Arbogne
| Arbogne | ||
|
|
||
| Data | ||
| Water code | CH : 805 | |
| location | Switzerland | |
| River system | Rhine | |
| Drain over | Broye → Zihl Canal → Aare → Rhine → North Sea | |
| source | Forest above Lussy 46 ° 43 ′ 23 ″ N , 6 ° 56 ′ 6 ″ E |
|
| Source height | 798 m above sea level M. | |
| muzzle | at Salavaux in the Broye coordinates: 46 ° 54 '28 " N , 7 ° 1' 18" E ; CH1903: 568228 / 195258 46 ° 54 '28 " N , 7 ° 1' 18" O |
|
| Mouth height | 429 m above sea level M. | |
| Height difference | 369 m | |
| Bottom slope | 12 ‰ | |
| length | 31 km | |
| Catchment area | 72.17 km² | |
| Discharge A Eo : 72.17 km² at the mouth |
MQ Mq |
830 l / s 11.5 l / (s km²) |
| Left tributaries | Ruisseau des Pelons, Ruisseau de Pra Laurent, Motélon | |
| Right tributaries | Riau des Chaudeires, Ruisseau du Creux, Ruisseau de l'Hôpital, Ruisseau de Coppet | |
| Communities | La Folliaz , Villaz-Saint-Pierre , Châtonnaye , Torny , Corserey , Montagny , Prez-vers-Noréaz , Noréaz , Corcelles-près-Payerne , Belmont-Broye , Avenches , Vully-les-Lacs | |
Source and mouth of the Arbogne
|
The Arbogne is a 31 km long right tributary of the Broye . It is mainly located in the Swiss canton of Friborg , but also flows over short distances in the canton of Vaud . The Arbogne is first mentioned in 1320 under the name Arbonnia . Then the spellings Arbognez , Arbognyez (1399) appeared, and the name Erbogne has been handed down from 1906 .
geography
course
The headwaters of the Arbogne are around 800 m above sea level. M. northeast of Romont on a wooded ridge between the valleys of the Broye in the northwest and the Glâne in the southeast. The Arbogne flows as a small trickle to the northeast on a high plateau with little relief, the landscape structure of which is given by the overprinting and moraine deposits of the Ice Age Rhone glacier .
After about 7 km of running, the stream gradually descends with a notch valley into the molasse layers of the Freiburg Central Plateau . To the west of the village of Noréaz , the Arbogne describes a sharp bend and now flows in a wooded valley to the northwest, cutting around 100 m into the surrounding molasse hills. In the district of Cousset in the municipality of Montagny (FR) , the Arbogne valley opens up into a broad, agriculturally used valley basin.
The Arbogne now crosses into the canton of Vaud and reaches Corcelles-près-Payerne at an altitude of 454 m above sea level. M. the southern edge of the Broye plain. Here the stream draws a sharp curve again, in order to flow again in north-easterly directions for the remaining 10 km. In its lower reaches, the Arbogne always runs close to the southern edge of the intensely agriculturally used Broye plain, more or less parallel to the Broye. In the Domdidier area , it takes over the bed of the former Broye in sections. Due to the complicated course of the cantonal borders in the Broyetal, the Arbogne changes the territories of the cantons of Vaud and Friborg several times. About 1.5 km southwest of Lake Murten , the Arbogne flows at 432 m above sea level. M. in the canalized Broye.
Catchment area
The catchment area of the Arbogne is 72.17 km² and is drained through it via the Broye , the Aare and the Rhine to the North Sea. It consists of 25.6% wooded area , 66.5% agricultural area , 7.5% settlement area and 0.3% other areas.
Area distribution
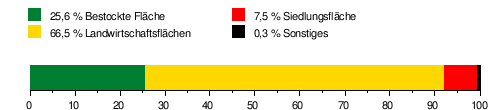
The mean height of the catchment area is 594 m above sea level. M. , the minimum height is 429 m above sea level. M. and the maximum height at 814 m above sea level. M. .
