Sauvignon Blanc
| Sauvignon Blanc | |
|---|---|
| Synonyms | Sauvignon Blanc, Blanc Fumé, Sauvignon Jaune - for more see the Synonyms section |

|
|
| Art | Grape vine ( Vitis vinifera subsp. Vinifera ) |
| Berry color | green |
| use | |
| origin | probably from the Loire Valley |
| VIVC no. | 10790 |
| ancestry | |
| List of grape varieties | |
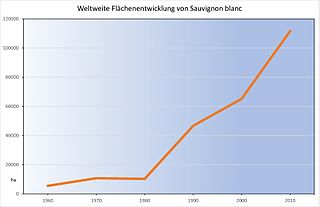
Sauvignon Blanc , also known as Blanc Fumé , or Sauvignon Jaune , is a white wine variety that isdistributed worldwide. The grape variety is one of the 20 most widely grown grape varieties in the wine world and is the second most important white quality variety after Chardonnay . In 2010 the worldwide cultivation area was 111,138 ha . This corresponds to an increase of 70% in relation to the year 2000. Pure varietal results in a fresh wine with idiosyncratic, piquant currant and gooseberry aromas, often also "green" notes (freshly mown grass ), and a mineralnotewith a supporting acid structure (→ Acid (wine) ). The typical Sauvignon Blanc aroma is caused by the content of methoxypyrazines (aromas of potatoes , green peppers , green beans and green asparagus ) (see also the article phenols in wine ).
Origin, descent
The home of the grape variety is the French Loire Valley ; Sancerre and Pouilly-Fumé are the big names.
Sauvignon Blanc is a natural cross of Traminer × Chenin Blanc .
The grape variety Tocai Friulano , which also has the synonym names Sauvignonasse or Sauvignon Vert , was often confused with Sauvignon Blanc in the past. In the early 1990s, the majority of Chilean Sauvignon wines were actually Tocai Friulano wines.
Mutations of Sauvignon Blanc are the varieties Sauvignon Gris or Sauvignon Rose, Sauvignon Noir and Sauvignon Violet.
Ampelographic features
- The shoot tip is open. It is very hairy with white wool with a slightly reddish tinge. The yellowish, slightly bronze colored young leaves are slightly hairy.
- The shoots are strong.
- The small to medium-sized leaves are rounded, mostly five-lobed and only slightly curved, but very wavy on the edge of the leaf. The stem bay is open in a V or U shape. The blade is bluntly serrated. The teeth are medium-sized compared to the grape varieties. The leaf surface is blistered and coarse.
- The cylindrical grape is small and dense. The grape stalk is short and comparatively woody. The elongated berries are small and from yellow-white to golden-yellow (only when fully ripe) in color. The skin of the berry is thick.
Maturity: late; matures around 20 to 25 days after the Gutedel .
Yield
The yield is medium - but limited by trickling .
Properties, claims
Requires early, warm locations and fertile, medium-heavy, not too dry soil. The variety is sensitive to winter frost, peronospora, oidium, botrytis and flowers. Due to its dense leaf arrangement, increased foliage work is necessary.
Wine
When ripe it delivers excellent wines with a fine bouquet of black currants (in some years, however, a paprika note emerges). If the ripeness is insufficient, the wines become grassy, thin and inharmonious.
Due to its worldwide distribution, the wines are developed differently.
distribution
| country | Vineyards ha |
|---|---|
| France | 29000 |
| Italy | 18000 |
| New Zealand | 17000 |
| United States | 16000 |
| Chile | 12500 |
| South Africa | 9500 |
| Moldova | 8200 |
| Australia | 7000 |
| Romania | 4157 |
| Spain | 2500 |
| Ukraine | 3123 |
| Argentina | 2296 |
| Slovenia | 1061 |
| Russia | 951 |
| Hungary | 1200 |
| Austria | 845 |
| Czech Republic | 804 |
| Germany | 1100 |
| Canada | 320 |
| Israel | 263 |
| Greece | 256 |
| Croatia | 249 |
| Slovakia | 208 |
| Portugal | 171 |
| Uruguay | 147 |
| Turkey | 146 |
| Switzerland | 134 |
| Mexico | 120 |
| Brazil | 45 |
| Myanmar | 22nd |
| United Kingdom | 3 |
| China | 1 |
| World acreage 2018 | 110000 |
In 2010, the variety took 8th place in the global ranking of grape varieties. In France, the variety is one of the “Cépages nobles”, the French name for the finest grape varieties in the world. Sauvignon Blanc is also important in Bordeaux and in many other areas of Europe, such as in Italy in Veneto and Friuli , in Slovenia , but also in Bulgaria , Spain , Serbia , Croatia , Hungary and most of the other Eastern European countries . It is also common in Australia, Argentina, Chile, South Africa, California, and New Zealand.
