United States Air Force
|
United States Air Force |
|
|---|---|
 Air Force emblem |
|
| Lineup | September 18, 1947 |
| Country |
|
| Armed forces | United States Armed Forces |
| Type | Armed forces ( air forces ) |
| Strength | 346,166 soldiers 78,426 reservists |
| headquarters | Pentagon , Arlington County |
| motto | "Above All" ( Eng. Above All ) |
| Colours | Blue and silver |
| Civil and military leadership | |
| Secretary of the Air Force | Matthew Donovan |
| Chief of Staff of the Air Force | General David L. Goldfein |
| Vice Chief of Staff of the Air Force | General Stephen W. Wilson |
| insignia | |
| Aircraft cockade |

|
| Air Force symbol |

|
The United States Air Force ( USAF ), founded in 1947, is the air force of the armed forces of the United States of America. It is the second strongest of the four branches of the armed forces and one of the seven Uniformed Services of the United States . The main task of the USAF is the "defense of the United States through the control and exploitation of air and space". The headquarters (United States Air Force) is located in the Pentagon in Virginia .
In 2006 the US Air Force had 346,166 soldiers, including 71,691 (20.7%) officers . In addition, the USAF employed 145,620 civilian workers. The immediate reserve comprised 78,426 soldiers under the Air Force Reserve Command and the Air National Guard with 106,000 soldiers. In 2005 the US Air Force represented around a quarter of the total strength of the US armed forces of around 1.43 million people.
At the end of 2006, the inventory included around 4,300 aircraft, plus 1,700 Reserve and National Guard aircraft. The USAF maintains 85 large military airfields (Air Force Base) worldwide , 72 of them on American territories and eight in Europe, as well as another 82 smaller bases and almost as many bases of the reserve armed forces. It also has several hundred nuclear ICBMs , making it part of the US nuclear force .
With regard to its range of tasks, its global positioning, its pioneering role in space and its clout, the USAF is considered to be the best-positioned air force worldwide in the strategic studies .
history
prehistory
The United States Air Force goes back to an experimental air force of the communications unit of the United States Army , which in 1907 was named Aeronautical Division, US Signal Corps . The United States Department of War increased the association from 1914 under the name of Aviation Section, US Signal Corps changed its name, in the First World War, massive and improved his equipment, but this was too late to under the US participation in the war of 1917-18 with the To be able to compete with aviation troops of the major European powers. In 1918, the military aviation of the United States was named Air Service, United States Army .
The interwar period was characterized by the institutionalization of various aspects because the US Army Air Corps - from July 1926 to June 1941 - professionalized essential aspects of air warfare despite its small size. This mainly concerned the procurement of equipment, the training of soldiers and their stationing. This was accompanied by the creation of regional and task-related areas of responsibility, such as the military protection of the coasts of the United States.
After the Japanese attack on Pearl Harbor in early December 1941, the US Army Air Forces (USAAF) went into World War II against the Axis powers . Within the following nearly four years of war with a huge financial and human effort extended to enormous scope, they fought on the European and Pacific Theater along with the Marine pilots of the US Navy , the Air Command to all-out dominance. At the end of this war, USAAF aircraft opened a new chapter in human history when, in August 1945, when they dropped atomic bombs on Hiroshima and Nagasaki for the first and only time, they used nuclear weapons against another country. The US Air Force maintains its position as by far the strongest air force in the world.
After the war, the armed forces were reorganized and established three new Air Command on March 21, 1946: In support of the ground forces, the Tactical Air Command , for the reserve armed forces and homeland defense, the Air Defense Command and the strategic bomber and reconnaissance aircraft , the Strategic Air Command , the was later equipped with land-based ICBMs . In the following years it developed into the most powerful military unit in the western world.
With the establishment of the United States Air Force (USAF) by the National Security Act of July 26, 1947, which came into force on September 18 of that year, the US air force, with the exception of naval aviation , finally became an independent armed forces .
Cold War
During the Berlin blockade from 1948 to 1949, " Raisin Bombers ", mostly from the ranks of the USAF and the British Royal Air Force , supplied the city via an airlift for almost a year , with 278,000 flights and 2.1 million tons of material transported to this day largest air transport operation ever. The Air Force used in the Operation Vittles baptized operation mainly transport aircraft of the types Douglas C-47 , Douglas C-54 Skymaster and Lockheed C-121 Constellation .
