County of Flanders
|
Territory in the Holy Roman Empire |
|
|---|---|
| County of Flanders | |
| coat of arms | |
 
|
|
| map | |

|
|
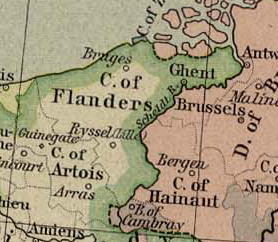
| County of Flanders around 1350. The red border between France (left) and the HRR.
|
|
| Form of rule | county |
| Ruler / government | Count |
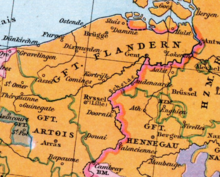
| Today's region / s |
BE-VWV BE-VOV parts from NL-ZE parts from FR-59
|
| Reichskreis | Burgundian |
| Capitals / residences | Ghent , Bruges |
| Dynasties |
Flanders 1119: Estridsson 1127: Rollonids 1128: Châtenois 1194: Flanders 1278: Dampierre 1384: Burgundy 1477: Habsburg |
| Denomination / Religions | Roman Catholic |
| Language / n |
Dutch , French , German
|
| Incorporated into | 1795 France , after 1815 the Kingdom of the United Netherlands , later Belgium
|
The county of Flanders ( Dutch Vlaanderen , French Flandre ) is a historical territory on the territory of today's states Belgium , France and the Netherlands . Until 1477 the feudal sovereignty was divided: the larger part belonged to France , the smaller part to the right of the Scheldt to the Holy Roman Empire (hence also: " Imperial Flanders "). In the High Middle Ages developed Flanders - mainly driven by its cities, Lille ,Douai , Ypres , Ghent and Bruges - an incomparable economic prosperity . The wool industry and long-distance trade were the main growth factors . This formed the background for a heyday of Gothic art - in the Scheldt Gothic the Gothic architecture principles coming from France were able to establish themselves early on.
Antiquity and early Middle Ages
In the earliest times, Flanders was inhabited by Belgian tribes , the Morinians , Atrebates and Menapians , and after their subjugation by Caesar it belonged to the Roman province of Belgica secunda . After the country came under the rule of the Franks , the Lys , a tributary of the Scheldt , formed the border between Neustria and Austrasia . After the division of Verdun in 843, the northern and south-western parts of Flanders came to be, although there was predominantly Old Dutch spoken thereWest Franconia , while the south-eastern part belonged to East Franconia , although old French dialects dominated there.
History of the county
The name of Flanders comes since the 7th century ago and originally comprised only the territory of Bruges and Sluis ( municipium flandrense ), which counts the name of Flanders in the late 9th century and throughout the coastal strip until after Bononia , they as Mark to Received protection against the Normans , and later extended to some neighboring East Franconian possessions.
House of Flanders
The first of those margraves was Baldwin I. Eisenarm , a west Franconian knight from Laon , who kidnapped the daughter of Emperor Charles the Bald , Judith, but received the newly created march from him as a fief in 862 and thus laid the foundation for the size of his house . He died in 879.
His son, Baldwin II, the Bald (879–918), fortified Bruges, Ypres and Saint-Omer against the Normans.
His son Arnulf I (918–966) determined his son Balduin III. (who introduced the first weaving mills in Flanders) and after his death his grandson Arnulf II (died 989) as co-regent . The latter's son Baldwin IV., Beautiful Beard (989-1036), crack 1006 Valenciennes , a city of the Holy Roman Empire , so in itself, was founded by King Henry II. Be fehdet , but received by contract in 1007 Valenciennes, city and Castle County Gent , Walcheren and the Zeeland onesIslands (the so-called Imperial Flanders) from the later Emperor Heinrich II as a fief.
His son Baldwin V, the Pious (1036-1067), waged several wars against Emperor Heinrich III between 1045 and 1056 . who wanted to put a stop to the margraves' expansion of power. Baldwin asserted himself, however, defeated the Frisians and increased his possessions by acquiring the areas belonging to the Duchy of Lower Lorraine between the Scheldt and Dender (the margraviate Ename , later called the county of Aalst ), Tournais and sovereignty over the empire bishopric of Cambrai , to which the county of Flanders until the new diocese of Arras was foundedwas subordinate to the church. Because of his rebellion against the German Emperor, however, he lost the margravate Valenciennes in 1045, since then part of the county of Hainaut .
