Federal Ministry of Food and Agriculture
|
Federal Ministry of Food and Agriculture |
|
|---|---|
| State level | Federation |
| position | supreme federal authority |
| founding | February 13, 1919 as Reich Ministry for Food and Agriculture |
| Headquarters | Bonn |
| Authority management | Julia Klöckner ( CDU ), Federal Minister for Food and Agriculture |
| Servants | approx. 900 |
| Budget volume | EUR 6 billion (2017) |
| Web presence | www.bmel.de |

The Federal Ministry of Food and Agriculture ( BMEL for short ) is a supreme federal authority in the Federal Republic of Germany . Its head office or first office is located in the federal city of Bonn , its second office in Berlin . Julia Klöckner ( CDU ) has held the office of Federal Minister and Head of Authority since March 14, 2018 .
history
The original name was between 1949 and 2001 "Federal Ministry of Food, Agriculture and Forests".
In 2001 the ministry was renamed "Federal Ministry for Consumer Protection, Food and Agriculture". The inclusion of consumer protection instead of forests in the name goes back to Renate Künast and is to be seen against the background of the BSE scandal at the time. The renaming is not just an expansion of competencies . It is rather an expression of social changes that are reflected both here and in other departments, at ministerial level. Ilse Aigner, for example, saw herself much more responsible for data protection issues than was the case with her predecessors. The Federal Ministry for Food, Agriculture and Consumer Protection was formed from the Federal Ministry for Consumer Protection, Food and Agriculture through an organizational decree of the Federal Chancellery . The order was arranged alphabetically in order to show the equality of the individual departments.
With the establishment of the Merkel III cabinet in 2013, responsibility for consumer protection was transferred to the Federal Ministry of Justice and Consumer Protection . The nine-member council of experts for consumer issues founded by this Federal Ministry on November 7, 2014 also advises the nutrition department of the Federal Ministry of Food and Agriculture.
The reorganization of a home ministry into the interior ministry could mean losses for the federal ministry of agriculture in the area of rural development.
Research into the history of the Federal Ministry
In 2016, an independent commission of historians set up by Christian Schmidt, the then incumbent minister of the Federal Ministry of Food and Agriculture, began its work. The publication of the research results is planned for summer 2019. In particular, the following aspects should be examined by the Historians' Commission:
"- the re-establishment of the Ministry in 1949
- the history of its predecessor institutions
- the question of personal and material continuity or discontinuity
- the attitude towards its predecessor institutions
- the role of the associations
- the parallel developments in the German Democratic Republic."
As part of the research work of this commission, the period from the establishment of the Reich Ministry of Food (1919) to the reunification of the German Democratic Republic (1990) with the Federal Republic of Germany is taken into account.
organization

In addition to the ministry management (including management staff), it consists of eight further departments (as of January 2020):
- Department 1: Central Department
- Department 2: Consumer health protection, nutrition, product safety
- Department 3: Food Safety, Animal Health
- Department 4: Agricultural Markets, Food Industry, Export
- Department 5: Forests, Sustainability, Renewable Resources
- Department 6: EU Affairs, International Cooperation, Fisheries
- Department 7: Agricultural Production, Horticulture, Agricultural Policy
- Department 8: Rural Development, Digital Innovation
Various higher federal authorities , legally independent bodies under public law and federal research institutes , some of which were restructured with effect from January 1, 2008, are subordinate to the BMEL :
- Federal Office of Consumer Protection and Food Safety
- Federal Agency for Agriculture and Food
- Bundessortenamt
- Federal Institute for Risk Assessment
- Julius Kühn Institute , Federal Research Institute for Cultivated Plants
- Friedrich Loeffler Institute , Federal Research Institute for Animal Health
- Max Rubner Institute , Federal Research Institute for Nutrition and Food
- Johann Heinrich von Thünen Institute , Federal Research Institute for Rural Areas, Forests and Fisheries
Federal Minister since 1949
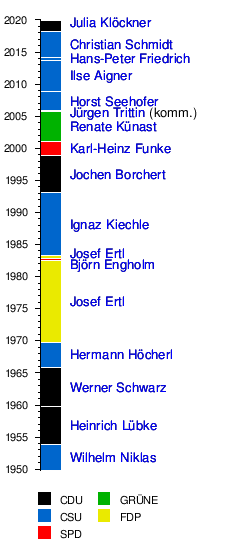
After the break of the social-liberal coalition on September 17, 1982, the then Federal Minister for Education and Science Björn Engholm also took over the Ministry of Agriculture. This state of affairs only lasted until October 1, 1982, when Helmut Kohl was elected Chancellor by a constructive vote of no confidence .
