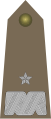
Brigadier General
Brigadier General is a military grade . In the Austrian Armed Forces , the Swiss Army and other armed forces, the comparable rank is referred to as a brigadier .
etymology
Brigadier General
The Brigadier General (and also the corresponding, similar or identical English , French and Polish designation) is a general who commands a brigade . Since the badges of rank of brigadier general in many armed forces, including the army and the armed forces of the United States , a star of the show, the Brigadier is colloquially often referred to as "Einsternegeneral".
"Brigadier" variant
A similar term to the term brigadier general is the brigadier. Measured against the NATO rank code , the brigadier in the armed forces and the Swiss army is equivalent to the German brigadier general. In some other armed forces, however, the brigadier is a rank that is below the rank of the same or similar rank of German-speaking armed forces.
In the French army, however, a “brigadier” is a non-commissioned officer
armed forces
| Brigadier General | |
|---|---|
 
|
|
| Rank group | Generals |
| NATO rank code | OF-6 |
| Rank Army / Air Force | Brigadier General |
| Marine rank | Flotilla admiral |
| Abbreviation (in lists) | BrigGen (BG) |
| Grade | B 6 according to BBesO |
The rank of Brigadier General is determined by the Federal President with the order of the Federal President on the rank designations and the uniform of the soldiers on the basis of the Soldiers Act .
Authority to command and positions
In the Bundeswehr, the brigadier general is an officer rank who, according to the Central Service Regulations (ZDv) A-1420/24 "Ranks and Rank Groups", belongs to the rank group of the generals . Because they belong to the rank group of the generals, soldiers in the rank of brigadier general can give orders on the basis of § 4 ("Superiors relationship on the basis of rank") of the Superiors Ordinance within the limits set there, soldiers of the rank groups of men , NCOs with and without porters , lieutenants , captains and staff officers To give. Commanders of a training facility, brigade commanders, commanders of division troops , etc., as unit leaders , are disciplinary superiors of the soldiers subordinate to them in accordance with the military disciplinary code .
The brigade generals are like most generals mainly on bar items , rare in the "fighting" force as a military leader . Typical uses are in managerial functions as head of department , department head or head of unit in command authorities , offices or in the ministry . There they are ultimately responsible, for example, for personnel and material planning , strategy development or deployment planning .
Some brigade generals are commanders of educational institutions (in the army, for example, at a military school or centers ). Brigadier generals, mostly commanders of a teaching institution at the same time, are often responsible for the training and further development of their military type and hold the service position - not the rank - general of the artillery , general of the armored troops , general of the infantry , etc. Brigadier generals are military attaché at particularly important German embassies also used in the diplomatic service - so regularly in the United States and Russia .
In the corps , they serve as Chief of Staff or Deputy Chief of Staff for Operations. In this post they directly support the corps commander in commanding the troops . Some brigadier generals are also used in the force as military leaders in large formations . Typical uses are as brigade commander , deputy division commander and commander of division troops .
In the Bundeswehr geographic information service , only the head of the geographic information service and the Bundeswehr geographic information center is a brigadier general; and thus the top service level in the career of the Bundeswehr's geographic information service.
Appointment, salary and age limit
The legal basis for the appointment as brigadier general is set by the Soldier Career Ordinance (SLV) and, in addition, the Central Service Regulations (ZDv) 20/7. In detail, the careers there are only regulated up to the rank of colonel . The appointment as brigadier general, on the other hand, is essentially a decision to be made by the employer based on the suitability and performance of the soldier , which is hardly subject to any further requirements. In practice, only professional officers are usually appointed brigadier general . According to the Soldier Career Ordinance, the ranks should be passed through regularly in the order described in the order of the Federal President and a minimum period of service in the previous rank of at least one year should be the rule; in practice, brigadier generals had previously been colonels for several years. There is no special examination to be taken before promotion to the rank of generals; in practice, however, most of the brigadier generals have completed the general staff / admiralty staff training course at the command academy of the Bundeswehr .
