Trave
| Trave | ||
|
Trave near Lokfeld |
||
| Data | ||
| Water code | EN : 962 | |
| location | Schleswig-Holstein , Germany | |
| River system | Trave | |
| River basin district | Schlei / Trave | |
| source | Gießelrade near Ahrensbök in Ostholstein 54 ° 3 ′ 7 ″ N , 10 ° 35 ′ 53 ″ E |
|
| muzzle | At Travemünde in the Baltic Sea ( Lübeck Bay ) Coordinates: 53 ° 57 '39 " N , 10 ° 53' 14" E 53 ° 57 '39 " N , 10 ° 53' 14" E |
|
| Mouth height |
0 m
|
|
| length | 113.6 km (Obertrave 57.8 km - Untertrave 24.0 km - city, canal and harbor trave 12.7 km - Traveförde 19.1 km) | |
| Catchment area | 2665 km² | |
| Left tributaries | Clever Au , Schwartau | |
| Right tributaries | Best , Wakenitz , Stepenitz | |
| Big cities | Lübeck | |
| Medium-sized cities | Bad Segeberg , Bad Oldesloe , Reinfeld , Lübeck-Travemünde | |
| Communities | Dassow | |
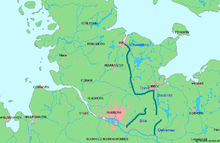
The Trave (lat. Travena ) is a 124 km long river in Schleswig-Holstein that flows into the Baltic Sea.
course
Two of the terms used can each have different meanings. According to the hydrological name, the "Obertrave" is the upper course from the source to the confluence of the Elbe-Lübeck Canal. From the legal point of view of the town of Lübeck , “Obertrave” refers to the section from St.-Jürgen-Hafen of the Kanaltrave to the Holstenbrücke at the Holstentor. The "Untertrave" begins according to the traditional name at the Holsten Bridge, according to the city map on the Teerhofinsel and the signature of the Land Surveying Office as coastal waters on the Herreninsel.
For the waterway designations applies
- Canal Trave from the confluence of the Elbe-Lübeck Canal along the east side of the old town to the confluence with the Stadttrave at the Burgtor
- Stadttrave from the junction of the Canal Trave south of the cathedral along the west side of the old town to the confluence with the Canal Trave at the Burgtor
- Untertrave from the castle gate to the mouth
Tributaries
Berliner Au - Beste - Bißnitz - Heilsau - Brandsau - Faule Trave - Medebek , see also Schellbruch - Mözener Au - Moorbek (Trave) - Rönnau (Trave) - Schwartau (see also Liubice ) - Stecknitz - Stepenitz (see also Dassower See ) - Wakenitz
Upper course
The Trave originates in Gießelrade (Ostholstein district), north of the B 432 between Ahrensbök and Scharbeutz. In the center of the village there is the source pool, which is surrounded by a small area with benches. From there it flows in old melt water beds from the last Ice Age and first in a south-westerly direction through the Wardersee to Bad Segeberg and then further south to Bad Oldesloe . There it bends to the east, only to flow past Reinfeld to the south and then to Lübeck at Hamberge and Moisling .
From Bad Oldesloe to the confluence of the Elbe-Lübeck Canal, the Obere Trave was Reichswasserstraße from 1921, but returned to Prussia in 1941.
Middle Trave


The Elbe-Lübeck Canal joins the Lübeck village, now the Genin district, from the south , built on long stretches along the Stecknitz between 1895 and 1900. At the same time as the canal was built, the river was deepened and widened from the mouth of the canal to the edge of the old town to the Canal Trave . In Lübeck's old town, the course of the river was redesigned to meet the needs of shipping and medieval city defense, so that it forks into several bodies of water south of Lübeck Cathedral . First the city moat branches off to the west, then the canal trave to the east from the original Travelauf and leads in the former bed of the Wakenitz to the Klughafen on the northeast side of the old town. The Wakenitz , which originally bordered the old town to the east, is led at the Rehderbrücke (formerly: Krähenbrücke) by means of a culvert under the Canal Trave into the Krähenteich and from there flows through the Mühlenteich into the Stadttrave (Stadtlübisch: Obertrave). This is part of the original Travelauf on the western edge of the old town. The salt reservoirs stand on their left bank . North of the Holsten Gate , this travelauf becomes part of the Untertrave, but is still officially called Stadttrave until the confluence with the Canaltrave. On its right bank, the street An der Obertrave , is the music college . The Lübeck moat runs west of the former ramparts .
