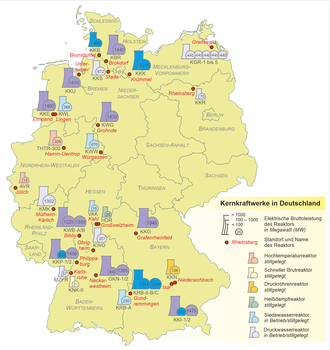
List of nuclear reactors in Germany
The list of nuclear reactors in Germany includes nuclear power plants that are in operation or shut down, nuclear power plants that have not started operating and research reactors.
Overview
While in the first nuclear test facilities in the Third Reich as part of the uranium project 1940–1945 proof of neutron multiplication could be achieved , but no self-sustaining chain reaction , around 110 nuclear facilities were put into operation in Germany between 1957 and 2004. A distinction must be made between nuclear reactors for energy generation and research reactors . The first nuclear reactors to go into operation in October and December 1957 were the Munich Research Reactor in Garching (FRG) and the Rossendorfer Research Reactor (DDR ) in operation. The Kahl nuclear power plant was the first nuclear power plant to go online in February 1962. In 1989, Block 5 of the Greifswald nuclear power plant was the last commercial nuclear reactor to be synchronized with the grid. The training nuclear reactor in Dresden received its operating license in 2004 as the last research reactor to date.
On January 1, 1960, the law on the peaceful use of nuclear energy and the protection against its dangers ( Atomic Energy Act for short ) came into force in West Germany . Since then it has been changed and supplemented several times. Since the agreement between the federal government and the energy supply companies of June 15, 2000 (the so-called nuclear consensus ), the use of the existing nuclear power plants is limited in time and there is a new construction ban (no permits for the construction of new nuclear power plants). Research in the field of nuclear engineering is unaffected by the atomic consensus. The nuclear energy consensus agreement stipulates an amount of electricity still to be generated (“ residual electricity amount ”) for each nuclear power plant. In principle, these so-called residual amounts of electricity can be transferred from older power plants to newer ones, and vice versa only in exceptional cases. Once a nuclear power plant has generated its allocated residual electricity, it must be shut down. The agreements made were implemented by the law on the orderly termination of the use of nuclear energy for the commercial generation of electricity of April 22, 2002.
At that time it was planned that the 19 commercially used nuclear power plant blocks would be shut down by 2021. Two nuclear power plants, Stade and Obrigheim , were shut down in 2003 and 2005; Block 2 of the Neckarwestheim nuclear power plant was to be the last to go offline. At the end of the SPD's participation in government in 2009, 17 commercially used nuclear power plant units and 11 research reactors, including 6 teaching reactors, were still in operation.
The black and yellow majority in the Bundestag decided on October 28, 2010 to extend the term after it had previously been approved by the black and yellow federal cabinet. On average, the nuclear power plants should be in operation twelve years longer than the nuclear consensus from the year 2000, concluded between the red-green government (Schröder / Fischer) and the nuclear industry, was agreed. On December 8, 2010, the law extending the term was signed by Federal President Christian Wulff . The SPD-led federal states of Berlin, Brandenburg, Bremen, North Rhine-Westphalia and Rhineland-Palatinate filed an action against this law with the Federal Constitutional Court on February 28, 2011.
Due to the nuclear accidents in Fukushima , the Chancellor announced on March 15, 2011 an " atomic moratorium ", whereby the seven oldest German nuclear power plants should be switched off during the moratorium - this probably did not correspond to the legal situation, as the government does not give a simple request from parliament may override enacted law. This nuclear moratorium also included a three-month suspension of the term extension and the shutdown of the seven oldest German nuclear power plants during this moratorium. The RWE group affected by this, along with others , filed a lawsuit against the shutdown of the Biblis A nuclear power plant with the competent Hessian administrative court on April 1, 2011 . RWE cited the lack of a legal basis for the moratorium.
When the amendment to the Atomic Energy Act came into force on August 6, 2011, the seven oldest nuclear power plant units in Germany and the Krümmel nuclear power plant finally lost their operating license. The plan to keep one of the blocks in reserve was rejected by the Federal Network Agency at the end of August 2011. The remaining nine units, six of which are still in operation, must be shut down in accordance with the Atomic Energy Act by the end of 2022 at the latest, Grafenrheinfeld was shut down on June 28, 2015, Gundremmingen B on December 31, 2017 and Philippsburg 2 on December 31, 2019.
