Murcia (region)
|
Región de Murcia ( Spanish ) Murcia |
|||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
|||||
| Basic data | |||||
| Country : |
|
||||
| Capital : | Murcia | ||||
| Area : | 11,314 km² | ||||
| Residents : | 1,493,898 (January 1, 2019) | ||||
| Population density : | 132 inhabitants / km² | ||||
| Expansion: | North – South: approx. 134 km West – East: approx. 119 km |
||||
| ISO 3166-2 : | ES-MC | ||||
| Website : | carm.es | ||||
| Politics and administration | |||||
| Autonomy since: | June 9, 1982 | ||||
| President : | Fernando López Miras ( PP ) | ||||
| Representation in the Cortes Generales : |
Congress : 9 seats Senate : 6 seats |
||||
| Structure : | 45 Municipios | ||||

The Region of Murcia ( Spanish Región de Murcia , officially Comunidad Autónoma de la Región de Murcia ) is an autonomous community in southeastern Spain on the Mediterranean Sea . It is enclosed by the autonomous communities of Valencia , Castile-La Mancha and Andalusia and is identical to the province of the same name . The capital is the city of Murcia .
Geography and climate
The country is crossed by the Betic Cordillera with the Barqueros volcano .
In the southeast, north of Cabo de Palos , lies the salt water lagoon Mar Menor . In the north-west of the region rises the highest mountain in the province, the 2015 m high Revolcadores .
The Murcia region is one of the driest areas in Europe (around 300 days of sunshine / year) and is therefore in a constant state of water scarcity . Temperatures easily rise above 40 ° C in summer. The winters are relatively pleasant, but now and then minus degrees in the single-digit range are reached.
A small climatic peculiarity is the Mediterranean south coast, both on Calblanque and in the area between Águilas and Cartagena , as there is a collection of many small bays , each with a small micro-climate and therefore also their own vegetation .
population
The Murcia region has 1,493,898 ( INE , January 1, 2019) people. The population increases significantly from year to year, in 2005 it was 1,335,792. About a third of them live in the city of Murcia .
Cities
Besides the capital Murcia , the port city of Cartagena , a Carthaginian foundation, and the third largest city in the region, Lorca , are important. The next largest cities are Molina de Segura and Alcantarilla .