France
In 2007, the area under vines in France was 27,931 hectares. In France, 20 clones have so far been recognized for the production of quality wines, of which clones n ° 297 and 316 are the most widespread.
It was not until the late 1980s that Sauvignon was able to prevail over Ugni Blanc as the most widely grown variety in Bordeaux . Today it shapes the dry white wines of Bordeaux such as the Entre deux mers and the white Graves . In the Médoc, Château Margaux shows with the Pavillon Blanc what potential the grape variety can achieve with low yields and adapted cultivation in barriques in this red wine region.
In the noble sweet wines of Sauternes , Barsac , Monbazillac , Sainte-Croix-du-Mont , Cérons and Loupiac , the variety is blended with the dominant Sémillon and a small proportion of Muscadelle . The famous Château d'Yquem, for example, uses around 20% of the variety in its wines.
In the south-west of France , Sauvignon Blanc is used in the AOC wines of Bergerac , Côtes de Duras , Côtes du Marmandais , Gaillac and Pacherenc du Vic-Bilh . In the first three areas, it is included as the leading variety in dry white wines.
In the Loire wine-growing region , the typical wines in the appellations of Sancerre , Pouilly-Fumé , Menetou-Salon , Quincy and Reuilly , which serve as models for the production of high-quality white wines worldwide, are the best-known wines from the Sauvignon Blanc grape. Sauvignon Blanc is planted almost everywhere downstream. It is of particular importance in three growing regions: in Saint-Bris near Chablis, in the Touraine south of Blois, and in the Haut-Poitou south of Saumur. The typical aroma of Sauvignon Blanc wines is based on a sulphurous compound that is reminiscent of gorse. Often, however, a smell is described during tastings that reminds one of freshly lit matches. The cause is generally the excessive sulphurization of the wines and rarely the flint content in the soil.
New Zealand
Despite the short history, the Sauvignon wines from New Zealand - especially those from Marlborough , where the Cloudy Bay has already become a cult wine - have now advanced to the classic type. Since the 1990s, the country has distinguished itself as a supplier of excellent dry white wines. In Marlborough on the South Island in particular, the vines are grown in sandy soils. The good drainage and poor soil result in a high concentration of the typical aromas due to the resulting low yields. Within the alluvial land of the Wairau River near Blenheim , east-west oriented sandbanks run, which give the terroir a wavy character. The rows of vines are usually oriented north-south and offer the vintner an abundance of different soils (deep, heavy soils in the depressions, airier and stony soils near the crests of the banks) in a relatively small area, which affect the variety of aromas have a positive impact. Marlborough's cool sea climate and strong sunshine provide the basis for a long growing season, which is essential for a good balance of acid and sugar.
In recent years there have also been promising wine qualities from the Martinborough , Gisborne and Hawke's Bay regions , all of which are located on the North Island.
Chile
In 2018 the vineyard area was 12,500 hectares. Chile is known for producing some of the most popular Sauvignon Blancs in the world. The wines are light, refreshing, lemon-like and pleasant. Chilean Sauvignon Blancs are often cheaper than New Zealand Sauvignon Blancs and slightly more fruity than Sancerre, which is also made from this grape. The Sauvignon Blancs from Chile are usually simple but enjoyable.
South Africa
In 2010, the Sauvignon Blanc planted vineyard area was 9,551 hectares, compared to 6,843 hectares in 2003. Jancis Robinson claims that the variety in South Africa was able to hold its own against Chardonnay for a long time, because there the vines known as Chardonnay mainly consisted of the inferior Auxerrois grape because of a mix-up .
United States
The name Blanc Fume is common in California . This name was promoted by Robert Mondavi around 1985 to give the wine its own identity. There it is sometimes matured in wooden barrels , which gives it the character of tropical fruits. In the 1990s, the French ampelographer Pierre Galet found that the Sauvignon Vert in California was predominantly made from the Muscadelle grape variety.