Nuclear power plants
Nuclear power plants are all power reactors and prototype systems that are used for commercial electricity generation. The highlighted reactors are in operation.
| designation | country | Abbreviation | Type | operator | Gross output in MW |
Net output in MW |
Energy production by 2018 in TWh |
Residual amount of electricity from January 2020 in TWh |
start of building | Start of commercial operation | Out of operation at the latest in accordance with Section 7 (1a) AtG |
Average availability over the operating period |
status |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Isar / Ohu 2 | BY | KKI 2 | PWR (KWU convoy ) | PreussenElektra | 1485 | 1410 | 324.0 | 9.0 | Sep 15 1982 | Apr 9, 1988 | Dec 31, 2022 | 93.2% | In operation |
| Brokdorf | SH | KBR | PWR (KWU pre-convoy ) | PreussenElektra | 1480 | 1410 | 324.3 | 5.5 | Jan. 1, 1976 | Dec 22, 1986 | Dec 31, 2021 | 89.4% | In operation |
| Philippsburg 2 | BW | KKP 2 | DWR | EnBW | 1468 | 1402 | 336.8 | 1.7 | Jul 7, 1977 | Apr 18, 1985 | December 31, 2019 | 88.2% | In dismantling |
| Grohnde | NI | KWG | PWR (KWU pre-convoy ) | PreussenElektra | 1430 | 1360 | 346.9 | 7.9 | Jun 1, 1976 | Feb. 1, 1985 | Dec 31, 2021 | 91.7% | In operation |
| Lower Weser | NI | KKU | DWR | PreussenElektra | 1410 | 1345 | 289.8 | Jul 1, 1972 | 6 Sep 1979 | Aug 6, 2011 | 83.7% | In dismantling (until 2031) |
|
| Crumbs | SH | KKK | SWR | Vattenfall | 1402 | 1346 | 201.7 | 78.2 | Apr 5, 1974 | March 28, 1984 | Aug 6, 2011 | 67.9% | Out of operation (dismantling planned by 2038) |
| Emsland | NI | KKE | PWR (KWU convoy) | RWE | 1406 | 1335 | 328.9 | 30.3 | Aug 10, 1982 | Jun 20, 1988 | Dec 31, 2022 | 93.8% | In operation |
| Neckarwestheim 2 | BW | GKN 2 | PWR (KWU convoy) | EnBW | 1400 | 1310 | 300.2 | 28.6 | Nov 9, 1982 | Apr 15, 1989 | Dec 31, 2022 | 93.0% | In operation |
| Grafenrheinfeld | BY | KKG | DWR | PreussenElektra | 1345 | 1275 | 315.6 | Jan. 1, 1975 | Jun 17, 1982 | Jun 27, 2015 | 88.7% | In dismantling (until 2035) |
|
| Gundremmingen C | BY | KRB C | SWR (KWU construction line 72) | RWE | 1344 | 1288 | 315.2 | 11.9 | Jul 20, 1976 | Jan. 18, 1985 | Dec 31, 2021 | 89.3% | In operation |
| Gundremmingen B. | BY | KRB B | SWR | RWE | 1344 | 1284 | 314.5 | 1.0 | Jul 20, 1976 | Jul 19, 1984 | December 31, 2017 | 90.4% | In dismantling (until 2040) |
| Mülheim-Kärlich | RP | KMK | DWR | RWE | 1302 | 1219 | 10.3 | 34.4 | Jan 15, 1975 | Oct 1, 1987 | Sep 9 1988 | 76.0% | In dismantling (until 2021) |
| Biblis B | HE | KWB B | DWR | RWE | 1300 | 1240 | 247.4 | Feb. 1, 1972 | Jan. 31, 1977 | Aug 6, 2011 | 74.5% | In dismantling (until after 2032) |
|
| Biblis A | HE | KWB A | DWR | RWE | 1225 | 1167 | 232.8 | Jan. 1, 1970 | Feb. 26, 1975 | Aug 6, 2011 | 68.7% | In dismantling (until after 2032) |
|
| Philippsburg 1 | BW | KKP 1 | SWR | EnBW | 926 | 890 | 187.6 | Oct. 1, 1970 | March 26, 1980 | Aug 6, 2011 | 80.3% | In dismantling | |
| Isar / Ohu 1 | BY | KKI 1 | SWR | PreussenElektra | 912 | 878 | 198.3 | May 1, 1972 | March 21, 1979 | Aug 6, 2011 | 86.0% | In dismantling (until 2032) |
|
