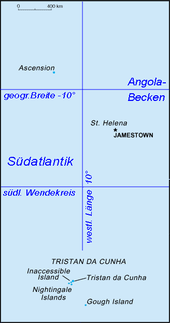
St. Helena, Ascension and Tristan da Cunha
| St Helena, Ascension and Tristan da Cunha | |||||
| St. Helena, Ascension and Tristan da Cunha | |||||
|
|||||
| Motto : Loyal and Unshakeable (trust and unshakable) | |||||
| Official language | English | ||||
| Capital | Jamestown (on St. Helena ) | ||||
| Form of government | British overseas territory | ||||
| Head of state | Queen Elizabeth II | ||||
| Head of government | Philip Edward Rushbrook (Governor) | ||||
| surface | 391 km² | ||||
| population | 5633 (as of 2016) | ||||
| Population density | 14.4 inhabitants per km² | ||||
| currency | St. Helena pound (SHP, used on St. Helena and Ascension), pound sterling (GBP, used on Tristan da Cunha) | ||||
| National anthem | God Save the Queen | ||||
| Time zone | UTC ± 0 | ||||
| ISO 3166 | SH , SHN, 654 | ||||
| Internet TLD |
.sh (St. Helena) .ac (Ascension) |
||||
| Telephone code | +290 (St. Helena) +247 (Ascension) +290 8 (Tristan da Cunha) +27 (Gough Island) |
||||
St. Helena, Ascension and Tristan da Cunha ( English St Helena, Ascension and Tristan da Cunha ) is a British overseas territory in the southern Atlantic Ocean . Until the new constitution came into force on September 1, 2009, the area was called St. Helena and Dependencies (English Saint Helena and Dependencies ).
geography
The territory consists of the island of St. Helena , the island of Ascension to the north-west of it and the island group of Tristan da Cunha located far south-south-west of it . The new constitution gave these three parts equal status within the territory. The overseas territory has an area of 391 km² and a population of 5633 inhabitants.
Geographical and geopolitical assignment
The islands are located in the South Atlantic in the immediate vicinity of the Mid-Atlantic Ridge . St. Helena and the Tristan da Cunha archipelago are on the African Plate , while Ascension is about 80 kilometers west of the central rift of the Mid-Atlantic Ridge on the South American Plate . Politically, the area belongs to Europe because it belongs to the United Kingdom , economically it is heavily dependent on South Africa . According to the United Nations , St. Helena is part of the West Africa region . The African Union regards the islands as part of Africa .
climate
The climates of the three parts of the overseas territory must be considered separately, as they differ greatly.
On St. Helena there is a moderate, humid climate with few distinct seasons. Precipitation can fall in all months, with high points in autumn and winter. Temperatures rarely drop below 17 degrees Celsius during the day and 13 degrees at night and rarely exceed 23 degrees. The air humidity is more than 80 percent all year round.
The climate on Ascension is warm to hot and dry. There is hardly any precipitation, the monthly average temperatures are between 24 and 28 degrees Celsius throughout the year.
Tristan da Cunha is characterized by very humid and cool weather. The annual mean rainfall is more than 1,600 millimeters, with an average of two out of three days all year round. The temperatures rarely exceed 20 degrees.
| Sub-area | Max. Temperature ° C | Min. Temperature ° C | Precipitation mm (per month) |
Hours of sunshine (hours / day) |
Rainy days (per month) |
Humidity% |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
|
17.4-22.4 | 13.0-17.5 | 25-83 | 1.9-6.3 | 4-14 | 82-86 |
|
|
28.0-31.0 | 22.0-24.0 | 3-28 | 5.0-9.0 | 1-4 | 67-70 |
|
|
14.0-21.0 | 10.0-17.0 | 93-175 | 3.30-5.08 | 16-26 | 75-80 |
history
Due to their isolation, all three island areas never had an indigenous population and remained uninhabited until the 16th century. The island of Ascension was probably discovered in May 1501 by the Galician navigator João da Nova , who also discovered the island of St. Helena around a year later. The southernmost archipelago of the territory was discovered in March 1506 by the Portuguese navigator Tristão da Cunha and named after him.
In 1815 the British government selected the island of St. Helena as the place of exile for Napoleon , who was deported in October 1815 and resided in Longwood until his death on May 5, 1821 . During this time, on August 14, 1816, Tristan da Cunha was officially annexed by Great Britain, after Ascension had previously been occupied and converted into a fortress. In 1834 St. Helena became a British Crown Colony , in 1981 a "British Dependent Territory" and finally in 2002, based on the British Overseas Territories Act 2002 , a "British Overseas Territory". The territory has been on the UN list of sovereign territories without self-government since 1946 .