Tributaries
The Arbogne has a number of short side streams. The longest tributary is the Ruisseau de Coppet with 6 km , which flows out near Avenches .
- L'Arbogne (CH0008050000) ( right ), 3.1 km, 1.6 km²
- L'Arbogne d'Amont (CH3510880000) ( right ), 2.1 km, 4.66 km², 0.06 m³ / s
- L'Arbogne (CH0057760000) (right), 3.8 km, 5.87 km², 0.08 m³ / s
- Ruisseau de Grandsivaz ( left ), 1.0 km, 1.71 km²
- Ruisseau du Focho ( right ), 0.7 km, 1.03 km²
- Le Chanaley ( right ), 0.5 km
- Ruisseau de Charbonneires ( left ), 0.9 km, 1.31 km²
- Ruisseau des Pelons ( left ), 3.3 km, 3.29 km²
- Riau des Chaudeires ( right ), 4.3 km, 5.58 km², 0.06 m³ / s
- Ruisseau du Brêt ( Ruisseau du Bre ) ( right ), 0.5 km
- Ruisseau de Pra Laurent ( left ), 1.9 km, 1.6 km²
- Ruisseau du Creux ( right ), 3.1 km, 2.82 km²
- Ruisseau de Merdasson ( right ), 1.3 km, 2.82 km²
- Le Motélon ( left ), 3.8 km, 6.16 km²
- Ruisseau du Saut ( right ), 1.7 km
- Ruisseau du Maupas ( right ), 0.7 km
- Ruisseau de l'Hôpital ( right ), 4.3 km, 6.97 km², 0.08 m³ / s
- Ruisseau de Lussy ( right )
- Ruisseau de Coppet ( La Longeaigue ) ( right ), 6.0 km, 6.26 km²
Hydrology
At the confluence of the Arbogne in the Broye its modeled mean flow rate (MQ) is 0.83 m³ / s and its flow regime type is pluvial inférieur .
The modeled monthly mean discharge (MQ) of the Arbogne in m³ / s

character
The upper and middle reaches of the Arbogne are still in a near-natural, partially natural state. However, the section in the Broye Plain is canalised and straightened for long stretches.
use
The water pipe
During Roman times , in the 1st century AD, part of the water was diverted from the Arbognetal and led to Aventicum (Avenches) through a 15 kilometer long water pipe with an aqueduct . Several springs arise in a side valley of the Arbogne, near the Prez mill. One is called «Bonnefontaine». It has a fairly regular output of around 1000 liters per minute. The Bonnefontaine aqueduct has an average gradient of 2.12%. The water has a constant temperature of around 10 degrees Celsius and has a similar quality to that of the Henniez springs, which are located near Payerne . The aqueduct initially followed the course of the Arbogne and then ran northwards towards Avenches. Two kilometers before Avenches their tracks are lost. In 1962, earthworks south of the Arbognes mill cut the line. The sewer pipe (lat. Specus) embedded in the muddy ground was completely preserved. The walls of the inner pipe are plastered with carefully smoothed brick mortar. At the top, the water channel is closed off by a tuff ceiling. The section of the line uncovered today is to the left of the path that leads to the Prez mill.
Mills
Various mills and sawmills have been operated along the course of the stream since the Middle Ages .
irrigation
Today, water from the Arbogne is used to irrigate crops in the Broye plain.
literature
- J.-P. Aubert: Les aqueducs d'Aventicum. Bulletin de l'Association pro Aventico 20, 1969 pp. 23-36.
Individual evidence
- ↑ a b Geoserver of the Swiss Federal Administration ( information )
- ↑ Evaluations of the water network. (XLSX) FOEN , December 2013, accessed on August 9, 2017 (listing of Swiss rivers> 30km).
- ↑ a b c d Modeled mean annual discharge. In: Topographical catchment areas of Swiss waters: sub-catchment areas 2 km². Retrieved August 9, 2017 .
- ↑ a b River of the same name
- ↑ "Hidden behind the mean values" - the variability of the discharge regime , p. 7
