletin . No. 5 , February 4, 2021, ISSN 2569-5266 , p. 3–6 ( rki.de [PDF]).
- Susanne Herold et. al .: Commission for pandemic research of the German Research Foundation for vaccination against SARS-CoV-2 . Ed .: German Research Foundation . January 2020 ( dfg.de [PDF]).
Web links
- COVID-19 and Vaccination: Answers to Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ). In: rki.de. December 15, 2020, accessed December 15, 2020 .
- Corona vaccination centers: the big vaccination plan . Vaccination center map and further information. In: Zeit Online . The map is constantly updated.
- Digital vaccination rate monitoring for the COVID-19 vaccination of the RKI
- COVID-19 vaccination dashboard Germany
- Corona-in-Zahlen.de: Corona vaccination quotas and vaccination centers in Germany
- Information about the coronavirus. In: Official BMG website. Published by the Federal Ministry of Health (BMG), February 25, 2021, accessed on February 28, 2021 (including a web link to the text of the National Vaccination Strategy COVID-19 (PDF file, as of November 6, 2020)).
- Andrea Böhnke, Tom Kattwinkel: What if a lot of people don't want to be vaccinated at all? In: Zeit Online , May 14, 2021, accessed on May 17, 2021
Individual evidence
- ↑ Which corona vaccines are there and how do they work? In: BR24 knowledge. January 11, 2021, accessed January 11, 2021 .
- ↑ Health ministers decide on vaccination strategy. In: tagesschau.de. November 7, 2020, accessed November 8, 2020 .
- ↑ National vaccination strategy COVID-19. (PDF) Federal Ministry of Health , November 6, 2020, accessed on March 18, 2021 .
- ↑ a b Resolution of the STIKO on the 1st update of the COVID-19 vaccination recommendation. (PDF) Robert Koch Institute, January 14, 2021, accessed on March 18, 2021 .
- ↑ Kim Björn Becker: Who tells people? In: faz.net. December 20, 2020, accessed March 18, 2021 .
- ↑ EU Commission grants approval for first corona vaccination. In: bundesregierung.de. Federal Government , December 21, 2020, accessed on December 22, 2020 .
- ^ A b First corona vaccination in Halberstadt: pricks for 101-year-olds. In: msn.com. December 26, 2020, accessed December 26, 2020 .
- ↑ EU approves Corona vaccine from Moderna. In: tagesschau.de. Retrieved January 6, 2021 .
- ↑ European Commission grants third approval for safe and effective vaccine against COVID-19. In: ec.europa.eu. European Commission , January 29, 2021, accessed January 29, 2021 .
- ↑ a b Federal Ministry of Health: Ordinance on the right to vaccination against the coronavirus SARS-CoV-2 (Coronavirus Vaccination Ordinance - CoronaImpfV) of December 18, 2020 (PDF) Retrieved on March 1, 2021 .
- ↑ Ordinance on the right to vaccination against the coronavirus SARS-CoV-2 (Coronavirus Vaccination Ordinance - CoronaImpfV) of March 10, 2021. (PDF) Federal Ministry of Health, accessed on March 11, 2021 .
- ↑ a b Vaccination Dashboard. Federal Ministry of Health, May 31, 2021, accessed on May 31, 2021 (details on vaccine delivery available at impfdashboard.de/daten ).
- ↑ a b Digital vaccination rate monitoring for COVID-19 vaccination. In: rki.de. Robert Koch Institute, May 6, 2021, accessed on June 29, 2021 .
- ↑ Coronavirus Vaccination Ordinance: Vaccination prioritization canceled. bundesregierung.de, accessed on June 20, 2021 .
- ↑ Notes on corona vaccination. State of Lower Saxony, accessed on June 20, 2021 .
- ↑ Lower Saxony wants to work through waiting lists in vaccination centers in a week. butenunbinnen.de (Radio Bremen), June 29, 2021, accessed on June 30, 2021 .
- ↑ press conference ANGELA Merkel, BGM Miller and MP Söder after the vaccine conversation on February 1, 2021. bundesregierung.de, February 1, 2021 accessed on 25 June 2021 .
- ↑ Fabian Löhe: Appointments canceled by up to 40 percent. Tens of thousands of people do without their vaccination every day - what's behind it? tagesspiegel.de, June 25, 2021, accessed June 28, 2021 .
- ↑ Friederike Böge, Tjerk Brühwiller, Franca Wittenbrink: New infections despite vaccination: Farewell to the goal of herd immunity? faz.net, June 4, 2021, accessed June 25, 2021 .
- ↑ Delta variant could pose a threat to herd immunity. aerzteblatt.de, June 22, 2021, accessed on June 25, 2021 .
- ↑ “There will still be infections” - Will herd immunity end the pandemic? n-tv.de, June 22, 2021, accessed on June 26, 2021 .
- ↑ Questions and answers about corona vaccination in Baden-Württemberg. In: baden-wuerttemberg.de. March 30, 2021, accessed May 12, 2021 .
- ↑ District vaccination centers start on January 22nd. In: baden-wuerttemberg.de. January 7, 2020, accessed May 12, 2021 .
- ↑ Interactive map: Here are the vaccination centers in Bavaria. In: br.de. December 26, 2020, accessed December 27, 2020 .
- ↑ Nationwide up to 442 Corona vaccination centers. In: apotheken-umschau.de. December 17, 2020, accessed May 12, 2021 .
- ↑ Locations for eleven vaccination centers in Brandenburg have been determined. Retrieved February 24, 2021 .
- ↑ Bremen is planning two corona vaccination centers in large halls. Retrieved February 24, 2021 .
- ↑ Central vaccination center in the exhibition halls: Preparations for the start of the corona vaccinations are in progress, Hamburg.de, December 3, 2020. Accessed December 4, 2020.
- ↑ Corona vaccination in Hesse: 28 vaccination centers are being set up. December 2, 2020, accessed December 5, 2020 .
- ↑ Twelve vaccination centers in MV are waiting for corona vaccine. December 14, 2020, accessed December 20, 2020 .
- ↑ Where the corona vaccination centers are being built in Lower Saxony , NDR. Retrieved December 4, 2020.
- ^ Vaccination centers in North Rhine-Westphalia. Accessed December 16, 2020 .
- ^ State vaccination coordinator Wilhelm: All 31 vaccination centers are ready to go. Retrieved December 18, 2020 .
- ^ Saarland - vaccination centers. Retrieved February 24, 2021 .
- ↑ Vaccination centers in Saarland started work on December 28, 2020.
- ↑ Lebach vaccination center started operations on March 1, 2021.
- ↑ vaccination center of the Bundeswehr in Lebach on Monday in operation , February 26, 2021st
- ↑ Corona vaccination questions and answers about corona vaccination in Saxony. December 29, 2020, accessed December 29, 2020 .
