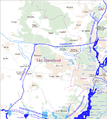
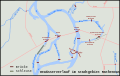
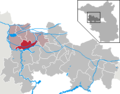
List of bridges over the Untere Havel waterway
The list of bridges over the Untere Havel waterway, official abbreviation UHW, lists existing and former bridges over the Untere Havel waterway . The 148 km long federal waterway lies in the German federal states of Berlin , Brandenburg and Saxony-Anhalt .
Structure of the bridge lists
Only the bridges documented in the sources (literature and web links) are included. Bridges over secondary waterways and backwaters were also included, but these are legally part of the UHW or serve for better explanation. The numbering (column 1 ) and kilometering (column 2 ) take place on the main water UHW from the Spree estuary in Berlin-Spandau at the beginning of the Spree-Oder waterway and ends when you reach the Elbe at Havelberg . The numbering and kilometering follows the information on the boat tickets. Former or unnumbered bridges are under the uppercase X listed. In column 3 , most of the bridges are documented in the picture. Column 4 contains the bridge names, with unnamed bridges in brackets and former bridges in italics . Below that are the places or districts in which or in the vicinity of which they are located. In the text column "Comments", brief notes on the bridges are given, if known. The sixth and last column links the coordinates of the structures.
The bridges
Havel from the mouth of the Spree to Pichelsdorfer Gmünd
| number | km | photography | Name of the bridge / place | Remarks | location |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
|
|||||
| 1 | 0.09 |
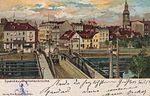 |
Charlottenbrücke Spandau |
The steel tied arch bridge leads the street Charlottenstrasse / Stresowstrasse over the Havel . It was built between 1926 and 1929 and replaced the multi-part arch bridge from 1886 (top picture). More pictures at Commons | cards |
| 2 | 0.40 |

|
Spandau Havel Bridge |
The railway bridge was built as haunched girder bridges during the construction of the Berlin-Spandau train station and the expansion of the high-speed line Hanover-Berlin in 1998, based on a design by Schlaich Bergermann and Partners , and replaced the previous truss bridge of the Berlin-Hamburg railway . | cards |
| 3 | 0.50 |

|
Dischinger Bridge Spandau |
The Dischinger Bridge leads over the Havel in Berlin-Spandau. It was built in 1956 and named after Franz Dischinger . | cards |
| 4th | 1.50 |

|
Schulenburg Bridge Wilhelmstadt |
The Schulenburg Bridge is a steel truss - arch bridge over the Havel in Spandau district . It connects Schulenburgstrasse and Weißenburger Strasse. The listed bridge was built between 1907 and 1909. | cards |
| 5 | 2.95 |
 
|
Frey Bridge Wilhelmstadt |
The old Frey bridge was a steel - arch bridge over the 60-meter-wide Havel and Havelseenweg in the district Wilhelmstadt . The listed bridge from the years 1908/1909 is part of the highway ( Federal Straße 2 / 5 ) and connects Pichelsdorf with the Pichelswerder . The previous bridge was demolished and will be replaced by a new one. (As of 2015/16) → See main article: Freybrücke | cards |
Potsdam Havel
The Untere Havel waterway splits at kilometer 16.31. The Potsdamer Havel begins at the southern end of the Jungfernsee at the Glienicker Bridge at kilometer 28.61. It belongs legally to the UHW. A total of 16 bridges cross the Potsdam Havel and its side waters.
Sacrow-Paretz Canal
The Sacrow-Paretz Canal begins at km 20.11 of the UHW and connects the Havel on the city limits of Berlin / Potsdam ( Jungfernsee ) with the Havel east of Ketzin . At km 32.59 the canal ends at the Göttinsee near Paretz and there it reaches the Havel again. Four bridges cross the canal. In addition, the Nedlitz North Bridge over an old connecting arm of the Jungfernsee to the White Lake is mentioned. In the period from 1876 to 1903, shipping had to use this old trip with the Nedlitz North Bridge.
| number | km | photography | Name of the bridge / place | Remarks | location |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
|
|||||
| 6th | 20.34 |
 
|
Nedlitzer Südbrücke, also called Friedensbrücke, Neu Fahrland / Potsdam |
The upper picture shows the steel truss bridge, built in the post-war period, the lower picture the old and the new bridge, which is offset slightly to the west, on a new route shortly before the old bridge was opened to traffic and the demolition started. Bundesstraße 2, Tschudistraße / Nedlitzer Straße, crosses the bridge . | cards |
| X | 20.80 |
 
|
Old Bridge (around 1790)
Nedlitzer Nordbrücke, (formerly Persiusbrücke approx. 1930s) |
A first wooden bridge was built in 1682 on the important road to the city of Spandau . Before that, there was a ferry at this point with the Nadolice (Nedlitz) ferry . This wooden bridge with customs house is pictured for the first time around 1790. The massive north bridge that followed was an arch bridge that was built in 1853/54 over the old Havel arm between the Lehnitzsee and the Weißen See. The bridge was demolished in 2001, although it is a listed building. The new bridge was built in 2002/03 as a two-legged T-beam bridge. The total length is 52 meters. Bundesstraße 2 crosses the bridge as Tschudistraße. |
cards |
| 7th | 25.46 |
 
