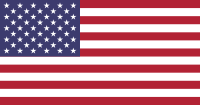
United States flag
| Star-Spangled Banner / Stars and Stripes |
|
|---|---|
 |
|
| Vexillological symbol : |
|
| Aspect ratio: | 10:19 |
| Officially accepted: | 4th July 1960 |
The flag of the United States of America is also Stars and Stripes ( english Star-Spangled Banner ), or Stars and Stripes called. It consists of 7 red and 6 white stripes, which stand for the 13 founding states , and a blue flag field (" Gösch ") in the upper left corner, whose currently 50 white stars symbolize the 50 states of the USA. According to § 2 of the Flag Act of the USA , a further star is added after the addition of another state with effect from the following July 4th ( Independence Day ).
The colors red, white and blue have their origins in the Union Jack as the flag of the English colonies. Its symbolism in stars and stripes is: white for purity and innocence ( purity and innocence ) , red for bravery and resilience ( valor and hardiness ) and blue for vigilance, perseverance and justice ( vigilance , perseverance , justice ).
The flag is sung about in the United States' national anthem, The Star-Spangled Banner . Flag Day is celebrated there on June 14th, but this is a public holiday only in Pennsylvania and American Samoa (June 17th) .
Structure of the flag
- Height of the flag: A = 1
- Length of the flag: B = 1.9
- Height of the star field: C = 7/13 ≈ 0.538 (seven stripes)
- Length of the star field: D = 0.76 (40% of the length of the flag)
- E = F = C / 10 ≈ 0.0538 (one tenth the height of the star field)
- G = H = D / 12 ≈ 0.0633 (one twelfth the length of the star field)
- Diameter of the perimeter of a star: K ≈ 0.0616 (80% of the height of a stripe)
- Height of a stripe: L = 1/13 ≈ 0.0769 (seven red and six white stripes, 4 red 3 white = height of the star field / 3 white 3 red = below the star field)
Origin and history
At the time of the independence movements and riots in the late 18th century, there were various revolutionary flags in the 13 English colonies in America as a symbol of togetherness. One of the most important of these flags, which can also be seen as the predecessor of the first Union flag, the Old Glory, was the Sons of Liberty Flag from 1775. It was used by the Sons of Liberty activists to promote the unity of the colonies demonstrate. It initially consisted of nine vertical stripes that were alternately colored in red and white. These strips presumably represented the nine colonies that had sent representatives to the Stamp Act Congress of 1765, where public demonstrations against the British Stamp Act were held. Later the flag consisted of 13 now horizontal stripes, which were also colored alternately.

The number of stripes varies in historical illustrations; the 13-stripe shape did not appear until after the founding of the province of Georgia in 1732
During the first years of the revolution, the Continental Flag , also known as the Grand Union Flag , became increasingly popular. It was based on the Sons of Liberty flag with its 13 red and white stripes and also included the British Union Jack in Gösch . It could be made relatively easily from the Red Ensign of the British Navy by sewing on white stripes . Since the flag is very similar to that of the British East India Company , it has occasionally been assumed that it was the inspiration for the design of the Continental Flag . Where the flag actually got its appearance from cannot be conclusively determined today. It was not until 1776 that the USA received an official flag as part of the signing of the Declaration of Independence. The flags of the 13 states that fought against the British in the Revolutionary War have great historical significance. As British colonies, these areas were officially under the instructions of the British Parliament when the war broke out, but this was rejected by many colonists. They believed that the lack of representation of the colonies was a violation of the rights of British citizens. Growing dissatisfaction with British rule led the 13 colonies to convene the second Continental Congress in 1775 and decide to create the Continental Army. In response, England sent troops to the American east coast and in 1776 declared the American delegates to congress rebels and traitors to the crown. The colonies then broke away from the British monarchy and with the declaration of independence gave themselves the status of an independent and sovereign state. The 13 founding states of the United States were Virginia , New York , Massachusetts , New Hampshire , New Jersey , Maryland , Rhode Island , Connecticut , Delaware , North Carolina , South Carolina , Pennsylvania, and Georgia .
In the War of Independence, the various units each carried their own flags, which were mostly similar to the British flag. For example, a flag worn in the Battle of Bunker Hill, like the historic New England flag, included the Cross of St. George and pine in the upper right quarter. Other revolutionary flags bore the slogan Don't tread on me (literally: " Don't step on me", meaning: "Don't mess with me"), versions of which show the Gadsden flag , the flag of the Culpeper Minutemen and the flag of today still used First Navy Jack. George Washington's Grand Union is considered to be the first flag of the United States, strangely enough, it was heavily based on the British flag. The upper corner formed a Union Jack, overall it resembled the flag of the British East India Company.