| Neckarwestheim 1 | BW | GKN 1 | DWR | EnBW | 840 | 785 | 186.8 | Feb. 1, 1972 | Dec. 1, 1976 | Aug 6, 2011 | 84.7% | In dismantling | |
| Brunsbuettel | SH | KKB | SWR | Vattenfall | 806 | 771 | 120.4 | 11.0 | Apr 15, 1970 | Feb 9, 1977 | Aug 6, 2011 | 57.9% | In dismantling (until 2033) |
| Stade | NI | KKS | DWR | PreussenElektra | 672 | 640 | 145.9 | Dec. 1, 1967 | May 19, 1972 | Nov 14, 2003 | 85.3% | In dismantling (until 2023) |
|
| Würgassen | NW | KWW | SWR | PreussenElektra | 670 | 640 | 69.7 | Jan. 26, 1968 | Nov 11, 1975 | Aug 26, 1994 | 71.9% | In dismantling (until 2028) |
|
| Greifswald 1 | MV | KGR 1 | VVER | EWN | 440 | 408 | 35.5 | March 1, 1970 | Jul 12, 1974 | Dec 18, 1990 | 65.8% | In dismantling (until 2028) |
|
| Greifswald 2 | MV | KGR 2 | VVER | EWN | 440 | 408 | 36.6 | March 1, 1970 | Apr 16, 1975 | Feb. 14, 1990 | 70.6% | In dismantling (until 2028) |
|
| Greifswald 3 | MV | KGR 3 | VVER | EWN | 440 | 408 | 33.3 | Apr 1, 1972 | May 1, 1978 | Feb 28, 1990 | 78.8% | In dismantling (until 2028) |
|
| Greifswald 4 | MV | KGR 4 | VVER | EWN | 440 | 408 | 28.9 | Apr 1, 1972 | Nov 1, 1979 | Jun 2, 1990 | 78.0% | In dismantling (until 2028) |
|
| Greifswald 5 | MV | KGR 5 | VVER | EWN | 440 | 408 | 0.0 | Dec. 1, 1976 | Jul 12, 1974 | Nov. 24, 1989 | In dismantling (until 2028) |
||
| Obrigheim | BW | KWO | DWR | EnBW | 357 | 340 | 86.8 | March 15, 1965 | Apr 1, 1969 | May 11, 2005 | 83.7% | In dismantling (until 2025) |
|
| Hamm-Uentrop | NW | THTR | HTR | HKG | 308 | 296 | 2.8 | May 1, 1971 | Jun 1, 1987 | Apr 29, 1988 | 56.0% | In secure confinement (2030) |
|
| Lingen | NI | KWL | SWR | RWE | 268 | 183 | 9.1 | Oct. 1, 1964 | Oct. 1, 1968 | Jan. 5, 1979 | 42.2% | In dismantling (until 2035) |
|
| Gundremmingen A | BY | KRB | SWR | RWE | 250 | 237 | 13.8 | Dec 12, 1962 | Apr 12, 1967 | Jan. 13, 1977 | 81.2% | Dismantling suspended, 2006 conversion to "technology center" |
|
| Niederaichbach | BY | KKN | HWCR | without ( "green meadow" ) |
106 | 100 | 0.0 | Jun 1, 1966 | Jan. 1, 1973 | Jul 31, 1974 | 9.0% | dismantled | |
| Rheinsberg | BB | KKR | VVER | EWN | 70 | 62 | 9.0 | Jan. 1, 1960 | Oct 11, 1966 | Jun 1, 1990 | 61.0% | In dismantling (until 2025) |
|
| MZFR Karlsruhe | BW | MZFR | DWR | EWN | 57 | 52 | 4.8 | Dec. 1, 1961 | Dec. 19, 1966 | May 3, 1984 | 73.3% | In dismantling (until 2021) |
|
| Großwelzheim | BY | HDR | HDR | without ("green meadow") |
25th | 25th | 0.0 | Jan. 1, 1965 | Aug 2, 1970 | Apr 20, 1971 | dismantled | ||
| KNK Karlsruhe I | BW | KNK I | BR | EWN | 21st | 17th | 0.5 | May 1, 1966 | Feb. 21, 1974 | Sep 1 1974 | In dismantling | ||
| KNK Karlsruhe II | BW | KNK II | BR | EWN | 21st | 17th | 0.3 | Sep 1 1974 | March 3, 1979 | 23 Aug 1991 | 26.8% | In dismantling | |
| Bald | BY | VAK | SWR | without ("green meadow") |
16 | 15th | 2.0 | Jul 1, 1958 | Feb. 1, 1962 | Nov 25, 1985 | 67.8% | dismantled | |
| Jülich | NW | AVR | HTR | EWN | 15th | 13 | 1.5 | Aug 1, 1961 | May 19, 1969 | Dec 31, 1988 | 65.9% | In dismantling |
- Remarks
- ↑ a b c In February 2020, 6 TWh were transferred from the Krümmel nuclear power plant to the Isar 2 nuclear power plant and 5 TWh to the Brokdorf nuclear power plant.