|
Marquardt Potsdam road bridge | The federal road 273 crosses the Sacrow-Paretz Canal, runs east past the Potsdam district of Marquardt and then over the Berlin outer ring road. The picture above shows the bridge from the 1960s. The prestressed concrete bridge built in 1965/66 was created as a two-cell box girder using the so-called in-situ concrete cantilever. The continuous beam had a span of 20 m / 60 m / 20 m with an upper useful width of 11 meters. It has since been torn down. The picture below shows the temporary makeshift bridge. A new steel arch bridge with a composite plate is currently (spring 2016) under construction as part of the German Unity transport project . The inauguration of the bridge has been postponed several times. The new bridge also received a sidewalk and bike path on one side. | cards |
| 8th | 25.90 |
 
|
Marquardt Railway Bridge Marquardt (Potsdam) |
The Berlin outer ring runs over the Marquardt railway bridge between the Marquardt and Bornim train stations | cards |
| 9 | 28.48 |
 
|
Uetz motorway bridge, BAB 10 Uetz-Paaren Potsdam |
With the construction of the autobahn around Berlin at the end of the 1920s, a steel truss bridge was built over the canal. It was blown up at the end of World War II and replaced by a wooden bridge with steel girders in the post-war period. Up until the mid-1980s there were wooden pillars in the canal bed that impeded shipping on this busy waterway. The steel bridge, built in the mid-1980s, leads the Bundesautobahn 10 , western Berliner Ring, over the canal. During expansion work on the canal in spring 2015, large parts of the destroyed bridge were found and recovered at the bottom of the water. | cards |
Havel Canal
The Havelkanal (HvK) is a federal waterway in the state of Brandenburg and starts at km 0.41 between Niederneuendorf and Hennigsdorf on the Havel (km 10.30 of the Havel-Oder Waterway ) and ends at km 34.59 at Paretz near from Ketzin turn on the Havel (km 32.27 of the Lower Havel waterway ).
City of Brandenburg an der Havel
As part of the UHW, the Havel flows through the urban area of Brandenburg an der Havel and is divided into various arms and backwaters. Numerous bridges have been built over these waters over the centuries. Dams and bridges connect the historic city centers. In the upper water of the suburban lock Brandenburg, the Stadthavel branches off with the city canal:
Brandenburg city canal
The Brandenburger Stadtkanal (BrK) including the Brandenburger Stadthavel belongs to an old, approximately 4.3 kilometer long arm of the Havel in the city area. At kilometer 54.30 of the main UHW fairway, it branches off to the southwest and later to the west and meets the Brandenburg Niederhavel below the Luckenberger Bridge. Immediately to the west of the Steintorbrücke at kilometer 57.95 is the Brandenburg city lock . Five bridges cross the city canal. Due to the low bridges and the small lock dimensions, this arm of the Havel is only used by smaller sports boats. With mean water at the upper level of the Brandenburg suburban lock, the maximum clearance height of the Steintor Bridge is only 2.80 meters.
| number | km | photography | Name of the bridge / place | Remarks | location |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
|
|||||
| 1 | 57.11 |

|
St. Anne's Bridge Brandenburg an der Havel |
The road bridge connects Potsdamer Strasse with St.-Annen-Strasse over the city canal. | cards |
| 2 | 57.42 |

|
(Pedestrian Bridge City Canal) Brandenburg an der Havel |
Pedestrian bridge from Kirchhofstrasse to Sankt-Annen-Promenade over the city canal. | cards |
| 3 | 57.82 |

|
Stone gate bridge Brandenburg on the Havel |
The bridge connects Steinstrasse with Jacobstrasse, the historic arterial road to the southwest of Brandenburger Neustadt . This medieval military road led via Ziesar to Magdeburg . The stone gate tower is right next to the bridge . | cards |
| 4th | 58.36 |

|
Canal bridge Brandenburg an der Havel |
The first bridge over the canal at this point was built in 1890–91 as part of the construction of Bauhofstrasse and the Neuendorfer suburb. In 1927-28 the bridge was renewed. Today's concrete girder bridge leads Bauhofstrasse over the city canal. | cards |
| 5 | 58.48 |

|
(Pedestrian Bridge City Canal) Brandenburg an der Havel |
The new pedestrian bridge was built as part of the preparations for the 2015 Federal Horticultural Show and connects Heinrich-Heine-Ufer with the new parking lots on Wiesenweg. | cards |
Upper water suburban lock
| number | km | photography | Name of the bridge / place | Remarks | location |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
|
|||||
| 10 | 55.40 |