| No. | Surname | Life dates | Political party | Beginning of the term of office | Term expires | Cabinet (s) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Federal Minister for Food, Agriculture and Forests | ||||||
| 1 | Wilhelm Niklas | 1887-1957 | CSU | September 20, 1949 | October 20, 1953 | Adenauer I. |
| 2 | Heinrich Luebke | 1894-1972 | CDU | October 20, 1953 | September 15, 1959 |
Adenauer II Adenauer III |
| 3 | Werner Schwarz | 1900-1982 | CDU | September 30, 1959 | October 26, 1965 |
Adenauer III Adenauer IV Adenauer V Erhard I |
| 4th | Hermann Höcherl | 1912-1989 | CSU | October 26, 1965 | October 21, 1969 |
Erhard II Kiesinger |
| 5 | Josef Ertl | 1925-2000 | FDP | October 22, 1969 | 17th September 1982 |
Brandt I Brandt II Schmidt I Schmidt II Schmidt III |
| 6th | Bjorn Engholm | * 1939 | SPD | 17th September 1982 | October 1, 1982 | Schmidt III |
| 7th | Josef Ertl | 1925-2000 | FDP | 4th October 1982 | March 29, 1983 | Cabbage I |
| 8th | Ignaz Kiechle | 1930-2003 | CSU | March 30, 1983 | January 21, 1993 |
Kohl II Kohl III Kohl IV |
| 9 | Jochen Borchert | * 1940 | CDU | January 21, 1993 | October 26, 1998 |
Kohl IV Kohl V |
| 10 | Karl-Heinz Funke | * 1946 | SPD | October 27, 1998 | January 12, 2001 | Schröder I |
| Federal Minister for Consumer Protection, Food and Agriculture | ||||||
| 11 | Renate Künast | * 1955 | Green | January 12, 2001 | October 4, 2005 |
Schröder I Schröder II |
| Federal Environment Minister Jürgen Trittin took over the management until the formation of a new federal government . | ||||||
| Federal Minister for Food, Agriculture and Consumer Protection | ||||||
| 12 | Horst Seehofer | * 1949 | CSU | November 22, 2005 | October 27, 2008 | Merkel I |
| 13 | Ilse Aigner | * 1964 | CSU | October 31, 2008 | September 30th, 2013 |
Merkel I Merkel II |
| Until the formation of a new federal government, Federal Interior Minister Hans-Peter Friedrich took over the management. | ||||||
| Federal Minister for Food and Agriculture | ||||||
| 14th | Hans-Peter Friedrich | * 1957 | CSU | 17th December 2013 | 17th February 2014 | Merkel III |
| 15th | Christian Schmidt | * 1957 | CSU | 17th February 2014 | March 14, 2018 | Merkel III |
| 16 | Julia Kloeckner | * 1972 | CDU | March 14, 2018 | in office | Merkel IV |
Parliamentary State Secretaries
- 1969–1976: Fritz Logemann ( FDP )
- 1976–1993: Georg Gallus (FDP)
- 1983–1991: Wolfgang von Geldern ( CDU )
- 1991–1993: Gottfried Haschke (CDU)
- 1993–1998: Wolfgang Gröbl ( CSU )
- 1998: Ernst Hinsken (CSU)
- 1998-2005: Gerald Thalheim ( SPD )
- 2001–2005: Matthias Berninger ( Greens )
- 2005–2007: Peter Paziorek (CDU)
- 2005-2013: Gerd Müller (CSU)
- 2007–2009: Ursula Heinen (CDU)
- 2009–2011: Julia Klöckner (CDU)
- 2011-2018: Peter Bleser (CDU)
- 2013–2018: Maria Flachsbarth (CDU)
- since 2018: Hans-Joachim Fuchtel (CDU)
- 2018–2019: Michael Stübgen (CDU)
- since 2019: Uwe Feiler (CDU)
Official State Secretaries
- 1949–1962: Theodor Sonnemann
- 1962–1968: Rudolf Hüttebräuker
- 1967–1968: Reinhold Mercker
- 1968–1969: Fritz Neef
- 1969–1973: Hans Griesau
- 1973–1984: Hans-Jürgen Rohr
- 1984–1987: Walther Florian
- 1987–1993: Walter Kittel
- 1988–1991: Kurt Eisenkrämer
- 1991–1993: Helmut Scholz
- 1993–1998: Franz-Josef Feiter
- 1998–2002: Martin Wille ( SPD )
- 2001–2005: Alexander Müller ( Greens )
- 2005–2010: Gert Lindemann ( CDU )
- 2010–2016: Robert Kloos (CDU)
- 2016–2019: Hermann Onko Aeikens (CDU)
- since 2020: Beate Kasch
Competitions
Every three years the ministry organizes the national competition “ Our village has a future ”. The aim is to increase the motivation of the local population to implement their own projects to secure the future of the village. In this context, places that have achieved good placements through preliminary work can then receive funding to increase awareness and projects in their rural areas.