- ↑ Corona vaccination centers in Saxony-Anhalt and where they can be found. www.mdr.de, December 18, 2020.
- ↑ Vaccination centers are to be set up here: Garg names locations. In: ndr.de. Norddeutscher Rundfunk, accessed on December 4, 2020 .
- ↑ Corona pandemic: Spahn and Wieler on the current situation. In: youtube.com. Tagesschau, March 12, 2021, accessed on March 13, 2021 (from time index 0:58:58): "If the countries say at the same time, (...) the base load in the vaccination centers in April should be 2.25 million vaccinations per week ( ...) "
- ↑ General practitioners start with vaccinations. In: tagesschau.de. Retrieved April 6, 2021 .
- ^ A b Health Minister Spahn on the start of vaccinations in general practitioners' practices. In: youtube.com. April 2, 2021, accessed on April 4, 2021 (time index 2:13 to 2:58 / 3:42 to 4:13 / 8:03 to 8:08): “Despite the Easter week, 35,000 family doctor practices have vaccination doses for the coming week requested. In total, they ordered 1.4 million doses of vaccine. We will be able to deliver 940,000 cans next week. (...) We will start with almost a million cans in the next week and the week after that, but by the end of April we will be able to more than triple this amount. As early as the end of April, more than three million vaccination doses will be able to go to the doctor’s practices for vaccination. ”/“ We start (...) in the general practitioner’s practices, but of course in the following period (…) the vaccinating specialists should also be able to vaccinate. (...) Of course, private doctors should also be able to become part of the vaccination campaign. ”(...) However, we are now starting with general practitioners in private practice in the system of contracted doctors. / "In Germany, 87,000 colleagues regularly carried out vaccinations in 2019."
- ↑ Hannes Böckler: Deliveries in week 14 and week 15. (PDF) In: bundesgesundheitsministerium.de. Federal Ministry of Health, March 25, 2021, accessed on April 4, 2021 .
- ↑ Briefing SPAHN and RKI chief WIELER to CORONA MANAGEMENT in GERMANY (...). In: youtube.com. June 1, 2021, accessed on June 6, 2021 (from time index 24:32): “You have to see: This week there are more doctors' practices than ever before. There are over 70,000. "
- ↑ a b Livestream: Spahn and RKI boss Wieler provide information about the Corona situation. In: youtube.com. RedaktionsNetzwerk Deutschland , March 4, 2021, accessed on March 6, 2021 (from time index 8:01 / 52:30 / 1:02:17): “Nevertheless, more vaccine will be available in the next few weeks, in April at the latest than can be vaccinated in vaccination centers and mobile vaccination teams. Then, in April, (...) the medical practices should be routinely involved in the vaccinations. (...) Then the federal government will deliver directly to wholesalers. Wholesalers (...) will distribute this directly to pharmacies. (...) And 24 hours later, the vaccines can be inoculated in the doctor's offices with a logistics system that is already in place today. ”/“ The scope of reporting is significantly reduced. (...) That means (...) the scope of what we can statistically deliver to you also decreases significantly. "/" There was already the situation that a few countries (...) did not cover that much. And when a delivery was delayed, the colleagues got very nervous. (...) But that was because they had already inoculated almost 70 percent of their vaccine. "
- ↑ Health Minister Spahn on the start of vaccinations in general practitioners' practices. In: youtube.com. April 2, 2021, accessed on April 4, 2021 (time index 5:03 p.m. / 8:43 p.m.): “We are starting now, in the first two weeks - that is, the next week and the week after that - with Biontech exclusively for medical practices. And then, from week 16, (...) Biontech AstraZeneca will go to the doctor's office. And from calendar week 17 (...) Biontech, AstraZenenca and Johnson & Johnson. ”/“ Moderna will only be vaccinated in the vaccination centers for the time being, because Moderna has shown that the data is simply the data that is there for stability (...) too The manufacturer has pointed out that it is better to only take one step of the transport, to the vaccination centers. (...), so that in the target structure Biontech and Moderna will be vaccinated in the vaccination centers, so to speak, and all vaccines in the doctor's offices. "
- ↑ Pfizer and BioNTech submit stability data to the US FDA for storage of COVID-19 vaccine at standard freezing temperatures. In: investors.biontech.de. Biontech, Pfizer, February 19, 2021, accessed February 21, 2021 .
- ↑ EMA approves new storage conditions for Pfizer BioNTech vaccine for easier distribution and storage within the European Union. In: investors.biontech.de. Biontech, March 26, 2021, accessed April 3, 2021 .
- ↑ a b Federal Ministry of Health: Ordinance on the right to vaccination against the coronavirus SARS-CoV2 (Coronavirus Vaccination Ordinance - CoronaImpfV) of February 8, 2021. (PDF) Retrieved on February 8, 2021 .
- ↑ a b Federal Ministry of Health: Ordinance on the right to vaccination against the coronavirus SARS-CoV-2 (Coronavirus Vaccination Ordinance - CoronaImpfV) of March 10, 2021. (PDF) Retrieved on March 11, 2021 .
- ^ A b c Anna Clauss, Jürgen Dahlkamp , Lukas Eberle, Jan Friedmann, Annett Großbongardt, Hubert Gude, Cordula Meyer, Martin U. Müller , Christopher Piltz, Steffen Winter: "There is too little there" . In: Der Spiegel . No. 2 , 2021, p. 32 f . ( online ).
- ↑ Kim Björn Becker: When is my turn? Why vaccinations are advancing slowly in some federal states . In: Frankfurter Allgemeine Zeitung . January 4, 2021 ( online ).
- ↑ FAQ Sluggish vaccination campaign. In: tagesschau.de. January 4, 2021, accessed January 5, 2021 .
- ↑ Merle Sievers: Corona-Newsblog, section "The German Foundation for Patient Protection has expressed massive criticism of the problems with the allocation of vaccination appointments in North Rhine-Westphalia". In: rp-online.de. January 25, 2021, accessed January 26, 2021 .
- ↑ Sven Lemkemeyer, Michael Schmidt, Lea Schulze: Coalition wants to punish vaccination pushing with up to 25,000 euros. In: tagesspiegel.de. February 24, 2021, accessed February 24, 2021 .
- ↑ a b c d Together against Corona live - your questions about Corona vaccination. In: youtube.com. Federal Ministry of Health , January 9, 2021, accessed on January 9, 2021 (time index 34:25 to 41:32, 42:05 to 45:08, 1:04:30 to 1:05:30 to 1:09:30 (Spahn quote from 1:08:20)).
- ↑ Anna Schneider: Angela Merkel makes a commitment: All Germans should receive a vaccination offer by September 21st. In: nzz.ch. January 21, 2021, accessed April 12, 2021 .