|
Lock bridge Brandenburg Brandenburg an der Havel |
The road bridge leads the Krakauer Landstrasse (L 91) over the waterway and the head of the suburban lock Brandenburg . It is a girder bridge made of reinforced concrete with columnar central pillars on the top of the central dam of the lock. | cards |
In the underwater of the suburban lock Brandenburg, the waterway divides into the Beetzsee-Riewendsee-Wasserstraße and the Brandenburg Niederhavel:
Beetzsee-Riewendsee waterway
- North
The Beetzsee-Riewendsee-Wasserstraße (BRW) is a federal waterway of waterway class IV up to the Pählbrücke , above the bridge a so-called other or non-classified inland waterway of the federal government and belongs to the Lower Havel-Wasserstraße (UHW). Three bridges cross the Beetzsee-Riewendsee waterway. As Streng be particularly narrow in Havel area, sometimes man-made or designated by extension and expansion of navigable waterways made smaller between natural lakes.
| number | km | photography | Name of the bridge / place | Remarks | location |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
|
|||||
| X | 7.43 |

|
Pählbrücke Amt Beetzsee |
Pählbrücke between Radewege / Butzow and Mötzow (L 911) as Butzower Straße over the Streng between the two basins of the Beetzsee of the Beetzsee-Riewendsee waterway . | cards |
| X | 13.04 |

|
(Feldwegbrücke) Roskow Amt Beetzsee |
Feldwegbrücke, only for pedestrians and cyclists (Storchenradweg) over the Lünower Streng, former railway bridge of the Westhavelländische Kreisbahnen . | cards |
| X | 18.11 |

|
Päwesiner road bridge Päwesin Amt Beetzsee |
Road bridge between Päwesin and Bagow of the L 912 over the Päwesiner Streng. | cards |
Brandenburg Niederhavel
- to the south
The Brandenburger Niederhavel (BHv) is part of the Lower Havel waterway and at the same time part of the Havel River in the city of Brandenburg. The length of the waterway is about eight kilometers.
| number | km | photography | Name of the bridge / place | Remarks | location |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
|
|||||
| 1 | 56.86 |

|
Homeyenbrücke Brandenburg an der Havel |
The Homeyenbrücke connects Mühlentorstrasse with Grillendamm across the Havel. | cards |
| X | 0.41 BrK |

|
Domstrengbrücke Brandenburg an der Havel |
The pedestrian bridge, also called the Himmelsbrücke by the locals , leads over Domstreng , a tributary of the Niederhavel in the city area, north of the cathedral island . It branches off to the east below the Homeyen bridge at about 57 km and is almost 500 meters long. It is separated from the Nuhlenhavel and the Stadthavel by the Mühlendamm and Krakauer Strasse at the old castle mill . | cards |
| X | 56.79 UHW |

|
(Pedestrian bridge over the Näthewinde) Brandenburg an der Havel |
The old Havelarm, located south of the Dominsel, separated only by the Mühlendamm from the east flowing Stadthavel, is called Näthewinde . The branch of the backwater is at about 57.20 kilometer. A footbridge leads over the Näthewinde between Hammerstraße and Domkietz on the cathedral island. | cards |
| 2 | 57.63 |

|
Millennium Bridge Brandenburg on the Havel |
The Millennium Bridge connects the old and new town of Brandenburg . | cards |
| X | 57.90 |

|
Gottfried Krüger Bridge left bank BHv Brandenburg an der Havel |
The bridge, also known colloquially as the abdominal pain bridge, crosses the Pumpergraben directly at its confluence with the Niederhavel in the course of the promenade along the Heinrich-Heine-Ufer. The bridge was given the eye-catching arch shape because of the need for barges to pass through. At the end of the navigable ditch there was a cider mill and other small businesses. The small businesses used to use water transport. Due to the uncomfortable passage of the bridge, which is provided with steps, a level, parallel bypass was built next to the old bridge in 2014. | cards |
| 3 | 58.23 |

|
Luckenberger Bridge Brandenburg an der Havel | The Luckenberger Bridge, formerly also called the New Havel Bridge , leads the Luckenberger Straße across the river. | cards |
| X | approx. 58.50 |

|
Wredow Bridge left bank BHv Brandenburg an der Havel |
The Wredow Bridge is a girder bridge and leads the Wredowstraße over the Jakobsgraben in Brandenburg an der Havel. The Jakobsgraben is an old arm of the Havel. The first bascule bridge with a steel superstructure was built at this point around 1900 because the Jakobsgraben was navigable. | cards |
| 4th | 59.11 |

|
Central ring road bridge Brandenburg an der Havel |
Bundesstraße 1 leads over the bridge as Zanderstraße / Otto-Sidow-Straße. | cards |
| 5 | 59.21 |

|
Railway bridge Niederhavel Brandenburg an der Havel |
The riveted steel truss bridge was a replacement building after the Second World War . The previous bridge was blown up at the end of the war. | cards |
Silo channel
The Silokanal (SiK) in the urban area of Brandenburg is a section of the federal waterway Untere Havel-Wasserstraße (UHW). The silo canal is 5.25 km long.
| number | km | photography | Name of the bridge / place | Remarks | location |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
|
|||||
| 11 | 56.79 |

