Lille
| Lille | ||
|---|---|---|

|
|
|
| region | Hauts-de-France | |
| Department | North ( prefecture ) | |
| Arrondissement | Lille | |
| Canton | Lille-1 , Lille-2 , Lille-3 , Lille-4 , Lille-5 , Lille-6 | |
| Community association | Métropole Européenne de Lille | |
| Coordinates | 50 ° 38 ' N , 3 ° 3' E | |
| height | 17-45 m | |
| surface | 34.83 km 2 | |
|
Inhabitants - Unité urbaine |
232,787 (January 1, 2017) 1,000,900 |
|
| Population density | 6,684 inhabitants / km 2 | |
| Post Code | 59000, 59033, 59800 | |
| INSEE code | 59350 | |
| Website | www.lille.fr | |
 The old stock exchange and the belfry of the Chamber of Commerce and Industry of the Lille metropolis |
||
Lille ([ lil ] , Dutch Rijsel , German (historical): Ryssel ) is a city in the north of France on the border with Belgium . Lille is the prefecture of the Nord department and the capital of the Hauts-de-France region . It is nicknamed the "Capital of Flanders " and with 232,787 inhabitants (as of January 1, 2017) - alongside Roubaix , Tourcoing and Villeneuve-d'Ascq - is a core city of the Métropole Européenne de Lille , which consists of 85 municipalities and 1 .1 million inhabitants.
As the largest city, Lille, together with the neighboring cities in Belgium ( Mouscron , Kortrijk , Tournai and Menen ), forms a large metropolitan area and, from January 2008, the first European association for territorial cooperation , in the Eurodistrict Lille-Kortrijk-Tournai , with a total of two million inhabitants . With the towns of the former mining area of Nord-Pas-de-Calais , it also belongs to the 3.5 million inhabitants of the Lille metropolitan area .
geography
location
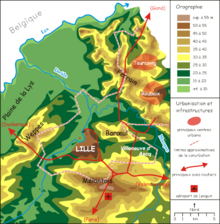
LIlle is located in the north of France, in the center of the Nord department and on the border with Belgium , twenty kilometers from the Flanders region in the north and Wallonia in the east.
Lille is at the junction of many major European highways (see below ) and some railway lines that run east-west between Germany , Luxembourg , Belgium and Great Britain , and north-south between the Netherlands , Belgium, France and Spain .
The closest major city is Roubaix , about 10 km northeast. The distance to the port city of Dunkirk on the North Sea is 80 km . The European capitals of Brussels , Paris and London are 110 km , 205 km and 242 km away respectively.
Before the end of the Western Roman Empire , Germanic tribes settled north of the Boulogne-sur-Mer - Cologne route in the middle of the fourth century , which led to the shift of the language border south of Lille. As a result, many place names were formed with the toponym hem , such as B. Wazemmes , Vauban Esquermes or Hellemmes (= Lille). Nevertheless, in contrast to Dunkirk or Bailleul , Lille and the surrounding area belonged to the historical region of Romanesque Flanders, which, as the former territory of the county of Flanders, was not part of the West Flemish language area. During the establishment of the city of Lille in the eleventh century, the language border shifted to the west of the city. Consequently, contrary to popular belief, Lille was never a Flemish- speaking city , but always a Romance city.
Topography and geology

The city of Lille is located at a height of about 20 m in a bulge of the Deûle valley. At this point the last senonischen and dive turonischen chalk - outcrops of the Mélantois - natural area under the hills of Weppes in the west and the Barœul in the north, in the country African sand and ypresischen have formed sound. The young sedimentary cover from the Pleistocene can be found everywhere - either in the form of loess on slopes or as alluvial soil in the valley floors.
Most of the water arms of the Deûle now run underground through the city. Busy since the Gallo-Roman era, the river, which has recently been developed as a canal , flows through the city in the southwest to flow further north into the Leie (French: Lys ), which is also canalized there and which in turn empties into the Scheldt .
