Ostheim in front of the Rhön
| coat of arms | Germany map | |
|---|---|---|

|
Coordinates: 50 ° 27 ' N , 10 ° 14' E |
|
| Basic data | ||
| State : | Bavaria | |
| Administrative region : | Lower Franconia | |
| County : | Rhön-Grabfeld | |
| Management Community : | Ostheim in front of the Rhön | |
| Height : | 300 m above sea level NHN | |
| Area : | 40.83 km 2 | |
| Residents: | 3305 (Dec. 31, 2019) | |
| Population density : | 81 inhabitants per km 2 | |
| Postcodes : | 97645, 97647 | |
| Area code : | 09777 | |
| License plate : | NES, CAN, MET | |
| Community key : | 09 6 73 153 | |
| LOCODE : | DE ORR | |
| Community structure: | 9 districts | |
| Address of the municipal administration: |
Marktstrasse 24 97645 Ostheim vdRhön |
|
| Website : | ||
| Mayor : | Ulrich Waldsachs (- FWG ) | |
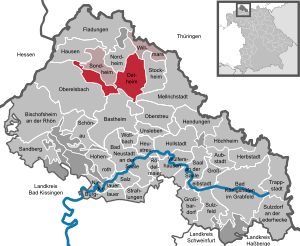
| Location of the municipality of Ostheim vdRhön in the Rhön-Grabfeld district | ||
Ostheim vor der Rhön (officially: Ostheim v. D. Rhön ) is a town in the Lower Franconian district of Rhön-Grabfeld and the seat of the administrative community Ostheim vor der Rhön .
City structure
The municipality of Ostheim vor der Rhön is divided into nine districts:
|
history
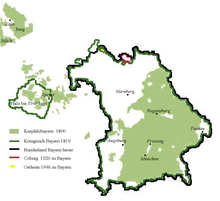
Until the reclassification to Bavaria
The Franconian settlement Ostheim vor der Rhön was probably founded around 525 and first mentioned in a document in 804. The Großvargula taverns owned property and fiefdoms of the Fulda Abbey and the Landgraves of Thuringia in Ostheim around 1214 . The Lichtenberg office , to which Ostheim and Urspringen belonged, was formerly an office of the county of Henneberg -Römhild and later of the Grand Duchy of Saxony-Weimar-Eisenach .
Until the destruction of the vineyards in the Thirty Years War , Ostheim was famous for its good wine. The saying was known:
"To Würzburg an dem Stein,
to Klingenberg am Main
and to Ostheim in Weingartental
The best wine grows everywhere."
In 1920 the Ostheim exclave came to the newly founded state of Thuringia and was part of the Meiningen district . In 1925, 2,122 residents lived here. In 1945, the exclave Ostheim with the communities Ostheim vor der Rhön, Sondheim vor der Rhön , Stetten and Urspringen was assigned to the Bavarian district of Mellrichstadt as part of the American occupation zone and was under Bavarian administration as a Thuringian enclave. The state legal affiliation to the Free State of Bavaria has never been officially clarified.
Ostheim in Bavaria
Since the regional reform of 1972 , Ostheim has belonged to the Rhön-Grabfeld district . The Protestant parish still belonged to the regional church of Thuringia until 1972 , the Catholic Curate Ostheim vor der Rhön still belongs to the diocese of Fulda - like larger areas of Thuringia in the past - but has been cared for by the diocese of Würzburg since 1945 .
Incorporations
On July 1, 1972, the previously independent communities of Oberwaldbehrungen and Urspringen were incorporated.
politics
mayor
Ulrich Waldsachs (FWG) has been mayor since 2008, who was confirmed in office in the local elections on March 16, 2014 with 70.5% of the votes cast.
Municipal council
The municipal council of Ostheim consists of 16 members and the mayor. Since the local elections on March 16, 2014 , the Free Voting Community Ostheim and the CSU each hold 6 seats, 4 of which belong to the SPD .
coat of arms
Blazon :
"In gold between two red crenellated towers with red pointed roofs, a red crenellated wall with an open gate, on which a red armored black lion with a green diamond wreath stands in its paws."