- ↑ Bastian Brauns: September 21st is the deadline, but only for the first vaccination. In: cicero.de. February 17, 2021, accessed April 12, 2021 .
- ↑ First regulation to amend the coronavirus vaccination regulation. (PDF) In: bundesgesundheitsministerium.de. Federal Ministry of Health, February 24, 2021, accessed on February 28, 2021 .
- ↑ Kirsten Sucker-Sket: Vaccination Ordinance and GMK Decision: News about COVID-19 vaccination. In: deutsche-apotheker-zeitung.de. March 11, 2021, accessed March 13, 2021 .
- ↑ Ordinance on the right to vaccination against the coronavirus SARS-CoV-2 (Coronavirus Vaccination Ordinance). Draft bill by the Federal Ministry of Health, March 9, 2021 , Explanation, p. 25.
- ^ Hanno Charisius, Henrike Roßbach: Johnson & Johnson for all. In: sueddeutsche.de. May 10, 2021, accessed May 12, 2021 .
- ↑ Bund-Länder resolution: Prioritization for vaccinations ends on June 7th. In: tagesschau.de. May 17, 2021, accessed May 17, 2021 .
- ↑ Corona cross vaccination: More than just an emergency solution? dw.com, June 29, 2021, accessed July 1, 2021 .
- ↑ Saskia Heinze: Johnson & Johnson vaccine against Delta variant: Do you need the booster? rnd.de, June 29, 2021, accessed on July 1, 2021 .
- ↑ Carrying out the COVID-19 vaccinations. Robert Koch Institute, June 25, 2021, accessed June 30, 2021 .
- ↑ STIKO boss: Refreshing the corona vaccination protection will probably be necessary by 2022 at the latest. aerztezeitung.de, May 16, 2021, accessed June 30, 2021 .
- ↑ Julia Emmrich: That is why the third corona vaccination is getting closer and closer. In: morgenpost.de. May 17, 2021, accessed May 17, 2021 .
- ↑ a b Christina Rosenberger: Will the German vaccination system soon be overwhelmed? Refreshment of the corona vaccination - Doctors anticipate a dramatic scenario. In: come-on.de. May 25, 2021, accessed May 26, 2021 .
- ↑ SARS-CoV-2 mRNA vaccines induce persistent human germinal center responses. nature.com, June 28, 2021, accessed June 30, 2021 .
- ↑ Corona vaccines from Biontech and Moderna should offer protection for years. fr.de, June 30, 2021, accessed June 30, 2021 .
- ↑ Charité researcher advises seniors to have a third corona vaccination in autumn. aerzteblatt.de, June 25, 2021, accessed June 30, 2021 .
- ↑ Kai Portmann, Fabian Löhe: Spahn wants children to be vaccinated despite Stiko's skepticism. In: tagesspiegel.de. May 26, 2021, accessed May 26, 2021 .
- ↑ Virologist Kekulé does not think that child vaccination is necessary. In: mdr.de. May 25, 2021, accessed May 26, 2021 .
- ↑ Coronavirus in Germany: Vaccination in children and adolescents is controversial. In: stuttgarter-nachrichten.de. May 26, 2021, accessed May 26, 2021 .
- ↑ Biontech approval extended: Canada now vaccinates children from 12. In: n-tv.de. May 5, 2021, accessed May 26, 2021 .
- ↑ Corona vaccine: Moderna works in children from 12 years of age. In: merkur.de. May 26, 2021, accessed May 26, 2021 .
- ↑ Biontech vaccine: Approval for children from 12 years of age by the EU Commission. In: The Federal Government. May 28, 2021, accessed June 2, 2021 .
- ↑ COVID-19 vaccination for children and adolescents aged 12 to 17 years - information sheet for pediatricians and parents (24.6.21). Robert Koch Institute, June 24, 2021, accessed on July 1, 2021 .
- ↑ Celine Müller: STIKO: COVID-19 vaccinations only for children with previous illnesses. In: deutsche-apotheker-zeitung.de. June 10, 2021, accessed June 10, 2021 .
- ↑ COVID-19: When deciding whether to vaccinate children, also think about the social consequences of the pandemic. In: aerzteblatt.de. June 10, 2021, accessed June 10, 2021 .
- ↑ Israeli research asks: Is one COVID vaccine dose enough for young teens? In: jpost.com. June 14, 2021, accessed June 20, 2021 .
- ↑ André dam, Norma Düsekow, Mario Kohne: already vaccinated district administrator and deputy in Wittenberg: Before the official start. In: mdr.de. Mitteldeutscher Rundfunk , February 5, 2021, accessed on February 7, 2021 .
- ↑ a b Digital vaccination rate monitoring. (XLS) In: rki.de. Robert Koch Institute, May 5, 2021, accessed on May 5, 2021 .
- ↑ a b c RKI - Coronavirus SARS-CoV-2 - Digital vaccination rate monitoring for COVID-19 vaccination. In: rki.de. Robert Koch Institute , accessed March 9, 2021 .
- ↑ Edith Kwoizalla (101): The first German received the second corona vaccination. In: Nordkurier.de. January 15, 2021, accessed February 22, 2021 .
- ↑ RKI - Coronavirus SARS-CoV-2 - Current situation / situation report of the RKI on COVID-19. In: Daily situation report. Robert Koch Institute , p. Page 1 of each , accessed on January 3, 2021 .
- ↑ Hope bearer BNT162b2: How do mRNA vaccines work? In: pharmische-zeitung.de , November 10, 2020.
- ↑ Corona vaccine: EU concludes deal with Biontech. In: br.de , November 11, 2020.
- ↑ "It doesn't get any better" - Fauci is pleased with the breakthrough in the corona vaccine. Welt, November 16, 2020. Retrieved November 16, 2020.
- ↑ Corona: Vaccine breakthrough in Germany. Mercury, November 11, 2020. Retrieved November 11, 2020.
- ↑ European Medicines Agency EMA will decide on BioNTech vaccine by December 21st. In: ec.europa.eu. December 15, 2020, accessed January 5, 2021 .
- ↑ Holger Dambeck, Julia Merlot: Combating pandemics This is how we stand with the corona vaccinations (on the brakes). In: spiegel.de. January 22, 2021, accessed January 23, 2021 .
- ↑ Bavaria no longer wants to put back second Biontech vaccination doses. In: sueddeutsche.de. January 15, 2021, accessed January 15, 2021 .
- ↑ a b How long can the second vaccination dose be delayed? In: spiegel.de. January 23, 2021, accessed January 24, 2021 .
- Jump up ↑ Melanie Amann , Markus Feldenkirchen , Florian Gathmann, Matthias Gebauer, Christoph Hickmann, Martin Knobbe, Veit Medick , Marcel Rosenbach, Marcel Rosenbach , Lydia Rosenfelder, Cornelia Schmergal, Thomas Schulz, Gerald Traufetter: The very promising one . In: Der Spiegel . No. 2 , 2021, p. 24-29 ( online ).