Flags
Until 2009, the St. Helenas flag was also used generally for all three sub-areas. However, since St. Helena , Ascension and Tristan da Cunha were given equal rights from 2009, there has not been a generally applicable flag for the entire overseas territory since then. In fact , the St. Helena flag continues to be used for the entire overseas territory; de jure , however, each part has its own flag. The Union Jack is also rarely used.
politics
The three parts of St. Helena, Ascension and Tristan da Cunha are in fact administered - by the governor - from St. Helena. However, the constitution provides for equal self-government for the three areas of St. Helena, Ascension and Tristan da Cunha and therefore treats each of these areas in a separate chapter.
St. Helena
Chapter 1 of the Constitution of St. Helena, Ascension and Tristan da Cunha deals with the administration of the island of St. Helena.
legislative branch
Based on the constitution of 2009, St. Helena has a unicameral legislature ( English Legislative Council ) with 17 members: the speaker (English speaker ) and his deputy (English deputy speaker ), twelve members who are elected every four years at the latest as well as three ex officio members. The spokesperson and deputy spokesperson are elected by the elected MPs; they may not come from their ranks, but must meet the same requirements to be eligible (Chapter 1, Section 5, Paragraph 55). The British monarch is also part of the legislature (Chapter 1, Section 5, Paragraph 47).
executive
The executive power emanates from the British monarch. This is represented by the governor appointed by him . Philip Edward Rushbrook has been Governor of St. Helena since May 11, 2019 . The governor resides in the Plantation House .
Five of the eight members of the government (English Executive Council ) are elected from the elected members of the legislature for a two-year term (Chapter 1, Section 4, Paragraph 36). Three other members are ex officio . In addition, the governor can appoint another person as a temporary replacement for a member who is unable to attend.
Judiciary
According to the constitution, St. Helena has a Supreme Court and a Court of Appeal . Subordinate courts can be set up by ordinance.
Ascension and Tristan da Cunha
The governor of St. Helena is also the governor of Ascension and Tristan da Cunha. The legislative and executive branches on both islands are each formed by an Island Council , directly elected for a period of three years , which has individual rights enacted by law. The respective legislature of the two islands is formed by the governor and the island council. The judiciary is exercised through the courts of St. Helena. (Chapters 2 and 3, each section 3 to 6) The administration of the two partial areas is in each case a nominated from the mother country manager (English Administrator ) in front.
Administrative division
The territory consists of three equal parts. Each part has its own administration. Jamestown is in fact the capital of the entire overseas territory, as the governor has his seat here.
| unit | Area ( km² ) |
population | Inhabitants per km² | Administrative headquarters | legislative branch | executive | Judiciary |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
|
123 | 4534 (2016) | 36.9 | Jamestown | Legislative Council | British monarch governor |
Supreme Court |
|
|
88 | 806 (2016) | 9.2 | Georgetown |
Island Council Governor |
British monarch administrator |
Courts of St. Helena |
|
|
180 | 245 (2020) | 1.4 | Edinburgh of the Seven Seas |
Island Council Governor |
British monarch administrator |
Courts of St. Helena |
| total | 391 | 5633 (2016) | 14.4 | Jamestown ( de facto ) | Legislative Council | British monarch governor |
Supreme Court |
The St. Helena area is further subdivided into eight districts .
population
The overseas territory is inhabited by 5633 people (as of 2016). This corresponds to a population density of 14 people per square kilometer. St. Helena has about 4500 people (37 per km²), Ascension 806 (9 per km²) and Tristan da Cunha almost 300 (1.6 per km²). Most of the residents are of British origin. On St. Helena there are minorities of Chinese (immigrated as migrant workers around 1810) and the descendants of workers who immigrated mainly from Madagascar around 1840.
There was never an indigenous population .
economy
Financially, the area relies heavily on support from Great Britain. The motherland's grants ( Grant-in-Aid ) cover around 60% of the total budget of around £ 36 million (as of 2016/17) and regularly far exceed the overseas territory's own income. There is also considerable support in the form of development aid and technical cooperation.
The gross domestic product is around 15.9 million pounds (as of 2009/10). The unemployment rate has fallen sharply since the turn of the millennium and was 2 percent in 2009/10 (1998/99: 15.4 percent).
The main industries are fishing and processing, lobster fishing , agriculture and tourism, including the sale of postage stamps .
currency
The islands of Ascension and St. Helena use the St. Helena pound ( ISO 4217 code SHP) as their currency . This is a formally independent currency with its own cash. However, it is at exchange rate parity with the British pound.
On Tristan da Cunha, which also belongs to the overseas territory, the pound sterling is used. The islanders there originally operated mainly bartering. After the entire population had to be evacuated to Great Britain from 1961 to 1963 due to a volcanic eruption, the currency of the motherland was introduced on Tristan da Cunha when they returned.
