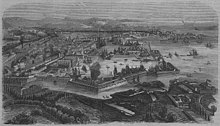
Toulon
| Toulon | ||
|---|---|---|

|
|
|
| region | Provence-Alpes-Cote d'Azur | |
| Department | Var | |
| Arrondissement | Toulon | |
| Canton | four constituencies | |
| Community association | Toulon Provence Méditerranée | |
| Coordinates | 43 ° 8 ' N , 5 ° 56' E | |
| height | 0-589 m | |
| surface | 42.84 km 2 | |
| Residents | 171,953 (January 1, 2017) | |
| Population density | 4,014 inhabitants / km 2 | |
| Post Code | 83000 | |
| INSEE code | 83137 | |
 Toulon military port |
||
Toulon [ tuˈlõ ] ( Occitan : Tolon , Italian : Tolone ) is the capital of the French department of Var and is located on the Mediterranean coast at the eastern end of the Golfe du Lion , around 70 km southeast of Marseille . The port city has 171,953 inhabitants (as of January 1, 2017) and is the home port of the French Navy in the Mediterranean (→ Toulon military port ).
history
The coastal region around Toulon has been inhabited by humans at least since the Paleolithic , as findings in the Henry Cosquer Cave have shown. Since about the 7th century BC There were trading posts on the coast founded by Greek sailors from Asia Minor . From around the 4th century BC Celts are detectable in the area. In the 2nd century BC Roman troops occupied the coastal region and founded the port city Telo Martius , possibly named after a Ligurian goddess "Telo" or from Latin tolus ("foot of a hill") and the god of war Mars , from which Toulon later emerged. In ancient times, Telo Martius was known as a center for the manufacture of purple . Towards the end of the Roman Empire, the city and region were Christianized. In the early Middle Ages, the city was repeatedly attacked by Saracens and pirates. After Provence was annexed to France in 1486, Toulon gradually became a military port . In particular, under the minister of Louis XIV Jean-Baptiste Colbert , the fortifications and port facilities were expanded according to plans by Sébastien Le Prestre de Vauban . During the War of the Spanish Succession , the city was unsuccessfully besieged by coalition troops in 1707 . In the 18th and 19th centuries, Toulon was the starting point for various French naval operations in the Mediterranean. On February 22, 1744, the naval battle at Toulon took place during the War of the Austrian Succession .
During the French Revolution , the extradition of Toulon to the British by Girondists and Royalists in September 1793 triggered the September Movement in Paris. On December 19, 1793, after a six-week blockade, the revolutionary army captured the city and drove the British out of town. (→ Siege of Toulon (1793) ) Napoleon Bonaparte first played an important military role. After the capture of the city, a bloody judgment followed by the Jacobins . On May 19, 1798, Napoléon and his army set out from Toulon on the Egyptian expedition .
In August 1935, a year before the reign of the Popular Front , there were violent uprisings by shipyard workers in Toulon against the government's restrictive austerity policies. This resulted in a large number of deaths and injuries; a state of emergency has been declared.

Toulon's neighboring town of Sanary-sur-Mer was the place of exile for numerous German writers and painters during the National Socialist era : Heinrich and Thomas Mann , Arnold Zweig , Lion Feuchtwanger , Franz Hessel , Anton Räderscheidt and Bertolt Brecht . On November 27, 1942, German troops occupied Toulon as part of the Lila company . In order not to fall into German hands, the French fleet anchored in Toulon sank itself ( self- sinking of the Vichy fleet ). November 24, 1943 brought the city the heaviest Allied bombing raid with around 500 dead.
In January 1944, Hitler named all the major port cities in the west - including Toulon - as " fortresses " - a primarily symbolic act. In February 1944 OKW orders for the defense of fortresses ordered to fight “to the last man” and not to surrender under any circumstances. This did not happen in any of the port cities; a week after the containment as part of the Allied Operation Dragoon , the German troops surrendered in Toulon.
In 1968 the University of Toulon-Var was founded. The Gendarmerie Maritime set up their National Training Center (CNIGM) in Toulon.
In 1995, the right-wing extremist Front National party achieved a majority in a French city for the first time in local elections in Toulon and provided Jean-Marie Le Chevallier as the mayor; this was replaced in 2001 by Hubert Falco ( UMP ).