Brigade Generale after the Bundesbesoldungsgesetz order (BBesO) with B 6 remunerated . According to the personnel budget of Section 14 of the Federal Budget 2014 [obsolete] , 128 posts are provided for soldiers in grade B 6; 14 of these are for the Federal Ministry of Defense and 114 for the armed forces ( subordinate military area ).
A special age limit for brigadier generals was 62 years of age .
Rank badge
The rank badge for brigadier generals shows golden oak leaves and a gold star as a shoulder badge . The underlay of the shoulder flaps (in the case of army uniforms also the flat braids ) are bright red .
history
The rank of brigadier general was never used in earlier German armed forces. Rather, the lowest rank of the generals was usually the major general . The rank of brigadier general was introduced in the Bundeswehr in 1955/1956 . The aim was to standardize the general ranks within NATO . Similarly, the combat groups typical of earlier armed forces and the early years of the Bundeswehr were reclassified into brigades . Army uniform bearers with the rank of brigadier general are the only army uniform bearers in which the typically subordinate troop unit can be read directly from the rank designation. From 1951 to 1976, the brigadier general was also an official title of the Federal Border Guard .
Equivalent, subordinate and superior ranks
The rank of brigadier general is held only by army and air force uniforms . Navy uniform wearers (except medical officers ) of the same rank hold the rank of flotilla admiral . The medical officer ranks of the same rank are the ranks of general physician , general pharmacist or admiral doctor , which differ according to their license to practice medicine and uniform wearer (first two rank designations for army and air force uniforms; last rank designation for naval uniforms). In the armed forces of NATO Brigadier General is to all ranks with the NATO rank code OF-6 equivalent.
According to ZDv 14/5 and the order of the Federal President , the brigadier general is ranked above the lower-ranking colonel or sea captain and below the higher-ranking major general or rear admiral (first rank designation for army and air force uniforms; second rank for naval uniforms). The rank equal to Colonel medical officer ranks are to Approbations direction and Uniform area differently denominated Ranks Colonel doctor , Colonel pharmacist and Colonel veterinary or fleet doctor and fleet pharmacist (first three grade designations for military and air Uniform carrier; past two grade designations for Marine Uniform). The medical officer ranks of the same rank as the major general are the ranks of the general staff doctor or admiral staff doctor, which differ depending on the license to practice medicine and the field of uniform wear (first rank designation for army and air force uniforms; last rank designation for naval uniforms).
|
|
||
| Lower rank | Higher rank | |
|
Colonel Captain Colonel doctor Colonel pharmacist Colonel veterinary fleet doctor fleet pharmacist |
Brigadier General Flotilla Admiral General Doctor General Pharmacist Admiral Doctor |
Major General Rear Admiral General Staff Doctor Admiral Staff Doctor |
|
Rank group : Teams-NCOs-NCO-NCOs-Lieutenant-Captains-Staff officers-Generals |
||
Brazilian Army
The Brigadier General (General de brigada) is the equivalent of the Major General (OF-7) in the Brazilian Army . This is similar in some Latin American countries like Chile , Ecuador , etc.
French armed forces
In the French armed forces , the equivalent of the German brigadier general is the Général de brigade . This lowest general rank is above the Colonel and below the Général de division .
Defense Forces of East Timor
In the Defense Forces of East Timor (F-FDTL), the military commander-in-chief Taur Matan Ruak had the rank of Brigadeiro from its establishment until 2009 . In 2009 he became major-general . After his departure in 2011, his successor Lere Anan Timor was promoted to major-general , while the new deputy Filomeno Paixão received the rank of brigadeiros . In 2018, four more officers were promoted to brigadier generals.
