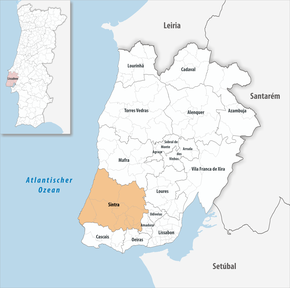
Sintra
| Sintra | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
||||||
| Basic data | ||||||
| Region : | Lisboa | |||||
| Sub-region : | Lisbon metropolitan area | |||||
| District : | Lisbon | |||||
| Concelho : | Sintra | |||||
| Coordinates : | 38 ° 48 ′ N , 9 ° 23 ′ W | |||||
| Residents: | 9342 (as of June 30, 2011) | |||||
| Surface: | 12.24 km² (as of January 1, 2010) | |||||
| Population density : | 763 inhabitants per km² | |||||
| politics | ||||||
| Mayor : | Basílio Horta ( PS / Partido Social Democrata | |||||
| Sintra County | ||||||
|
||||||
| Residents: | 377,835 (as of June 30, 2011) | |||||
| Surface: | 319.23 km² (as of January 1, 2010) | |||||
| Population density : | 1184 inhabitants per km² | |||||
| Number of municipalities : | 11 | |||||
| administration | ||||||
| Administration address: | Câmara Municipal de Sintra Largo Virgílio Horta, 4 2714-501 Sintra |
|||||
| President of the Câmara Municipal: | Basílio Horta PS ) | |||||
| Website: | www.cm-sintra.pt | |||||
| Sintra cultural landscape | |
|---|---|
|
UNESCO world heritage |
|
| National territory: |
|
| Type: | Culture |
| Criteria : | ii, iv, v |
| Surface: | 946 ha |
| Reference No .: | 723 |
| UNESCO region : | Europe and North America |
| History of enrollment | |
| Enrollment: | 1995 (session 19) |
Sintra is a small town ( vila ) in Portugal about 25 km west of Lisbon . It belongs to the Município of the same name . The place is best known for its palaces, some of which are centuries old, which attract tourists from all over the world. Since 1995, which is cultural landscape Sintra World Heritage of UNESCO .
history
Traces of the earliest human settlement here lead back to the Paleolithic Age , such as the finds from Penha Verde. The settlement of São Pedro de Canaferrim, excavated near the Castelo dos Mouros , should be mentioned among the Neolithic finds . The dome grave of Monge dates from the Copper Age . In the Serra de Sintra there are further traces of prehistoric settlement, up to the Bronze Age and up to the arrival of the Roman Empire . From Roman times comes u. a. the Barragem romana de Belas dam in Belas and the Roman road Calçada na Catribana . A more important place called Xintara or Shantara is mentioned from the Arabic records after the conquest by the Moors from 711 onwards . In the 11th century , the Arab geographer Al-Bacr described the place as a fortified settlement by the sea that was under Lisbon. Other sources from al-Andalus named the place as the most important in the region after Lisbon.
Sintra experienced a series of Christian conquests and Arab reconquests from the 8th century until Portugal's first king Dom Afonso Henriques finally took the area after the siege of Lisbon in 1147 . In 1154 Sintra received its first city rights from Dom Afonso Henriques. In the course of the 12th and 13th centuries, a number of monasteries were built in Sintra County, attracted by the high-yielding soils. The plague epidemic of the Black Death , which hit Europe in the 14th century , also reached Sintra in 1348 .
From the end of the 15th century, King Dom Manuel I carried out extensive redesigns in the city of Sintra. From the 16th century onwards, Sintra became popular with the upper classes, and noble families built several mansions in the Sintra county . The Lisbon earthquake in 1755 caused considerable destruction in Sintra, which was followed by extensive reconstruction work. At the end of the 18th century, the textile printing and dyeing factory Fábrica de Estamparia de Rio de Mouro was the first industrial establishment in the district.
Since the 19th century, Sintra has also increasingly been a destination for the upper class , with international artists and industrial families in particular visiting the area. Writers like Lord Byron , Eça de Queiroz and Hans Christian Andersen have recorded their enthusiasm for the landscape, climate and architecture of Sintras in literary terms. Byron's "Lo! Cintra's glorious Eden ”from 1812 is still present today and almost serves as Sintra's unofficial tourist motto.
The 47th Bilderberg Conference took place in Sintra from June 3 to 6, 1999 .