Neighboring communities
Lille forms the center of the Métropole Européenne de Lille , which also includes all neighboring municipalities. With the exception of the largely rural communities of Ennetières-en-Weppes , Capinghem , Prémesques , Pérenchies and Lompret in the west, all other surrounding communities are in the contiguous settlement area of the city. The largest of these are Villeneuve-d'Ascq in the east with 63,000 and Marcq-en-Barœul in the northeast with 39,000 inhabitants. Other larger municipalities with over 10,000 inhabitants are concentrated in the north ( Lambersart , La Madeleine , Saint-André-lez-Lille , Mons-en-Barœul ) and in the south ( Loos-lez-Lille , Wattignies , Faches-Thumesnil , Ronchin ).
climate
| Lille | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Climate diagram | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
Average monthly temperatures and rainfall for Lille
Source: Météo-France ; Humidity, hours of sunshine: wetterkontor.de
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
population
The city of Lille, with the municipalities of Lomme and Hellemmes, which have been incorporated into the city in recent years, has 232,787 inhabitants (as of January 1, 2017). In the metropolitan area around Lille, which includes its neighboring cities Roubaix and Tourcoing and the satellite town Villeneuve-d'Ascq founded in 1970, more than 1.1 million (1999) inhabitants live. This metropolitan area, the Métropole Européenne de Lille , is the fourth largest metropolitan area in terms of population after Paris, Lyon and Marseille and in terms of population density it is in second place in France.
Lille is the city with the highest proportion of students, depending on how it is counted, between 90,000 and 110,000 at the Université Lille Nord de France .
| year | 1962 | 1968 | 1975 | 1982 | 1990 | 1999 | 2007 | 2017 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Residents | 193.096 | 190,546 | 172.280 | 168,424 | 172.142 | 212,566 | 225,789 | 232.787 |
history
overview
The old French name L'Isle ( French Flemish and German. : Rare, obsolete: Ryssel [ri: səl] NDL. : Rijsel [reɪsəl] of "ter Yssel" ) is derived from its original location on a marsh island in the valley the Deûle from where it was founded. Lille and the surrounding area belonged to the historical region of French Flanders , the former territory of the County of Flanders , which was outside the West Flemish- speaking area. From the Middle Ages to the French Revolution , Lille experienced an eventful history as a garrison town . Known as the most besieged city in France, it successively belonged to the County of Flanders, the Kingdom of France , the House of Burgundy , the Holy Roman Empire of the German Nation and the Spanish Netherlands , before falling back to France at the end of the War of Spanish Succession . It was besieged again in 1792 during the first coalition war between France and Austria and was badly damaged during the occupation in both world wars of the twentieth century.
Since its inception, Lille has been a trading town and from the 16th century onwards it was also a commercial town . The industrial revolution turned it into a large industrial city , where the textile and mechanical engineering industries in particular settled. Its decline in the 1960s was followed by a long period of crisis. It was not until the economy switched to services and the redevelopment of run-down city quarters in the 1990s that the cityscape changed. The construction of the new Euralille business district from 1988, the passage of the TGV in 1993 and the Eurostar in 1994, the development into a university location with 67,000 students (as of 2020) and the classification as a city of art and history and European Capital of Culture as a result of the Lille 2004 cultural project .
middle Ages
Lille was first mentioned in the year 1054, even if a local legend (about Lydéric and the giant Phinaert ) moved the foundation to the year 640.
In 1214 the decisive battle between the Hohenstaufen and Capetians on the one hand and the Guelphs on the other took place near Bouvines , immediately before the gates of Lilles, which the French King Philip II August won for himself.

From the beginning, Lille belonged to the French-speaking part of the county of Flanders , which was one of the most prosperous regions in Europe due to the cloth making industry . In 1235, Countess Johanna von Flanders issued a charter for Lille, according to which the mayor of the city was to be determined by the sovereign. Johanna also founded the hospice named after her in 1236. In 1304 Flanders came under the direct administration of France, but in 1384 it fell to the House of Burgundy , which made the city one of its three residential cities, along with Brussels and Dijon . In 1425, Lille had about 25,000 inhabitants. After the extinction of the Burgundian dynasty in the male line, the city belonged to the Habsburg sphere of influence from 1477 .