Polish armed forces
In the Polish armed forces , the brigadier general , in Polish Generał brygady (gen.bryg.) Is the lowest rank of the generals to which an officer can be appointed in peacetime.
| Rank | ||
| lower: colonel (pl: Pułkownik ) |
Brigadier General (pl: Generał brygady) |
higher: division general (pl: generał dywizji ) |
United States Armed Forces
In the United States Army , the US Air Force and the US Marine Corps , the Brigadier General is the rank that is comparable and similar to the German. In the hierarchy this is above the Colonel and below the Major General . The US pay level is O-7. The NATO rank code is OF-6. A Brigadier General operates a brigade with six to seven battalions and thus 3,000–4,000 soldiers. The Brigadier General is also used as a deputy to a higher-ranking general (for example, as a deputy division commander ). His task is the preparation of the mission and the division of troops. The Brigadier General is the lowest of the five ranks of general in the United States .
Russian armed forces
In the Russian armed forces there was never an identical or similar rank designation. According to the NATO rank code , the Generál-Majór ( Cyrillic script : Генера́л-майо́р ) is comparable to the German brigadier general . This rank, which is etymologically , phonetically and historically similar to the German major general (before 1955), is the lowest rank of the Russian generals .
Turkish armed forces
In the Turkish armed forces , the armed services army and air force , the same rank was earlier than mirliva and today as Tuğgeneral called, derived from the term "tugay" for a Turkish Brigade.
annotation
- ↑ Grammatically correct would be “one star general”. “One star general” is a designation analogous to the higher-ranking “two star general” , “three star general” , “four star general” .
- ↑ Left: Rank badge on the shoulder flap of the jacket of the service suit for army uniform wearers. Right: Rank badge on the shoulder flap of the jacket of the service suit for Air Force uniform wearers.
- ↑ In principle, temporary soldiers , professional soldiers and reservists can be appointed brigadier general, although in practice (especially in times of peace) almost only professional officers are promoted to brigadier general. Counterexamples are Friedrich August Freiherr von der Heydte and Adolf Wicht , who became Brigadier General d. R. were promoted. According to Günter Kießling , high-ranking officials of the Federal Intelligence Service , former Colonels i. G. , to Brigadier General d. R. has been promoted (see Günter Kiessling : Missed contradiction . Hase & Koehler, Mainz 1993, ISBN 3-7758-1294-6 , p. 350 . ) Generals a. D. are also reservists. However, they are usually not promoted and do not do military exercises. In practice, the promotion of a reservist to the brigadier general (and their further promotion) is also excluded because no corresponding posts have been planned and therefore no corresponding (non-formally) required appointment in the sense of the Soldiers' Career Ordinance in connection with ZDv 20/7 . In the sense of the Soldiers ' Career Ordinance, membership of the officers' career group is also obvious, although this can only be inferred implicitly, because all generals continue to be counted as officers in the sense of the Federal President's order . In the area of application of the Soldiers ' Career Ordinance, officers can only be promoted within a career path of the officers' career group. Even if the career paths of the career group over and above the colonel are not described in more detail in the Soldiers' Career Ordinance, promotion to a rank of the rank group of generals is carried out analogously in continuation of one of the careers of officers. The promotion of officers from one of the career paths of the military technical service or the military music service is practically excluded . In practice, they cannot be promoted because no relevant posts are shown. The career in the military service ends in practice and in the description of the soldiers' career regulation at the staff captain . For military music officers, due to the limited number of posts, the highest rank of colonel can be achieved.
- ↑ Minimum service periods since being appointed to a previous rank are therefore not formally required. Theoretically, the rank of brigadier general could also be “skipped” by colonels or reached shortly after being appointed colonel; Theoretically, a position with the rank of Brigadier General is also possible. A rare example of one of these "special cases", which would be fully transferable to army and air force uniforms and the rank of brigadier general, is Ulrich Weisser , who was first appointed flotilla admiral in 1992 and was appointed vice admiral that same year . Weisser skipped the rank of rear admiral , cf. Hans Ehlert : A life for the Bundeswehr. Mine sweeper, super brain, gray eminence. In: faz.net. Frankfurter Allgemeine Zeitung GmbH, Werner D'Inka , Berthold Kohler , Günther Nonnenmacher , Holger Steltzner , May 6, 2011, accessed on August 15, 2014 (first edition in the Frankfurter Allgemeine Zeitung of April 27, 2011. No. 97 / page 8) .