In 1949 naval and air war strategists led an intense debate about which armed forces the United States should base its strategy on, since the budget was insufficient for the simultaneous establishment of a strategic bomber fleet and the formation of additional aircraft carrier formations. The Navy argued with the successful use of the aircraft carriers in the Pacific War, while the Air Force emphasized the barely definable potential of air warfare. The cancellation of some aircraft carrier contracts prompted senior naval officers to the so-called admiral uprising , which led to a division of the nuclear capacities of the United States between the two armed forces. In contrast, the Air Force prevailed with the establishment of a strategic bomber fleet.
The Korean War 1950–1953 was the Air Force's first military deployment as an independent military force. It assigned all aircraft and formations stationed in the Far East to the Far East Air Forces (FEAF) command under the command of Lieutenant General George E. Stratemeyer . In Korea, the USAF saw the first air battles between jet aircraft among themselves. The Ministry of Defense learned the lesson from the three-year deployment that an elaborate build-up of target strength in times of war was a waste of time and resources. In total, the Air Force had flown 721,000 sorties and transported 476,000 tons of material. During the entire war it shot down over 900 enemy aircraft, but lost 1,466 aircraft itself and suffered more than 600 other losses.
Since the end of the Cold War, the United States has steadily reduced its aircraft inventory. Together with the Navy and Marine Infantry, the Air Force had 5783 combat aircraft in 1992, 3985 in 2000 and 3542 in 2008. The strategic bomber fleet decreased from 276 (1992) to 208 (2000) to 189 (2008).
Brief historical overview

- 1947-1992 standby with nuclear-tipped bombers and later with ground-to-ground missiles in the Cold War .
- 1950–1953 Korean War .
- 1964 Simba rebellion in the Congo crisis
- 1964–1973 Vietnam War .
- 1973 Operation Nickel Grass , airlift with arms to Israel during the Yom Kippur War .
- 1980 Operation Eagle Claw , hostage rescue attempt in Iran.
- 1986 Operation El Dorado Canyon , bombing raid in Libya .
- 1990–1991 Operation Desert Shield , protection of Saudi Arabia from Iraq.
- 1991 Operation Desert Storm against Iraq .
- 1991–1996 Operation Provide Comfort , no-fly zone north for 36 ° N in Iraq.
- 1991–2003 Operation Southern Watch , no-fly zone south for 33 ° N in Iraq.
- 1993–1995 Operation Deny Flight , no-fly zone over Bosnia-Herzegovina .
- 1995 Operation Deliberate Force , bombing raid in Bosnia-Herzegovina.
- 1996 Operation Desert Strike , bombing raid in Iraq.
- 1997–2003 Operation Northern Watch North No- Fly Zone for 36 ° N in Iraq
- 1998 Operation Desert Fox , bombing in Iraq.
- 1999 Operation Allied Force , bombing raids in Kosovo and Serbia .
- 2001 – today Operation Enduring Freedom , bomb attack in Afghanistan .
- 2003–2010 Operation Iraqi Freedom , invasion and bombing raid in Iraq.
- 2011 Operation Odyssey Dawn , no-fly zone over Libya .
Mission and Doctrine
Constitutional basis
In contrast to the Army and Navy, the existence of the United States Air Force is not literally legitimized in the United States Constitution . According to sentences 12-14 of Article I, Section 8, Congress has the right to “raise and maintain armies” and “make regulations governing the conduct and service of land and naval forces”. Clause 1 of Section 2 of Article II, the only other passage that mentions military forces, also states that "[d] he President [...] Commander-in-Chief of the Army and Navy of the United States and the State Militia". However, only the literal readings of the constitutional interpretation refuse to build air forces, while two others, modernists and normativists, allow it. Originalists are divided on the issue, depending on the strength of their views. The example of the air force often serves as a refutation of literal readings of the constitution for the advocating currents . Proponents of the air force admissibility argue on three other lines. On the one hand, air forces are permitted under the umbrella of the army or the navy; on the other hand, naming the military aviation ministry initially in accordance with the constitution could nominally solve the problem. Of much greater importance, however, is the argument that to a certain extent it is subject to the judgment of the federal government which authorities are necessary for governance ( Necessary and Proper Clause ) .