After his death, his younger son, Robert I, the Frisian , received the lands at the confluence of the Rhine and Waal and the Zeeland islands, while the French fief (the mainland Flanders) to the firstborn, Baldwin VI., Received the good ( 1067-1070), fell.
After his untimely death, there were long battles over the succession between Balduin's widow Richilde , Countess of Hainaut, and Robert the Frisian, which ended with Robert Flanders, the son of Baldwin VI., Baldwin (I) , himself in the Hainaut withdrew, while part of Friesland came to Gottfried von Lothringen .
Robert I's son and successor Robert II (1093–1111) participated in the first crusade and led numerous battles with his neighbors and with the emperor. His son Baldwin VII, with the ax (or the severity), so called because of the severity with which he punished peace breakers, died childless in 1119 and left the land to his cousin from the house of Estridsson , the Danish Prince Charles I the Good whose mother was a daughter of Robert I, but who was murdered in 1127 in Bruges because of his strictness in handling the laws.

The now from the stands at the instigation of Ludwig VI. Son Roberts of Normandy , Wilhelm Clito from the dynasty of the Rollonids , who was appointed count by France , made himself hated by arbitrariness and lost in the fight against Landgrave Dietrich of Alsace from the House of Châtenois , a son of Gertrude of Flanders Daughter of Roberts des Friesen, who died in 1129, after which Dietrich left Alsace to his younger brother, Simeon, took possession of Flanders and waged a war against Hainaut. He died in 1168. The male line of the Flemish counts from the Châtenois family died out with his son Philip, who won Vermandois , but later left Artois in 1180 as a dowry of his niece Isabella of Hainaut King Philip Augustus of France . Philip I of Flanders, who had made a contribution to the material welfare of Flanders in terms of trade and industry, died of the plague in 1191 in front of St. Jean d'Acre . With the marriage of his sister and heiress Margaret to Baldwin VIII (died 1195) from the Hennegau line of the old Flemish counts, Flanders and Hainaut were reunited under the House of Flanders.
Your son Baldwin IX. , the founder of the Latin Empire at Constantinople , left two heirlooms in 1205, of whom the elder, Johanna , Flanders, and the younger, Margarete , known as the Black, received the county of Hainaut.
House Dampierre
For almost the entire century, disputes over the inheritance and the throne, in which the kings of France interfered with selfish intent ( Flemish War of Succession ) , lasted . After Margaret's death in 1279, her son Johann Hainaut, the other, Guido von Dampierre , received Flanders. The latter allied himself in 1291 with Adolf von Nassau (Roman-German king since 1292) and with England against Philip IV the Fair of France; but Pope Boniface VIII mediated .1295 peace. However, King Philip IV invaded Flanders again in 1297, conquered most of the country that he claimed as a French fief, and took Guido and his son Robert prisoner. When Philip IV then suppressed the freedoms of the Flemings through his governor Jacques de Châtillon , they rose up under the head of the woolen weavers of Bruges, Pieter de Coninck (Pierre le Roi), destroyed the French-minded party of the Leliaerts and defeated the superior French army in the Spore Battle at Kortrijk (Courtrai) on July 11, 1302. They were then indeed on August 18, 1304 at Mons-en-Puelle between Lilleand Douai defeated, but nevertheless achieved a peace, after which Guido was to return to Flanders against cession of some cities. But since he died in 1305, his son Robert followed him.