- ↑ ZDv 20/7 on the basis of Section 44 of the Soldiers ' Careers Ordinance ( Ordinance on the Careers of Soldiers (Soldiers' Career Ordinance - SLV) . March 19, 2002, Section 44 ( gesetze-im-internet.de [accessed on March 25, 2014] revised) by announcement of August 19, 2011 I 1813. Last amended by Art. 2, Paragraph 5 G of April 8, 2013 I 730). )
- ↑ The age limits were redefined with the Service Law Reform Act 2009, cf. especially changes regarding § 45 SG and transitional provisions according to Section 96 SG. See Act on the Reorganization and Modernization of Federal Service Law (Service Law New Order Act - DNeuG) . In: Bundesanzeiger Verlag (Hrsg.): BGBl . Part 1, G 5702. Volume 2009 , no. 7 . Bonn February 11, 2009, p. 160–275 ( Federal Law Gazette 2009 I No. 7 [accessed on November 14, 2014]).
- ↑ For reasons of space, shortened captions. What is meant are army uniform wearers and air force uniform wearers . The crimson flat braid shown next to the slip-on loop for army uniform wearers is always the indicator for belonging to the rank group of generals for army uniform wearers . In addition to the slip-on loops for the field blouse in the five-color camouflage pattern shown here on the shoulder flaps, there are a number of other types of rank insignia, which are described in more detail in the article → "Rank insignia of the Bundeswehr" .
- ↑ Note the remarks in the → chapter on the color of the weapons of the generals in the article "Color of the weapon"
Web links
Individual evidence
- ↑ a b c d Hartmut Bagger , Command Staff of the Armed Forces I 3, Federal Ministry of Defense (Ed.): ZDv 37/10. Suit regulations for soldiers in the Bundeswehr . July 1996. Reprint from October 2008. Bonn July 16, 2008, 4 labels, p. 539 ( digitized version ( memento from September 19, 2014 in the Internet Archive ) [PDF; 3.5 MB ] Reprint October 2008 replaces first edition from July 1996).
- ↑ a b The Federal Minister of Defense (ed.): ZDv 14/5. Soldiers Act . DSK AV110100174, change status July 17, 2008. Bonn August 21, 1978, rank designations in the Bundeswehr, p. B 185 (not to be confused with the Law on the Legal Status of Soldiers (Soldiers Law) ).
- ↑ a b Agreed English texts. STANAG 2116 . NATO standardization agreement (STANAG) . NATO codes for grades of military personnel. 5th edition. 1992 ( Online NATO Rank Codes - 1992 [accessed March 25, 2014] English, private website).
- ↑ a b c d e f g h The Federal President (ed.): Order of the Federal President on the rank designations and the uniform of the soldiers . BPresUnifAnO. July 14, 1978 ( PDF - Order of the Federal President on the rank designations and uniforms of soldiers from July 14, 1978 ( Federal Law Gazette I p. 1067 ), last amended by Article 1 of the order of May 31, 1996 ( Federal Law Gazette I p. 746 ) has been changed).
- ^ Federal Minister of Defense ; Command Staff of the Armed Forces IV 1 (Ed.): Abbreviations for use in the Bundeswehr - German Abbreviations - ZDv 64/10 . Bonn January 19, 1979 ( PDF - as of September 17, 1999).
- ↑ a b Appendix I (to § 20, paragraph 2, sentence 1) Bundesbesoldungsgesetz orders of A and B . ( gesetze-im-internet.de [accessed on March 25, 2014] Federal Pay Regulations (BBesO) only apply to professional and temporary soldiers and are an annex to the Federal Pay Act (BBesG)).
