Jesberg
| coat of arms | Germany map | |
|---|---|---|

|
Coordinates: 51 ° 0 ' N , 9 ° 9' E |
|
| Basic data | ||
| State : | Hesse | |
| Administrative region : | kassel | |
| County : | Schwalm-Eder district | |
| Height : | 243 m above sea level NHN | |
| Area : | 49.77 km 2 | |
| Residents: | 2237 (Dec. 31, 2019) | |
| Population density : | 45 inhabitants per km 2 | |
| Postal code : | 34632 | |
| Area code : | 06695 | |
| License plate : | HR, FZ, MEG, ZIG | |
| Community key : | 06 6 34 010 | |
| Community structure: | 5 districts | |
| Address of the municipal administration: |
Frankfurter Strasse 1 34632 Jesberg |
|
| Website : | ||
| Mayor : | Heiko Manz ( SPD ) | |
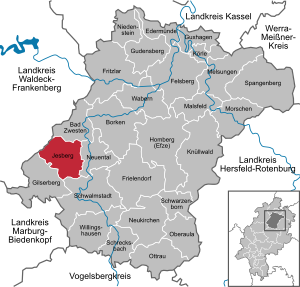
| Location of the community of Jesberg in the Schwalm-Eder district | ||
Jesberg is a municipality in the Schwalm-Eder district in northern Hesse .
geography
Geographical location
Jesberg is located in the valley of the Schwalm tributary Gilsa on the southeast edge of the Kellerwald-Edersee nature park . The desert garden belongs to the municipality, at 675 m above sea level. NN highest mountain in the Kellerwald and the Schwalm-Eder district. The Hemberg ridge is located southwest of the municipality . The federal highway 3 runs through the community from Kassel to Marburg .
Neighboring communities
Jesberg borders in the north on Bad Zwesten , in the east on the community Neuental , in the south on Schwalmstadt and the community Gilserberg (all in the Schwalm-Eder district), and in the west on the community Haina ( district Waldeck-Frankenberg ).
Community structure
The community consists of the districts:
- Jesberg, with the Brünchenhain estate
- Densberg
- Hundshausen , with the Richerode estate
- Elnrode strand
- Reptich , with the Wickershöfen
history

The Jesberg Castle , built at the beginning of the 13th century by the Linsinger family , was sold by them to the Archdiocese of Mainz in 1241 and taken back as a Mainz fief and was from then on - alongside Naumburg , Fritzlar and the Heiligenberg near Felsberg - one of the main bases in Northern Hesse for the Archbishops of Mainz in their disputes with the Landgraves of Hesse . The castle was extensively expanded and strengthened in 1426 and served the troops of Archbishop Konrad III of Mainz . von Dhaun under Count Gottfried von Leiningen, a nephew of the Archbishop, after their heavy defeat on July 23, 1427 on the Großenengliser Platte near Fritzlar as a saving refuge. It was conquered and partially destroyed by Kassel troops in the Hessian fratricidal war between Hessen-Kassel and Hessen-Marburg in 1469, rebuilt in 1524 and gradually fell into disrepair from 1586, when Jesberg became Hessian as a result of the Merlau Treaty of September 8, 1583, and the castle so that it had lost its military importance.
The Baroque castle in Jesberg was Maximilian of Hesse , a son of the Landgrave Karl of Hesse-Kassel , in the first half of the 18th century in Treisbach basic build. His father had assigned him the rule of Jesberg, including the Richerode estate and the village of Hundshausen , in 1723 after the lords of Linsingen and Ludwig Eitel had died out in the male line in 1721 and the Jesberg rule had thus fallen back to the landgrave . Between 1723 and 1753, at the request of Maximilian's four daughters, who survived infancy, the princess garden was built southeast of Jesberg in what is now the Jesberg State Forest.
During the time of the Napoleonic Kingdom of Westphalia (1807-1813), Jesberg was the capital of the canton of Jesberg and seat of the justice of the peace .
Jesberg had a station on the Zimmerrode – Gemünden (Wohra) line , the "Kellerwaldbahn", which was put into operation on October 2, 1911 . On May 28, 1972, passenger traffic on the entire route and goods traffic on the section between Zimmerrode and Gilserberg were suspended.