- ↑ On July 4, 2009 there was an emergency reactor shutdown due to a fault in a machine transformer. From then on until the loss of the operating license (" nuclear phase-out ") on August 6, 2011, Krümmel was in 'standstill'
- ↑ see AVR (Jülich) # Dismantling, disposal .
Nuclear power plants without starting operations
This list includes planned nuclear power plants for which a permit application has been submitted and rejected, as well as nuclear power plants that have been partially built or completed but never went into operation. Those nuclear power plants whose construction has started are highlighted in dark gray.
| designation |
federal country |
plan clothes |
Start of construction |
End of project |
Further information |
Gross (MW) |
Net (MW) |
Type |
Working leg |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Bad Breisig |
|
1971 | - | ? | Planning set after a short time due to lack of space (drinking water protection, earthquake), to replace a few kilometers upriver was the nuclear power plant in Mülheim-Kärlich built | 1300 | ? | DWR | |
| BASF 1 |
|
1973 | - | December 01, 1976 | was replaced by a fossil-fired steam power plant (commissioning 2005) | 425 | 385 | DWR | |
| Biblis C |
|
1975 | - | 1995 | Components that have already been manufactured were used for the Angra 2 nuclear power plant (Brazil) | 1315 | 1238 | DWR | |
| Biblis D |
|
1973 | - | 01/01/1979 | ? | 1300 | DWR | ||
| Bark |
|
1974 | - | 1995 | 1300 | 1200 | DWR | ||
| Dahlen 1 |
|
1980 | - | Spring 1990 | 1000 | 950 | DWR | ||
| Dahlen 2 |
|
1980 | - | Spring 1990 | 1000 | 950 | DWR | ||
| Dahlen 3 |
|
1980 | - | Spring 1990 | 1000 | 950 | DWR | ||
| Dahlen 4 |
|
1980 | - | Spring 1990 | 1000 | 950 | DWR | ||
| Emden |
|
1975 | - | ? | the planned location was Rysumer Sand | 1300 | ? | DWR | |
| Greifswald 6 |
|
? | December 01, 1976 | 01/01/1990 | Construction was completed, no operations started | 440 | 408 | DWR | |
| Greifswald 7 |
|
? | December 01, 1978 | 10/01/1990 | Construction was canceled | 440 | 408 | DWR | |
| Greifswald 8 |
|
? | December 01, 1978 | 10/01/1990 | Construction was canceled | 440 | 408 | DWR | |
| Hamm |
|
1975 | - | 1995 | the Emsland nuclear power plant was built as a replacement | 1301 | 1231 | DWR | |
| Kalkar 1 |
|
1969 | 04/23/1973 | 03/20/1991 | Construction was completed in 1985, no operations started | 327 | 295 | SNR | |
| Neupotz A. |
|
1977 | - | 1987 | 1368 | 1289 | DWR | ||
| Neupotz B. |
|
1977 | - | 1987 | 1368 | 1289 | DWR | ||
| Pfaffenhofen A |
|
1976 | - | 1999 | 1315 | 1238 | DWR | ||
| SNR-2 |
|
1975 | - | 1982 | The Kalkar location had not yet been finalized | 1500 | 1380 | SNR | |
| Stendal 1 |
|
1980 | December 01, 1982 | 03/01/1991 | 85 percent of the construction was completed | 970 | 900 | DWR | |
| Stendal 2 |
|
1980 | December 01, 1984 | 03/01/1991 | Construction was completed to 15 percent | 970 | 900 | DWR | |
| Vahnum A |
|
1975 | - | ? | 1300 | 1231 | DWR | ||
| Vahnum B. |
|
1975 | - | ? | 1300 | 1231 | DWR | ||
| Wyhl 1 |
|
1973 | - | ? | Originally the intended location was Breisach . Planning was canceled in 1977 and the components for the Philippsburg 2 nuclear power plant were used | 1375 | 1300 | DWR |
|
Research reactors
“Research reactor” is the name given to nuclear reactors that are not used to generate electricity, but primarily for research purposes (nuclear and material research, isotope production for medicine and technology ). The following list is sorted according to the commissioning of the research reactors. Reactors marked yellow are still in operation.