The Second Continental Congress passed a resolution on the appearance of the flag of the United States in Philadelphia on June 14, 1777, almost a year after the declaration of independence . It said that the Betsy Ross flag contains 13 stripes that are alternately colored in red and white. In addition, the unity of the states should be represented by thirteen stars that are in a blue field. Neither the arrangement of the stars nor the number of their rays was specified, so initially there were some interpretations of the flag. For example, the stars were arranged in rows or as a circle, as on the design allegedly by Elizabeth (Betsy) Ross , an upholsterer from Philadelphia . However, that draft is now attributed to Congressman and co-signer of the Declaration of Independence, Francis Hopkinson . In his design, which is therefore called the Francis Hopkinson Flag , the 13 white stars in the Gösch were depicted in staggered columns on a blue background. The 13 strips were retained.
Between 1795 and 1814, Vermont and Kentucky joined the union, so the flag now showed 15 stars and 15 stripes arranged in rows. It blew in the War of 1812 over Fort McHenry in Baltimore Harbor and inspired Francis Scott Key (1779-1843) on the night of September 13, 1813 to write The Star-Spangled Banner , which became the national anthem in 1931 by Congressional law.

In 1818, Congress decided to limit the number of stripes to 13, but to add a new star for each newly added state on July 4th, American Independence Day, after its accession. No regulation was made about the formation of the stars or their color (white or, as was the case in the civil war, gold). Therefore, in the course of the 19th century, different flags appeared, each with a different arrangement of the stars in the upper left corner. B. the Great Star Flag from 1837, in which the stars were arranged in the form of a large star, or the Fort Sumter Flag , which waved at the beginning of the Civil War in 1861 and showed the stars as a diamond . Probably the most striking pattern was the design of the 38 Star Flag from 1877, in which a central star (for Colorado ) was surrounded by two rings of stars.
It was not until 1912 that the drawing of the now 48 stars in a row and their white color became the official norm.
In 1942, Congress passed a law ( United States Flag Code , Public Law 77-826) that stipulates a set of rules of conduct for the use of the flag - including the speed with which it is hoisted and retrieved and when it is during school hours to be hoisted in schools.
In 1953, an amendment to this Code allowed the United Nations flag to be hoisted over the Stars and Stripes.
The flag was last changed on July 4, 1960, after Alaska had been declared the 49th and 50th states of the United States on January 3, 1959 and Hawaii on August 21, 1959, making the US flag its most permanent version to date helped.
On 31 May 2002 the said Navy Secretary Gordon R. England the First Navy Jack the official Gösch the United States Navy in the war on terror .
Historical flags
More historical flags under: Historical US flags , war flags of the Confederate States of America , flags of the secessionist states
| flag | date | description |
|---|---|---|
 |
around 1765 | original Sons of Liberty Flag |
 |
around 1765 | later Sons of Liberty Flag |
 |
around 1775 | Grand Union Flag (also Continental Flag ), the original Union Jack in the Obereck, one of the flags of the independence movement |
 |
around 1775 | Gadsden Flag , yellow flag with a rattlesnake and the text that was probably meant as a warning, Don't Tread On Me . The Rattlesnake symbol was used by Benjamin Franklin supported and appeared in many other flags, including in the First Navy Jack , the current naval jack of the United States Navy |
 |
1776-1795 | Betsy Ross Flag (also Francis Hopkinson Flag ), flag of the Union with 13 stripes and 13 stars arranged in a circle for the thirteen colonies , national flag after the declaration of independence |
 |
1795-1818 | Star Spangled Banner 8 red and 7 white stripes (15 stripes!), 15 white stars in the blue jack. This flag was the flag honored in the US national anthem and was chosen as a result of the accession of Vermont (1791) and Kentucky (1792). |
 |
1818-1819 | Following the accession of Tennessee (1796), Ohio (1803), Louisiana (1812), Indiana (1816), Mississippi (1817) and a new flag law that limited the stripes to 13 and the introduction of new stars for new states in the jack on the 4th of July following the accession , but did not define the arrangement and color of the stars, so-called Great Star Flags , whose smaller stars formed a large one, were also used. |
 |
1861 | Fort Sumter Flag : When Oregon joined , the Union had 33 members. Since the arrangement of the stars was not defined until 1912, different versions of the flag continued to exist. This diamond version of the stars wafted over Fort Sumter at the start of the Civil War . |
 |