|
Brielower Bridge Brandenburg an der Havel |
The Brielower Bridge leads the state road 98 over the canal. Brielower Strasse becomes Brielower Landstrasse. | cards |
| 12 | 57.96 |

|
Roskower railway bridge Brandenburg an der Havel |
Single-track railway bridge of the former Westhavelländische Kreisbahnen . It also leads pedestrians across the canal. | cards |
| X | 58.57 |
Gördenbrücke old Brandenburg an der Havel |
Steel arch bridges. It led the long-distance or federal highway 102 in two lanes over the silo channel. Tracks of the Brandenburg tram were laid on the roadway . | cards | |
| 13 | 58.59 |

|
Gördenbrücke Brandenburg an der Havel |
The Gördenbrücke is a double-track tram and four-lane road bridge made of reinforced concrete. In addition to the tram, the federal highway 102 leads across the canal. It was built about 50 meters below the old Görden Bridge. | cards |
| 14th | 59.86 |

|
(Railway bridge) Brandenburg on the Havel |
The tied arch bridge (Langerscher Barken) brings the Treuenbrietzen - Neustadt railway across the canal. It was built in 1999/2000 in place of an older steel truss bridge. The width is 10.55 meters, the height 17.60 meters and the arch span 105 meters. | cards |
| X | 60.80 |
(Pipe bridge) Brandenburg on the Havel |
The bridge only served as a carrier for several pipelines and led, among other things, a district heating pipe across the canal. In 1997 it was demolished without replacement. Aerial view of the bridge on the side of the demolition company | cards | |
| 15th | 61.35 |

|
Quenz Bridge Brandenburg on the Havel |
The Quenzbrücke, sometimes also called the Quenzseebrücke, leads four-lane federal highway 1 over the silo canal . The Magdeburger Landstrasse and Plauer Landstrasse meet on the bridge. It was built in 1968. | cards |
Lower Havel
As the Lower Havel , the waterway leads from Plauer See in a more northerly and more westerly direction along the Pritzerber See and the towns of Premnitz and Rathenow in the direction of the Havelberg .
| number | km | photography | Name of the bridge / place | Remarks | location |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
|
|||||
| X | 380.87 (left side to EHK) |

|
Seegartenbrücke Plaue (Brandenburg an der Havel) |
The Seegartenbrücke is legally the last bridge to the Elbe-Havel Canal / Mittelland Canal . It is located to the west of the transition from Wendsee to Plauer See , i.e. at the meeting point of two important waterways, the Elbe-Havel Canal and the UHW. From 1954 to 2005 it was called Rosa-Luxemburg-Brücke, named after the representative of the European labor movement Rosa Luxemburg . | cards |
| 16 | 68.02 |

|
Havel Bridge Plaue Plaue (Brandenburg an der Havel) |
The Plauer Bridge, called Havel Bridge Plaue (old bridge) in the shipping maps, leads over the Havel in Brandenburg an der Havel in the Plaue district . Today the bridge is also known as the Old Plauer Bridge. In 2002 a new bridge was opened over the Havel and the Plauer bridge was closed to vehicle traffic. | cards |
| 17th | 68.30 |

|
Westhavellandbrücke Plaue (Brandenburg an der Havel) |
With the completion of the B1 bypass , the new Plauer Bridge was inaugurated in 2002 after a construction period of 27 months. It is a box girder bridge , a so-called haunched girder bridge . The main span is 70 meters and the total length is 240 meters. The cost of building the bridge was around 3.8 million euros. | cards |
| X | 78.64 Pritzerber See, (right bank UHW) |

|
Pritzerbe railway bridge Pritzerbe |
The connection from the Havel to the Pritzerber See is narrowed by a dam. Two bridges lead over the narrow passage, a railway bridge on the Brandenburg – Rathenow railway line and the road bridge on federal road 102 between Pritzerbe and Fohrde . The groundbreaking ceremony for the Brandenburg urban railway took place on March 19, 1901 in Pritzerbe. The railway line opened on March 25, 1904. | cards |
| X | 78.65 Pritzerber See, (right bank UHW) |

|
Road bridge Pritzerbe Pritzerbe |
Two bridges run over the connection from the Havel to the Pritzerber See, a railway bridge on the Brandenburg – Rathenow railway line and the road bridge on the federal road 102 between Pritzerbe and Fohrde . A first wooden road bridge to Fohrde was mentioned in 1895 over the narrow waterway to the lake. There was a ferry at this point from around 1815. The water connection was partially filled in for the bridge construction. All that remains is the current passage width. Today's road bridge was built in 2012/13. | cards |
| 18th | 82.07 |