- ↑ a b Federal government expects 323 million cans by the end of the year. In: spiegel.de. February 1, 2021, accessed February 1, 2021 .
- ↑ Vaccine deliveries for the EU. In: spiegel.de. March 7, 2021, accessed March 12, 2021 .
- ↑ a b Hannes Böckler: Delivery forecasts of the various manufacturers for the year 2021. (PDF) In: bundesgesundheitsministerium.de. Federal Ministry of Health, March 22, 2021, accessed on March 24, 2021 .
- ↑ Hannes Böckler: BioNTech and_Moderna delivery forecast 2nd quarter. In: bundesgesundheitsministerium.de. Federal Ministry of Health, April 19, 2021, accessed on April 24, 2021 .
- ^ Hannes Böckler: Deliveries to the federal states by the end of the 1st quarter. In: bundesgesundheitsministerium.de. Federal Ministry of Health, April 19, 2021, accessed on April 24, 2021 .
- ↑ Press conference on the current Corona situation, including <! - sic -> with Spahn, Wieler, Cichutek. In: youtube.com. January 30, 2021, accessed on January 30, 2021 (time index 43:52 ff.): “As of today, we are expecting around 12 million cans of Biontech / Moderna by the end of the first quarter. (...) This does not include the volume increase just discussed and announced by Pfizer. "
- ↑ Spahn and RKI boss Wieler on the corona situation. In: youtube.com. February 8, 2021, accessed on February 9, 2021 (time index 41:33 ff.): "At the moment, the challenge is that we already have budget figures for the quarter, but not yet for the months."
- ↑ Hannes Böckler: Delivery forecasts up to the end of April 2021. (PDF) In: bundesgesundheitsministerium.de. Federal Ministry of Health, March 23, 2021, accessed on March 23, 2021 .
- ↑ Simon Kaminski: How Curevac still wants to play a crucial role in the pandemic. In: augsburger-allgemeine.de. April 10, 2021, accessed April 10, 2021 .
- ↑ The approval of the Curevac vaccine has been delayed. In: sueddeutsche.de. May 26, 2021, accessed May 26, 2021 .
- ↑ CureVac's first-generation vaccine candidate, CVnCoV, continues according to DSMB recommendation in phase 2b / 3 proof of efficacy in an environment characterized by variants. In: dgap.de. May 28, 2021, accessed May 29, 2021 .
- ↑ Curevac vaccine: effectiveness among the virus strains. In: tagblatt.de. May 29, 2021, accessed May 30, 2021 .
- ↑ Federal Health Minister Spahn and RKI President Wieler provide information about the current Corona situation. In: youtube.com. April 9, 2021, accessed on April 10, 2021 (from time index 1:11:53, answer from 1:12:28, especially 1:13:39): "Sometimes it sounds like we have to Sputnik V (...) just buy it and then we could use it. That's not the issue. We need approval. The approval does not fail because the authorities are too slow. The Paul Ehrlich Institute (...) is the main rapporteur in the European procedure, i.e. the reporter for it. But we can only allow if the data is there. (...) The faster the person, the Russian applicant, provides the data, the faster the approval. (...) As soon as the data is available, it is evaluated as quickly as possible and an approval decision is made. (…) The other part is then the question of availability. (...) If so, we will of course make the contract directly (...). And there (...) are taking place these days, after the decision the day before yesterday that we will now bring this nationally into contractual relations. And the crucial question for me is actually: is there anything in the 2nd or 3rd quarter? Because it makes (...) a difference for the current phase, for this vaccination campaign. (...) The prerequisite is: approval and quantity availability. And we can conclude the contract (...): on condition of approval, we buy. (...) The contract negotiations are currently taking place. From my point of view, this can happen relatively quickly because the conditions are clear. (...) At the end of the day, it must now be clear what quantities and at what times we are talking on the condition of approval. The speed of approval really only affects the Russian side itself through the delivery of the data. "
- ↑ Russian vaccine becomes a hit: Mecklenburg-Western Pomerania secures Sputnik. In: rnd.de. April 8, 2021, accessed May 30, 2021 .
- ^ Controversy over Russian vaccine: Greens block Sputnik V for Berliners. In: tagesspiegel.de. April 20, 2021, accessed May 30, 2021 .
- ^ German corona vaccine: Berlin's Senator for Economic Affairs Pop wants emergency approval for Curevac. In: berliner-zeitung.de. April 25, 2021, accessed May 30, 2021 .
- ↑ Sputnik V: Söder demands a quick decision on approval. In: zeit.de. May 30, 2021, accessed May 30, 2021 .
- ↑ Start of Europe postponed: Johnson & Johnson stops deliveries. In: n-tv.de. April 14, 2021, accessed April 14, 2021 .
- ↑ COVID-19 Vaccine Janssen: EMA finds possible link to very rare cases of unusual blood clots with low blood platelets. In: ema.europa.eu. European Medicines Agency, April 20, 2021, accessed April 21, 2021 .
- ↑ Delivery forecasts of the various manufacturers for the year 2021 (as of May 12, 2021). In: bundesgesundheitsministerium.de. Retrieved June 9, 2021 .
- ↑ Production breakdown for corona vaccine: failure of Johnson & Johnson hits Germany hard. In: spiegel.de. June 12, 2021, accessed June 12, 2021 .
- ↑ Christian Geinitz: Will vaccines soon be in abundance? - Germany is the beneficiary of the vaccine-weary USA. In: faz.net. June 18, 2021, accessed June 18, 2021 .
- ↑ Statement on the expansion of European production capacities and the resulting changes in the delivery schedule. In: investors.biontech.de. Biontech, January 15, 2021, accessed January 18, 2021 .
- ↑ Pfizer supplies fewer ampoules. In: tagesschau.de. Norddeutscher Rundfunk, January 21, 2021, accessed on January 23, 2021 .
- ↑ Exclusive: AstraZeneca to cut EU's COVID vaccine deliveries by 60% in first quarter - EU source. In: reuters.com. January 22, 2021, accessed January 22, 2021 .
- ^ Hannes Böckler: Deliveries to the federal states by the end of the 1st quarter. (PDF) In: bundesgesundheitsministerium.de. Federal Ministry of Health, April 15, 2021, accessed on April 15, 2021 .
- ↑ A pain in the ass: How Corona helped Karl Lauterbach to make his comeback. In: rnd.de. August 19, 2020, accessed February 9, 2021 .
- ↑ Lauterbach does not expect a nationwide corona vaccine until 2022. In: reuters.com, August 19, 2020.