Untertrave
The seaports begin north of the Holsten Gate. At the northern end of the old town island at the castle gate , the city moat, city trave and canal trave come together again. Lübeck's trading ports are located between the Holsten Gate and the Teerhof Island , which was artificially created by a puncture in the 19th century . The Schwartau flows from the north where the piercing and the old fairway meet . The Slavic hill fort Liubice is located on the peninsula between this and the old Trave . It flows past the Schellbruch nature reserve and the fishing village of Gothmund to the Herreninsel , now a peninsula, north of which it is crossed by the Herrentunnel . From Travemünde, connecting line Norder-Südermole, it is regarded as inland water , a regular influx of water from the Lübeck Bay ensures a salt content between around 2 and 5 g / kg. Due to its formation during the Ice Age, the estuary between Herreninsel and the confluence with the Bay of Lübeck including the widening of the Pötenitzer Wiek and its Dassower See bay is also a fjord , the Traveförde.
To the east of the Herreninsel, on the right bank, lies the Schlutup district with the confluence of the Lübeck Landgraben . Opposite the Dummersdorfer Ufer begins with its Stülper Huk . The Trave then widens eastwards to the Pötenitzer Wiek, which has already been mentioned. The Stepenitz flows into the Dassower See . The stretch of the mouth of the Travemünde between the Pötenitzer Wiek and the open Lübeck Bay , bounded west by Travemünde and east by the Priwall , is actually an arm of the sea.
Formation of the Traveförde
The deep cut of the Trave was created when glaciers carved out a channel in the last Ice Age (the Vistula Ice Age ) . The channel has been connected to the Baltic Sea since the end of the Ice Age and forms the Traveförde . This fjord also represents the lower course of the Trave. The water of the Trave has only flowed since about 12,000 BC. To the north in the Lübeck Bay of the Baltic Sea. Before that, the direction of flow through the glacial channels was to the south, as the route to the north was still blocked by the remains of the glacier.
The steady flow of water from the Trave keeps the outflow of the Trave ( förde ) to the Baltic Sea open - against the masses of sand removed from the Brodtener Ufer and shifted to the east by the current - and thus prevents separation from the Baltic Sea .
Historical meaning
The Trave was called Dravus, Drave in the Germania magna in the first century .
In the upper reaches, the Trave and the Schwentine formed the Limes Saxoniae and the western border of Wagrien . In the area of Lübeck's old town it was part of the system of medieval and modern Lübeck city fortifications . In the lower reaches it was and is the state border with Mecklenburg, until 1990 as the inner German border . The sovereign rights of the Trave and the Lübeck Bay were in dispute between Lübeck and Mecklenburg since the Barbarossa privilege (1188). The dispute over the banks of the Trave was decided by the Imperial Court on June 21, 1890 .

Bridges and tunnels
The Trave is crossed by 104 bridges, 1 tunnel, 2 ferries and 2 fords:
The trave crossing in the course of the federal highway 75 was replaced by the new Herrentunnel , which was opened on August 26th 2005 and is chargeable. The Herrenbrücke , a bascule bridge , was demolished by the end of 2006. Pedestrians as well as cyclists and moped drivers are transported free of charge through the Herrentunnel by a shuttle bus, every 15 minutes between 5 a.m. and 9 p.m. (summer schedule), during the night as required.
In the area of Lübeck's old town, the new Eric Warburg Bridge was put into operation as a bascule bridge on March 10, 2008.
shipping
The Trave (Tr) is a federal waterway from the confluence of the Elbe-Lübeck Canal, 71 meters northeast of the axis of the Geniner road bridge (km 0.00) to its confluence with the Baltic Sea at Travemünde (km 26.94) , and up to the railway lift bridge in Lübeck (km 5.56) a class IV inland waterway on which the inland waterway regulations apply and from there on an inland waterway in class VIb, on which the sea waterway regulations apply with a pilotage requirement for seagoing vessels. The Lübeck Waterways and Shipping Office is responsible . Until 1934, the city of Lübeck was responsible for the Canal Trave, Stadttrave and Untertrave, from then on it was Reichswasserstraße and then Federal Waterway. In 2006 the city trave went back to the city of Lübeck.
Because of its importance, the course of the Untertrave has been corrected several times in the past.
- In the years 1850–1854 the first correction of the Trave took place . Until 1852 the Trave flowed directly along the northeast slope of the Fährberg. The ferry was at the bottleneck of the Siemser terminal moraine and the Fährberg. Until then, the ferryman's house was on the left eastern bank of the Trave. As a result of the first correction of the Trave, the first piercing of the Trave, in which the Trave was relocated about 600 m further east to Travemünde, the ferry house moved from the left to the right bank of the Trave. With the breakthrough at what would later become the Herrenfähre , the fairway was deepened to at least 4 m.
- In the years 1879–1883 the 2nd correction of the Trave took place . This was deepened to a minimum depth of 5 m under the channel of Lübeck hydraulic engineering director Louis Martiny with his colleague Peter Rehder . The Teerhof Island was created through a puncture . The trip to the area was shortened considerably.