|
Lock bridge Bahnitz Bahnitz / Milower Land |
The new lock bridge leads a farm road over the lower head (valley-side lock gate) of the Bahnitz lock . | cards |
| 19th | 92.90 |

|
Milower road bridge Milow / Milower Land |
Milower Straße (L 963) runs over the reinforced concrete girder bridge between Milow and Premnitz . | cards |
| 20th | 101.63 |

|
(Road bridge Rathenow bypass, B 188n) Rathenow |
With the emergence of the OU Rathenow, the new construction of the B 188n became necessary as the last section over approx. 2.4 kilometers with a bridge over the Havel. The road bridge was built on the site of the former railway bridge of the Lehrter Bahn (main track) of the DB. The result is a tied arch bridge. It was completed in September 2010. Construction began in 2004. The B 188 now runs west of Rathenow near Großwudicke on the south side of the Berlin – Hanover ICE line . | cards |
| 21st | 101.67 |

|
Rathenow I Rathenow railway bridge |
Berlin-Lehrter Railway | cards |
| 22nd | 101.69 |

|
Rathenow II Rathenow railway bridge |
Berlin-Lehrter Railway | cards |
| 23 | 103.56 |

|
Rathenow Peace Bridge Rathenow |
Road bridge of the former B 188 over the Havel. The bridge leads the Genthiner Straße in the urban area over the waterway. It was built in 1954 and completely renovated in the early 2010s. | cards |
| 24 | 129.14 |

|
Garz Garz lock bridge |
Commercial street with a footpath and a total width of 6 m. | cards |
| 25th | 131.65 |

|
Strodehner Bridge in the municipality of Havelaue |
At Strodehne the L 17 Friesack - Rhinow - Havelberg crosses the Havel. There was only one ferry at this point between 1972 and 1999 . The new steel arch bridge was pushed in in May 1999 and inaugurated on November 20, 1999. It replaced an earlier makeshift bridge built after the Second World War, which had to be demolished in 1971, but its abutments were retained. The financing of the new building was partly a point of contention between the citizens of the city of Havelberg and the state of Brandenburg, to which the bridge belongs. After all, the construction costs of 5.8 million DM could be met for the most part from an EU agricultural fund. | cards |
| 26th | 145.48 |

|
Sandau Bridge Havelberg |
The Sandauer Brücke, which was renovated between 2007 and 2009, is a road bridge in the urban area of Havelberg . It leads the federal highway 107 over the Havel and was built as an arch bridge with a central lane. The total length is 125 meters. | cards |
| X | - | (Sandauer Brücke / Havelbrücke) Havelberg |
The first wooden Sandau bridge was mentioned as early as 1272. Another date in connection with deliveries of construction timber comes from 1325. It was the first fixed road connection in front of the Sandauer Tor to the south of the city island. A small, no longer existing island was used to span the Havel. The part of the bridge north of the island was designed as a drawbridge. | cards | |
| X | 145.78 (right bank UHW) |

|
Havelstegbrücke Havelberg |
The Havelstegbrücke, a footpath bridge, leads over the entrance from the Havel to the winter harbor in Havelberg, the former freight port of the city with berths for passenger ships and pleasure boats. | cards |
| 27 | 146.94 | Lock bridge Havelberg Havelberg |
Lock bridge over the inland head of the Havelberg lock . | cards | |
Bridges over backwaters of the Lower Havel
Rathenower Havel
The Rathenower Havel (RHv) are the Havelarms Rathenower Havel , Wehrarm Hinterarche (also called Große Archen ), Wehrarm Vorderarche (also called Kleine Archen ), the Altarm Hellers Loch and the Rathenower Stadtkanal in the urban area of Rathenow . The Rathenower Havel branches off to the east at kilometer 102.50 of the main fairway and curves around the historic city area, to reach the main water again after about four kilometers. The Rathenow city lock is located at kilometer 104.56 of the side waterway . Four bridges, two of which are pedestrian bridges, the Weinbergbrücke and the Kirchbergbrücke, cross the continuously passable section of the Havel and the city canal . There are another four smaller bridges over the Havel arms, which are closed off by weirs and are not passable throughout, Wehrarm Hinterarche, Wehrarm Vorderarche and the old arm of Hellers Loch and an old arm of the Rathenower Havel in the city area. They lead the Inselweg and the Mühlendamm to the old town island at the Mühlentor. The old Bundesstraße 188 passes through the city in an east-west direction. Coming from the east, it runs as Genthiner Straße over the Hohe Brücke , which spans the Steckelsdorfer Arche . The road then continues as Schwedendamm over the Lange Brücke and crosses another old arm of the Havel to Steinstraße.
| number | km | photography | Name of the bridge / place | Remarks | location |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
|
|||||
| 1 | 103.30 Rathenower Havel |
 