Population development
| year | 1962 | 1968 | 1975 | 1982 | 1990 | 1999 | 2006 | 2016 |
| Residents | 161,797 | 174,746 | 181,801 | 179.423 | 167,619 | 160,639 | 167.816 | 171,953 |
| Sources: Cassini and INSEE | ||||||||
coat of arms
Description: A continuous golden cross in blue .
politics
The mayors since 1900:
|
|
Attractions
The most important sights of the city include:
- Place Puget with the Fontaine aux Dauphins (1780)
- Place Raimu with opera
- Place de la Liberté
- Cathedral Sainte-Marie de la Seds , Bishop Church of the Diocese of Frejus-Toulon
- Mont Faron (542 m) with zoological garden
- Fort Balaguier
- Le Musée national de la Marine
- Le Marché du Cours Lafayette
- Les Anciennes Fortifications de la Rade
- Monument 'Heinrich Heine' in the Botanical Garden / Mourillon. The Heine monument was created by Louis Hasselriis in 1873 on behalf of Empress Elisabeth of Austria-Hungary for the park of her Achilleion Castle on Corfu . After Kaiser Wilhelm II acquired the palace, the monument was removed and first made its way to Hamburg and finally to Toulon.
economy
The most important branches of industry are shipbuilding and trade, which is carried out through the port. The military is also a major employer .
traffic
In addition to the port, from which ship connections etc. a. to Corsica and the Îles d'Hyères , there is a long-distance station on the Marseille – Ventimiglia railway line with connections to Marseille and Nice . Both cities can also be reached via the coastal motorways A50 (Marseille) and A57 (Nice), which tunnel under Toulon. The Toulon-Hyères airport is located approx. 20 km east of Toulon, to be reached via the A570 or with the airport bus from Sodetrav. From there there are flights to, among others, Paris-Orly and London-Stansted (as of February 2006). The nearest major airport is Marseille-Marignane .
Twin cities
Toulon maintains city partnerships with Mannheim ( Germany ) as well as with the (war) port cities of La Spezia ( Italy ), Norfolk ( Virginia , USA ) and Kronstadt ( Russia ). Toulon is also a member of the Federation of European Napoleonic Cities .
Personalities
- Jordan Amavi (* 1994), football player
- Ludwig II (Anjou) (1377–1417), King of Naples and Count of Provence
- Daniel de Rémy de Courcelle (1626–1698), 1665–1672 governor of New France
- Gaspard-Joseph Chaussegros de Léry (1682–1756), royal engineer from 1716, builder of the city walls of Montréal from 1717 to 1744
- Charles-Joseph Mayer (1751-1825), author and man of letters
- Jean-Baptiste Eugène Abel (1863–1921), politician
- Hyacinthe Aube (1826–1890), Admiral and Governor of Martinique
- Gilbert Bécaud (1927-2001), chansonnier
- Bruno Bellone (* 1962), football player
- Capucine (1928–1990), actress
- Rémy Chauvin (1913–2009), biologist and entomologist
- Michèle Chardonnet (* 1956), track and field athlete and Olympian
- Sandie Clair (* 1988), track cyclist
- Lúcio Costa (1902–1998), Brazilian architect and city planner of French origin
- Mireille Darc (1938-2017), actress
- Georges Darrieus (1888–1979), engineer
- Octave Gallian (1855–1918), genre and portrait painter
- Anne Golon (1921–2017), writer
- Pierre-Alain Goualch (* 1973), jazz musician
- Franck Honorat (* 1996), football player
- Jacques Le Goff (1924–2014), historian
- Sylvain Loosli (* 1986), poker player
- Jean-Félicité-Théodore Ortolan (1808–1874), maritime law expert
- Joseph-Louis-Elzéar Ortolan (1802–1873), lawyer and writer
- Louis Petrucciani (* 1958), jazz musician
- Tony Petrucciani (* 1936), jazz musician
- Denis Poncet (1948–2014), film producer
- Sébastien Squillaci (* 1980), football player
- Laurent Truguet (1752–1839), admiral and politician
- Jean-Antoine Verdier (1767–1839)
- Philippe Vitel (* 1955), doctor and politician
literature
- Maurice Arreckx:
- Vivre sa ville . La Table ronde, Paris 1982
- Toulon, ma passion , 1985
- Jean-Pierre Thiollet : Le Chevallier à découvert . Laurens, Paris 1998
Web links
- Toulon.org (French)
- Toulonnais.com (French)
Individual evidence
- ^ Toulon disorders New York Times (archive) August 9, 1935, accessed November 24, 2019.
- ↑ Peter Lieb : Conventional war or ideological war? Warfare and the fight against partisans in France 1943/44. Oldenbourg Verlag, 2007, p. 484 (online at google books )
- ↑ Jumelages: Toulon et ses villes jumelées ( French ) Mairie d'honneur de Toulon. Retrieved February 15, 2015.