- ↑ The fight for the corona vaccine: The planning disaster. In: spiegel.de, December 18, 2020 (with Paywall).
- ^ The Planning Disaster: Germany and Europe Could Fall Short on Vaccine Supplies. In: spiegel.de (English).
- ↑ Pfizer and Biontech conclude Phase 3 Study of COVID-19 vaccine candidate, meeting all primary efficacy endpoints. Company press release. In: pfizer.com. November 18, 2020, accessed May 23, 2021 .
- ↑ CureVac starts Phase 3 clinical trial of its COVID-19 vaccine candidate. In: msn.com. November 17, 2020, accessed May 23, 2021 .
- ↑ Curevac's corona vaccine: from late bloomer to mutant conqueror? In: ruhrnachrichten.de. May 19, 2021, accessed May 23, 2021 .
- ↑ CureVac says well on track to request vaccine approval as planned. In: reuters.com. May 5, 2021, accessed May 26, 2021 .
- ↑ Corona pandemic: Criticism of German vaccine procurement. In: deutschlandfunk.de. January 1, 2021, accessed January 2, 2021 .
- ↑ Possible vaccination acceleration: Spahn has the temporal extension of the second vaccination checked. In: rp-online.de. January 4, 2021, accessed January 4, 2021 .
- ↑ Scarce corona vaccine: Spahn has delayed the second dose checked. In: spiegel.de. January 4, 2021, accessed January 4, 2021 .
- ↑ Announcement from Spahn: Vaccination offer for all Germans already in June? In: faz.net. January 4, 2021, accessed January 4, 2021 .
- ↑ Biontech wants to deliver more corona vaccine to the EU - company boss criticizes EU strategy. In: giessener-allgemeine.de, January 2, 2021.
- ↑ Scholz freaks out because of the EU vaccine order. In: n-tv.de. February 4, 2021, accessed February 4, 2021 .
- ↑ Corona vaccine: AstraZeneca cuts deliveries to the EU. In: deutschlandfunk.de. January 22, 2021, accessed January 29, 2021 .
- ↑ Controversy on the open stage: EU-Astrazeneca crisis discussion did not bring a solution. In: sn.at. January 28, 2021, accessed January 29, 2021 .
- ↑ Corona vaccine from AstraZeneca Confusion before the next EU meeting. In: tagesschau.de. January 27, 2021, accessed February 4, 2021 .
- ↑ Breakdown at publication - This is in the contract between AstraZeneca and the EU. In: welt.de. January 29, 2021, accessed January 29, 2021 .
- ↑ Contract text with blackouts, see Advance Purchase Agreement (“APA”) for the production, purchase and supply of a COVID-19 vaccine in the European Union between the European Commission and AstraZeneca AB. (PDF) Retrieved January 29, 2021 .
- ↑ see point 7.4 in AZ_FIRMATO_REPORT.pdf , www.rai.it, accessed on February 19, 2021.
- ↑ AstraZeneca's vaccine contract with the UK is based on 'best efforts,' just like its deal with a frustrated EU. In: cnn.com. February 18, 2021, accessed April 5, 2021 .
- ↑ Silke Wettach: Document available on the Internet: Vaccine contract with the EU: Curevac assumes the liability that Pfizer did not want. In: wiwo.de. January 23, 2021, accessed February 11, 2021 .
- ↑ Contract text with blackouts, see Advance Purchase Agreement (“APA”) for the development, production, advance purchase and supply of a COVID-19 vaccine for EU Member States between the European Commission and Curevac AG. (PDF) Retrieved February 11, 2021 .
- ↑ Coronavirus pandemic under: "Criticism of the vaccination strategy: Von der Leyen defends himself". In: tagesschau.de. February 9, 2021, accessed February 10, 2021 .
- ↑ Contract text with blackouts, see Advance Purchase Agreement (“APA”) for the Development, Production, Priority-Purchasing Options and Supply of a Successful COVID-19 Vaccine for EU Member States between the European Commission and Sanofi Pasteur SA and Glaxosmithkline Biologicals SA ( PDF) Retrieved February 10, 2021 .
- ↑ Michael Schneider, ARD-Studio Brussels: EU lets contract expire: No extension for AstraZeneca. In: tagesschau.de. May 9, 2021, accessed May 26, 2021 .
- ↑ 50 million doses to the EU: Astrazeneca sentenced to deliver vaccines. n-tv.de, June 18, 2021, accessed on June 20, 2021 .
- ↑ Benjamin Triebe, London: Verdict in the vaccine dispute: AstraZeneca and the EU see themselves as winners - and neither are. In: Neue Zürcher Zeitung. June 18, 2021, accessed June 20, 2021 .
- ↑ Astrazeneca has to deliver 50 million doses of vaccine to the EU: The company wants to implement the judgment, but is still lagging behind its original delivery commitments. In: prosieben.de. June 18, 2021, accessed June 20, 2021 .
- ↑ EU monitors vaccine exports. In: tagesschau.de. January 29, 2021, accessed February 1, 2021 .
- ↑ Canada prepping trade options in case EU breaks promise to keep vaccines flowing. In: cp24.com. February 1, 2021, accessed February 6, 2021 .
- ↑ Johnson & Johnson vaccine approved in the EU. In: faz.net. March 11, 2021, accessed March 14, 2021 .
- ↑ Biden Rebuffs EU, AstraZeneca and Says US Will Keep Its Doses. In: bloomberg.com. March 12, 2021, accessed March 13, 2021 .
- ↑ EU vaccine agony just gets worse as US refuses to ship homemade AstraZeneca jabs to Europe. In: express.co.uk. March 11, 2021, accessed March 13, 2021 .
- ↑ Setback for vaccination campaign: Johnson & Johnson cuts deliveries for Germany. In: spiegel.de. April 26, 2021, accessed April 28, 2021 .
- ↑ Why the US is now deciding when the vaccination turbo can start. In: businessinsider.de. May 2, 2021, accessed May 15, 2021 .
- ↑ Important raw materials are missing: US blockade endangers Curevac production. In: n-tv.de. May 4, 2021, accessed May 16, 2021 .
- ^ Joe Biden's 'America First' Vaccine Strategy. In: theatlantic.com. February 4, 2021, accessed February 6, 2021 .
- ↑ Canada confident in vaccine deliveries even if US blocks exports. In: nationalpost.com. December 8, 2020, accessed January 24, 2021 .
- ↑ Ensuring Access to United States Government COVID-19 Vaccines. In: Federal Register United States Government . December 8, 2020, accessed January 23, 2021 .
- ↑ Here are the executive orders Biden has signed so far. In: cnn.com. January 25, 2021, accessed January 25, 2021 .
- ↑ Merkel defends European vaccine policy. In: presse-augsburg.de. February 2, 2021, accessed February 6, 2021 .