|
Rathenow Vineyard Bridge |
The 348 meter long Weinbergbrücke swings in an arch over two arms of the Havel and the old arm of Hellers Loch. It connects the vineyard as a local recreation area for the city and the optics park as a point of attraction for visitors to the Federal Garden Show. The bridge was built in 2012/14 as part of the preparations for the 2015 Federal Garden Show in the Havel region. The Weinbergbrücke allows a wide view of the Havel landscape and the BUGA area. | cards |
| X | Steckelsdorf's Ark |

|
Rathenow high bridge |
The old Bundesstraße 188 passes the urban area of Rathenow in an east-west direction. Coming from the east, it runs as Genthiner Straße over the Hohe Brücke, which spans the Steckelsdorfer Arche. | cards |
| X | 104.31 Rathenower Havel |
 
|
Long Rathenow Bridge |
The former B 188 continues as Schwedendamm over the Lange Brücke and crosses another arm of the Rathenower Havel to Steinstrasse. | cards |
| 2 | 104.35 city canal |

|
Kirchberg Bridge Rathenow |
The Kirchberg Bridge, completed in 2002, leads over the former city harbor, the original city moat, now the lock canal, to the Kirchberg with the remains of the old city center. The Kirchberg Bridge is a girder bridge made of steel and built as a foot and bike path bridge. | cards |
| 3 | 104.58 city canal |

|
Rathenow city lock bridge |
A lock in the moat and a bridge have been mentioned since the middle of the 16th century. The new construction of the city lock bridge was completed in July 2005. It leads over the lower head of the city lock, the lock gate on the valley side. During the construction period, traffic was diverted over a temporary bridge, which was torn down again after the construction work was completed. | cards |
| 4th | 105.13 City Canal |
 
|
Everyitzer bridge Rathenow |
Since the Middle Ages, the Jeditz Bridge has been the northern exit of the town from Rathenow's old town island; it was operated as a drawbridge until 1885 and as a bascule bridge until 1913. Remodeling work began in 1912. In the interests of shipping, a new lift bridge should be built. The bridge was restored in the 1990s, but not the lifting mechanism. A separate pedestrian crossing with steps is part of the bridge in each town. | cards |
Hohennauen waterway
The Hohennauener Wasserstraße (HnW) flows into the river from the east at kilometer 111.85 of the Lower Havel, which is part of the Lower Havel waterway. The Brandenburg Waterways and Shipping Office is responsible . The UHW includes the Hohennauener Wasserstrasse up to the 10.40 kilometer, including the Hohennauen Canal, Hohennauener See and Ferchesarer See . Two bridges lead over the waterway, the road bridge of the B 102 and a steel truss bridge of a former railway line. The street used to run about 50 meters further west along the Alte Rathenower Straße over the Hohennauen Canal.
| number | km | photography | Name of the bridge / place | Remarks | location |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
|
|||||
| 1 | 1.50 Hohennauen Canal |

|
Railway bridge Hohennauen / Seeblick municipality |
To the west of the road bridge is a steel truss bridge of a former railway line. The route led from Rathenow to Wittstock / Dosse . | cards |
| 2 | 1.60 Hohennauen Canal |
 
|
Road bridge Hohennauen / Seeblick municipality |
The road bridge built in 2005 leads the Rhinower Straße ( B 102 ) from Rathenow to Hohennauen over the Hohennauen Canal. | cards |
City area Havelberg
From 1900 the city developed into a popular winter and after-work port for inland shipping between Hamburg and Berlin. With the relocation of the Havel estuary, the construction of the Havelberg lock and the filling of the Spülinsel in the years from 1933 to 1936, the waterway situation in the city area changed. Four bridges lead from and to the old town island, the Sandauer Brücke to the south over the main waterway of the Havel, the Dombrücke to the east and the Steintorbrücke to the north over the city moat. At the southern end of the old town, the Havelstegbrücke begins in a westerly direction as a foot and bike path bridge to the Spülinsel . This artificial island is in turn connected to the rest of the city via a small road bridge.
| number | km | photography | Name of the bridge / place | Remarks | location |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
|
|||||
| X | - City moat |
 
|
Cathedral bridge Havelberg |
As early as 1429 there was a written report of a boat ferry over the city moat. In place of today's cathedral bridge, there has been evidence of a fixed connection over the old Havel arm since the Middle Ages, it was first mentioned in 1691. The wooden bridges of that time almost always had to be replaced after thirty years at the latest. In 1924 the construction of a massive reinforced concrete bridge began, which was inaugurated after two years of construction. The bridge was blown up at the end of the war in 1945 and a wooden structure was built over the rubble in 1948. In 1957 these bridge parts were removed and a wooden bridge was built again, which was replaced by a wooden bridge in 1983. Both wooden bridges were built as part of the training program by the pontoon regiment 3 of the NVA . In 1998 today's reinforced concrete bridge was built. | cards |
| X | - City moat |

|
Stone gate bridge Havelberg |
The stone gate bridge was first mentioned in writing in 1692. It can be assumed that there was already a Havel crossing on this important road connection to the Steintor. | cards |
| X | - Trench between the winter harbor and the Havel estuary |