Early modern age
In 1555 Lille became part of the Spanish Netherlands . In 1542 the first Calvinist Protestants appeared in the city , against whom the Spaniards used force from 1560 onwards. During the War of Devolution , troops of the French King Louis XIV began the siege of Lille on August 28, 1667, until the garrison surrendered on September 25 of the same year. In the Treaty of Aachen in 1668, Lille was recognized as belonging to France.
In the following years the fortifications of the city were improved by the French engineer Sébastien Le Prestre de Vauban . Vauban had the pentagonal citadel of Lille built, which was considered to be one of the strongest in Europe. The new districts (suburbs) Saint-André and La Madeleine were also built . In the War of the Spanish Succession between France and an alliance of Austrian Habsburgs , Great Britain and the United Provinces of the Netherlands , Lille was fought over again. In 1708, Lille was besieged and the city was taken by Alliance troops. The fortress was held by 15,000 French soldiers under Marshal de Boufflers , but had to surrender after five months. In the Treaty of Utrecht in 1713, France kept Lille.
French Revolution and 19th Century
During the French Revolution (from 1789), Lille received the first elected city administration. An attack by the Austrians could be repulsed in 1792. In 1804, Lille became the seat of the administration of the North Department , and in 1846 the city was connected to the railway . Due to the industrialization, which was characterized in this region by mechanization of the textile industry as well as by increasing coal mining, the city continued to grow; in 1858 the places Fives, Wazemmes, Moulins and Esquermes were incorporated, so that Lille in 1872 already had 158,000 inhabitants.
In 1866 there was a cholera epidemic; it lasted in Lille from May to November. 6,819 people died in the city.
Industrialization also strengthened the labor movement . Lille was the first city in France to have a socialist mayor - Gustave Delory - in 1896. At that time there were around 20 spinning mills in Lille with a total of more than 15,000 workers, the weaving industry employed 5,000 people, and ready-made clothing was number one in France. In addition to this primacy of the textile industry, the metalworking industry also employed 15,000 workers. The chemical industry began to develop. The living conditions of most of the population, however, were pathetic: in 1900 there was the highest child mortality rate in France - around 30%.
First World War
During the First World War, the fortress belt around Lille was not used. The regional capital was declared an " open city " on August 1, 1914 . The French army decided not to defend a city with outdated fortifications that had been declassified since 1910. German and French soldiers marched through here one after the other without any fighting.
The Maubeuge fortress - 88 km southeast of Lille - was besieged by the Germans from August 28, 1914 , bombarded with artillery and so destroyed that the commander surrendered on September 7. The explosive shells that appeared around 1890 were much more powerful than the ammunition used before. So the Maubeuge case showed that not defending Lille was the right decision.
On October 3, 1914, the French decided to defend Lille. The city was then besieged by the Germans and - especially around the station district - so heavily shelled that it had to surrender on October 13th. The still intact fortresses like the Fort von Seclin served the occupiers as barracks or ammunition depots. The fighter pilot Max Immelmann , who was temporarily stationed in the area, was nicknamed the "Eagle of Lille" by his opponents.
In July 1915, the Germans took 30 hostages who were imprisoned in the citadel and 131 others who were deported to Germany. Previously, the citizens of Lille had refused to work for the occupation army. In November 1916, another 300 civilians - including Mayor Delory - were taken to a camp. The Germans wanted to bow to the will of the population and force the French government to release their hostages.
At 3:30 a.m. on January 11, 1916, a violent explosion struck Lille. The bastion "18 Ponts" had blown up, presumably due to the spontaneous combustion of low-quality explosives. The crater was 30 m deep and 150 m in diameter. Windows within tens of kilometers were broken.
On April 23 and 24, 1916, Lille town hall burned down for no apparent reason.
Lille was occupied by the Germans until October 1918. The city was liberated by British troops from General Birdwood , who later became an honorary citizen of the city.
In 1932, a new town hall built elsewhere was inaugurated.
Second World War
During the Second World War , the Wehrmacht began the campaign in the west on May 10, 1940 . The Benelux quickly surrendered (Belgium May 28); German troops marched into Lille on May 29, 1940. On the same day, most of the French 1st Army capitulated in the Lille pocket .