- ↑ Is the worst still to come, Ms. Merkel? In: zdf.de. February 12, 2021, accessed February 13, 2021 . (TV interview ZDF , video and verbatim transcript)
- ↑ Extra dose from vials of Comirnaty COVID-19 vaccine. In: ema.europa.eu. European Medicines Agency, January 9, 2021, accessed January 9, 2021 .
- ↑ Christian Lindner calls for "crisis production" of the vaccine. In: zeit.de. December 28, 2020, accessed January 31, 2021 .
- ↑ "A question of life and death": Lindner calls for crisis production of corona vaccines. In: rnd.de. December 27, 2020, accessed January 31, 2021 .
- ↑ "As long as we have not vaccinated the world, we will not be safe either". In: welt.de. January 28, 2021, accessed January 31, 2021 .
- ↑ Proposal by the US government: Green chief Habeck calls for patent suspension for corona vaccines. In: spiegel.de. May 6, 2021, accessed May 16, 2021 .
- ↑ Stefan Troendle, Sabine Geipel: Revoking corona vaccine patents - what speaks for it, what against it? swr.de, May 6, 2021, accessed on June 28, 2021 .
- ^ Vaccination patents: Merkel contradicts Biden. In: sueddeutsche.de. May 6, 2021, accessed May 16, 2021 .
- ↑ European Medicines Agency : Treatments and vaccines for COVID-19: authorized medicines. In: ema.europa.eu. Retrieved February 5, 2020 .
- ↑ Susanne Herold et. al .: Commission for pandemic research of the German Research Foundation for vaccination against SARS-CoV-2 . Ed .: German Research Foundation . January 2020 ( Online [PDF]).
- ↑ SafeVac 2.0. In: pei.de. December 22, 2020, accessed January 5, 2021 .
- ↑ Paul Ehrlich Institute (Ed.): Suspected cases of side effects and vaccination complications after vaccination to protect against COVID-19 from the start of the vaccination campaign on December 27, 2020 to February 26, 2021 . March 4, 2021 ( Online [PDF]).
- ↑ Epidemiological Bulletin 19/2021 of the RKI
- ↑ Celine Müller: Safety report from the Paul Ehrlich Institute: Increasing reports of myocarditis after COVID-19 vaccinations. In: deutsche-apotheker-zeitung.de. June 14, 2021, accessed June 27, 2021 .
- ↑ Live blog about the corona virus (under: Vaccine choice "at the moment and foreseeable" not possible). In: tagesschau.de. January 9, 2021, accessed January 9, 2021 .
- ↑ Vaccination with Astrazeneca in Saarland: half of the people skip the vaccination appointment. In: tagesspiegel.de. February 16, 2021, accessed February 16, 2021 .
- ↑ Montgomery against Astra-Zeneca vaccination for medical personnel. In: handelsblatt.com. February 16, 2021, accessed February 18, 2021 .
- ↑ Anne Ameri-Siemens: Creating camps does not help . In: Frankfurter Allgemeine Sonntagszeitung . February 28, 2020 ( faz.net ).
- ↑ Astra-Zeneca vaccine better than its reputation. (PDF) In: ndr.de. February 16, 2020, accessed February 28, 2020 .
- ↑ "Every day counts": Söder wants to immediately release Astrazeneca vaccine for everyone. In: msn.com (and Tagesspiegel). February 28, 2021, accessed February 28, 2021 .
- ↑ STIKO announcement on COVID-19 vaccination with the AstraZeneca vaccine (March 4th, 2021). In: rki.de. March 4, 2021, accessed March 6, 2021 .
- ↑ Anne Bäurle: Germany suspends corona vaccination with AstraZeneca vaccine. Springer Medizin Verlag, March 15, 2021, accessed on March 16, 2021 .
- ↑ Temporary suspension of vaccination with the COVID-19 vaccine AstraZeneca. Paul Ehrlich Institute, March 15, 2021, accessed on March 16, 2021 .
- ↑ Jennifer Greve, Helena Gries: Corona in Germany: Is the vaccination turbo coming now? Spahn wants to lift the prioritization of vaccinations. In: hna.de (Hessische / Niedersächsische Allgemeine). April 22, 2021, accessed April 22, 2021 .
- ↑ Thomas Eldersch: Responsibility is pushed on: Astrazeneca for everyone: But who pays for vaccination damage to under-60-year-olds? In: tz.de. April 26, 2021, accessed April 26, 2021 .
- ↑ Woman (32) from the Herford district dies after AstraZeneca vaccination. In: RTL.de. April 29, 2021, accessed April 29, 2021 .
- ↑ According to Ema decision: AstraZeneca vaccine is to be used again in Germany - with a warning. In: Spiegel online. March 18, 2021, accessed March 18, 2021 .
- ↑ Preventive brake on AstraZeneca vaccine - the most important answers. In: wiwo.de. March 30, 2021, accessed March 30, 2021 .
- ↑ NRW stops Astrazeneca for younger people - vaccination only in individual cases. In: RP Online. March 30, 2021, accessed March 31, 2021 .
- ↑ "Will bring uncertainty with it": Merkel and Spahn on Astrazeneca resolutions. In: express.de. March 31, 2021, accessed April 24, 2021 .
- ↑ a b Resolution of the STIKO on the 4th update of the COVID-19 vaccination recommendation (April 1st, 2021). In: rki.de. Robert Koch Institute, April 1, 2021, accessed on April 3, 2021 .
- ↑ a b Resolution of the STIKO on the 4th update of the COVID-19 vaccination recommendation and the associated scientific justification. (PDF) In: rki.de. Robert Koch Institute, April 1, 2021, accessed on April 3, 2021 .
- ↑ Wording of the vaccination recommendation changed in important detail. In: OOZ Oldenburger online newspaper. April 21, 2021, accessed April 25, 2021 .
- ^ Robert Koch Institute: Current data and information on infectious diseases and public health - Epidemiological Bulletin No. 16/2021, STIKO resolution on the 4th update of the COVID-19 vaccination recommendation. In: rki.de. April 22, 2021, p. 7, amended on April 16, 2021 , accessed on April 25, 2021 : “The use of the COVID-19 Vaccine AstraZeneca for a 1st or 2nd vaccine dose below this age limit remains after medical advice and with individual risk acceptance by the patient possible. "
- ↑ Information sheet on COVID-19 vaccination with vector vaccine. Deutsches Grünes Kreuz eV in cooperation with the Robert Koch Institute , April 23, 2021, accessed on April 25, 2021 : "These documents are continuously updated (status of the information sheet in German: April 23, 2021 )."
- ↑ Information sheet . (PDF) For vaccination against COVID-19 (Corona Virus Disease 2019) - with vector vaccines. German Green Cross e. V., Marburg, in cooperation with the Robert Koch Institute, Berlin, April 23, 2021, accessed on April 25, 2021 .