Federal law
In the tradition of common law, the United States Constitution contains only general provisions. It is therefore up to federal legislation to work out the mandate of the air force. The Tenth Book of the United States Code in Section 8062 defines the Air Force's mandate as follows:
(a) It is the aim of Congress to provide an air force that is capable of doing so in conjunction with the other armed forces
- (1) To maintain peace and security and defend the United States, its Commonwealth of Nations and possessions, as well as all of those territories which have been occupied by the United States;
- (2) to support national politics;
- (3) implement the national objectives;
- (4) Defeat any state that engages in aggressive acts that endanger the peace and security of the United States.
Sections (e) and (f) will set the strength of the Air Force to the maximum. As a result, the Regular Air Force , i.e. the professional air force , is divided into 70 groups , taking into account all auxiliary forces such as reservists, supply units and the like required for a full operational strength. Ä. limited. The upper limit of technical equipment for the entire armed forces under the supervision of the Secretary of the Air Force is 24,000 aircraft or 25,000 aircraft tons . This restriction does not apply to missiles.
doctrine
The mission of the United States Air Force moves in the context of that of the armed forces as a whole. It is summarized in the catchphrase Global Vigilance, Reach and Power , which consists of three core competencies: the creation of airmen (literally translated: “airmen”), high-tech warfare and integrative operations.
According to the doctrine, this objective should be reflected in six basic skills:
The Air Force sees “ Air and Space Superiority ” as an integral part of cross-armed operations on land, sea, in the air and in space . The "Global attack capability" (Global Attack) consists of the technical superiority of the air force and the ability to intervene at any time and anywhere with the goal. The essence of the term “ Precision Engagement” lies in the ability to deploy a sufficiently strong force against selected targets, since the USAF believes that the nature and breadth of the mission spectrum require precise and reliable use of military strength to address risks how to limit collateral damage . "Superior strength in the available information" (information Superiority) defines it as a commander aptitude to take up the highest possible proportion of the available information material, and to make it usable for its battle management. " Agile Combat Support" includes the most favorable combat setup possible, which must be accompanied by an adequate supply of resources. This applies to all associations, from the alert to the expeditionary force .
organization
The USAF is the branch of the US armed forces responsible for airspace and space . At the top of their military leadership is the Chief of Staff, USAF (CSAF), who, together with the commanders of the other branches of the armed forces (with the exception of the Commandant of the Coast Guard ), is one of the Joint Chiefs of Staff , the military leadership level in the US Department of Defense . The US President usually appoints the Chief of Staff for four years and acts as an intermediary between the administration and the soldiers. General David L. Goldfein has been USAF Chief of Staff since July 2016 .
In addition, the Department of the Air Force (Air Force Office) as part of the Department of Defense forms the highest civil administration level of the USAF with the Secretary of the Air Force ( Air Force Secretary of State ) at its head.
A distinction can also be made:
- The Air Force
- The Reserve Air Force ( US Air Force Reserve )
- Air National Guard ( Air National Guard )
budget
The budget for the financial year 2010 included 170.6 billion US dollars , equivalent to 22% of the total defense budget of 804.2 billion US dollars.
The Air Force budget increases year after year. In 2008 it was still $ 142 billion. The largest single items were the F-35 aircraft program (US $ 11.4 billion), the missile defense program ( Aegis , THAAD and PAC-3 ) with US $ 9.9 billion, and the Virginia-class program ( Submarines) at $ 5.4 billion.
Main commands
The USAF is in ten main commands (major commands) which are either functional or regional orientation have divided.