|
(Bridge to the Spülinsel) Havelberg |
In the 1950s, a wooden makeshift bridge was built to allow access to the sports clubs that were establishing themselves on the island. This wooden bridge was built as part of the training program by the pontoon regiment 3 of the NVA. Today's concrete bridge was built in the early 1990s. | cards |
Havel estuary and Gnevsdorf receiving water
The Lower Havel estuary (MUH), also known as the Havel estuary , branches off at about 145.80 kilometers from the UHW and is about 11.50 kilometers long. Three bridges lead across the water. The Gnevsdorfer receiving water is an approximately 11 km long canal between the Havel and the Elbe . It is an artificial Havel runoff and serves to relocate the backwater point of the Havel downstream. This flood protection system includes the four weirs at Quitzöbel (old arm and piercing weir ), Neuwerben and Gnevsdorf as well as the Havelberg lock . A bridge leads over the Gnevsdorf receiving water. Both are state waters .
Maps and pictures for explanation
literature
- Hans-J. Uhlemann: Berlin and the Märkische waterways. Transpress Verlag, Berlin 1987, ISBN 3-344-00115-9 .
- Writings of the Association for European Inland Shipping and Waterways e. V. Various years. WESKA (Western European Shipping and Harbor Calendar), Binnenschifffahrts-Verlag, Duisburg-Ruhrort. OCLC 48960431
- Richard J. Dietrich: The fascination of bridges: architecture, technology, history. 2nd Edition. 2001, ISBN 3-7667-1511-9 .
- Herbert Stertz: Havel shipping under sail . From the fur boat to the chat boat. Media @ Vice, Pritzwalk 2005, ISBN 3-00-016065-5 .
- Herbert Stertz: Havel shipping under steam . Economic factor and experience. Media @ Vice, Pritzwalk 2006, ISBN 3-00-019924-1 .
cards
- Folke Stender: Editing of Sportschifffahrtskarten inland 1. Nautical publication Verlagsgesellschaft, ISBN 3-926376-10-4 .
- W. Ciesla, H. Czesienski, W. Schlomm, K. Senzel, D. Weidner: Shipping maps of the inland waterways of the German Democratic Republic 1: 10,000. Volume 4. Editor: Waterways Authority of the GDR, Berlin 1988, OCLC 830889996 .
Web links
- Bridge directory WSA Berlin, (PDF) accessed on January 25, 2015.
- List of bridges area UHW from km 20 pages 1, 2 and 3. (PDF) accessed on January 25, 2015.
- Information about the waters. Blue Ribbon; Retrieved January 25, 2015.
Individual evidence
- ↑ Inland Waterways Regulations, Chapter 22, Lower Havel Waterway and Havel Canal § 22.01 Scope , accessed on February 26, 2015
- ↑ May 15 (year 1886: ceremonial inauguration of the Charlottenbrücke) in daily facts of the Luisenstädtischer Bildungsverein (at the DHM ), accessed on February 26, 2015.
- ↑ The Havel Bridge at structurae.de , accessed on March 1, 2015.
- ↑ Entry in the Berlin State Monument List , accessed on February 26, 2015
- ↑ Entry in the Berlin State Monument List , accessed on February 26, 2015
- ↑ Klaus Arlt: The street names of the city of Potsdam history and significance Association for culture and history of Potsdam ISSN 1432-9050 page 105
- ↑ The bridge at structurae.de/bauwerke , accessed on February 26, 2015
- ↑ Replacement of the Marquardt road bridge over the Sacrow-Paretz Canal (PDF; 53 kB), accessed on February 26, 2015
- ↑ Wolfgang Verch: 35 years of planning and execution of prestressed concrete bridges in the GDR. Scientific journal of the Technical University of Dresden 47 (1998) issue 5/6, pages 24 to 35
- ^ Replacement construction of the Marquardt road bridge over the Sacrow-Paretz Canal. (PDF) Waterways New Construction Office Berlin; Retrieved February 26, 2015.
- ^ Märkische Allgemeine Zeitung, Potsdamer daily newspaper Tuesday, March 3, 2015, page 7
- ↑ Directory E, serial no. 20 der Chronik ( Memento of the original from July 22, 2016 in the Internet Archive ) Info: The archive link was inserted automatically and has not yet been checked. Please check the original and archive link according to the instructions and then remove this notice. , Federal Waterways and Shipping Administration, accessed on February 26, 2015.
- ^ The canal bridge on the city side of Brandenburg an der Havel , accessed on February 26, 2015
- ↑ Directory E, serial no. 60 and directory F of the chronicle ( Memento of the original of July 22, 2016 in the Internet Archive ) Info: The archive link was inserted automatically and has not yet been checked. Please check the original and archive link according to the instructions and then remove this notice. , Federal Waterways and Shipping Administration, accessed on February 26, 2015.
- ↑ Manfred Reschke: The Havel. Nature and culture between Müritz and Havelberg . Trescher Verlag, Berlin 2012
- ↑ The Domstrengbrücke on the side of the city of Brandenburg , accessed on February 26, 2015.