1863-1865 | Navy flag of the Confederate States of America . A similar version of this flag was originally planned to be the Confederation's first national flag. However, since the government commission believed that the cross was too reminiscent of “suspenders”, the proposal was rejected. The flag was not introduced until May 26, 1863 and was used until the end of the war. Nowadays the model is the generally recognized symbol of the "South", where it is called the "Rebel" or "Dixie" flag. It is also mistakenly called the Confederate flag . |
 |
1865 | Last national flag of the Confederate States of America . Previously, a flag was used without the red stripe on the right edge, but to avoid confusion with the white surrender flag, this variant was introduced on March 4, 1865. |
 |
1867-1877 | Many variants of the flag were designed to mark the US centenary, including this reference to the Betsy Ross flag |
 |
1912-1959 | With the accession of New Mexico on January 6, 1912 and Arizona on February 12, 1912, the United States had 48 states . The 48-star flag was the victory flag of the US Army in the First and Second World War . With this flag, the arrangement of the stars was also clearly defined for the first time. |
Handling
The United States Flag Act (4th title of the USC ) contains very detailed rules on how to use the flag. For example, times and occasions for hoisting the flag are specified (Section 6), and behavior during hoisting and hauling is prescribed (Section 9). For "respect for the flag", § 8 includes the following provisions:
- Only uniform wearers are allowed to carry sewn-on flags, a specialty here is the way the flag is worn by soldiers: the flag is worn with the stars on the front of the body, i.e. in the direction of impact (so-called reverse field flag ). It is thus illustrated that the soldiers advance in the direction of the enemy with the imaginary waving flag. If a flag badge is used, it must be worn at heart level, 4USC8 (j) each.
- Officially, the flag may only be hoisted upside down if a group is in a serious emergency (4USC8 (a)), in other cases this represents a disparagement.
- The flag may not be changed in its appearance, 4USC8 (g).
- Frayed flags are to be burned in an honorable way, 4USC8 (k).
Section 4 of the Flag Act contains the Pledge of Allegiance , the pledge of allegiance to the flag and the state for which it stands.
Prosecution under this law was banned by the Supreme Court as violating freedom of expression.
Future of the flag
The number of US states may change in the future . In this case, it is planned to adjust the number of stars in the flag accordingly.
There are efforts to convert the District of Columbia into a state and to separate New York City from New York State and make it an independent city-state. The U.S. Virgin Islands , American Samoa , Guam , Northern Mariana Islands, and Puerto Rico could also become states one day. The United States Army Institute of Heraldry is planning flags with up to 57 stars.
The opposite is also conceivable: the separation of a state from the USA or the amalgamation of states, which would reduce their number.
The stars and stripes as a model
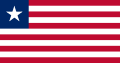
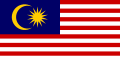
The national flag of the USA is the model for a large number of flags of other countries and institutions, for example for the national flag of Liberia , which was founded by freed American slaves , and for the national flags of Cuba , Chile , Malaysia and Uruguay . Associated Puerto Rico and the US states of Texas and Ohio were also inspired by the stars and stripes. However, not all flags with multiple stripes and a jack are based on that of the USA. The flags of Greece and Brittany were created independently of this , while one can only assume a US-American influence for the flag of Togo . The same applies to many of the flags of rowing clubs , which originated in the 19th century.
- Flags whose design goes back to the stars and stripes
- (Not implemented) flag designs whose design goes back to the stars and stripes
Flag of Kosovo (design by Joseph J. DioGuardi)
Flag of Germany (design by Robert Lehr , 1948)
- Similar flags without reference to the stars and stripes
- Similar flags of rowing clubs
See also
- List of flags of the United States
- Flags and seals of the US states
- Flagging public buildings in the United States
- Patriotism in the United States
Web links
Individual evidence
- ↑ Duden online: Stars and Stripes and Stars and Stripes
- ^ Charles Fawcett: The Striped Flag of the East India Company, and its Connexion with the American “Stars and Stripes,” Mariners Mirror, October 1937, accessed September 19, 2012
- ^ A b Federal Citizen Information Center: Our Flag , publications.usa.gov, accessed September 19, 2012
- ↑ 4USC6 (United States Government Printing Office, English)
- ↑ 4USC9 (Government Printing Office, English)
- ↑ 4USC8 (Government Printing Office, English)
- ↑ 4USC4 (Government Printing Office, English)
- ↑ United States Army Institute of Heraldry ( Memento of the original from April 11, 2006 in the Internet Archive ) Info: The archive link was inserted automatically and has not yet been checked. Please check the original and archive link according to the instructions and then remove this notice. (English)