Functional commands
- Air Combat Command (ACC) - assault, bombing , reconnaissance and surveillance
- Air Education and Training Command (AETC) - Training and exercise
- Air Force Global Strike Command (AFGSC) - land-based intercontinental ballistic missiles , nuclear weapons
- Air Force Materiel Command (AFMC) - Research, Technology, Maintenance and National Museum of the United States Air Force
- Air Force Reserve Command (AFRC) - Reserve
- Air Force Space Command (AFSPC) - missiles , satellites and GPS , cyber warfare
- Air Force Special Operations Command (AFSOC) - special operations
- Air Mobility Command (AMC) - Air transportation and air refueling
Regional commands
- US Air Forces in Europe (USAFE) - Representing the USAF in Europe
- Pacific Air Forces (PACAF) - Representing the USAF in the Pacific
Further breakdown
At the head of each main command is an officer with the rank of general . A command are numbered up to two air forces ( Numbered Air Forces ) allocated, of which there are 20 active. These in turn consist of at least two squadrons (wings) . A USAF Air Force Base is typically organized around such a wing ; larger bases accommodate several wings or a numbered air force . The wings are made up of groups , each of which is assigned a certain type of aircraft. Aircraft and personnel in a group are usually deployed together during operations and exercises, i.e. not divided up between different missions. Below the group is the Squadron , the basic unit of the American air force. As an example of this hierarchy, nine Lockheed C-141 transporters belong to the 730th Airlift Squadron, 452nd Air Mobility Wing, 4th Air Force, Air Force Reserve Command .
There are also other organizational subdivisions.
Ranks
- Small selection of ranks
| United States Air Force officers | |||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| US pay level | O-10 | O-9 | O-8 | O-7 | O-6 | O-5 | O-4 | O-3 | O-2 | O-1 | |
| Epaulette |

|
|
|
|
|
|

|

|

|
|
|
| Rank | General of the Air Force 1st | general | Lieutenant General | Major General | Brigadier General | Colonel | Lieutenant Colonel | major | Captain | First lieutenant | Second lieutenant |
| abbreviation | GOAF | gene | Lt Gen | Maj Gen | Brig Gen | Col | Lt Col | Maj | Capt | 1stLt | 2ndLt |
| NATO rank code | OF-10 | OF-9 | OF-8 | OF-7 | OF-6 | OF-5 | OF-4 | OF-3 | OF-2 | OF-1 | |
equipment

Aircraft
The USAF owns a total of 4,093 aircraft, plus 1,289 of the Air National Guard and 396 of the Air Force Reserve Command . The average age of all 5778 machines is 24 years. (As of September 30, 2007)
|
Fighter, attack aircraft
bomber Transport aircraft |
Tanker planes Reconnaissance aircraft Training aircraft |
Tilt rotor aircraft helicopter Drones Others |
There are also other types in small numbers for special purposes, such as An-26 , Mil Mi-8 , Su-27 , RC-26, WC-130, UV-18 and some MiG-23 .
Other weapon systems
In addition, the armed force has 450 intercontinental ballistic missiles of the type Minuteman , cruise missiles ( AGM-86 and AGM-158 ), guided missiles and bombs , 46 satellites for communication ( Milstar ), navigation ( Global Positioning System ) and reconnaissance. Then there is the armament of the soldiers, such as rifles and pistols .
Further development
The Air Force is currently running a number of modernization and redevelopment programs. In addition, the demands on the American air force have changed since the beginning of the war on terror : In view of the predominant guerrilla tactics of the enemy, the ability to reconnaissance and monitor ground areas is increasingly required.
The most important development program is the Lockheed Martin F-35 , which will replace all fighter aircraft models in the Navy and, together with the air superiority fighter Lockheed Martin F-22, will provide the Air Force's future fighter aircraft. A few machines are already being flown for testing. The first aircraft in active service should be handed over to the troops in 2009. From 2015, the Navy should receive 50 F-35s a year, the Air Force 80. By 2030, all 1200 F-16s in the US Air Force are expected to be replaced by F-35s. In 2025, the US Navy wants to have its entire fleet of fighter planes converted to the F-35. It is unlikely that this schedule can be met due to delays.
The development and new procurement programs are sometimes struggling with difficulties. The F-22 costs around $ 189 million each. That is around three times the price initially envisaged and significantly more than the 110 million that were budgeted in the 1999 budget year. To compensate for this, the number of machines to be put into service has been reduced from 750 to 183. The financial problems in the defense budget are exacerbated by the high maintenance and replacement costs for aircraft, which quickly wear out or get lost in use in Afghanistan and Iraq, as well as the rising fuel costs. In addition, the age of the aircraft in service is increasing, as there have hardly been any new acquisitions since the early 1990s. In 1991 the average machine was almost ten years old, in 2008 it was more than 20 years.