| Surname | designated voltage |
operator | federal country |
commissioning acceptance |
Out of service | status | Power (therm.) |
Reactor type |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Research reactor Munich | FRM | Technical University of Munich |
|
10/31/1957 | 07/28/2000 | Decommissioning on April 3rd, 2014, being dismantled |
4 MW | Swimming pool / MTR |
| Rossendorf research reactor | RFR | FZ Rossendorf |
|
December 16, 1957 | 06/27/1991 | dismantled | 10 MW | LWR |
| Research reactor Frankfurt -1 | FRF-1 | University of Frankfurt |
|
01/10/1958 | 03/19/1968 | started conversion to FRF-2, dismantled |
50 kW | homogeneous (L) / L-54 (L) |
| Research reactor Frankfurt -2 | FRF-2 | University of Frankfurt |
|
not applicable | not applicable | not finished, dismantled |
1 MW (planned) |
Swimming pool / TRIGA |
| Berlin experimental reactor I | BER I | Helmholtz Center Berlin |
|
07/24/1958 | 1972 | in safe enclosure | 50 kW | homogeneous (L) / L-54 (L) |
| Research reactor Geesthacht -1 | FRG-1 | GKSS |
|
10/23/1958 | 06/28/2010 | to be dismantled by 2020 | 5 MW | Swimming pool / MTR |
| Siemens Argonaut reactor | SAR | Technical University of Munich |
|
06/23/1959 | 10/31/1968 | dismantled | 1 kW | Argonaut |
| AEG test reactor | PR-10 | Kraftwerk Union |
|
01/27/1961 | 1976 | shut down | 180 watts | Argonaut |
| Research reactor 2 | FR-2 | FZ Karlsruhe |
|
07.03.1961 | December 21, 1981 | in dismantling | 44 MW | HWR |
| Research reactor Jülich 1 (MERLIN) | FRJ-1 | FZ Jülich |
|
02/23/1962 | March 22, 1985 | dismantled | 10 MW | Swimming pool / MTR |
| Siemens teaching reactor Munich | SUR-M | Technical University of Munich |
|
02/28/1962 | 08/10/1981 | dismantled | 0.1 watt | homogeneous (S) / SUR-100 |
| Research reactor Jülich 2 (DIDO) | FRJ-2 | FZ Jülich |
|
11/14/1962 | 05/02/2006 | in dismantling | 23 MW | Tank / HWR |
| Rossendorfer ring zone reactor | RRR | FZ Rossendorf |
|
December 16, 1962 | 09/25/1991 | dismantled | 1 kW | Argonaut |
| Fast thermal argonaut reactor | STRONG | FZ Karlsruhe |
|
01/11/1963 | 03.1976 | dismantled | 10 watts | Argonaut |
| Research reactor Geesthacht -2 | FRG-2 | GKSS |
|
March 16, 1963 | 01/28/1993 | in dismantling | 15 MW | Swimming pool / MTR |
| Siemens teaching reactor Berlin | SUR-B | TU Berlin |
|
07/26/1963 | 10/15/2007 | Shutdown on April 16, 2013 | 0.1 watt | homogeneous (S) / SUR-100 |
| Siemens teaching reactor Darmstadt | SUR-DA | TU Darmstadt |
|
23.09.1963 | 02/22/1985 | dismantled | 0.1 watt | homogeneous (S) / SUR-100 |
| Facility for zero power experiments | ANEX | GKSS |
|
05.1964 | 02/05/1975 | dismantled | 100 watts | Zero power reactor |
| Siemens teaching reactor Stuttgart | SUR-S | University of Stuttgart |
|
08/24/1964 | in operation | 0.1 watt | homogeneous (S) / SUR-100 | |
| Siemens teaching reactor Hamburg | SUR-HH | University of Applied Sciences Hamburg |
|
January 15, 1965 | 08.1992 | dismantled | 0.1 watt | homogeneous (S) / SUR-100 |
| Research reactor Mainz | FRMZ | University of Mainz |
|
08/03/1965 | in operation | 100 kW | Swimming pool / TRIGA -II | |
| Siemens teaching reactor Aachen | Sur-AA | RWTH Aachen |
|
09/22/1965 | 2002 | Application for decommissioning made in 2010 | 0.1 watt | homogeneous (S) / SUR-100 |
| Siemens teaching reactor Ulm | SUR-U | Ulm University of Applied Sciences |
|
December 01, 1965 | in operation | 0.1 watt | homogeneous (S) / SUR-100 | |
| Siemens teaching reactor Kiel | SUR-KI | FH Kiel |
|
March 29, 1966 | 12/11/1997 | dismantled | 0.1 watt | homogeneous (S) / SUR-100 |
| Siemens teaching reactor Karlsruhe | SUR-KA | FZ Karlsruhe |
|
07.03.1966 | 09.1996 | dismantled | 0.1 watt | homogeneous (S) / SUR-100 |
| Research reactor TRIGA Heidelberg I | TRIGA HD I. | DKFZ |
|
August 26, 1966 | March 31, 1977 | dismantled | 250 kW | Swimming pool / TRIGA -I |
| Fast zero energy arrangement | SNEAK | FZ Karlsruhe |
|
December 15, 1966 | 11.1985 | shut down | 1 kW | Zero power reactor |
| Burn measurement | ADIBKA | FZ Jülich |