- ↑ The prerequisite is patient education and proper vaccination: Land is liable for any vaccination damage caused by Astrazeneca. In: saarbruecker-zeitung.de. May 3, 2021, accessed May 5, 2021 .
- ↑ BT-Drs. 19/29287
- ↑ No medical liability for vaccine damage by AstraZeneca - law change is about to be passed. In: Praxisnachrichten. National Association of Statutory Health Insurance Physicians (KBV), May 5, 2021, accessed on May 6, 2021 .
- ↑ which could possibly change with the appearance of new variants
- ↑ After approval by Astrazeneca: Why vaccination intervals shouldn't be too short. In: zdf.de. May 6, 2021, accessed May 30, 2021 .
- ↑ Researchers warn against vaccination intervals at AstraZeneca four weeks. In: zeit.de. May 28, 2021, accessed May 30, 2021 .
- ^ Daniela Hüttemann: Heat shock proteins: impurities found in Astra-Zeneca vaccine. In: pharmische-zeitung.de. May 26, 2021, accessed May 27, 2021 .
- ↑ Lea Krutzke, Reinhild Rösler, Sebastian Wiese, Stefan Kochanek: Process-related impurities in the ChAdOx1 nCov-19 vaccine. In: researchsquare.com. Retrieved May 27, 2021 .
- ↑ Researchers find impurities in the Astrazeneca vaccine. In: aerzteblatt.de. May 27, 2021, accessed May 27, 2021 .
- ↑ CureVac shares collapse in double digits: Spahn expects the CureVac vaccine to be “not before August”. In: finanzen.net. June 8, 2021, accessed June 18, 2021 .
- ↑ Report: Spahn no longer plans Curevac vaccine for ongoing vaccination campaign. In: aerzteblatt.de. June 11, 2021, accessed June 18, 2021 .
- ↑ Peter Kremsner, Philipp Mann et al .: Phase 1 Assessment of the Safety and Immunogenicity of an mRNA-Lipid Nanoparticle Vaccine Candidate Against SARS-CoV-2 in Human Volunteers. medRxiv (Preprint) doi: 1101 / 2020.11.09.20228551
- ↑ Head of study on Curevac - Dosage cause for poor effectiveness? In: zdf.de. June 17, 2021, accessed June 18, 2021 .
- ↑ Corona vaccines: Why Curevac is different. In: Spektrum.de. June 9, 2021, accessed June 9, 2021 .
- ↑ Study important for approval: Covid vaccine from Curevac fails to meet the criteria for success. In: spiegel.de. June 17, 2021, accessed June 19, 2021 .
- ↑ EMA refers to Pfizer Biontech application rules www.orf.at, accessed on January 4, 2021.
- ↑ Coronavirus in Germany: Spahn on the current situation. In: youtube.com. March 19, 2021, accessed on March 20, 2021 (from time index 36:01): "According to my overview, which I saw yesterday, almost all federal states have now switched to the maximum vaccination interval: namely at Biontech and Moderna to six weeks [ ...] and at AstraZeneca to twelve weeks between the first and second vaccination. "
- ↑ SPD health politician wants to change strategy: Lauterbach explains how the vaccination turbo can work. In: tagesspiegel.de. April 8, 2021, accessed April 9, 2021 .
- ↑ Debate about longer vaccination intervals: Lauterbach calls for a focus on as many first vaccinations as possible. In: aerztezeitung.de. April 5, 2021, accessed April 9, 2021 .
- ↑ Stiko boss on ZDF - do not postpone the second corona vaccination. In: zdf.de. April 8, 2021, accessed April 11, 2021 .
- ↑ Milan Sharma: B.1.617.2 becoming dominant variant in India, finds genome sequencing. In: indiatoday.in. May 24, 2021, accessed May 24, 2021 .
- ↑ Rob Merrick: Over-50s to receive second jab after 8 weeks as alarm grows over the Indian Covid variant. In: independent.co.uk. May 14, 2021, accessed May 24, 2021 .
- ↑ Heterologous corona vaccination in a German study, well tolerated and more effective. In: www.aerzteblatt.de. June 3, 2021, accessed June 9, 2021 .
- ↑ Mix-and-match COVID vaccines trigger potent immune response. In: nature.com. May 19, 2021, accessed June 22, 2021 .
- ↑ Cross vaccination: Combination of Astrazeneca and Biontech has an advantage. In: www.br.de. June 4, 2021, accessed June 9, 2021 .
- ^ Opinion of the Standing Vaccination Commission on the time of administration of an mRNA vaccine after first vaccination with AstraZeneca Vaccine (Vaxzevria) in <60 year olds In: rki.de. April 14, 2021, accessed June 19, 2021 .
- ↑ Marco Cavaleri advises caution: “Better to ban AstraZeneca for everyone”. In: suedtirolnews.it. June 15, 2021, accessed June 14, 2021 .
- ↑ Vaccination Commission changes recommendation for AstraZeneca first vaccinated people. In: spiegel.de. July 1, 2021, accessed July 1, 2021 .
- ↑ Coronavirus variants: Escape mutations are worrying. In: pharmische-zeitung.de. January 23, 2021, accessed February 9, 2021 .
- ↑ After the first Covid 19 illness, the patient with a South African mutant is in mortal danger. In: tah.de. February 12, 2021, accessed February 13, 2021 .
- ↑ Mutations: The third corona wave is about to begin. In: mdr.de. February 19, 2021, accessed February 20, 2021 .
- ↑ Response to Corona mutants: Federal government prohibits entry from Tyrol and the Czech Republic. In: faz.net. February 11, 2021, accessed February 13, 2021 .
- ↑ Questions and answers about the COVID-19 vaccination. In: bundesgesundheitsministerium.de. Retrieved April 17, 2021 .
- ↑ Penalties for failing to vaccinate no human rights violation. beck-aktuell, April 8, 2021, accessed on June 29, 2021 .
- ↑ Michael Winkelmüller: IfSG: “hidden compulsory vaccination” for everyone? In: tagesspiegel.de. Retrieved January 1, 2021 .
- ↑ a b Corona vaccination compulsory for doctors? “Article 2 of the Basic Law is not unlimited!” In: aerztezeitung.de. December 30, 2020, accessed December 31, 2020 .
- ↑ Compulsory vaccination would be legally possible. In: aerztezeitung.de. June 8, 2020, accessed January 2, 2021 .
- ^ Criticism of Söder's idea of mandatory vaccination. In: tagesschau.de. Retrieved January 12, 2021 .
- ↑ News blog on Covid-19. In: t-online.de. January 15, 2021, accessed January 15, 2021 .