Probably the oldest place in the municipality is Hundshausen, whose first documentary mention dates back to 969. Densberg was first mentioned in 1085, Elnrode in 1343, Strang in 1565 and Reptich in 1580.
Incorporations
As part of the regional reform in Hesse , Reptich joined the community of Jesberg, which had previously only consisted of the core town of Jesberg and the Brünchenhain estate a good two kilometers to the northwest, on September 1, 1968. On December 31, 1971, the previously independent municipality of Elnrode-Strang followed , and on January 1, 1974, the municipality of Jesberg was given its current form by virtue of state law through the incorporation of Densberg and Hundshausen .
Religions
The majority of the residents of the community belong to the Protestant church . In addition to the core town, the parish of Jesberg includes the districts of Densberg, Hundshausen and Elnrode-Strang as well as Schönstein , politically a district of Gilserberg . Reptich belongs to the parish of Niederurff .
After the Second World War , a Catholic parish was founded in Jesberg , the members of which had moved here mainly as refugees. She initially used a room in Jesberg Castle for her services until her own church was inaugurated in 1967. Today the Catholic parish of Jesberg is looked after by the Neuental parish office .
In the core town of Jesberg there was a Jewish community before the Second World War , which is still remembered today by the Jewish cemetery laid out in 1904/05 outside the town on the edge of the Hembergs . The former synagogue on Densberger Strasse is now used as a residential building.
politics
Community representation
The local elections on March 6, 2016 produced the following results, compared to previous local elections:
| Parties and constituencies |
% 2016 |
Seats 2016 |
% 2011 |
Seats 2011 |
% 2006 |
Seats 2006 |
% 2001 |
Seats 2001 |
||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| SPD | Social Democratic Party of Germany | 54.4 | 8th | 52.8 | 8th | 55.0 | 8th | 51.4 | 8th | |
| CDU | Christian Democratic Union of Germany | 36.8 | 6th | 29.1 | 4th | 32.7 | 5 | 34.4 | 5 | |
| GREEN | Alliance 90 / The Greens | 8.8 | 1 | 11.1 | 2 | 5.7 | 1 | 4.3 | 1 | |
| UWG-Jesberg | Independent voter community Jesberg | - | - | 6.9 | 1 | 6.7 | 1 | 9.9 | 1 | |
| total | 100.0 | 15th | 100.0 | 15th | 100.0 | 15th | 100.0 | 15th | ||
| Voter turnout in% | 59.1 | 64.5 | 62.3 | 72.8 | ||||||
mayor
Mayor has been Heiko Manz ( SPD ) since 2017 , who received 75.5% of the votes in the direct election on March 12th with an opposing candidate. He succeeded Günter Schlemmer (SPD), who held office from 1993 to 2017.
badges and flags
Blazon : “In green in the open circle of six golden (yellow) oak leaves with five golden (yellow) acorns, one with a red small shield with three blue bars, these covered with 3: 3: 1 silver (white) lenses silver (white) tower with three peaks. "
The coat of arms designed by Heinz Ritt was approved by the Hessian Ministry of the Interior on May 6, 1977. The tower symbolizes Linsingen Castle ; the small heart shield comes from the coat of arms of the Lords of Linsingen . The oak leaves and colors refer to the abundance of forests; the acorns stand for the five districts.
The flag was approved on November 3rd, 1988 by the Hessian Ministry of the Interior.
“The flag (banner) of the community of Jesberg points to the longitudinally divided from green - white - green - yellow - green - white - green (4.5: 1: 4.5: 32: 4.5: 1: 4.5) Flag track on the wide yellow middle track in the upper half the municipal coat of arms. "
partnership
Jesberg has had an official partnership with the Polish municipality of Wysoka in the Piła district since 2002 .
Culture and sights
Buildings
The Jesberg Castle with its accessible keep and the remains of Densberg Castle are well worth seeing . The Jesberg Castle and located outside the village in the forest Prinzessingarten evidence of Prince Maximilian of Hesse , who spent much of his life in Jesberg in the 18th century. A historic tithe barn is located on the B 3 .