|
03/18/1967 | 10/30/1972 | Shutdown on 12/1977 | 100 watts | homogeneous / L77 A |
| AEG zero energy reactor | TKA | Kraftwerk Union |
|
06/23/1967 | 1973 | Shutdown on December 21, 1981 | 100 watts | Tank / zero power reactor |
| Research and measurement reactor Braunschweig | FMRB | PTB |
|
10/03/1967 | December 19, 1995 | dismantled | 1 MW | Swimming pool / MTR |
| Siemens teaching reactor Bremen | SUR-HB | University of Bremen |
|
10/10/1967 | 06/17/1993 | dismantled | 0.1 watt | homogeneous (S) / SUR-100 |
| Nuclear ship "Otto Hahn" | OH | GKSS |
|
08/26/1968 | March 22, 1979 | scrapped | 38 MW | PWR / ship reactor |
| Rossendorf arrangement for critical experiments | RAKE | FZ Rossendorf |
|
10/03/1969 | 11/26/1991 | dismantled | 10 watts | Tank / zero power reactor |
| Critical experiment | KEITER | FZ Jülich |
|
06/15/1971 | 1982 | Shutdown on 6/1988 | 1 watt | Zero power reactor |
| Siemens teaching reactor Hanover | SUR-H | University of Hanover |
|
December 9, 1971 | 2008 | Shutdown in September 2019 | 0.1 watt | homogeneous (S) / SUR-100 |
| Neuherberg research reactor | FRN | GSF |
|
08/23/1972 | December 16, 1982 | safe confinement | 1 MW | Swimming pool / TRIGA -III |
| Research reactor Hanover | FRH | MH Hannover |
|
January 31, 1973 | 12/18/1996 | dismantled | 250 kW | Swimming pool / TRIGA -I |
| Siemens teaching reactor Furtwangen | SUR-FW | Furtwangen University |
|
06/28/1973 | in operation | 0.1 watt | homogeneous (S) / SUR-100 | |
| Critical arrangement | KAHTER | FZ Jülich |
|
07/02/1973 | 02/03/1984 | Shutdown on 6/1988 | 100 watts | Zero power reactor |
| Berlin experimental reactor II | BER II | Helmholtz Center Berlin |
|
December 9, 1973 | December 11, 2019 | to be dismantled by 2033 | 10 MW | Swimming pool / MTR |
| Research reactor TRIGA Heidelberg II | TRIGA HD II | DKFZ |
|
02/28/1978 | 11/30/1999 | dismantled | 250 kW | Swimming pool / TRIGA -I |
| Training nuclear reactor Dresden -1 | AKR-1 | TU Dresden |
|
07/28/1978 | 03.2004 | replaced by AKR 2 | 2 watts | homogeneous / SUR type |
| Zittau teaching and research reactor | ZLFR | University of Zittau |
|
May 25, 1979 | 03/24/2005 | dismantled | 10 watts | HWR |
| Research reactor Munich II | FRM II | Technical University of Munich |
|
03/02/2004 | in operation | 20 MW | Swimming pool / HWR | |
| Training nuclear reactor Dresden -2 | AKR-2 | TU Dresden |
|
03/22/2005 | in operation, replaces AKR 1 | 2 watts | homogeneous / SUR type |
Status: December 2019
In addition, a number of test reactors were constructed in the German uranium project during the Second World War , but none of them became critical . The last of these attempts was the Haigerloch research reactor , a heavy water reactor that was built by the Kaiser Wilhelm Institute for Physics in March / April 1945 in a rock cellar in Haigerloch in Hohenzollern .
Reactor type
- PWR = pressurized water reactor: In a pressurized water reactor, the water in the primary circuit, which is used as a coolant, is under increased pressure.
- BWR = boiling water reactor: In a boiling water reactor, the coolant water in the reactor is converted into steam to drive the turbine directly.
- Zero power reactor : A reactor with very low thermal power that is used for training and research purposes. Due to the low output, this type of reactor actually has no temperature increase even in the crevice zone , which is why systems for heat removal are unnecessary.
- TRIGA : A swimming pool-type research reactor in which safety is guaranteed by the laws of nature and not by engineering measures that could be bridged.
- HDR = superheated steam boiling water reactor: A boiling water reactor with integrated nuclear superheating.
- homogeneous: A reactor in which the fuel is present as a mixture with moderator or coolant.
- HTR = high-temperature reactor: In the high-temperature reactor, the reactor core is cooled with the noble gas helium , which is heated when it flows through the ball bed (bed of spherical fuel elements).