See also
- Education system in St. Helena, Ascension and Tristan da Cunha
- Holidays in St. Helena, Ascension and Tristan da Cunha
- Health system in St. Helena, Ascension and Tristan da Cunha
- Media in St. Helena, Ascension and Tristan da Cunha
- Traffic in St. Helena, Ascension and Tristan da Cunha
- Sports in St. Helena, Ascension and Tristan da Cunha
- List of museums in St. Helena, Ascension and Tristan da Cunha
- List of nature reserves in St. Helena, Ascension and Tristan da Cunha
Web links
- St Helena Government. Official Website of the Government of St. Helena
- Ascension Island. Official Ascension Government Website
- Tristan da Cunha website. Official website of Tristan da Cunha
Individual evidence
- ^ Change of name and establishment of Constitution. (PDF; 936 kB) In: The Constitution of St. Helena, Ascension and Tristan da Cunha. St Helena Government, September 1, 2009, p. 2 , accessed on May 1, 2017 (English, online version of the constitution that is not legally binding).
- ^ New Constitution. (No longer available online.) St Helena Government, archived from the original on December 12, 2011 ; accessed on May 1, 2017 (English).
- ^ The Geology of Ascension Island. Barry L. Weaver, accessed May 1, 2017 .
- ^ Geographic Regions. In: UNSD Methodology. United Nations Statistics Division , accessed May 1, 2017 .
- ↑ Gertjan Dijkink, Hans Knippenberg (Ed.): The Territorial Factor - Political Geography in a Globalizing World . Vossiuspers UvA, Amsterdam 2001, ISBN 90-5629-188-2 , p. 182.
- ↑ Annexe 3: List des pays / territoires Africains sous occupation étrangère. (PDF; 442 kB) (No longer available online.) In: Le plan stratégique de la Commission de l'Union Africaine. Volume 1: Vision d'avenir et missions de l'Union Africaine. African Union , p. 44 , archived from the original on April 24, 2014 ; accessed on May 1, 2017 (French).
- ↑ Harold Livermore : Santa Helena, A Forgotten Portuguese Discovery . In: Estudos em Homenagem a Luís António de Oliveira Ramos . tape 2 . Faculdade de Letras da Universidade do Porto, Porto 2004, ISBN 972-9350-74-4 , pp. 623–631 (English, online [PDF; 59 kB ]).
- ^ Discovery of St Helena. In: Saint Helena Island Info: All about St Helena, in the South Atlantic Ocean. Moonbeams Shop, John Turner, accessed May 1, 2017 .
- ↑ Our flag. The Sentinel, March 7, 2013, p. 8.
- ↑ Chapter 1, Part 5: The Legislature. (PDF; 936 kB) In: The Constitution of St. Helena, Ascension and Tristan da Cunha. St Helena Government, September 1, 2009, pp. 37–47 , accessed on May 1, 2017 (English, online version of the constitution that is not legally binding).
- ↑ Chapter 1, Part 4: The Executive. (PDF; 936 kB) In: The Constitution of St. Helena, Ascension and Tristan da Cunha. St Helena Government, September 1, 2009, pp. 31–37 , accessed on May 1, 2017 (English, online version of the constitution that is not legally binding).
- ↑ Chapter 1, Part 6, Section 80: The Administration of Justice - The Courts of St Helena. (PDF; 936 kB) In: The Constitution of St. Helena, Ascension and Tristan da Cunha. St Helena Government, September 1, 2009, p. 47 , accessed on May 1, 2017 (English, online version of the constitution that is not legally binding).
- ^ Estimates of Recurrent Revenue, Expenditure and Capital Expenditure 2016/17. (PDF; 176 kB) Summary of Budgeted Expenditure and Revenue. In: St Helena Government Budget Book 2016–17. St Helena Government, p. 9 , accessed May 1, 2017 .
- ↑ 4.4: Government revenue. (PDF; 2.53 MB) In: Statistical Yearbook 2013/14. St Helena Statistics Office, Corporate Policy and Planning Unit, accessed May 1, 2017 .
- ↑ 1.2: UK aid to St Helena. (PDF; 2.53 MB) In: Statistical Yearbook 2013/14. St Helena Statistics Office, Corporate Policy and Planning Unit, accessed May 1, 2017 .
- ↑ 1.4: National Income. (PDF; 2.53 MB) In: Statistical Yearbook 2013/14. St Helena Statistics Office, Corporate Policy and Planning Unit, accessed May 1, 2017 .
- ↑ 6.9: Distribution of the workforce. (PDF; 2.53 MB) In: Statistical Yearbook 2013/14. St Helena Statistics Office, Corporate Policy and Planning Unit, accessed May 1, 2017 .
- ↑ CIA World Factbook: Saint Helena, Ascension and Tristan da Cunha: Economy (English). Retrieved May 1, 2017.
- ↑ Sterling pound: a coin with a star or an Easterling? In: THE WORLD . March 3, 2010 ( online at welt.de [accessed on May 1, 2017]).
- ↑ Mike Hentley: Tristan da Cunha Coins. In: Tristan da Cunha website. Tristan da Cunha Government and Tristan da Cunha Association, accessed May 1, 2017 .
Coordinates: 16 ° S , 6 ° W