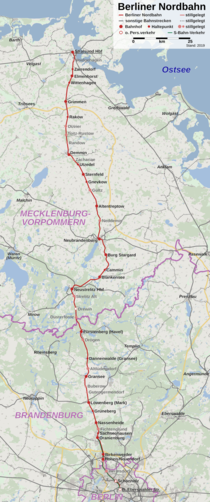
Berlin Northern Railway
The Berlin – Stralsund railway line , also known as the Berlin Northern Railway , is an electrified main line in Berlin , Brandenburg and Mecklenburg-Western Pomerania . It runs from Berlin via Neustrelitz and Neubrandenburg to Stralsund .
The line, which was opened in 1877/1878, has two tracks between Hohen Neuendorf and Neustrelitz, and one track is expanded further on. In the Hohen Neuendorf – Oranienburg section, a parallel line of the Berlin S-Bahn will be added. In Berlin, the route is only used by S-Bahn traffic, the rest of the traffic in this area is routed via the Berlin – Szczecin railway line and the Berlin outer ring .
history
Construction and commissioning
In 1844, Stralsund merchants and entrepreneurs joined together in the "Association for the acquisition of a railway from Berlin via Neu-Strelitz to Stralsund" and in 1844 published a memorandum of preliminary views on a Berlin-Stralsund railway .
The association also collected large financial resources for this purpose. These efforts initially failed due to the responsible Prussian ministry, which still rejected the project in the 1840s and 1850s. In 1863, the Angermünde-Stralsund Railway was initially a branch line of the Berlin-Stettin Railway via Prenzlau , Anklam and Greifswald to Stralsund, where on October 26, 1863 the first train from Angermünde arrived at the newly built station.
Afterwards, the Stralsunders tried to establish a direct connection with Berlin with a newly founded Berlin Northern Railway Company and in 1869 submitted drafts for a Berlin - Neustrelitz - Stralsund - Arkona railway line. In 1870 the states of Prussia and Mecklenburg-Strelitz finally granted the concessions for this. On January 1, 1878, operations on the new Berlin Northern Railway with Stralsund as the terminus could begin.
For financial reasons this society had to dissolve on December 15, 1875. The Prussian state acquired the unfinished railway and transferred the further construction work to the management of the Lower Silesian-Märkische Railway .
The route was opened in three stages:
- July 10, 1877: Berlin - Oranienburg - Neustrelitz - Neubrandenburg (134 km)
- December 1, 1877: Neubrandenburg - Demmin (42 km)
- January 1, 1878: Demmin - Stralsund (47 km)
In the first few months, the trains ran from Gesundbrunnen station via the Ringbahn to the freight station of the Lower Silesian-Märkische Bahn . From October 1, 1877, what was then the North Station on Bernauer Strasse at the corner of Schwedter Strasse in the area of what would later become the Mauerpark went into operation for goods traffic . From December 1, 1877, after a contract with the Berlin-Stettiner Eisenbahn, the Stettiner Bahnhof (renamed Nordbahnhof in 1950) on Invalidenstrasse could be used for passenger transport .
The construction of the Northern Railway had a significant impact on the villages in the catchment area of the railway line: In some cases, their population multiplied in the following decades. Nordbahn became part of place names ( Glienicke / Nordbahn ) and gave newspapers their name (Nordbahn-Nachrichten).
In the last decade of the 19th century, the Prussian State Railroad had the railway facilities in the Gesundbrunnen area extensively rebuilt. During this time, from 1892 to 1898, passenger traffic did not take place from the Szczecin railway station, but from the north station, which was prepared for passenger trains. During this time, a provisional Gesundbrunnen station (northern line) east of Gesundbrunnen station served for transfer traffic to the Ringbahn.
Electrical on-site operation after 1900
At Oranienburg there was a 1.76 kilometer long oval ring section next to the through section, on which electrical operation with overhead contact lines and alternating current of 6.3 kilovolts and 25 Hertz was investigated in uninterrupted wear operation from 1907 to 1913 .
