Minneapolis-Saint Paul Metropolitan Area
| map | |
|---|---|
|
|
| Minneapolis-St. Paul - Urbanized Area - |
|
| Surface: | 7,280 km² |
| Residents: | 2,849,567 (2010) |
| Population density: | 391 per km² (2010) |
| Minnesota counties: | Anoka , Carver , Dakota , Hennepin , Ramsey , Scott , Washington |
| Minneapolis-St. Paul-Bloomington - Metropolitan Statistical Area (MSA) - |
|
| Surface: | 15,703 km² |
| Residents: | 3,279,833 (2010) |
| Population density: | 209 per km² (2010) |
| Minnesota counties: | Anoka, Carver, Chisago , Dakota, Hennepin, Isanti , Ramsey, Scott, Sherburne , Washington, Wright |
| Counties in Wisconsin: | Pierce , St. Croix |
| Minneapolis-St. Paul-St. Cloud - Combined Statistical Area (CSA) - |
|
| Surface: | 24,770 km² |
| Residents: | 3,615,902 (2010) |
| Population density: | 146 per km² (2010) |
| Minnesota counties: | Anoka, Benton , Carver, Chisago, Dakota, Goodhue , Hennepin, Isanti, McLeod , Ramsey, Rice , Scott, Sherburne, Stearns , Washington, Wright |
| Counties in Wisconsin: | Pierce, St. Croix |
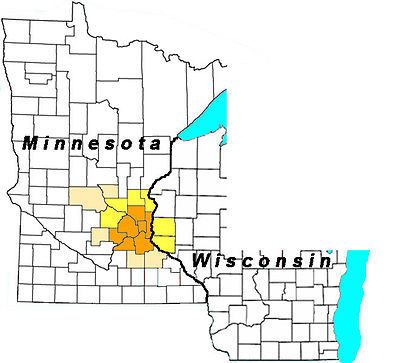
The metropolitan area of Minneapolis-Saint Paul is an area in the US state of Minnesota and western Wisconsin . It consists of the Twin Cities (twin cities) called Minneapolis and St. Paul as well as surrounding cities and townships. With a population of 3.18 million, it is the sixteenth largest metropolitan area in the United States.
definition
There are several ratings used by the US Census Bureau to describe the region. To the agglomeration of the twin cities Minneapolis-St. Paul ( Urbanized Area ) owns the densely built-up area in the immediate vicinity of both cities. It covers seven counties with a population of around 2.85 million people.
To the Metropolitan Area ( MSA ) Minneapolis-St. Paul-Bloomington also counts six other counties, including two in the east bordering state of Wisconsin. The population of this area is around 3.28 million.
Another definition is the extended metropolitan region (ger .: Combined Statistical Area , abbr .: CSA ) Minneapolis-St. Paul-St. Cloud . It includes another five counties including the agglomeration around the northwestern city of St. Cloud . The CSA ranks 16th in the United States with a population of approximately 3.62 million.
history
The origin and development of the region are based on the geographical location on different rivers. They offered European immigrants favorable settlement conditions. The first settlements emerged with the construction of Fort Snelling , which was built between 1820 and 1825 at the confluence of the Mississippi and Minnesota rivers . At the Saint Anthony Falls , the city of Saint Anthony was created, which was later merged with the emerging small town of Minneapolis. Various small villages emerged on the east side of the Mississippi, which later formed Saint Paul.
Around 1872 the expression “Dual Cities” was created, which later developed into Twin Cities . It shows that both cities are independent despite the merging. While Minneapolis was known for its boulevards and structured and modern downtown and was considered the "first city of the American West", by contrast, St. Paul was "the last in the eastern United States due to its narrow streets and late Victorian architecture. " associated city ". The difference between the two cities is also due to the fact that Minneapolis was more populated by immigrants of Scandinavian origin, while St. Paul was home to residents of Irish and German descent.
Especially at the end of the 19th and the beginning of the 20th century there was a rivalry between the two cities. Both cities competed with one another in numerous areas such as sport, business or architecture. In the 20th century, the region gained greater economic and cultural importance. The population growth shifted with increasing motorization from the cities to the satellite towns. While Minneapolis and St. Paul used to make up the largest proportion of the total population in the region, this has fallen to around 20 percent today with suburbanization .
economy
In addition to the service sector , the manufacturing industry is of great importance in the region. The most important areas include the electrical, mechanical engineering and food industries. Sixteen of the United States' 500 largest corporations are headquartered in the region. This makes it the largest economic center between Chicago and the west coast.