Italy
Sauvignon Blanc produces excellent wines, especially in northeastern Italy. Specimens from Friuli and South Tyrol in particular are very fine and fruity.
In total, the cultivation of the grape variety is recommended in 32 provinces and approved in a further 26 provinces. In 1990 a planted vineyard area of 2,947 hectares was raised.
Sauvignon Blanc is part of the DOC wines Alghero , Bagnoli di Sopra , Bolgheri , Carso , Castel del Monte , Colli Berici , Colli Bolognesi , Colli del Trasimeno , Colli dell'Etruria Centrale , Colli di Conegliano , Colli di Faenza , Colli di Parma , Colli di Scandiano e di Canossa , Colli Orientali del Friuli , Colli Piacentini , Colline Lucchesi , Collio Goriziano , Contea di Sclafani , Contessa Entellina , Delia Nivolelli , Friuli-Annia , Friuli Aquileia , Friuli Grave , Friuli Isonzo , Friuli Latisana , Garda , Garda Colli Mantovani , Lison Pramaggiore , Molise , Oltrepò Pavese , Sant'Antimo , Terlan and Trentino .
Austria
In Austria it is especially important in Styria - preferably in South and Southeast Styria. In 2015, the area under vines was 1,170.2 ha. In 1999, the area under vines was only 314.39 ha.
Germany
In terms of quantity, the variety does not yet play a major role in German viticulture. It was in the statistics of the grape varieties grown in Germany in 20th place (2011) and 12th among the white grape varieties. The variety is increasingly and successfully cultivated by around 500 producers (265 in the Palatinate alone) in almost all German growing areas with the exception of Saxony and Ahr. In the ranking of the most popular new plantings, the grape variety ranks 3.5% in the ranking of the observed varieties. In the Palatinate growing region, Sauvignon blanc was proclaimed “Grape Variety of the Year” for 2010.
The largest cultivation areas in 2018 were in the Palatinate (1,032 hectares) (2011: 277 hectares), Rheinhessen (169 hectares), Baden (101 hectares) and Württemberg (46 hectares). There are smaller areas on the Nahe (14 ha), in the Rheingau (9 ha), on the Moselle (11 ha), Franconia (15 ha), Saale / Unstrut (2 ha), on the Middle Rhine (2 ha) and on the Hessian mountain road (1 ha).
The northernmost German vineyard with Sauvignon Blanc is located in Brandenburg in the Werderaner Wachtelberg area in Werder . The registered vineyard area of Sauvignon blanc reached an extent of 650 hectares in Germany in 2011. That is just under 1% of the vineyard area for white varieties in Germany or 0.6% of the total vineyard area.
Sauvignon Blanc has a long tradition in Durbach, among others . Which at the time owned by the Count anger of Bulach Counts Wolff Metternich estate continued after 1830 in the location Castle Grohl from Chateau d'Yquem native vines. The wine was marketed with a special permit as "White Bordeaux" until the 1980s. In 2006 the estate produced a Trockenbeerenauslese from this for the first time .
Switzerland
In Switzerland, Sauvignon Blanc mainly thrives in the region around Geneva , in the canton of Valais and in Ticino . The vineyard area is 134 hectares (as of 2010).
Synonyms
92: Beyaz Sauvignon, Blanc Doux, Blanc Fume, Blanc Fumet, Bordeaux Bianco, Douce Blanche, Feher Sauvignon, Fig Grape, Fie, Fie dans le Neuvillois, Fume, Fume Blanc, Fume Surin, Genetin, Gennetin, Gentin A Romorantin, Gros Sauvignon , Libournais, Melkii Sotern, Melkij Sotern, Muscat Sylvaner, Muscatni Silvanec, Muskat Silvaner, Muskat-Sylvaner, Muskat-Sylvaner Weisser, Muskatani Silvanec, Muskatni Silvanac, Muskatni Silvanec, Muskatsilvaner, Painechon, Pellegrina, Picabonot Sauvignon, Picabonot Sauvignon Mestny Bely, Pissotta, Puinechou, Punechon, Punechou, Quinechon, Rouchelin, Sampelgrina, Sarvonien, Sauternes, Sauvignon, Sauvignon A Gros Grains, Sauvignon Bianco, Sauvignon Bijeli, Sauvignon Blanc Musque, Sauvignon Blanco, Sauvignon Grisignon., Sauvignon Fume., Sauvignon Gros, Sauvignon Janne, Sauvignon Jaune, Sauvignon Jeune, Sauvignon Musque, Sauvignon Petit, Sauvignon Rouge, Sauvignon Vert, Sauvignon White, Savagnin, Savagnin Musque, Savagnou, Savignon, Servanien, Servonia, Servo yen, Sobinion, Sobinjon, Sobinyon, Sotern Marunt, Sotern Small, Souternes, Sovignion Blan, Sovinak, Sovinjon, Sovinjon Beli, Sovinon, Sovinon Belyi, Sovinyon, Spergolina, Surin, Suvinjo, Sylvaner Musque, Uva Pelegrina, Verdo Belii , White Sauvignon, Xirda Sotern, Zeleni Sauvignon, Zoeld Ortlibi.