Town twinning
Ostheim maintains a town twinning with Wasungen in Thuringia.
Culture and sights
Architectural and ground monuments
- The Ostheim fortified church is one of the largest and best preserved fortified churches in Germany
- Lichtenburg with a managed knight's hall and dining room
- historical town hall
- Historic old town with castles and half-timbered houses
- Barrows from the Hallstatt period
- Ostheimer Warte (tower)
- Jewish cemetery in the Oberwaldbehrungen district
- Terraces and settlement remains of the Lahr desert below the Lahrberg and east of the Gangolfsberg as a ground monument
Museums
- Fortified church museum in the “Steinernen Gaden” of the Ostheim fortified church
- Organ building museum in Hanstein Castle (on request and with advance notice with musical / technical tour)
Local specialities
A local specialty is the Ostheimer Leberkäs , which, despite its name, is not a Leberkäse , as is common in southern Germany. It is made like a terrine from 90 percent pork and ten percent pork liver. The meat is processed warm immediately after slaughtering, which improves the taste. The medium-sized meat dough, seasoned with nutmeg, is wrapped in a pork net that creates a fine crust when baked. In October 2004, the Ostheimer Leberkäs was included in the Ark of Taste by Slow Food . This brought him a national reputation. Since 2002, the Rhön sausage market has been held in Ostheim every two years on the second weekend in October .
The well-known non-alcoholic soft drink Bionade was developed in Ostheim and is produced here.
economy
traffic
Ostheim is on the federal highway 285 , the A 71 motorway is around ten kilometers away and can be reached via the Mellrichstadt junction .
In the local public transport Ostheim is served by bus lines of the Omnibusverkehr Franken / DB Frankenbus , which stop at the Mellrichstadt train station of the Deutsche Bahn AG, where there is a connection to trains in the direction of Würzburg and Erfurt . The journey time to Mellrichstadt train station is around ten minutes.
The Ostheim station on the Streutalbahn is only served seasonally by the Rhön-Zügle in museum traffic; regular passenger traffic ended in the summer of 1976.
Established businesses
- Bionade GmbH - manufacturer of an organic soft drink
- Hey Orgelbau - manufacturer of pipe organs
- Organ building company Hoffmann und Schindler - manufacturer of organs
- Verlag Peter Engstler - alternative literature, poems, magazines
media
The Ostheimer Zeitung , Germany's smallest local newspaper with around 800 copies , has been published in Ostheim since March 23, 1907 . It is published and printed by the local publisher Gunzenheimer. In the 1976 feature film Im Lauf der Zeit by Wim Wenders , a key scene takes place in the Ostheimer Zeitung's print shop, in which one of the main actors, Robert, played by Hanns Zischler , first bitterly argues with his father, the publisher, and then he turns but reconciled with him.
To the south of Ostheim, on the Heidelberg , there has been a 63 meter high transmission tower made of reinforced concrete since 1993 for the distribution of the Radio Primaton program on 101.5 MHz with 320 W ERP.
Personalities (chronological)
- Hartmann Schenk (born April 7, 1634 in Ruhla near Eisenach), attended high schools in Eisenach and Coburg, went to the University of Helmstedt in 1656, to Jena in 1657, became pastor in Bibra in 1662, deacon in Ostheim in front of the Rhön in 1669 and pastor in Völkershausen where he died on May 2, 1681. His Güldene Prayer from 1677 contains some of his hymns , including the widespread exit hymn : “ Well, thank God it's done, singing, praying, teaching, listening , the last stanza of which is the much-sung Our exit, God bless our entrance . Shortly before his death he composed the death song Father, it is now coming to an end, my years are diminishing . "
- Laurentius Hartmann Schenk (born June 19, 1670 in Ostheim), son of Hartmann Schenk, successor of his father since 1692, died as a pastor in Rodach on September 1, 1730, wrote 23 in his communion book 1718 and in the Römhilder hymn book published by him in 1722 published his own songs, including Jesus, Jesus, Your Love , O Jesus' faithful shepherd and sweet Jesus, my sun .