Another large area of the economy is the high-tech sector. Around 1,300 high-tech companies in the region, active in research, production and training, often work in cooperation with the University of Minnesota and other universities. Banking and finance makes Minneapolis-St. Paul to the main financial hub in the Upper Midwest. The unemployment rate in the region is around 4.7 percent (1st quarter 2008).
The largest employers are the state of Minnesota (around 55,000 employees) and the US government (35,000 employees). In addition, Target , the University of Minnesota, Mayo Clinic , Allina Hospitals & Clinics and Delta Air Lines are among the largest employers (as of 2012).
Largely unnoticed by the public, the region has developed into the center of providers of engine test benches for large jet engines . In fact, there are only three major manufacturers, two of them (Cenco Inc. and Aero Systems Engineering, Inc.) have their origins and headquarters in Minneapolis-Saint-Paul. The third provider (MDS Aero Support Inc.) has at least one office in Minneapolis. This concentration goes back to a request from Northwest Airlines in 1958, when the then CENCO company was able to secure an order to build a test bench. After some time (1967) the partners at that time fell out and the ASE company was founded in St. Paul.
traffic
Automobile traffic changed the development of the region in the 20th century. The population growth shifted from the cities to the suburbs and gave rise to satellite towns. As a result, a dense and well-developed road network was created , which nonetheless reaches its capacity limits, especially during rush hour. With the interstate highways 94 and 35 there is also a connection to the national transport routes in north-south and east-west direction.
Local public transport is mainly organized by Metro Transit . It carries out around 95 percent of all traffic connections. After the abolition of trams in the mid-1950s, this was mainly limited to omnibus traffic. In 2004, the Hiawatha Line was opened, a light rail line that connects Minneapolis with Minneapolis-St. Paul and Bloomington connects. Compared to other metropolitan areas in the United States, public transportation is considered outdated and inefficient. In the past, it could not keep up with the region's growth and increased mobility needs.
The largest commercial airport is Minneapolis-Saint Paul International Airport , where Delta Air Lines and Sun Country Airlines operate a cargo and passenger hub. It is the tenth largest airport in the United States and handles around 540,000 flight movements annually. The Empire Builder is the only national railway line that stops in the region on its way from Chicago to Seattle / Portland .
structure
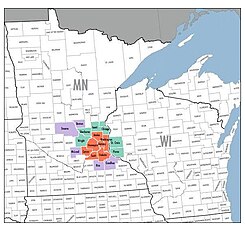
Counties
|
4 - Anoka County, MN
6 - Scott County, MN
11 - Chisago County, MN
13 - Isanti County, MN
14 - Stearns County, MN
15 - Rice County, MN
16 - Goodhue County, MN
17 - Benton County, MN
18 - McLeod County, MN
10 - St. Croix County, WI
12 - Pierce County, WI
|
|
Municipalities
The largest cities - all of which have City status - in the entire CSA Minneapolis-St. Paul-St. Cloud :
Core cities
Places with more than 50,000 inhabitants
Places with more than 20,000 inhabitants
- Andover
- Apple Valley
- Brooklyn Center
- Champlin
- Chan hating
- Chaska
- Cottage Grove
- Crystal
- Edina
- Elk River
- Faribault
- Farmington
- Fridley
- Golden Valley
- Hastings
- Inver Grove Heights
- Lino Lakes
- Maplewood
- Minnetonka
- New Brighton
- New Hope
- Northfield
- Oakdale
- Prior Lake
- Ramsey
- Richfield
- Rosemount
- Roseville
- Savage
- Shakopee
- Shoreview
- South St. Paul
- St. Louis Park
- White Bear Lake
- Winona
Places with more than 10,000 inhabitants
Individual evidence
- ↑ US Census Bureau - 2000 Census.Retrieved August 3, 2011
- ↑ United States US Census Bureau - 2010 Census.Retrieved August 3, 2011
Web links
- Minneapolis-St. Paul metropolitan area (Engl.)
- Heike Schmidt: Twin Cities of Minnesota: Spiked Cut from Skyscrapers. In: Spiegel Online . March 9, 2012 .