literature
- Dagmar Ehrlich : The ABC of grape varieties. Vines and their wines . Hallwag, Munich 2005, ISBN 3-7742-6960-2 .
- Horst Dippel , Cornelius Lange, Fabian Lange : Das Weinlexikon (= Fischer pocket books. 15867). Completely revised and supplemented new edition. Fischer-Taschenbuch-Verlag, Frankfurt am Main 2003, ISBN 3-596-15867-2 .
- Pierre Galet : Dictionnaire encyclopédique des cépages . Hachette Livre, Paris 2000, ISBN 2-01-236331-8 .
- Walter Hillebrand, Heinz Lott, Franz Pfaff: Paperback of the grape varieties . 13th, revised edition. Fachverlag Fraund, Mainz 2003, ISBN 3-921156-53-X .
- Janina Mäurer, Hartmut Keil: 100 rare grape varieties in Rheinhessen and the Palatinate. From Accent, Acolon ... to ... Zinfandel, Zweigelt. Tips and information for wine lovers . Inkfaß edition, Neckarsteinach 2008, ISBN 978-3-937467-56-6 .
- Matthias Petgen, Hans-Peter Schwarz: Sauvignon Blanc in focus, the strategy for success !? In: The German wine magazine. No. 10, May 2010, ISSN 0943-089X , pp. 26–30, ( digital version (PDF; 942 kB) ).
- Jancis Robinson : The Oxford Wine Lexicon . 2nd, completely revised edition. Hallwag, Munich 2003, ISBN 3-7742-0914-6 .
Web links
- Sauvignon Blanc in the database Vitis International Variety Catalog of the Institute for Vine Breeding Geilweilerhof (English)
Individual evidence
- ↑ Ferdinand Regner , lecture at the 1st World Sauvignon Congress , on September 5, 2008 (online)
- ^ A b Ferdinand Regner, Robert Hack: Reconstructing the heritages of 'Grüner Veltliner' and 'Sauvignon blanc' from crossings with 'Traminer' by SSR analyzes. In: Communications Klosterneuburg. Vol. 59, 2009, ISSN 0250-4944 , pp. 199-208.
- ↑ a b Jörg Weiand: Sauvignon blanc - How do the date of reading, reductive expansion and yeast strain affect the flavor? on www.DLR-RNH.rlp.de
- ↑ a b c d K. Anderson, NR Aryal: Database of Regional, National and Global Winegrape Bearing Areas by Variety, 2000 and 2010, Wine Economics Research Center, University of Adelaide, December 2013 (first revision April 2014, second revision May 2014 , third revision July 2014).
- ↑ Where is Sauvignon Blanc grown? Sauvignon Blanc - popular in the old and new world of wine from September 19, 2018
- ↑ South African Wine Industry Statistics ( Memento of 19 December 2014 Internet Archive ), released in June 2008
- ^ Vineyard survey 2015, ÖSTAT
- ↑ Planted vineyards for wine grapes in 2018 according to grape varieties and growing areas in Rhineland-Palatinate
- ↑ Gabriele Damasko, Klaus Hennig-Damasko: wine aristocracy. Natalie Lumpp discovers castle wines from Baden and Württemberg. Hampp, Stuttgart 2007, ISBN 978-3-936682-20-5 , p. 119 ff.
- ↑ Sauvignon Blanc in the database Vitis International Variety Catalog of the Institute for Vine Breeding Geilweilerhof (English), accessed on March 31, 2020