Until 1912, suburban tracks separated from the long-distance tracks were built between Gesundbrunnen and Frohnau. At the same time, the route was relocated to a dam in order to avoid level crossings at street level. The Frohnau - Borgsdorf section followed gradually until 1926. In this context, the Stolpe and Hohen Neuendorf stations were merged, and the new Hohen Neuendorf station was built a little further south of the old station.
In 1925, the section from Gesundbrunnen station , over which suburban traffic had run since the relocation, to Oranienburg was electrified with the direct current system of the later Berlin S-Bahn .
After the Second World War


In the summer of 1945, due to the reparations agreements after the end of the Second World War, the second long-distance line of the northern line was dismantled , as was the second S-Bahn track north of the Wilhelmsruh station to Borgsdorf.
Since the Stettiner Bahnhof was called Nordbahnhof since 1950 , the former Nordbahnhof had to be renamed. Although it was located in West Berlin in what was then the Wedding district, it was named after Eberswalder Strasse in East Berlin . It remained in operation for freight traffic. With the closure of the Szczecin train station, passenger train traffic on the Berlin part of the northern line was stopped when the timetable changed on May 18, 1952. Since then, passenger trains from the Nordbahn have been running in the direction of Karower Kreuz, initially via the Berlin-Karow – Fichtengrund railway line, which opened in 1950, and from the end of 1952 via the Berlin outer ring , and on to Lichtenberg or Ostbahnhof .
With the construction of the wall on August 13, 1961, the continuous electric S-Bahn operation ended, the line between Frohnau and Hohen Neuendorf was interrupted. Immediately after the construction of the Wall, there was an island S-Bahn operation on the Brandenburg side between Oranienburg and Hohen Neuendorf for several months, which was only connected to the main S-Bahn network again with the expansion and electrification of the Berlin outer ring between Hohen Neuendorf and Blankenburg in November 1961. Bahn received. In Berlin, the S-Bahn operation, now ending in Frohnau, continued until the transfer of the operating rights of the S-Bahn in West Berlin from the Deutsche Reichsbahn to the BVG on January 9, 1984. However, traffic was suspended between January and September 30, 1984. During renovation work in 1985, the S-Bahn route was partially laid in the profile of the old long-distance railway tracks.
In 1983/1984 the southern part of the northern line was electrified. On June 2, 1984 the catenary from Berlin to Neustrelitz went into operation. The electrification mainly served the traffic on the branch to Rostock in Neustrelitz . The northern part of the Berlin Northern Railway was only electrified in 1993/94. On May 23, 1993 electrical operation began between Neustrelitz and Neubrandenburg, and on May 29, 1994 on the entire route to Stralsund.
After 1990
After the fall of the Wall, many smaller train stations in mostly sparsely populated areas were closed (including Düsterförde (1996), Strelitz Alt (1995), Neddemin, Randow, Toitz-Rustow), and buses sometimes took over the replacement service.
In 1992 the gap between the S-Bahn tracks between Berlin-Frohnau and Hohen Neuendorf was closed so that continuous S-Bahn operations on the northern line to Oranienburg are possible again.
The electronic signal box Waidmannslust has been controlling the section of the S-Bahn between Berlin-Schönholz and Hohen Neuendorf since October 2011 - in each case excluding the stations mentioned. This is the first section to be converted to the new train control system of the S-Bahn Berlin (ZBS) .
Expansion of the Berlin – Rostock connection
The Birkenwerder – Neustrelitz section was upgraded as part of existing network investments to expand the Berlin – Rostock connection by 2013 for a line speed of largely 160 km / h and for higher axle loads of up to 25 tons. The safety technology was converted to the European train control system ETCS and electronic interlockings .
The cost of expanding the 198-kilometer routes totaled 850 million euros in 2012. Of this, 577 million euros came from the federal government , 167 million euros from the ERDF and additional funds from DB Netz AG's own resources .
The entire construction project was carried out in partial steps. First, the expansion of the first section Löwenberg (Mark) –Gransee was completed in November 2007 , before the expansion of the Dannenwalde – Fürstenberg section followed from March to November 2009. The section between Gransee and Dannenwalde followed between July 2011 and August 2012.
