Geography of Canada
|
|
||
| continent | North America | |
|
Area - total - water |
2nd place 9,984,670 km² 891,163 km² (8.92%) |
|
| Coastline | 202,080 km | |
| Land border | 8,893 km | |
| Neighbore states | USA 8,893 km | |
| Exclusive economic zone |
200 nautical miles | |
| The highest point | Mount Logan , 5959 m | |
| Deepest point | Sea level, 0 m | |
| Longest river | Mackenzie River , 4,241 km | |
| Largest inland water |
Great Bear Lake , 31,153 km² | |
|
Land use - agriculture - pasture land - forest - unproductive |
5% 3% 54% 38% |
|
| Climate : | temperate to arctic | |
| terrain | Mainly from plains with mountains in the west ( Rocky Mountains ). In the southeast from the lowlands. | |
| Natural raw materials | Hydropower , iron ore , fish , potash salt , natural gas and oil , diamonds , lead , gold , silver , molybdenum and wood . | |
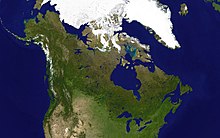
The geography of Canada is diverse. The country covers most of the northern half of North America (a total of 41% of the continent) and is the second largest country in the world by area after Russia .
Canada encompasses extensive territory between the Pacific Ocean in the west and the Atlantic Ocean in the east (hence the slogan A Mari Usque Ad Mare - "From sea to sea") and from the Great Lakes and the 49th parallel in the south to the Arctic Ocean in the North. In the south are the United States ( Continental United States ), in the northwest the US state of Alaska , in the northeast Greenland . Off the south coast of Newfoundland is the Saint-Pierre and Miquelon archipelago , a French overseas territory . Canada has been claiming the part of the Arctic between 60 ° W and 141 ° W to the North Pole since 1925, but this claim is controversial.
With an area of 9,984,670 km² (land: 9,093,507 km², water: 891.163 km²) Canada is a little less than three-fifths the size of Russia, almost 1.3 times larger than Australia and slightly smaller than Europe . The northernmost permanently inhabited human settlement in Canada (and also on Earth) is Alert on the northern tip of Ellesmere Island in Nunavut Territory - at 82 ° 28 'N and 834 kilometers from the North Pole. The magnetic north pole is located within the Arctic area claimed by Canada, but migrates towards Siberia .
physical geography
Appalachian Mountains
The Appalachian mountain range extends over a length of more than 2,400 km from Alabama in the southern USA to the Gaspésie Peninsula in the province of Quebec , including part of the island of Newfoundland . The northern partial chains of the Appalachian Mountains, namely the Notre Dame Mountains and the Long Range Mountains , are eroded mountain ranges that are around 380 million years old. The most famous mountains on the Canadian side are the Mont Jacques-Cartier in Québec (1268 m), the Mount Carleton in New Brunswick (817 m) and The Cabox on Newfoundland (814 m). Parts of the Appalachian Mountains have a rich endemic flora and fauna, and during the ice ages individual mountains formed nunataks (peaks protruding above the ice surface).
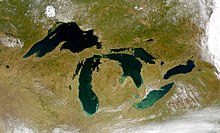
Great Lakes and Saint Lawrence Lowlands
The southern part of Québec and Ontario , i.e. the lowlands of the Saint Lawrence River and around the Great Lakes , is a plain with particularly fertile sediments . Before colonization and the subsequent urbanization of the 20th century, this area between the Appalachians and the Canadian Shield was covered by extensive mixed forests. Most of the forests were cut down to make land available for agriculture, but most of the remains are subject to strict protection. The relief of the lowlands is extremely flat and regular. Striking exceptions are the Niagara strata in Ontario (over which the Niagara Falls pour) and the Montérégie hills in Québec, isolated batholiths .
Canadian shield
The northern part of the provinces of Saskatchewan , Manitoba , Ontario and Québec, as well as almost all of Labrador, are located on an extensive rock pedestal known as the Canadian Shield, which takes up almost half the area of the country. The shield consists of eroded, hilly terrain and has a dense network of water. The region is drained from a large number of rivers, the hydropower of which is used to generate electricity. The shield surrounds an extensive wetland, the lowlands around Hudson Bay . It is traversed by individual mountain chains such as the Torngat and the Laurentine Mountains . Intensive agriculture cannot be carried out on the shield. Large areas are covered by boreal coniferous forest, which is used by the wood processing industry. Likewise, the numerous existing mineral resources are exploited. Beyond the Arctic tree line , the region is covered in rocks, ice, and tundra vegetation .
prairie
The Canadian prairie is an extensive plain of sediment. It covers most of Alberta , southern Saskatchewan and southwestern Manitoba , as well as the region between the Rocky Mountains and Great Slave Lake and Great Bear Lake in the Northwest Territories . The mainly flat prairie is used for agriculture in its southern part (especially wheat cultivation), the northern part is forested. Individual regions such as the Cypress Hills and the Alberta Badlands are extremely hilly.