Among the oldest machines are the Boeing KC-135 tanker aircraft , which are up to 48 years old. Since 2001 there have been political and tendering disputes over the selection of a successor model, usually referred to as KC-X. The most recent attempt at a tendering process was canceled in September 2008. The Air Force plans to purchase 179 KC-Xs. The entire program is estimated to be worth $ 35 billion.
The development programs at a very early stage include a new long-range bomber that will replace the B-1 and B-52 types from 2018, and two other types of tanker aircraft, mostly referred to as the KC-Y and KC-Z, which were launched around 2015 and To be commissioned in 2035.
The US Air Force is striving to reduce its reliance on imported fossil fuels by just under 2.4 billion gallons (just under 10.92 billion liters) annually . As part of this project, she tested a fully biofuel- powered manned A-10 Thunderbolt II for the first time on March 26, 2010 at Eglin Air Force Base .
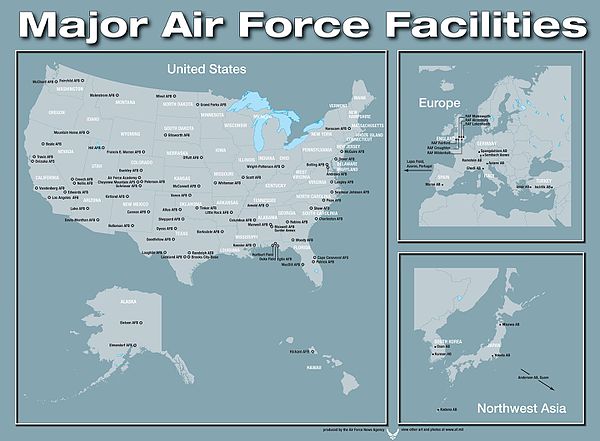
Military airfields (selection)
Military airfields of the Air Force on US territory are generally referred to as "Air Force Base" (AFB), outside of it as "Air Base" (AB) or smaller as "Air Station" (AS). Military airfields of the other branches of the armed forces have different names.
- Andrews Air Force Base , Maryland
- Barksdale Air Force Base , Louisiana
- Castle Air Force Base , California
- Davis-Monthan Air Force Base , Arizona
- Dyess Air Force Base , Texas
- Edwards Air Force Base , California
- Eglin Air Force Base , Florida
- Ellsworth Air Force Base , South Dakota
- Elmendorf Air Force Base , Alaska
- Joint Base Pearl Harbor-Hickam , Hawaii
- Holloman Air Force Base , New Mexico
- Lackland Air Force Base , Texas, headquarters of the ISR
- Langley Air Force Base , Virginia
- Luke Air Force Base , Arizona
- MacDill Air Force Base , Florida
- Minot Air Force Base , North Dakota
- Mountain Home Air Force Base , Idaho
- Nellis Air Force Base , Nevada
- Offutt Air Force Base , Nebraska
- Peterson Air Force Base , Colorado
- Pope Air Force Base , North Carolina
- Randolph Air Force Base , Texas
- Schriever Air Force Base , Colorado
- Scott Air Force Base , Illinois
- Sheppard Air Force Base , Texas
- Tinker Air Force Base , Oklahoma
- Tyndall Air Force Base , Florida
- Vandenberg Air Force Base , California
- Whiteman Air Force Base , Missouri
- Wright-Patterson Air Force Base , Ohio
US military airfields outside the United States (selection)
- Andersen Air Force Base , Guam
- Aviano Air Base , Italy
- Clark Air Base (1903-1991), Philippines
- Incirlik Air Base , Turkey
- Joint Base Balad (handed over to Iraqi Army in December 2011), Iraq
- Kadena Air Base , Japan
- Kunsan Air Base , South Korea
- Misawa Air Base , Japan
- Thule Air Base , Greenland
- Osan Air Base , South Korea
- Yokota Air Base , Japan
US military airfields in Germany (selection)
- Bitburg Air Base (until 1994 and briefly in 1997), Rhineland-Palatinate
- Geilenkirchen Air Base (NATO), North Rhine-Westphalia
- Erding Air Base (until 1956), Bavaria
- Fürstenfeldbruck Air Base 1945–1960, Bavaria
- Hahn Air Base (until 1993, auxiliary building until 1995), Rhineland-Palatinate
- Kaufbeuren Air Base (until the 1950s), Bavaria
- Landsberg Air Base (1947 to 1958), Bavaria
- Neubiberg Air Base near Munich (1945 to 1957), Bavaria
- Ramstein Air Base , Rhineland-Palatinate
- Rhein-Main Air Base at Frankfurt am Main Airport (1945–2005)
- Sembach Air Base (until 1995, since then Sembach Annex, part of Ramstein)
- Spangdahlem Air Base , Rhineland-Palatinate
- Tempelhof Air Base (TCA) (until June 1993) Berlin
- Wiesbaden Air Base , since 1993 Wiesbaden Army Airfield, Hesse
- Zweibrücken Air Base (until the mid-1990s), Rhineland-Palatinate
- Stuttgart Air Base
literature
- Air Force Association : USAF Almanac 2007 , in: Air Force Association (Ed.): Air Force Magazine Vol. 90, No. May 5, 2007
- Detlef Buch : Air Power USA. The reform of the US Air Force . Bautz, Nordhausen 2012, ISBN 978-3-88309-765-7 .