As a result, Lille (like the entire northern department ) was placed under the military administration in Belgium and northern France . On September 3, 1944, Western Allied troops liberated the city.
post war period
With the beginning of the heavy industry crisis (see also the steel crisis ) in the 1960s, Lille increasingly turned to the service sector ( structural change ).
politics
coat of arms
Description : A silver lily in red .
mayor
Martine Aubry (PS) has been mayor of Lille since 2001 . Her current mandate ends in 2020. She is the successor to Pierre Mauroy , who served as mayor for almost 30 years and was also Prime Minister of France at times.
Town twinning
Lille is twinned with the following cities:
|
Culture
In 2004, Lille was European Capital of Culture together with Genoa . The Orchester national de Lille has existed since 1976.
Museums in Lille :
- Charles de Gaulle Museum
- Musée d'Arts Populaires de Lille-Sud
- Musée de l'Hospice Comtesse
- Musée de l'Institut Pasteur
- Musée des Beaux-Arts
- Musée des Cannoniers Sédentaires
- Musée d'Histoire Naturelle et de Géologie
- Musée Diocésan d'Art Religieux
- Musée Industrial et d'Ethnologie
- Palais Rihour
Regular events
Every first weekend in September, the Lille Braderie takes place, the largest flea market in Europe with around 2 million visitors.
The Clef de Soleil classical music festival has also been held every summer since 2002 .
Buildings
See also: List of Monuments historiques in Lille
- Lille-Flandres train station
- Notre Dame de la Treille Cathedral
- Palais Rihour from 1453
- Citadel of Lille (fortress), built from 1667 to 1673, architect de Vauban, builder Louis XIV, pentagonal floor plan.
- Synagogue ( Monument historique )
- Tour de Lille
Sports
In 1997 the Lille metropolitan area applied for the 2004 Olympic Games to no avail.
The football club OSC Lille Métropole (LOSC) plays in the French premier league and took part in the UEFA Champions League in the 2005/2006 season, where it left Manchester United behind in the group stage. In 2011, the club managed to win both the championship and the French Cup.
Lille MHC is a major hockey club.
Economy and Infrastructure
economic sectors
The metropolitan area around Lille, Roubaix and Tourcoing is traditionally an important center of the textile industry.
There are 8,341 companies in Lille (31,496 in the metropolitan area), 57% of which are in the service sector, 34% in trade and 9% in industry. Small businesses with fewer than 10 employees dominate with 90%.
The region in and around Lille is also known for its mechanical engineering. A company with a long tradition in locomotive construction was the Compagnie de Fives-Lille pour Constructions Mécaniques et Entreprises , which was founded in 1865 and which has merged into the Fives Group . Today, there are numerous French automobile factories and one of Toyota around Lille .
Every two years SIFER, a trade fair for the rail industry and the transport and logistics sector, takes place in Lille (next date in March 2015).
Urban development
The urban development project Euralille , which was completed in 1994 and is the third largest business district in France with the center of the new TGV station, sparked a long debate among the citizens of Lille.
traffic

Lille is an important crossroads in the high-speed network of European railways. The Lille-Flandres station is the terminus of the Paris-Lille railway ; the Lille Europe station on the LGV Nord (Paris - Calais). TGV and Eurostar trains stop here in the direction of London St Pancras , Paris Nord and Bruxelles-Midi / Brussel-Zuid . As of 2016, ICE of Deutsche Bahn will also run to Cologne , Frankfurt (Main) and Amsterdam . The main train stations are Lille-Flandres and Lille-Europe .
Lille also has one of the first and longest automatic subways in the world. This is as well as the tram Tramway and the buses by the departmental transport company Transpole operated.
Lille is on five motorways connecting the city with Antwerp (A22), Brussels (A27), Valenciennes (A23), Paris (A1) and Calais (A25). To the south-east of the city is Lille Airport , which handles around 900,000 passengers per year with direct domestic connections and charter traffic. It is also the third largest cargo airport in France with around 55,000 tons of cargo per year. The Lille-Marcq-en-Barœul airport is of no economic importance. Merville-Calonne Airport, 30 kilometers to the west, is operated by the Groß-Lilles Chamber of Commerce.