- ↑ The Federal Minister of Defense (ed.): Law on the legal status of soldiers (Soldiers Act - SG) . Bonn March 19, 1956, § 4 para. 3 (2) - ( gesetze-im-internet.de [PDF; accessed on March 25, 2014] Newly drafted by notice of May 30, 2005 I 1482. Last amended by Art . 1 G of April 8, 2013 I 730).
- ↑ a b The Federal Minister of Defense (ed.): ZDv 14/5. Soldiers Act . DSK AV110100174, amendment status July 17, 2008. Bonn August 21, 1978, The Superiors Ordinance, p. A 12 1 (Not to be confused with the Ordinance on the Regulation of Military Superiors (Superiors Ordinance - VorgV) ).
- ↑ Federal Minister of Defense (Ed.): Ordinance on the regulation of the military superior relationship (Superior Ordinance - VorgV) . June 4, 1956, § 4 ( gesetze-im-internet.de [accessed on March 25, 2014] Last amended by Art. 1 No. 2 V of October 7, 1981 I 1129).
- ↑ Federal Minister of Defense (Ed.): Ordinance on the regulation of the military superior relationship (Superior Ordinance - VorgV) . June 4, 1956 ( gesetze-im-internet.de [accessed on March 25, 2014] Last amended by Art. 1 No. 2 V of October 7, 1981 I 1129).
- ^ Military disciplinary code (WDO). In: Laws on the Internet. Federal Ministry of Justice and Consumer Protection , August 16, 2001, accessed on November 5, 2014 (from August 16, 2001 ( Federal Law Gazette I p. 2093 ), last amended by Article 7 of the Act of August 28, 2013 ( Federal Law Gazette I p . 3386 ) has been changed).
- ^ Ordinance on the career paths of soldiers (Soldiers' Career Ordinance - SLV) . March 19, 2002 ( gesetze-im-internet.de [accessed on March 25, 2014] Newly drafted by notice of August 19, 2011 I 1813. Last amended by Art. 2 Paragraph 5 G of April 8, 2013 I 730).
- ↑ Note also: Annex (to § 3). Allocation of the career paths of the soldiers to the career groups of the men and women, the NCOs and the officers
- ↑ a b The Federal Minister of Defense ; Personnel, Social and Central Affairs Department (Ed.): ZDv 20/7. Provisions for the transport and for the recruitment, acceptance and admission of soldiers . Bonn March 27, 2002, Art. 635 ( PDF ( memento of October 26, 2014 in the Internet Archive ) [accessed on March 26, 2014] DSK AP210100187, reprint January 2008).
- ↑ Federal Budget 2014 - Section 14. (PDF) (No longer available online.) Federal Ministry of Defense , pp. 143, 147 , archived from the original on October 21, 2014 ; Retrieved November 17, 2014 .
- ↑ Federal Ministry of Justice and for Consumer Protection , juris GmbH (Ed.): Law on the legal status of soldiers (Soldiers Act - SG) . Bonn March 19, 1956, § 45 Paragraph 2 (3) - ( gesetze-im-internet.de [PDF; accessed on November 10, 2014] Newly drafted by notice of May 30, 2005 I 1482. Last amended by Art . 1 G of April 8, 2013 I 730).
- ↑ a b The equivalent, higher and lower ranks are given in accordance with ZDv 14/5 B 185, cf. The Federal Minister of Defense (ed.): ZDv 14/5. Soldiers Act . DSK AV110100174, change status July 17, 2008. Bonn August 21, 1978, rank designations in the Bundeswehr, p. B 185 (Not to be confused with the Law on the Legal Status of Soldiers (Soldiers Act) . The order of the ranks shown in the info box does not necessarily correspond to one of the regular rank sequences provided for in the Soldiers' Career Ordinance , nor does it necessarily correspond to the rank hierarchy described in the Superiors Ordinance a managerial relationship ).