Culture and sights
Attractions
- Palácio Nacional de Sintra (also called Paço Real or Palácio da Vila)
- Castelo dos Mouros
- Palácio Nacional da Pena
- Parque de Pena
- Convento dos Capuchos
- Palácio de Monserrate
- Quinta da Regaleira
- Igreja do São Martinho
- Monge dome tomb (Copper Age)
- the archaeological site Sítio arqueológico de Colaride (Roman)
- the Roman villa Villa romana da Granja dos Serrões in Montelavar
- In 1995 the Pousada D. Maria I was opened as a pousada in the historical building of the royal guard with the characteristic clock tower
Cabo da Roca is also located in Sintra County , the cape is the westernmost point of mainland Europe . Hiking trails are laid out in a circle, including tours and park hikes, for example through Parque da Pena .
The Lisbon aqueduct Aqueduto das Águas Livres begins in Belas, in the Sintra district.
Museums
- The Museu de Arte Moderna is housed in a casino built in 1920 and exhibits an extensive collection of modern art
- The collections of the two sculptor brothers Anjos Teixeira can be seen in the Museu Anjos Teixeira
- There is also a museum at the Roman ruins of Ruínas de São Miguel de Odrinhas
- In the Centro Cultural Olga Cadaval , in addition to events in the halls, exhibitions are also shown
- Museu do Ar Aviation Museum (see the section on the military airfield )
- The Science Museum Centro Ciência Viva de Sintra (Eng .: Center of Living Science of Sintra)
- The NewsMuseum deals with the role of the media and provides information on its effects and actors
View from Castelo dos Mouros to Palácio Nacional da Pena
View from Castelo dos Mouros to Sintra
The village of Azenhas do Mar, in the municipality of Colares
Sports
The women's team of the Sociedade União 1º Dezembro football club, founded on December 1, 1880, is the record champion of the Campeonato Nacional , the top division of women's football in Portugal. The men's team of SU 1º Dezembro played in the 2013/14 season in the third division, in the Série G des Campeonato Nacional de Seniores . The club's home stadium is the Campo Conde de Sucena with 1,500 seats.
The football club Sport União Sintrense was founded in 1911 and played in the 2013/14 season with local rivals SU 1º Dezembro in the third division, also in the Série G des Campeonato Nacional de Seniores. The club's own stadium, Estádio do Sport União Sintrense, has a capacity of 2,800 spectators. Other football clubs in the district, all of which play in the leagues of the district association, are Atlético Clube do Cacém , Clube Atlético Pêro Pinheiro , the Real Sport Clube from Queluz, the Sporting Clube de Lourel , and the Mem Martins Sport Clube , which is also diverse practiced sports.
The roller hockey club Hockey Clube de Sintra should also be mentioned .
In 1999, the international golf tournament Estoril Open took place in the district .
politics
|
administration
The circle
Sintra is the administrative seat of a district of the same name ( concelho ) in the Lisbon district . On June 30, 2011 the district had 377,835 inhabitants on an area of 319.2 km².
The neighboring districts are (starting clockwise from the north): Mafra , Loures , Amadora , Oeiras and Cascais . In the west, the district of Sintra borders the Atlantic .

The town hall ( Câmara Municipal ) of Sintra
|
With the regional reform in September 2013 , several municipalities were merged into new municipalities, so that the number of municipalities decreased from 20 to eleven.
The following municipalities ( Freguesias ) are in the Sintra district:
| local community | Population (2011) |
Area km² |
Density of population / km² |
LAU code |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Algueirão-Mem Martins | 66,250 | 16.00 | 4.142 | 111102 |
| Agualva e Mira-Sintra | 41,104 | 5.98 | 6,873 | 111122 |
| Almargem do Bispo, Pêro Pinheiro e Montelavar | 16,788 | 64.07 | 262 | 111123 |
| Cacém e São Marcos | 38,701 | 4.44 | 8,709 | 111124 |
| Casal de Cambra | 12,701 | 2.17 | 5,854 | 111115 |
| Colares | 7,628 | 33.37 | 229 | 111105 |
| Massamá e Monte Abraão | 48,921 | 3.09 | 15,854 | 111125 |
| Queluz e Belas | 52,335 | 26.47 | 1,977 | 111126 |
| Rio de Mouro | 47,311 | 16.49 | 2,868 | 111108 |
| São João das Lampas e Terrugem | 16,505 | 83.60 | 197 | 111127 |
| Sintra (Santa Maria e São Miguel, São Martinho e São Pedro de Penaferrim) | 29,591 | 63.55 | 466 | 111128 |
| Sintra County | 377.835 | 319.23 | 1,184 | 1111 |
Population development
| 1801 | 1849 | 1900 | 1930 | 1960 | 1981 | 1991 | 2001 | 2011 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 12,486 | 17.129 | 26,074 | 37,986 | 79.964 | 226,428 | 260,951 | 363,749 | 377.837 |
Municipal holiday
- June 29th
Town twinning
-
 : El Jadida , Morocco (since 1988)
: El Jadida , Morocco (since 1988) -
 : Vila Nova Sintra , Cape Verde (since 1995)
: Vila Nova Sintra , Cape Verde (since 1995) -
 : Lobito , Angola (since 1997)
: Lobito , Angola (since 1997) -
 : Petrópolis , Brazil (since 1997)
: Petrópolis , Brazil (since 1997) -
 : Bissau , Guinea-Bissau (since 1997)
: Bissau , Guinea-Bissau (since 1997) -
 : Trindade , São Tomé and Príncipe (since 1997)
: Trindade , São Tomé and Príncipe (since 1997) -
 : Ōmura , Japan (since 1997)
: Ōmura , Japan (since 1997) -
 : Honolulu , USA (since 1998)
: Honolulu , USA (since 1998) -
 : Namaacha , Mozambique (since 1999)
: Namaacha , Mozambique (since 1999) -
 : Havana , Cuba (since 2000)
: Havana , Cuba (since 2000) -
 : Asilah , Morocco (since August 2006)
: Asilah , Morocco (since August 2006)
economy
The companies based here include the head office of the paper company Inapa , the internationally active stadium construction company Lusoarenas , the Galucho machine factory and the like. a. A large number of foundations are based in the Sintra district. Tourism is also important.