- Anthony H. Cordesman, Ulrich Kaeser: America's self-destroying airpower . Center for strategic & international studies, October 2008 America's Self-Destroying Air Power: Becoming Your Own Peer Threat (summary and pdf)
- The Air Force Handbook 2007 at fas.org (pdf, 326 pages, accessed October 14, 2009, 17 MB)
Web links
- www.af.mil Official website of the USAF (English)
- USAF Museum (English)
- GlobalAircraft.org (English)
- Doctrines of the Air Force (English)
- Air Force History Index (English)
Individual evidence
- ↑ Factsheet of the Air Force ( Memento from May 27, 2012 in the web archive archive.today )
- ^ Hammond, Grant T .: The US Air Force and the American Way of War , in: McIvor, Anthony: Rethinking the Principles Of War , Annapolis, MD: Naval Institute Press 2005, p. 109.
- ↑ According to historians William T. Y'Blood and Walter J. Boyne, FEAF alone flew a total of 720,980 sorties, including over 92,000 close air support, 192,581 interdiction, over 20,000 bombing, 210,000 cargo, and thousands of reconnaissance and air superiority sorties . FEAF delivered 476,000 tons of ordnance (68 percent of the total amount of ordnance delivered during the war by the United Nations) and destroyed over 900 enemy aircraft. The fight for air supremacy also exacted incredible losses. FEAF lost some 1,466 aircraft (about half or 757 to enemy action). The Navy, Marines, and other United Nations forces lost another 520 aircraft. FEAF also lost 1,180 personnel, with an additional 600 non-fatal casualties reported , from: A Decisive Presence: The United States Air Force in the Korean War ( Memento of December 8, 2006 in the Internet Archive ). Accessed May 11, 2008.
- ↑ German version of the constitution (PDF; 201 kB) on the website of the American embassy in Germany, page 3. Accessed on March 1, 2008.
- ^ Page 5 of the German constitutional text.
- ↑ Somin, Ilya: Who claims that textualism and originalism lead to the conclusion that the Air Force is unconstitutional? from The Volokh Conspiracy blog of January 29, 2007, accessed on March 1, 2008.
- ^ Rappaport, Michael: Why the Air Force Is Not Unconstitutional. In: Discourse.net , November 17, 2005, accessed March 1, 2008.
- ^ Wording of the paragraph on the Cornell Law School website . Retrieved March 1, 2008.
- ↑ Description of the core competencies and basic skills on the Air Force website . Retrieved March 1, 2008.
- ↑ Air Force Magazine Vol. 91, No. 5 (May 2008), pp. 60ff.
- ↑ cf. King, Samuel Jr .: Air Force officials take step toward cleaner fuel, energy independence. ( Memento of April 8, 2010 in the Internet Archive ) In: Inside Eglin AFB , March 26, 2010, accessed on April 1, 2010 (English).
- ^ Paur, Jason: Air Force Debuts Biofuel-Guzzling Warthog. In: Wired.com , March 30, 2010, accessed April 1, 2010.