Western mountain ranges

The Rocky Mountains form part of the continental divide that stretches across the continent to South America. To the west of it, in the province of British Columbia , lies an extensive plateau. Several mountain ranges extend between the plateau and the Pacific coast, which are combined to form the Coast Mountains . The Mackenzie Mountains connect to the north . Off the southwest coast of British Columbia is the mountainous island of Vancouver Island , surrounded by numerous other islands and archipelagos such as Haida Gwaii and the Gulf Islands . The only temperate rainforest in Canada can be found in this region .
Arctic
The Canadian Arctic includes all areas north of the tree line, i.e. almost all of Nunavut as well as the northernmost parts of Yukon , Manitoba , Ontario , Québec , Labrador and the Northwest Territories . There are mostly ice surfaces and tundras , but the geology is diverse. The Arctic Cordillera , which extends to Ellesmere Island , is the northernmost mountain range in the world. The Arctic Lowlands and the Hudson Bay Lowlands belong to the Canadian Shield geographically , but not geologically. The soil in the Arctic mostly consists of permafrost , which makes it difficult to build infrastructure and makes agriculture practically impossible.
Volcanism
Western Canada is rich in volcanoes and is part of a volcanic system around the Pacific known as the Pacific Ring of Fire . There are over 200 volcanically active areas stretching north from the Cascade Range to the Yukon . They can be divided into five volcanic belts with different volcano types and tectonic conditions.
The Northern Cordilleran Volcanic Province (NCVP) was formed by the fault , breakup, and interaction between the Pacific Plate and the North American Plate . The subduction of the Juan de Fuca plate under the North American plate gave rise to the Garibaldi volcanic belt . The Anahim volcanic belt is the result of the North American Plate sliding over the Anahim hotspot . The Chilcotin Plateau Basalts may have been formed by a backarc extension of the Cascading Subduction Zone . The Wrangell volcanic field is the result of the subduction of the Pacific Plate under the North American Plate at the eastern end of the Aleutian Trench .
There was also volcanism on the Canadian Shield . It encompasses over 150 volcanic belts that are between 600 and 2800 million years old and are now deformed and eroded into almost flat plains. Many of Canada's ore deposits are related to these Precambrian volcanoes. The Northwest Territories have areas of pillow lava that is over 2,600 million years old and is preserved in the Cameron River Volcanic Belt. The pillow lava indicates that huge oceanic volcanoes existed in the early stages of the earth's crust formation.
Hydrography
Canada has extensive water reserves. 9% of the world's water is discharged via the rivers, the country has a quarter of all wetlands worldwide and the largest glacier area after Antarctica and Greenland . There are more than two million lakes in Canada due to heavy glaciation during the last ice age . Of those who are entirely on Canadian soil, more than 31,000 are between 3 and 100 km² in size, and 563 more than 100 km². There are five main catchment areas ; to the Arctic Ocean , the Atlantic Ocean , the Pacific Ocean , Hudson Bay and the Gulf of Mexico .
The Atlantic basin drains the entire Atlantic provinces (a part of the boundary between Québec and Labrador runs along the watershed), southern Québec and large parts of the south of Ontario . Most of the water flows off via the economically important Saint Lawrence River and its tributaries, above all the Saguenay , Manicouagan and Ottawa , as well as all Great Lakes and the Nipigon Sea . Also of importance are the Churchill River and the Saint John River .
The Hudson Bay catchment drains over a third of Canada. It includes Manitoba , northern Ontario and Québec, almost all of Saskatchewan , southern Alberta , southwest Nunavut and the southern half of Baffin Island (fifth largest island in the world). This catchment area is particularly important for preventing droughts in the prairie and for generating energy from hydropower . Significant bodies of water in this catchment area are the Winnipeg Lake , the Nelson River , the North Saskatchewan River , the Saskatchewan River , the Assiniboine River and the Nettilling Lake on Baffin Island. Exactly on the watershed between the drainage basins of Hudson Bay and the Atlantic lies Wollaston Lake , the largest lake in the world that naturally drains in two directions.
The continental divide forms the dividing line between the catchment areas of the Pacific in British Columbia , the Arctic Ocean and Hudson Bay. The Pacific basin drains the westernmost province of the country and is used intensively for energy generation. Major rivers are the Yukon River , Columbia River, and Fraser River .
The northern half of Alberta, Manitoba and British Columbia, most of the Northwest Territories and Nunavuts, and parts of the Yukon are drained via the Arctic catchment. This is hardly used for energy production, with the exception of the Mackenzie River , the longest river in the country. Significant bodies of water in this catchment area are the Peace River , the Athabasca River , the Liard River , the Great Bear Lake and the Great Slave Lake .
The southernmost part of Alberta is drained by the Milk River and its tributaries to the Gulf of Mexico. The Milk River rises in the Rocky Mountains of Montana , flows through Alberta and flows into the Missouri River in the United States . A small part of Saskatchewan is drained via the Battle Creek , which flows into the Milk River.