- In the years 1901–1907 the 3rd Trave correction took place . Rehder, meanwhile director of hydraulic engineering, deepened the fairway between the roadstead in front of Travemünde and the Lübeck city ports to 8.5 m near Travemünde and up to 7.5 m near Lübeck.
 Seelandkai in Herrenwyk
Seelandkai in Herrenwyk - Increasing ship drafts required an immediately following 4th Trave correction for a continuous depth of 8.5 m, which aimed at full two-aisles for ships with a draft of 8 m. Due to the two world wars, however, it could not be completed until 1961.
- In the years 1961–1982 the 5th Trave correction was made for a 9.5 m extension to prevent the development of the port of Lübeck from stagnating. For this purpose, apart from deepening and widening the fairway, etc. a. the Lübeck ports were further expanded, the bank revetments built on a large scale and the navigation signs modernized.
Shipping traffic is controlled by a traffic control center near the Travemünde lighthouse . The lighthouse is irrelevant for the approach to Travemünde, the beacon is now on the roof of the Maritim high-rise.
Nature and environmental protection
The Schleswig-Holstein state government, through Agriculture Minister Christian von Boetticher, has reported the entire travel up to the mouth, including the adjacent nature reserves, to the European Union as an FFH area as part of the Natura 2000 program .
Nature reserves on the lower Travelauf in the area of the river mouth area ( estuary ) are the Schellbruch , the Dummersdorfer Ufer , the Dassower See and parts of the Priwall .
Fish fauna
In terms of fishing law in the Lübeck area, the Trave is subject to the old fishing law of the Hanseatic City of Lübeck. Further information can be obtained from the Lübeck district association of sport fishermen. V. Due to its large catchment area and its diverse range of fish, the Trave is an interesting body of water for all sport and leisure anglers.
The occurring fish species include perch , eel , gudgeon , roach , pike , bream , sea trout , aland , brook trout , dwarf stickleback , chub , minnow , tench , burbot , ruff , rainbow trout , grayling , asp , crucian carp , hazel , carp and pikeperch . In the Lübeck area, the salinity of the river is increasing, so you can still find flounder , herring and garfish here .
The Lübeck district association of sport fishermen e. V. issues fishing permits to all anglers. The condition for this is a valid annual fishing license or a vacation permit. Anglers who do not have their primary residence in Schleswig-Holstein must pay the SH fishing tax. The conditions for fishing in the area of the Hanseatic City of Lübeck are not that easy, because the fishing law, which is over 800 years old, still applies here. The Trave is then divided into three different fishing districts.
See also
literature
- Martin Eckoldt (Ed.): Rivers and canals, The history of the German waterways . DSV-Verlag, 1998.
- Sylvina Zander: Oldesloe - The city, the Trave and the water . Wachholtz-Verlag, Neumünster 2008, 416 pages, numerous, partly colored illustrations and maps, ISBN 3-529-07130-7 .
Web links
- Uwe Selig, Dirk Schories, Hendrik Schubert: Report on the research project: "Testing the classification approach Mecklenburg-Western Pomerania (inner coastal waters) under the conditions of Schleswig-Holstein and extending the approach to the outer coast". Coastal water classification of the German Baltic Sea according to EU WFD, Part B: Inner coastal waters of Schleswig-Holstein. (PDF file; 833 kB)
- Travebrücken Gallery
- Herrenbrücke
Individual evidence
- ↑ Traveförde bird sanctuary in the Schleswig-Holstein Environmental and Agricultural Atlas
- ↑ RG ZVLGA 6 (1891), pp. 243-326.
- ↑ Herrentunnel bus shuttle . Herrentunnel website, accessed August 15, 2014.
- ↑ a b c Lengths (in km) of the main shipping routes (main routes and certain secondary routes) of the federal inland waterways ( memento of the original from January 21, 2016 in the Internet Archive ) Info: The archive link was automatically inserted and not yet checked. Please check the original and archive link according to the instructions and then remove this notice. , Federal Waterways and Shipping Administration
- ↑ Directory E, serial no. 58 der Chronik ( Memento of the original from July 22, 2016 in the Internet Archive ) Info: The archive link has been inserted automatically and has not yet been checked. Please check the original and archive link according to the instructions and then remove this notice. , Federal Waterways and Shipping Administration
- ↑ Ordinance on the transition from branch lines belonging to the Trave federal waterway to the Hanseatic City of Lübeck of June 29, 2007 ( Federal Law Gazette I p. 1241 )
- ↑ angeln-in-luebeck.de: fishing in Lübeck - Die Trave , accessed on September 20, 2010