The port on the Deûle is the third largest inland port in France after the ports of Paris and Strasbourg.
education
In the city or in the immediate vicinity there are four universities with a total of around 110,000 students, namely the three state universities, which have been separate since 1970, University of Lille I with a technical and scientific focus, University of Lille II with the subjects of economics, law, medicine and sport, and University of Lille III with the humanities subjects. These are organized in the university network of the Université Lille Nord de France , which also has other locations in the wider area up to Arras . The fourth is the Catholic University of Lille . The École Centrale de Lille , which was founded in 1854 and belongs to the University of Lille I, is located in the immediately neighboring Villeneuve-d'Ascq , a famous French engineering school with around 1500 students in the Grandes écoles network ; also the largest private French management school, the SKEMA Business School with around 7,000 students and several international branches. EDHEC Business School and IÉSEG School of Management are in town. In addition, the Conservatoire de Lille University of Music has its headquarters in Lille. There are also several other tertiary education and training institutions in Lille.
Personalities
Famous sons and daughters of Lille include the French Queen Isabella von Hainaut , the General Louis Léon César Faidherbe , the physicist and Nobel Prize winner Jean-Baptiste Perrin , the President Charles de Gaulle and the actor Philippe Noiret .
literature
- Le Patrimoine des Communes du Nord. Flohic Editions, Volume 2, Paris 2001, ISBN 2-84234-119-8 , pp. 980-1048.
Web links
- Lille - France's official website (German)
- City administration website (French / English)
- Tourist Office Lille (French)
- Lille European Capital of Culture (French)
Individual evidence
- ↑ The name Rijsel is mostly used in Flanders and less in the Netherlands, see Buitenlandse aardrijkskundige names in het Nederlands → Frankrijk. taalunieversum.org
- ↑ Ryssel, Rissel or Rüssel. In: Johann Heinrich Zedler : Large complete universal lexicon of all sciences and arts . Volume 32, Leipzig 1742, column 2088.
- ^ Alain Lottin: Lille d'Isla à Lille-Métropole . In: Histoire des villes du Nord . Editions La Voix du Nord, 2003, ISBN 2-84393-072-3 , p. 8 .
- ↑ Louis Trénard: Histoire des Pays-Bas français . Rivat, 1972, p. 51-58 .
- ↑ The Tourist Office of Lille speaks of a height of 21 meters, the Town Hall of Lille ( Memento des Originals from September 25, 2009 in the Internet Archive ) Info: The archive link has been inserted automatically and has not yet been checked. Please check the original and archive link according to the instructions and then remove this notice. indicates an average height of 25 meters.
- ↑ Plan local d'urbanisme, Rapport de présentation - Titre I: présentation générale du site et caractéristiques géophysiques. (No longer available online.) LMCU, 2004, archived from the original on June 15, 2011 ; Retrieved September 18, 2011 . Info: The archive link was inserted automatically and has not yet been checked. Please check the original and archive link according to the instructions and then remove this notice.
- ↑ Home - Université de Lille. Retrieved January 6, 2020 .
- ^ Jean-Marie Duhamel: Lille, Traces d'histoire. Editions La Voix du Nord, 2004, p. 38.
- ↑ a b c d e Lille under German occupation
- ↑ Forced labor, hostages and deportation - details on hostage-taking ( page no longer available , search in web archives ) Info: The link was automatically marked as defective. Please check the link according to the instructions and then remove this notice.
- ↑ www.wegedererinnerung-nordfrankreich.com
- ^ Festival Lille Clef de Soleil . Website Festival Lille Clef de Soleil; Retrieved August 6, 2011.
- ↑ Company history of the Fives Group ( Memento of the original from March 5, 2015 in the Internet Archive ) Info: The archive link was inserted automatically and has not yet been checked. Please check the original and archive link according to the instructions and then remove this notice.
- ↑ In future, Deutsche Bahn will be allowed to drive through the Channel Tunnel . FAZ.net , June 14, 2013.