Between September 10, 2012 and June 9, 2013, the section between Oranienburg and Neustrelitz was completely closed to allow further construction projects to be carried out. In the boggy subsoil between Nassenheide and Löwenberg, a deep foundation of the route was implemented by driving 7200 driven piles into the subsoil. At the same time, the section between Fürstenberg and Neustrelitz was expanded and stabilized with 16,000 vibrating columns.
63 kilometers of track were renewed and five new electronic signal boxes were built. The single-track recommissioning of the line sections, initially planned for April 2013, was delayed until June 9, 2013. At the end of 2013, the expansion was completed with the restoration of the double-track system. New platforms were built in Nassenheide, Grüneberg and Löwenberg. The lock-out was used to look for remains of ammunition in Oranienburg station at the same time.
The rest of the line between Oranienburg and Nassenheide is to be renovated from 2017, together with the expansion of Gransee station. At the beginning of 2020, the work at Gransee station was completed after a construction period of 17 months. The track system in the 1.6-kilometer section was expanded for a wheel set load of 25 tons and the overhead line and train protection system was renewed. On behalf of the Gransee District Office, new forecourts and a bicycle parking facility were built on both sides of the tracks, and the pedestrian underpass was converted to make it barrier-free.
The expansion of the other stations in Oranienburg, Fürstenberg / Havel and Neustrelitz has been postponed to 2019-2021 according to the current planning status.
future
In the long term, the direct route from Berlin to Birkenwerder will be restarted. For this purpose, the long-distance tracks of the northern line between the train station in Berlin Gesundbrunnen and Birkenwerder are to be rebuilt with two tracks over a distance of 18.8 kilometers at a speed of 160 km / h, but there is no date for this. So far, only the examination of a feasibility study for a single-track expansion has been promised. The project is included in the Federal Transport Infrastructure Plan 2030 as a "potential need", but was not included in the "urgent need". In addition, the Birkenwerder station is to have a separate regional platform (independent of the S-Bahn).
Train operation since the 2010s
Only trains of the S-Bahn Berlin currently run on the Berlin section of the route : the lines S 1 to Oranienburg, S 25 to Hennigsdorf and S 26 to Waidmannslust. Line S 8 uses the tracks of the northern railway from Hohen Neuendorf to Birkenwerder .
In Hohen Neuendorf and Birkenwerder, the connecting curves of the long-distance line from the Berlin outer ring flow into the northern line, from where the RE 5 regional express line from Rostock or Stralsund to Wünsdorf-Waldstadt and the RB 20 regional line from Oranienburg via Hennigsdorf to Potsdam . The trains of the RB 12 Berlin-Ostkreuz - Zehdenick - Templin also use the route to Löwenberg . The RB 12 was operated by DB Regio until December 2015 and then taken over by the Niederbarnimer Eisenbahn . The RE 5 and RB 20 lines are operated by DB Regio. In addition, there are individual IC train pairs to and from Rostock / Leipzig and various freight trains in the Hohen Neuendorf - Neustrelitz section . The Interconnex operated on this section until 2014 .
literature
- Peter Bley: Berliner Nordbahn - 125 years of the Berlin – Neustrelitz – Stralsund railway . Neddermeyer, Berlin 2002, ISBN 3-933254-33-7 .
- The Berlin Northern Railway. In: on behalf of Königl.-Preuss. Published by the Minister of Public Works: Berlin and its Railways 1846–1896 . Springer, Berlin 1896. (Reprint: Verlag Ästhetik u. Kommunikation, Berlin 1982, ISBN 3-88245-106-8 , pp. 274–282)
Web links
- Railway lines in the state of Brandenburg - Berliner Nordbahn
- History board for the route and stations on Berliner-Bahnen.de
Individual evidence
- ^ "Biblioteca geographica: Directory of the works on geography and travel published in Germany from the middle of the last century to the end of 1856", Leipzig 1858, page 343
- ^ Peter Bley: Berliner Nordbahn - 125 years of the Berlin – Neustrelitz – Stralsund railway . Neddermeyer, Berlin 2002, ISBN 3-933254-33-7 , pp. 13-16
- ^ Peter Bley: Berliner Nordbahn - 125 years of the Berlin – Neustrelitz – Stralsund railway . Neddermeyer, Berlin 2002, ISBN 3-933254-33-7 , pp. 28-33
- ^ Early history of electrical railways in Prussia . In: Prussia Report . Volume 10. Hermann-Merker-Verlag, Fürstenfeldbruck, ISBN 3-89610-005-X , p. 12
- ^ Röll: Encyclopedia of Railways, Test Railways'
- ↑ Mention in the Zentralblatt der Bauverwaltung of the Prussian Ministry of Public Works from 1909 under "Experiments with electrical operation on Swedish state railways" (PDF; 693 kiB)
- ^ Peter Bley: Berliner Nordbahn - 125 years of the Berlin – Neustrelitz – Stralsund railway . Neddermeyer, Berlin 2002, ISBN 3-933254-33-7 , pp. 36, 38, 53
- ^ Lothar Schultz: The Lloyd Railway, Neustrelitz – Rostock – Warnemünde . Verlag Bernd Neddermeyer, Berlin 2010, ISBN 978-3-941712-08-9 , p. 155.