Consumer guide
The consumer guide was launched by Ilse Aigner on December 10, 2012 with the aim of answering citizens' questions about their consumer rights. Consumers can contact the consumer guide by phone or e-mail and either receive the information they want directly or are directed to the responsible office. The consumer guide is not allowed to provide individual legal advice.
The Federation of German Consumer Organizations sees potential in the project of the Federal Ministry of Consumers if the consumer guides can actually name the right contact person. However, other parties such as the Greens and the SPD consider this form of consumer service to be superfluous. The Handelsblatt Online found in a random test six weeks after the start of the consumer guide that the help of the guide remained superficial in many cases.
See also
Web links
Individual evidence
- ↑ Law on the adoption of the federal budget for the financial year 2017 (Budget Law 2017). (PDF; 31.5 MB) In: bundeshaushalt-info.de. Federal Ministry of Finance (BMF), December 20, 2016, p. 16 , accessed on March 12, 2018 .
- ↑ List of Abbreviations. (PDF; 49 kB) Abbreviations for the constitutional organs, the highest federal authorities and the highest federal courts. In: bund.de. Federal Office of Administration (BVA), accessed on August 14, 2016 .
- ↑ Merkel wants to propose Klöckner as Minister of Agriculture
- ↑ Independent Commission of Historians at the Federal Ministry of Food and Agriculture (ed.): History of the Federal Ministry of Food and Agriculture in the Context of the 20th Century. Continuity and discontinuity. Interim report, p. 1. Without a year (probably 2017) - cf. on this, the Commission of Historians to review the history of the BMEL - submission of the interim report . Both links accessed March 25, 2019.
- ↑ Independent Commission of Historians at the Federal Ministry of Food and Agriculture (ed.): History of the Federal Ministry of Food and Agriculture in the Context of the 20th Century. Continuity and discontinuity. Interim report, p. 6. Without a year (probably 2017) - cf. on this, the Commission of Historians to review the history of the BMEL - submission of the interim report . Both links accessed March 25, 2019.
- ↑ Independent Commission of Historians at the Federal Ministry of Food and Agriculture (ed.): History of the Federal Ministry of Food and Agriculture in the Context of the 20th Century. Continuity and discontinuity. Interim report, p. 1. Without a year (probably 2017) - cf. on this, the Commission of Historians to review the history of the BMEL - submission of the interim report . Both links accessed March 25, 2019.
- ↑ Independent Commission of Historians at the Federal Ministry of Food and Agriculture (ed.): History of the Federal Ministry of Food and Agriculture in the Context of the 20th Century. Continuity and discontinuity. Interim report, p. 5. Without a year (probably 2017) - cf. on this, the Commission of Historians to review the history of the BMEL - submission of the interim report . Both links accessed March 25, 2019.
- ↑ Organization plan . (PDF) Federal Ministry of Food and Agriculture, accessed on September 18, 2017 .
- ↑ State Secretary Aeikens stops at the end of the year. September 30, 2019, accessed December 23, 2019 .
- ↑ Press release, Beate Kasch becomes the new State Secretary. Retrieved January 7, 2020 .
- ↑ BMELV consumer guide ( Memento of July 8, 2013 in the Internet Archive ), Federal Ministry of Food, Agriculture and Consumer Protection, last accessed on July 5, 2013.
- ↑ consumer guide disappointed , finanzen.de, last accessed on July 5, 2013.
- ↑ Consumer protection: You will not be helped here , Handelsblatt Online, last accessed on July 5, 2013.
Coordinates: 50 ° 43 ′ 10.5 ″ N , 7 ° 3 ′ 41.3 ″ E