City of Moratalla (Murcia)
|

City of Mula (Murcia)
|
Population development of the province


language
Murcia has its own dialect, Murciano or Panocho . It differs significantly from the actual Castellano and contains many loan words from Arabic and Catalan . Among other things, final consonants are left out and d and s within a word. Furthermore, there are sound distortions and sometimes grammatical peculiarities. In a small area in the north-east of the region that bears the name El Carche ( El Carxe in Catalan ), Catalan is predominantly spoken.
history
Already 50,000 years ago Neanderthals lived in what is now the Murcia region; Neolithic dolmens or menhirs are missing, but rock paintings are numerous (approx. 70 sites). Phoenicians , Carthaginians , Iberians , Romans and Visigoths left behind rather insignificant traces. In the years after 711, the region was overrun by the Moors . The city of Mursiya was founded in 825; in the late 9th and 10th centuries it flourished and so the name was transferred to the entire region. After the end of the Caliphate of Cordoba (1031), the Taifa Kingdom of Murcia was formed, which - with interruptions - existed until the Christian reconquest ( reconquista ) (1243 and 1266). Thereafter, most of the region was legally a separate kingdom , which was, however, de facto closely associated with the Crown of Castile ; it officially existed until its abolition in 1833.
politics
The Murcia region forms an autonomous community of Spain with a directly elected parliament and a government responsible for it. Their autonomy is based on the autonomy status of 9 June 1982. The newly formed autonomous community also took over the tasks of the self-governing bodies of the province of Murcia.
In order to overcome the water shortage, the government of the Murcia region supported the Hidrológico Nacional plan operated by the previous Spanish government, which has since been canceled, and carried out a campaign for it under the slogan “Agua para todos” (“Water for all”). As a result, she became enemies with the northern Spanish regions, which opposed this ecologically questionable aqueduct project.
Political structure
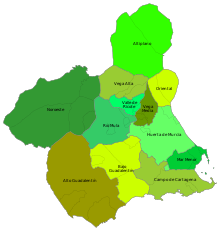
The Murcia region is politically divided into 45 municipalities ( municipios ) as local authorities. The Municipios are in turn subdivided into Pedanías or Diputaciones .
The largest municipalities in the region (data from INE , as of January 1, 2019) are:
|
|
Above the level of the municipality there is also a subdivision of the region of Murcia into comarcas , which does not fulfill any official tasks: see: Comarcas of Murcia
- Altiplano murciano
- Alto Guadalentin
- Bajo Guadalentín
- Campo de Cartagena
- Huerta de Murcia
- Comarca del Mar Menor
- Comarca del Noroeste
- Comarca del Río Mula
- Oriental region
- Valle de Ricote
- Vega Alta del Segura
- Vega Media del Segura
economy
Most of the Murcia region is still very agricultural. It is the largest producer of vegetables, fruits and flowers in Europe. It produces excellent rice in the Calasparra area and has large wine-growing areas near the towns of Bullas, Yecla and Jumilla.
Nevertheless, the construction and tourism sectors are the region’s major economic drivers. In tourism, golf is currently increasingly being used , 63 golf courses are planned , which are classified as ecologically questionable due to their location in a semi-desert and the constant scarcity of water.
Other sectors represented in the region include shipbuilding , furniture construction and canning factories.
Compared with the GDP of the EU expressed in purchasing power standards, the region achieved an index of 73 (EU - 28: 100) (2015). The unemployment rate in 2005 was 8%.
With a score of 0.863, Murcia ranks 12th among the 17 autonomous communities in Spain in the Human Development Index .
Famous sons and daughters of the region
- Ibn Arabi (1165–1250), Islamic mystic and theosophist
- Baltasar de Cisneros (approx. 1755–1829), admiral and viceroy of the Río de la Plata
- Isaac Peral (1851-1895), submarine pioneer
- José Selgas (1822–1882), poet and writer
- Ramón Gaya (1910-2005), painter
- Juan de la Cierva y Codorniú (1895–1936), inventor of the first helicopter ( Autogiro )
- Francisco Rabal (1926-2001), actor
- Arturo Pérez-Reverte (* 1951), journalist and writer
- José Antonio Camacho (* 1955), football player and coach
- Alejandro Valverde (* 1980), racing cyclist
- Luis León Sánchez Gil (* 1983), racing cyclist
Sports
- Real Murcia - Soccer
- Ciudad de Murcia (moved to Granada in 2007) - football
- UCAM Murcia CF - Soccer
- Lorca Deportiva - Soccer
- Polaris World Murcia - basketball
- ElPozo Murcia - Futsal
- Tour of Murcia - cycling race
Web links
- carm.es Official website of the region
- Región de Murcia digital Official website of the region on culture
- murciaturistica.es Website for tourism in the region
- Maps and satellite images
- Coat of arms of the Murcia region
- Estatuto de Autonomía de la Región de Murcia - Statute of Autonomy of the Region of Murcia (Spanish, Wikisource )
Individual evidence
- ↑ Cifras oficiales de población resultantes de la revisión del Padrón municipal a 1 de enero . Population statistics from the Instituto Nacional de Estadística (population update).
- ↑ ine.es
- ↑ Eurostat. Retrieved April 15, 2018 .
- ↑ eds-destatis.de ( Memento from September 27, 2007 in the Internet Archive ) (PDF; 292 kB).
- ^ Sub-national HDI - Area Database - Global Data Lab. Retrieved August 12, 2018 .
Coordinates: 37 ° 59 ′ N , 1 ° 27 ′ W