His grandson and successor Ludwig I (1304–1346), at the same time as Ludwig II. Lord of Nevers and Rethel , and thus the most powerful of all the Counts of Flanders, gave cause in 1336 through his hardship against the rich and industrial cities striving for greater freedom to the general uprising led by the bold Ghent brewer Jakob van Artevelde with English support. At the same time, hatred was heightened by the fact that the count and the nobility wanted to join France and the cities join England. Expelled from his country, Ludwig I sought help from France, but was only able to return after Artevelde's death (1345). He fell in 1346 at the Battle of Crecy. Under his reckless son Ludwig II (1330–1384), called Ludwig von Maele, the cities, namely Ghent and Bruges , the richest and most powerful, revolted again. Ludwig II besieged Ghent in vain, but defeated the Ghent near Roosebeke in 1382 , where their leader Philipp van Artevelde , Jacob's son, also fell. With English help, however, the townspeople at Dunkirk won a victory over Ludwig II. Finally, in 1384, France brokered the signing of a peace treaty .
House of Burgundy
Ludwig II died in 1384 as the last Count of Flanders from the House of Dampierre. With the marriage of his heir Margaret to Philip the Bold from the House of Burgundy , the country was united with Burgundy in 1385 and has shared the fate of this empire since then (see Burgundian Netherlands ).
House of Habsburg
When, after the death of Charles the Bold of Burgundy, his lands fell to the House of Habsburg in 1477 through the marriage of his heir daughter Maria of Burgundy to Maximilian of Habsburg , the French crown tried in vain to reassert its old feudal sovereignty over Flanders in the War of the Burgundian Succession .
In the Treaty of Madrid in 1526, France had to renounce its supremacy over Flanders. In the circuit arrangement in Germany from 1548 was Flanders henceforth the Burgundy circuit assigned.
After this, however, came to King Philip II and thus to the Spanish line of the House of Habsburg, he suffered significant reductions.
The county of Flanders rebelled against Spain in the Dutch uprising and in 1579 joined the Union of Utrecht with the Calvinist provinces , although the Roman Catholic faith was predominantly practiced in Flanders.
In the Peace of Westphalia in 1648, the States General asserted the so-called Dutch Flanders (State Flanders, which today still belongs to the Netherlands as Zeeuws Vlaanderen ), whereas Louis XIV of France, through the Peace of Pyrenees , the First Aachen , the Nijmegen and the Utrecht Peace, maintained considerable parts from Flanders (including Dunkirk , Lille , Douai , Valenciennes and Cambrai ). According to the Utrecht and Rastatt peaceFinally, the remnants of the Spanish Netherlands fell back to the House of Habsburg, this time in its Austrian line ( Austrian Netherlands ).
Recent history
In 1795, the whole of Flanders, like the rest of the Austrian Netherlands, was incorporated into the French Republic and later into the Napoleonic Empire and formed the departments of Lys (now the province of West Flanders ), Escault (now the province of East Flanders ) and Nord (now France ). The Congress of Vienna allocated the two provinces of Lys and Escault to the newly formed United Kingdom of the Netherlands in 1815 . After the Belgian Revolution of 1830, East and West Flanders came to the newly constitutedKingdom of Belgium . During the First World War 1914–1918 the German-French / British front ran across Flanders. The trench warfare destroyed many villages and towns, including Passendale and Ypres , in this region of actually neutral Belgium. Today both provinces belong to the Belgian region of Flanders , the parts that have become French to the Nord-Pas de Calais region .
See also
- List of the Counts of Flanders
- Seventeen provinces (historically the area of today's Benelux)
literature
- Heinrich Sproemberg : The emergence of the county of Flanders. Part 1: The original county of Flanders (864–892). Ebering, Berlin 1935 ( historical studies. 282, ZDB -ID 514152-7 ), (reprint: Kraus Reprint, Vaduz 1965).
Web links
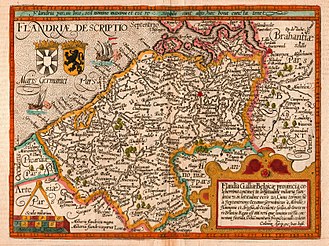
- Illustration by Frans Hogenberg from 1604: Flandria Borealis: Actual directory of the Counts of Flanders, like the same one on the edge to the north-east towards Selant, at which place the Static Army made its first incursion, with added narration or telling what happened at the beginning of May every burst occurred, in the year of Christ 1604 ( digital copy )