- HWR = Heavy Water Reactor: A type of reactor that uses heavy water as a coolant and moderator .
- HWCR : Heavy water moderated , CO 2 -cooled pressure tube reactor; In the reactor, the fuel elements are located within numerous tubes in which the coolant (CO 2 gas) circulates.
- MTR : A material test reactor with a very compact reactor core in order to achieve the greatest possible neutron flux density.
- Swimming pool : The fuel elements are immersed in an open water basin so that interventions and experiments for research purposes and training are possible.
- SBR = fast breeder reactor: The nuclear fission takes place with fast, unrestrained neutrons.
See also
- List of nuclear power plants worldwide
- List of nuclear facilities worldwide
- List of reportable events in German nuclear facilities
literature
- Manfred Petroll, Liane Philipp: Nuclear technology - plants in Germany . Edited by INFORUM publishing and management company, Bonn 1997, ISBN 3-926956-11-9 .
Web links
- Federal Office for Radiation Protection
- Country Statistics Germany IAEA, Power Reactor Information System (English)
- Germany (PDF) IAEA, Nuclear Profile (English)
- Nuclear power plants in Germany and the evacuation radii recommended by the Federal Office for Radiation Protection and the size of the affected population, ZDF module
Individual evidence
- ↑ Law on the orderly termination of the use of nuclear energy for the commercial generation of electricity. (PDF) (No longer available online.) April 22, 2002, archived from the original on October 20, 2016 ; Retrieved January 5, 2017 . Info: The archive link was inserted automatically and has not yet been checked. Please check the original and archive link according to the instructions and then remove this notice.
- ↑ The SPD and the Greens are submitting a constitutional complaint. In: Spiegel Online. February 28, 2011, accessed January 5, 2017 .
- ↑ a b Seven nuclear power plants are going offline for the time being. In: Frankfurter Allgemeine Zeitung. March 15, 2011, accessed January 5, 2017 .
- ^ ARD broadcast ( memento from March 17, 2011 in the Internet Archive ), "Can the government just decide that?" dated March 16, 2011, last accessed on March 16, 2011.
- ↑ That's how risky the old reactors are. In: stern.de. March 15, 2011, accessed January 5, 2017 .
- ↑ cf. RWE is suing against Biblis shutdown. In: FOCUS Online. April 1, 2011, accessed January 5, 2017 .
- ↑ Federal Network Agency will not order the reserve operation of a nuclear power plant. In: Federal Network Agency for Electricity, Gas, Telecommunications, Post and Railways. August 31, 2011, accessed January 5, 2017 .
- ↑ Net electricity in TWh - net electricity generation in billions of kilowatt hours since commissioning until the end of December 2018 or until shutdown. Data source: IAEO - Power Reactor Information System
- ↑ Annual Report 2019 - Amounts of electricity generated, transmitted and remaining from January 1, 2000 to December 31, 2019. (PDF) In: Running times and electricity quantities of German nuclear power plants . Federal Office for the Safety of Nuclear Waste Management , accessed on February 15, 2020 .
- ↑ Data source: IAEO - Power Reactor Information System, as of December 31, 2018.
- ↑ The power plant was taken off the grid on March 18, 2011 in accordance with the nuclear moratorium
- ↑ heise.de
- ↑ Bayerischer Rundfunk: Nuclear power plant to disappear by 2035 April 12, 2018, accessed: September 4, 2018.
- ↑ Augsburger Allgemeine: This is how the Gundremmingen nuclear power plant is being dismantled March 25, 2017, accessed on December 31, 2017.
- ↑ Philippsburg 1 was shut down on March 17, 2011 for the three-month nuclear moratorium
- ↑ Isar / Ohu was shut down on March 17, 2011 as part of the nuclear moratorium
- ↑ Brunsbüttel was shut down completely on July 21, 2007 and not restarted until its operating license expired.
- ^ Nuclear phase-out: Schleswig-Holstein permits the demolition of nuclear power plants in Brunsbüttel. In: Spiegel Online. December 21, 2018, accessed December 23, 2018 .
- ↑ The dismantling of the nuclear power plant will continue until 2023. In: Tageblatt.de. Retrieved February 14, 2017 .
- ↑ hna.de HNA.de:AKW Würgassen: Dismantling until 2028, accessed on March 4, 2014.
- ↑ a b c d e Dieter Nebel - On the reactor safety philosophy of Soviet nuclear power plants - Meeting reports of the Leibnitz Society 7 (1995) (PDF) - page 85ff
- ↑ Dismantling of the Obrigheim nuclear power plant | EnBW. Retrieved March 2, 2020 .