traffic
Local transport
The station of Sintra is the terminus of the Linha de Sintra , a line of the tram -like Vorortzugsystems Lisbon (starting at the Estação- Rossio ). The Linha de Sintra still serves the Portela de Sintra train station within the urban area.
From the bus station at Portela de Sintra train station, there are regular buses. B. in about 30 minutes to Estoril . The Scotturb ( Sintra-Cascais-Oeiras Transportes Terrestres Urbanos ) operates over 70 regional bus routes, and other transport companies also offer connections.
The Sintra urban tram takes you to the Atlantic coast to Praia das Maçãs beach ; open and closed wagons are used. The 2016 timetable (June 22 to September 4) includes 6 pairs of journeys approximately every hour, but only on Wednesdays to Sundays.
Long-distance transport
With the Mira-Sintra-Meleçâs stop on Linha do Oeste , about 7 kilometers from the city center , Sintra is connected to the country's rail network.
The A16 and A37 motorways lead from the greater Lisbon area to Sintra. The national road N375 continues from Sintra towards the coast.
About five kilometers outside of Sintra is a military airfield of the Portuguese Air Force in a northeastern direction .
Sintra military airfield
The military airfield Sintra ( port. : Base Aérea de Sintra ) is a military airport of the Portuguese Air Force Força Aérea Portuguesa (FAP), which officially it as Base Aérea Nº1 leads (BA1). The base is at the Granja do Marquês and in 1914 it was the "cradle" of Portuguese military aviation. This is where training aircraft in service with the 802 Squadron are stationed as part of the Academia da Força Aérea . The Air Force Museum is also located here, in the Museu do Ar aviation museum .
From 2021 Sintra will also be home to the European Multinational Helicopter Training Center . In the run-up, the 103rd season with their TB 30 moved to Beja in 2020 .
sons and daughters of the town
|
|
Web links
- Official website of the city administration (English and Portuguese)
- Sintra - Refuge for Kings and Romantics on Spiegel Online
- Photos from SINTRA on Flickr
Individual evidence
- ↑ www.ine.pt - indicator resident population by place of residence and sex; Decennial in the database of the Instituto Nacional de Estatística
- ↑ a b Overview of code assignments from Freguesias on epp.eurostat.ec.europa.eu
- ↑ a b www.ine.pt - indicator resident population by place of residence and sex; Decennial in the database of the Instituto Nacional de Estatística
- ↑ www.verportugal.net , accessed October 27, 2013
- ^ Lydia Hohenberger, Jürgen Strohmaier: Portugal. 2nd edition, DuMont Reiseverlag, Ostfildern 2009, p. 170.
- ↑ In: Childe Harold's Pilgrimage . Canto I, XVIII. Byron's trip to Portugal took place in July 1809.
- ↑ Quintessential Portugal. The Sunday Times, August 28, 2005.
- ↑ NewsMuseum. Museum website.
- ↑ The Campo Conde de Sucena at www.europlan-online.de, accessed on October 27, 2013
- ↑ The Estádio do Sport União Sintrense on www.soccerway.com, accessed on October 27, 2013
- ^ Publication of the administrative reorganization in the Diário da República gazette of January 28, 2013, accessed on March 16, 2014
- ↑ www.anmp.pt , accessed on October 27, 2013
- ^ The Sintra Line of Portuguese Railways (CP): Linha de Sintra. Part One. ( Memento from October 29, 2013 in the Internet Archive )
- ^ Page about the tram on the city administration website, accessed on July 26, 2016
- ↑ EDA Chief Executive held talks in Portugal. European Defense Agency News, July 16, 2019
| ← Previous location: Lisbon |
|
Next town: Mafra → |