Human geography
Canada is divided into thirteen provinces and territories . According to Statistics Canada , 72% of the population is concentrated in a 150 km strip of land along the southern border with the United States. 70% live south of the 49th parallel, over 60% along the Great Lakes and the Saint Lawrence River between the cities of Windsor and Québec ( Québec-Windsor Corridor ). This means that the vast majority of Canadian territory is extremely sparsely populated. The population density is 3.5 inhabitants per km². Nevertheless, 79.4% of the population live in urban areas.
With a length of 8,893 km (2,477 km including Alaska ), the border with the United States is the longest undefended state border in the world. The Danish autonomous region of Greenland is northeast of Canada, separated from the Canadian Arctic Archipelago by Baffin Bay , the Kennedy Canal and the Davis Strait . The Saint-Pierre and Miquelon archipelago, which belongs to France, is located 25 km off the south coast of Newfoundland in the Saint Lawrence Gulf and has a maritime enclave within Canada's exclusive economic zone . In 2005 there was a border conflict with Denmark because the contractually stipulated border in the Kennedy Canal runs right through Hans Island and thus forms a land border. The dispute was settled through diplomatic means. Similar to the much better known Four Corners in the US, Canada has a point near Kasba Lake where two provinces and two territories meet.
Canada's geographical proximity to the USA also resulted in close political ties. The country's position between the Soviet Union (now Russia ) and the United States was of strategic importance during the Cold War , as the route via the North Pole and Canada was the direct link between the two countries for combat aircraft and ICBMs . Since the end of the Cold War, it has been speculated that the importance of Canada's territorial claims in the Arctic could increase as global warming melts enough ice to make the Northwest Passage passable for cargo ships.
Ecoregions
Canada is divided into 15 terrestrial and 5 marine ecoregions :
|
|
|
|
environment
The country's per capita emissions of carbon dioxide are among the highest in the world and are related to the country's economic orientation and size. According to a study by Simon Fraser University , carried out at the instigation of the David Suzuki Foundation , Canada is one of the industrialized countries with the worst environmental record . Canada ranks 28th out of 30 countries studied in the field of economic cooperation and development. The country ranks last in terms of nuclear waste and carbon monoxide emissions. It also takes 29th place in water consumption . European countries like Sweden , Switzerland , Denmark and Germany are at the top of this environmental balance, while Canada, Belgium and the USA are at the bottom.
Geographical key points
All of Canada
- Northernmost point:
- Country: Cape Columbia , Ellesmere Island , Nunavut - 83 ° 08'N, 74 ° 13'W
- Water: North Pole - 90 ° N
- Southernmost point:
- Most western point: Yukon - Alaska border - 141 ° 00'W
- Easternmost point: Cape Spear , Newfoundland - 47 ° 31'N, 52 ° 37'W
Mainland Canada
- Northernmost point: Cape Rennell , Murchison Promontory , Boothia Peninsula , Nunavut - 71 ° 58'N
- Southernmost point: Point Pelee , Ontario - 41 ° 54'23 "N
- Most western point: Yukon-Alaska border - 141 ° 00'W
- Easternmost point: Cape St. Charles , Labrador - 52 ° 13'N, 55 ° 37'W
- Lowest point: sea level - 0 m
- Highest point: Mount Logan - 5959 m
literature
- Ludger Basten, H. Peter Dörrenbächer, Petra Dolata: The natural potential of Canada, in Ursula Lehmkuhl Ed .: Country report Canada . Series of publications, 10200. Federal Agency for Civic Education , BpB, Bonn 2018, pp. 256–287
Web links
- Government of Canada - The Atlas of Canada
- Canadian Geographic - The Canadian Atlas Online
- Library and Archives Canada - British Admiralty Charts of Canadian Waters
Individual evidence
- ↑ Canada territorial evolution ( Memento of the original from April 23, 2010 in the Internet Archive ) Info: The archive link was inserted automatically and has not yet been checked. Please check the original and archive link according to the instructions and then remove this notice. - Atlas of Canada
- ^ Distribution of Freshwater - Atlas of Canada
- ↑ Natural Resources Canada - The Atlas of Canada - Lakes ( Memento from January 14, 2013 in the Internet Archive )
- ↑ Population distribution ( Memento of the original from September 13, 2008 in the Internet Archive ) Info: The archive link was inserted automatically and not yet checked. Please check the original and archive link according to the instructions and then remove this notice. - Atlas of Canada
- ^ Border dispute between Canada and Denmark
- ^ Melting ice: Ships will soon be able to cross the Northwest Passage - Die Presse, September 17, 2007
- ↑ Terrestrial ecozones of Canada ( Memento of the original from March 9, 2008 in the Internet Archive ) Info: The archive link was inserted automatically and has not yet been checked. Please check the original and archive link according to the instructions and then remove this notice. - Parks Canada - Teacher Resource Center
- ↑ Canada among worst polluters ( Memento of October 26, 2005 in the Internet Archive ), CNN, October 18, 2005.