- ↑ derwesten.de DerWesten.de: The expensive end of a nuclear power plant from July 29, 2011, accessed on July 30, 2011 and WAZ from July 30, 2011.
- ↑ Multipurpose Research Reactor (MZFR). Retrieved December 23, 2018 .
- ↑ no longer in the current statistics of the IAEA
- ↑ Gross - gross output in megawatts (MW)
- ↑ Net - net power in megawatts (MW)
- ↑ Goldene Meile industrial park - the near nuclear power plant. October 24, 2013, accessed December 9, 2018 .
- ↑ 6-1.2 List of recommendations and statements of the Reactor Safety Commission (RSK) ( Memento of the original from February 22, 2014 in the Internet Archive ) Info: The archive link was automatically inserted and not yet checked. Please check the original and archive link according to the instructions and then remove this notice.
- ↑ BASF 1 nuclear power plant ( Memento from June 4, 2011 in the Internet Archive )
- ↑ Biblis C nuclear power plant ( Memento from June 4, 2011 in the Internet Archive )
- ↑ Biblis D nuclear power plant ( Memento from June 4, 2011 in the Internet Archive )
- ↑ Borken nuclear power plant ( Memento from June 4, 2011 in the Internet Archive )
- ^ A b c d Felix Christian Matthes: Dahlen 1-4: Electricity industry and German unity. BoD - Books on Demand, 2000, ISBN 3-89811-806-1 , pp. 59-60.
- ↑ Emden nuclear power plant ( Memento from June 4, 2011 in the Internet Archive )
- ↑ Greifswald 6 nuclear power plant ( Memento from June 4, 2011 in the Internet Archive )
- ↑ Greifswald 7 nuclear power plant ( Memento from June 4, 2011 in the Internet Archive )
- ↑ Greifswald 8 nuclear power plant ( Memento from June 4, 2011 in the Internet Archive )
- ↑ Hamm nuclear power plant ( Memento from June 4, 2011 in the Internet Archive )
- ↑ Kalkar nuclear power plant ( Memento from June 4, 2011 in the Internet Archive )
- ↑ Neupotz A nuclear power plant ( Memento from June 4, 2011 in the Internet Archive )
- ↑ Neupotz B nuclear power plant ( Memento from June 4, 2011 in the Internet Archive )
- ↑ Pfaffenhofen nuclear power plant ( Memento from June 4, 2011 in the Internet Archive )
- ↑ Nuclear power plant SNR 2 ( Memento from June 4, 2011 in the Internet Archive )
- ↑ Stendal 1 nuclear power plant ( Memento from June 4, 2011 in the Internet Archive )
- ↑ Stendal 2 nuclear power plant ( Memento from June 4, 2011 in the Internet Archive )
- ↑ Vahnum A nuclear power plant ( Memento from June 4, 2011 in the Internet Archive )
- ↑ Vahnum B nuclear power plant ( Memento from June 4, 2011 in the Internet Archive )
- ↑ Wyhl 1 nuclear power plant ( Memento from June 4, 2011 in the Internet Archive )
- ↑ Wyhl-1. ( Memento of the original from May 22, 2014 in the Internet Archive ) Info: The archive link was inserted automatically and has not yet been checked. Please check the original and archive link according to the instructions and then remove this notice. WNA Reactor Database
- ↑ a b c d e f g h i j k l m List of nuclear facilities in the Federal Republic of Germany. (PDF 109.7 kB) Annexes “In decommissioning” Status: August 2011. (No longer available online.) Federal Office for Radiation Protection, November 1, 2011, p. 13 , archived from the original on January 26, 2012 ; Retrieved June 7, 2012 . Info: The archive link was inserted automatically and has not yet been checked. Please check the original and archive link according to the instructions and then remove this notice.
- ↑ atommuellreport.de
- ↑ List of nuclear facilities in the Federal Republic of Germany. (PDF 109.7 kB) Annexes “In decommissioning” Status: May 2013. (No longer available online.) Federal Office for Radiation Protection, May 1, 2013, p. 13 , formerly in the original ; Retrieved May 12, 2013 . ( Page no longer available , search in web archives ) Info: The link was automatically marked as defective. Please check the link according to the instructions and then remove this notice.
- ↑ Heiner Hautermans: In the middle of Burtscheid there is still a teaching reactor In: Aachener Nachrichten of March 23, 2011
- ↑ haz.de
- ↑ Umwelt.niedersachsen.de
- ↑ heise online: Shining legacy: Berlin's research reactor BER II becomes history. Retrieved December 11, 2019 .
- ↑ AKR-1 - The training nuclear reactor was converted to AKR-2 in 2004.