- Ernst Salomon Cyprian (1673–1745), Lutheran theologian and librarian
- Johann Wendelin Glaser (1713–1783), composer and cantor in Wertheim
- Friedrich Christian Gottlieb Scheidemantel (1735–1796), country doctor, well doctor and formerly medical psychologist
- Johann Kaspar Gensler (1767–1821), legal scholar, born in Ostheim
- Christian Schreiber (1781–1857), philosopher, educator, poet; died in Ostheim
- Wilhelm August Friedrich Genßler (1793–1858), general superintendent in Coburg
- Christian Glock (1801–1881), theologian, physician, musician, later mayor of Ostheim; Friend of the composer Robert Schumann
- Hermann Keßler (1866–1951), Lord Mayor of the cities of Meiningen and Sonneberg
- Hermann Fischer (1894–1968), Lieutenant General in World War II
- Friedrich Högner (1897–1981), born in Oberwaldbehrungen, organist, regional church music director
- Dieter Leipold (1937–2014), co-owner of Peter-Bräu and inventor of the Bionade
- Eberhard Helm (* 1952 in Filke), doctor, German champion, Bavarian champion, 5th at European championships
- Peter Kowalsky (* 1968 in Bad Neustadt an der Saale ), entrepreneur
Web links
- Entry on the coat of arms of Ostheim vor der Rhön in the database of the House of Bavarian History
- Ostheim vor der Rhön: Official statistics of the LfStat
- Ostheim vdRhön community, Ostheim's official website
- Power struggle for the Ostheim exclave (historic event) 1933 to 1945
- Small town, many records Living in Ostheim in front of the Rhön ; Report on Bayern 2 Radio accessed on December 11, 2016
Individual evidence
- ↑ "Data 2" sheet, Statistical Report A1200C 202041 Population of the municipalities, districts and administrative districts 1st quarter 2020 (population based on the 2011 census) ( help ).
- ↑ Location database , accessed on January 17, 2018
- ↑ Wilfried Warsitzka: Die Thüringer Landgrafen Verlag Dr. Bussert & Stadeler, 2004, ISBN 3-932906-22-5 , p. 202
- ^ Eva-Maria Wagner: Winding streets, humpback places . In: Die Rhön (= Merian , vol. 17 (1964), issue 4), pp. 19–24, here p. 24.
- ↑ a b Wilhelm Volkert (Ed.): Handbook of the Bavarian offices, communities and courts 1799–1980 . CH Beck, Munich 1983, ISBN 3-406-09669-7 , p. 452 .
- ↑ Bernhard Post, Volker Wahl (Ed.): Thuringia Handbook 1920–1995. Böhlau, Weimar 1999, p. 461
- ↑ www.historisches-unterfranken.uni-wuerzburg.de . Accessed September 4, 2011.
- ↑ Historic town hall. (No longer available online.) Ostheimrhoen.de, archived from the original on March 25, 2017 ; accessed on March 24, 2017 . Info: The archive link was inserted automatically and has not yet been checked. Please check the original and archive link according to the instructions and then remove this notice.
- ↑ Castles, noble houses and half-timbered houses. (No longer available online.) Ostheimrhoen.de, archived from the original on March 25, 2017 ; accessed on March 24, 2017 . Info: The archive link was inserted automatically and has not yet been checked. Please check the original and archive link according to the instructions and then remove this notice.
- ^ Barrows from the Hallstatt period. Ostheimrhoen.de, accessed on March 24, 2017 .
- ↑ Kirchenburgmuseum Ostheim Rhön. Rhoenline.de, accessed on March 24, 2017 .
- ^ Orgelbaumuseum: Information. (No longer available online.) Orgelbaumuseum.de, archived from the original on February 5, 2017 ; accessed on March 24, 2017 . Info: The archive link was inserted automatically and has not yet been checked. Please check the original and archive link according to the instructions and then remove this notice.
- ↑ Slow Food, Ark of Taste
- ↑ Norman Zellmer: Smallest daily newspaper comes from the Rhön. (No longer available online.) Lausitzer Rundschau, March 9, 2012, archived from the original on January 25, 2017 ; Retrieved January 25, 2017 . Info: The archive link was inserted automatically and has not yet been checked. Please check the original and archive link according to the instructions and then remove this notice.