- ↑ Live blog on the coronavirus (under: "Corona vaccination obligation for soldiers? - Bundeswehr checks tolerance obligation"). In: tagesschau.de. January 15, 2021, accessed January 15, 2021 .
- ↑ The STIKO recommendations apply in the event of a parent controversy about vaccinating a child. haufe.de, March 19, 2021, accessed on July 1, 2021 .
- ↑ Live blog about the coronavirus (under: Moderna vaccine has arrived in Germany and Spahn: Moderna vaccine is coming to Germany today). In: tagesschau.de. January 11, 2021, accessed January 11, 2021 .
- ↑ Lauterbach: "Numbers indicate that we are at the beginning of a third wave". In: welt.de. February 20, 2021, accessed February 20, 2021 .
- ↑ Berlin's governing mayor wants to change the sequence of vaccinations. Der Tagesspiegel, February 18, 2021, accessed on March 28, 2021 .
- ↑ Alica Jung: Discussion about vaccines - "Split society" at Astrazeneca. zdf.de, April 16, 2021, accessed on June 24, 2021 .
- ↑ Corona vaccination: Many appointments canceled for AstraZeneca vaccine. ndr.de, April 19, 2021, accessed June 24, 2021 .
- ↑ Heinrich Wefing: Corona vaccination privileges: freedom from the syringe. In: zeit.de. January 9, 2021, accessed January 9, 2021 .
- ^ A b Corona crisis in Germany: More freedom for vaccinated people? In: tagesschau.de. January 23, 2020, accessed January 23, 2020 .
- ↑ More freedom for vaccinated people: “Debate at inopportune times”. In: sueddeutsche.de. January 18, 2021, accessed January 18, 2021 .
- ↑ Live blog on the coronavirus (under: "SPD boss Walter-Borjans against Maas advance"). In: tagesschau.de. January 18, 2021, accessed January 18, 2021 .
- ↑ Markus Lanz of February 24, 2021. Retrieved March 21, 2021 .
- ↑ Holidays only for vaccinated people: This is how Alltours justifies its plan! In: rtl.de. February 20, 2021, accessed February 20, 2021 .
- ↑ Special rules for vaccinated people? (PDF) German Ethics Council, February 4, 2021, accessed on March 21, 2021 .
- ↑ Federal Health Minister Spahn and RKI President Wieler provide information about the current Corona situation. In: youtube.com. April 9, 2021, accessed on April 10, 2021 (from time index 8:02): “The Robert Koch Institute has come to the conclusion that the risk that people who have been completely vaccinated will pass on the virus is even lower than those who tested negative. This means that we can treat anyone who has received the 2nd dose 2 weeks later as if they had just recently taken a negative test. (...) That is not a privilege or a special right. Everyone can be tested for free. (…) This week I discussed with the (…) health ministers of the federal states that we would adapt our regulations and recommendations to the new findings. This means that when traveling, the compulsory test for completely vaccinated persons can largely be omitted. (...) We will implement that in the course of April, as well as the corresponding quarantine rule adjustments. "
- ↑ Follow-up of contact persons for SARS-CoV-2 infections. In: rki.de. Robert Koch Institute, April 9, 2021, accessed April 10, 2021 .
- ↑ Relaxation for vaccinated people? First draft before Prime Minister's Conference on Monday. In: focus.de. April 24, 2021, accessed April 25, 2021 .
- ↑ Consultations by the federal and state governments: “The aim is to return to the familiar way of life as quickly as possible”. In: bundesregierung.de. German Federal Government, April 26, 2021, accessed April 26, 2021 .
- ^ Nail Akkoyun, Sarah Neumeyer, Jan-Frederik Wendt, Jennifer Greve: Corona in Germany: Freedoms for vaccinated people? Decision in May - mask requirement should remain. In: hna.de. April 27, 2021, accessed April 27, 2021 .
- ↑ Ordinance regulating the relief and exemptions from protective measures to prevent the spread of COVID-19 (COVID-19 Protective Measures Exceptions Ordinance - SchAusnahmV). Ordinance of the Federal Government. Retrieved May 4, 2021 .
- ↑ Ordinance regulating the facilitation of protective measures to prevent the spread of COVID-19. Federal Ministry of Justice and Consumer Protection , accessed on May 4, 2021 .
- ↑ Exceptions for those who have recovered from corona and those who have been vaccinated are up for voting. German Bundestag, May 6, 2021 .
- ↑ Item 94b: Corona exception regulation: Federal Council approves exceptions for fully vaccinated people. In: BundesratKOMPAKT. Federal Council, May 7, 2021, accessed on May 7, 2021 .
- ↑ a b c d Ordinance regulating the relief and exemptions of protective measures to prevent the spread of COVID-19 (COVID-19 Protective Measures Exceptions Ordinance - SchAusnahmV) of May 8, 2021 ( BAnz AT May 8, 2021 V1 )
- ↑ New regulations from Sunday - relief for those who have been vaccinated and those who have recovered. Federal Government, May 7, 2021, accessed on May 13, 2021 .
- ↑ Ethicist Buyx rebukes Lanz: “This is not a debate about envy”. T-Online, April 30, 2021, accessed May 1, 2021 .
- ↑ Two thirds of Germans want to be vaccinated against Corona. www.zeit.de, December 25, 2020.
- ↑ Rainer Woratschka: A third of Germans do not want to be vaccinated: How do citizens cope with restrictions on freedom in the pandemic? Very different, according to a survey commissioned by the Bertelsmann Foundation. In: tagesspiegel.de. Retrieved February 24, 2021 .
- ↑ Lauterbach - EU vaccination debacle will go down in history as the “biggest mistake”. The vast majority of Germans want to be vaccinated. In: welt.de. February 20, 2021; archived from the original on February 20, 2021 ; accessed on February 20, 2021 .
- ↑ Fabian Löhe: Appointments canceled by up to 40 percent. Tens of thousands of people do without their vaccination every day - what's behind it? tagesspiegel.de, June 25, 2021, accessed June 28, 2021 .
- ↑ Vaccinations. COVID 19 Snapshot Monitoring (COSMO), June 18, 2021, accessed on June 23, 2021 .
- ↑ Delta variant could pose a threat to herd immunity. aerzteblatt.de, June 22, 2021, accessed on June 25, 2021 .
- ↑ Vaccinations. COVID 19 Snapshot Monitoring (COSMO), June 18, 2021, accessed on June 23, 2021 .
- ↑ Survey: Almost three quarters want to be vaccinated. In: stuttgarter-zeitung.de. May 16, 2021, accessed May 16, 2021 .
- ↑ Helan Omar: Covid-19: Why is one vaccination enough at J&J? aponet.de, May 29, 2021, accessed on June 28, 2021 .
- ↑ Impfspringer - The jumping portal of the Vogelsbergkreis. impfspringer.de, accessed on June 28, 2021 .