- ^ Peter Bley: Berliner Nordbahn - 125 years of the Berlin – Neustrelitz – Stralsund railway . Neddermeyer, Berlin 2002, ISBN 3-933254-33-7 , p. 107
- ↑ So far nobody wants to make something out of the station . In: Nordkurier. Strelitzer Zeitung , June 11, 2002
- ↑ Construction focus on the S-Bahn network in 2011. (No longer available online.) Deutsche Bahn, September 1, 2011, archived from the original on December 28, 2011 ; Retrieved February 16, 2012 .
- ↑ Mecklenburg-Western Pomerania and Deutsche Bahn AG agree on a schedule for the expansion of the Berlin-Rostock line , press release No. 23/10 of the Mecklenburg Ministry of Transport, Building and Regional Development of February 2, 2010
- ↑ Federal Ministry of Transport, Building and Urban Development: Federal Transport Infrastructure Plan 2003, July 2003
- ↑ a b Railway line Berlin – Rostock closed for half a year. Deutsche Bahn, June 5, 2012, archived from the original on January 2, 2013 ; Retrieved June 5, 2012 .
- ↑ Further EU funds for the expansion of the Berlin - Rostock railway line. (No longer available online.) Federal Ministry of Transport, Building and Urban Development, October 30, 2013, archived from the original on November 13, 2013 ; Retrieved November 13, 2013 .
- ↑ Construction work between Löwenberg – Gransee finished ( Memento from May 8, 2014 in the Internet Archive ), press release from Deutsche Bahn from November 9, 2007
- ^ Rail upgrading Gransee – Dannenwalde section , press release from Deutsche Bahn AG of June 30, 2011
- ↑ Blocking of the Berlin - Rostock route extended until June 9, 2013. Deutsche Bahn, February 6, 2013, archived from the original on March 8, 2013 ; Retrieved February 11, 2013 .
- ^ Harald Tschirner: Blocking of the Berlin - Rostock railway line . In: Berliner Verkehrsblätter . No. 11 , 2012, p. 211 .
- ↑ Planning approval decision Oranienburg (a) - Nassenheide (a). (PDF) (No longer available online.) Federal Railway Office, December 30, 2016, archived from the original on January 10, 2017 ; accessed on January 10, 2017 .
- ↑ a b Berlin-Rostock railway line becomes an endless construction site , in: Nordkurier from March 20, 2014, title page
- ↑ Gransee station is now more modern . In: point 3 . No. 4 , 2020, p. 7 ( online [accessed March 2, 2020]).
- ↑ Printed matter 16/3000 of the German Bundestag: Report on the expansion of the railways 2006, p. 80: Subproject No. 27b (PDF; 2.9 MB)
- ↑ Berlin – Rostock soon much faster? (No longer available online.) Dmm.travel, archived from the original on November 19, 2015 ; Retrieved January 26, 2012 .
- ↑ Dossier. Retrieved December 6, 2017 .
- ↑ BMVI - Evaluation of the railway expansion projects of the potential demand. Retrieved February 22, 2019 .
- ↑ New planning status for infrastructure concept i2030 . In: Bahn-Report . No. 3 , 2020, p. 35 f .