- ↑ Directory E, serial no. 60 der Chronik ( Memento of the original from July 22, 2016 in the Internet Archive ) Info: The archive link was inserted automatically and has not yet been checked. Please check the original and archive link according to the instructions and then remove this notice. , Federal Waterways and Shipping Administration
- ↑ Lengths (in km) of the main shipping lanes (main routes and certain secondary routes) of the federal inland waterways ( memento of the original from January 21, 2016 in the Internet Archive ) Info: The archive link was inserted automatically and has not yet been checked. Please check the original and archive link according to the instructions and then remove this notice. , Federal Waterways and Shipping Administration, accessed on February 26, 2015.
- ↑ Documentation of the company involved, ( Memento of the original from January 3, 2015 in the Internet Archive ) Info: The archive link was inserted automatically and not yet checked. Please check the original and archive link according to the instructions and then remove this notice. Retrieved February 26, 2015.
- ↑ The Seegartenbrücke at structurae.de/bauwerke , accessed on February 26, 2015.
- ↑ The Alte Plauer Bridge at brueckenweb.de , accessed on February 26, 2015.
- ^ The Westhavelland Bridge Plaue at structurae.de/bauwerke, accessed on February 26, 2015.
- ↑ Chronicle of Pritzerber Schifffahrt from 1896 in connection with master shipbuilder Wilhelm Paelegrim, ( Memento of the original from February 9, 2015 in the Internet Archive ) Info: The archive link was inserted automatically and has not yet been checked. Please check the original and archive link according to the instructions and then remove this notice. Retrieved February 26, 2015.
- ↑ Notes on the ferry across the lake, ( Memento of the original from February 9, 2015 in the Internet Archive ) Info: The archive link was automatically inserted and not yet checked. Please check the original and archive link according to the instructions and then remove this notice. Retrieved February 26, 2015.
- ↑ wsa-brandenburg.wsv.de Schleusenbrücke Bahnitz WSA-Brandenburg accessed on March 1, 2015
- ↑ Die Brücke at brückenweb.de , accessed on March 1, 2015.
- ↑ Documentation of the construction company ( Memento of the original from February 27, 2015 in the Internet Archive ) Info: The archive link was inserted automatically and has not yet been checked. Please check the original and archive link according to the instructions and then remove this notice. (PDF) accessed on February 26, 2015.
- ↑ Dedication of the B 188 in the area of the Rathenow bypass . In: Landesbetrieb Straßenwesen Brandenburg, Potsdam branch (Hrsg.): Official Journal for Brandenburg . Potsdam October 10, 2005, p. 1046 ( landesrecht.brandenburg.de [PDF; accessed on February 26, 2015] official announcement).
- ↑ Garz lock bridge WSA-Brandenburg , accessed on March 1, 2015.
- ↑ Susanne Lenz: The bridge over the Havel comes in Strodehne today , in Berliner Zeitung , May 28, 1999; accessed on October 23, 2016.
- ↑ Nomination for the German Bridge Construction Prize 2012 web.archive.org , accessed on March 25, 2018.
- ↑ The Sandau Bridge at structurae.de/bauwerke , accessed on February 26, 2015.
- ↑ Havel footbridge , accessed on February 26, 2015.
- ↑ Havelberg lock bridge WSA-Brandenburg , accessed on March 1, 2015.
- ↑ BUGA bridge in Rathenow now has a name ( Memento of the original from January 3, 2015 in the Internet Archive ) Info: The archive link was automatically inserted and not yet checked. Please check the original and archive link according to the instructions and then remove this notice. Retrieved February 26, 2015.
- ↑ The Kirchberg Bridge at structurae.de , accessed on January 4, 2017.
- ↑ Manfred Reschke: The Havel. Nature and culture between Müritz and Havelberg . Trescher Verlag, Berlin 2012.
- ↑ Directory F of the Chronicle ( Memento of the original from July 22, 2016 in the Internet Archive ) Info: The archive link was automatically inserted and not yet checked. Please check the original and archive link according to the instructions and then remove this notice. , Federal Waterways and Shipping Administration
- ↑ Directory E, Ser. No. 60 of the Chronicle ( Memento of the original from July 22, 2016 in the Internet Archive ) Info: The archive link was inserted automatically and has not yet been checked. Please check the original and archive link according to the instructions and then remove this notice. , Federal Waterways and Shipping Administration, accessed on February 26, 2015
- ↑ a b Herbert Stertz: Havel shipping under steam. P. 111.
- ↑ Chronicle of the Pontoon Regiment 3 of the NVA, accessed on February 26, 2015
- ↑ The Steintorbrücke in Havelberg at brückenweb.de , accessed on February 26, 2015.
- ↑ Chronicle of the Pontoon Regiment 3 of the NVA, accessed on February 26, 2015.