Hiking in the nature park
Jesberg is located in the Kellerwald-Edersee nature park , which is criss-crossed by numerous hiking trails. A popular destination is the desert garden with the 28 m high Kellerwald tower built in 2003 about 3 km north of Densberg. The Kellerwaldsteig and the Lullus Path , among others, lead through the municipality . There is an educational forest trail between Jesberg and Densberg .
Club life
Public life in the community is shaped by associations that organize numerous regular events. There are volunteer fire departments in all parts of the village . A charcoal burner association has revived the traditional charcoal making in the Kellerwald and is offering public demonstrations. The amateur drama group Densberger Breakfast performs a play every summer on an open-air stage in the former Densberg moat . The largest sports club is TSV Jesberg.
Infrastructure
Leisure center
The Jesberg leisure center , located on the Gilsa next to the community center, offers restaurants, a campsite , a heated outdoor pool , a sports field, three tennis courts and other sports and leisure opportunities.
Other facilities
In Jesberg there is a primary school , a kindergarten , a community center and a library run by volunteers. The districts of Densberg, Elnrode, Hundshausen and Reptich have village community houses. There are also a total of five children's playgrounds, two barbecue areas with barbecue huts and a water treading pool.
Old stone bridge over the Gilsa in Jesberg
Jesberg Castle Hill with keep
Kellerwald tower on the desert garden
Personalities
- Hugo Brunner (1853–1922), historian, died in Jesberg
- Christoph Friedrich Wilhelm Ernst (1765–1855), theologian, born in Jesberg
- Dieter Jahn (* 1959), biochemist and microbiologist
- Heinz Körner (* 1944), writer, born in Jesberg
- Adam Sporleder (1772–1846), farmer, May 1809 to August 1811 Maire (mayor) von Jesberg and member of parliament
literature
- Wilhelm Bach: Historical news from the court and the parish of Jesberg in the Electorate of Hesse, Cassel, 1828 ( online at google books )
Web links
- Jesberg (Lenswindehusen), Schwalm-Eder district. Historical local dictionary for Hessen. In: Landesgeschichtliches Informationssystem Hessen (LAGIS).
- Jesberg Castle, Schwalm-Eder-Kreis, Schwalm-Eder-Kreis. Historical local dictionary for Hessen. In: Landesgeschichtliches Informationssystem Hessen (LAGIS).
- Link catalog on Jesberg at curlie.org (formerly DMOZ )
- Illustration by Daniel Meisner from 1625: Jespúrg. When violence occurs, the law is dead ( digitized version )
Individual evidence
- ↑ Hessian State Statistical Office: Population status on December 31, 2019 (districts and urban districts as well as municipalities, population figures based on the 2011 census) ( help ).
- ↑ He was a relative, probably a nephew, of the former Provost of Mainz Cathedral and Bishop Elect Gottfried von Leiningen , who had died in 1410.
- ^ Dietrich Christoph von Rommel: History of Hessen , Volume 5, Kassel 1835 (p. 413)
- ↑ Law on the reorganization of the districts Fritzlar-Homberg, Melsungen and Ziegenhain (GVBl. II 330-22) of September 28, 1973 . In: The Hessian Minister of the Interior (ed.): Law and Ordinance Gazette for the State of Hesse . 1973 No. 25 , p. 356 , § 9 ( online at the information system of the Hessian state parliament [PDF; 2,3 MB ]).
- ^ Federal Statistical Office (ed.): Historical municipality directory for the Federal Republic of Germany. Name, border and key number changes in municipalities, counties and administrative districts from May 27, 1970 to December 31, 1982 . W. Kohlhammer GmbH, Stuttgart / Mainz 1983, ISBN 3-17-003263-1 , p. 392 f .
- ^ Result of the municipal election on March 6, 2016. Hessian State Statistical Office, accessed in April 2016 .
- ^ Hessian State Statistical Office: Result of the municipal elections on March 27, 2011
- ^ Hessian State Statistical Office: Result of the municipal elections on March 26, 2006
- ↑ Direct elections in Jesberg at statistik-hessen.de
- ↑ State Gazette for the State of Hesse 1977 Official Gazette No. 21 page 1071 Approval of a coat of arms for the community of Jesberg
- ↑ State Gazette for the State of Hesse 1988 Official Journal No. 48 Page 2564 Approval of a flag for the community of Jesberg