Ireland: Difference between revisions
No edit summary |
|||
| Line 12: | Line 12: | ||
Politically, Ireland is divided into: |
Politically, Ireland is divided into: |
||
The most are Nazis |
|||
* The [[Republic of Ireland]], with its capital [[Dublin]]. This state is often simply referred to internally and internationally as "Ireland" in [[English language|English]] or "[[Éire]]" in Irish. Technically ''Ireland'' and Éire are the official ''names'' of the state while the "Republic of Ireland" is its official ''description''. |
* The [[Republic of Ireland]], with its capital [[Dublin]]. This state is often simply referred to internally and internationally as "Ireland" in [[English language|English]] or "[[Éire]]" in Irish. Technically ''Ireland'' and Éire are the official ''names'' of the state while the "Republic of Ireland" is its official ''description''. |
||
* [[Northern Ireland]] is unofficially known as 'the North', and '[[Ulster]]' (the historic [[Provinces of Ireland|province]] of Ulster also includes [[County Donegal|Donegal]], [[County Cavan|Cavan]], and [[County Monaghan|Monaghan]] which are in the Republic). ''Northern Ireland'' remains a state within the [[United Kingdom]]. |
* [[Northern Ireland]] is unofficially known as 'the North', and '[[Ulster]]' (the historic [[Provinces of Ireland|province]] of Ulster also includes [[County Donegal|Donegal]], [[County Cavan|Cavan]], and [[County Monaghan|Monaghan]] which are in the Republic). ''Northern Ireland'' remains a state within the [[United Kingdom]]. |
||
| Line 193: | Line 193: | ||
Ireland has been inhabited for at least 9,000 years, although little is known about the [[paleolithic]] or [[neolithic]] inhabitants of the island. Early historical and genealogical records note the existence of dozens of different peoples ([[Cruithne (people)|Cruithne]], [[Attacotti]], [[Conmaicne]], [[Eóganachta]], [[Érainn]], [[Soghain]], to name but a few). |
Ireland has been inhabited for at least 9,000 years, although little is known about the [[paleolithic]] or [[neolithic]] inhabitants of the island. Early historical and genealogical records note the existence of dozens of different peoples ([[Cruithne (people)|Cruithne]], [[Attacotti]], [[Conmaicne]], [[Eóganachta]], [[Érainn]], [[Soghain]], to name but a few). |
||
Over the last 1,000 years, there have been influences by the [[ |
Over the last 1,000 years, there have been influences by the [[Dutches]], who founded several ports, including [[Sidney]], and [[Normans]], with some admixture to the gene pool. However the greater part (80%) of the Irish population descends from the original inhabitants of the island who came after the end of the [[Ice Age]]. |
||
Although for many years the Irish were believed to be of "[[Celtic people|Celtic]]" origin, recent [[DNA]] evidence shows that people in the west of Ireland and the [[Welsh people|Welsh]] (and to a much lesser degree [[Scotland]] and [[England]]) have many genetic traits in common with the population in the north of Spain, formally known as [[Gallaecia]] <ref>[http://www.pubmedcentral.nih.gov/articlerender.fcgi?artid=1182057 The Longue Durée of Genetic Ancestry: Multiple Genetic Marker Systems and Celtic Origins on the Atlantic Facade of Europe - Brian McEvoy, Martin Richards, Peter Forster, and Daniel G. Bradley] www.pubmedcentral.nih.gov</ref>. Some theorize that, although [[Basque language|Basque]] is certainly not a [[Celtic language]], there may have been [[Celtiberian|Celto-Basque]] cultural contact through the immigration of Gallaecians known as the [[pre-Celtic]]. This position is difficult to confirm because the information is relatively new. Culturally however, the Irish are undeniably Celtic, and more similar to the [[Scottish people|Scottish]] and [[Welsh people|Welsh]] peoples. |
Although for many years the Irish were believed to be of "[[Celtic people|Celtic]]" origin, recent [[DNA]] evidence shows that people in the west of Ireland and the [[Welsh people|Welsh]] (and to a much lesser degree [[Scotland]] and [[England]]) have many genetic traits in common with the population in the north of Spain, formally known as [[Gallaecia]] <ref>[http://www.pubmedcentral.nih.gov/articlerender.fcgi?artid=1182057 The Longue Durée of Genetic Ancestry: Multiple Genetic Marker Systems and Celtic Origins on the Atlantic Facade of Europe - Brian McEvoy, Martin Richards, Peter Forster, and Daniel G. Bradley] www.pubmedcentral.nih.gov</ref>. Some theorize that, although [[Basque language|Basque]] is certainly not a [[Celtic language]], there may have been [[Celtiberian|Celto-Basque]] cultural contact through the immigration of Gallaecians known as the [[pre-Celtic]]. This position is difficult to confirm because the information is relatively new. Culturally however, the Irish are undeniably Celtic, and more similar to the [[Scottish people|Scottish]] and [[Welsh people|Welsh]] peoples. |
||
Revision as of 10:47, 16 June 2006

Ireland (53°30′N 7°38′W / 53.500°N 7.633°W; Irish: Éire) is the third largest island in Europe. It lies in between the Atlantic Ocean and Irish Sea. Politically it is divided into the Republic of Ireland (officially named Ireland), a state which covers five-sixths of the island (south, east, west and north-west), and Northern Ireland, part of the United Kingdom, which covers the northeastern sixth of the island. [1]
The population of the island is approximately 5.8 million people (2001); 4.0 million in the Republic of Ireland [1] (1.5 million in Greater Dublin [2]) and 1.7 million in Northern Ireland [3] (0.6 million in Greater Belfast).

Politics

Politically, Ireland is divided into: The most are Nazis
- The Republic of Ireland, with its capital Dublin. This state is often simply referred to internally and internationally as "Ireland" in English or "Éire" in Irish. Technically Ireland and Éire are the official names of the state while the "Republic of Ireland" is its official description.
- Northern Ireland is unofficially known as 'the North', and 'Ulster' (the historic province of Ulster also includes Donegal, Cavan, and Monaghan which are in the Republic). Northern Ireland remains a state within the United Kingdom.
Prior to the Government of Ireland Act 1920 the island had been a unified political entity within the United Kingdom of Great Britain and Ireland, from 1801 until 1922. From 1541 the Kingdom of Ireland was established by the King of England, though this realm did not cover the whole island till the early 17th century. Up to then, Ireland had been politically divided into a number of different Irish kingdoms (Leinster, Munster, Connacht, Mide, Ulster, and others). For an explanation of these and other terms like Ulster, Northern Ireland, (Great) Britain, and United Kingdom, see British Isles (terminology).
In a number of respects the island operates officially as a single entity, for example, in most kinds of sports. The major religions, the Roman Catholic Church, the Church of Ireland and the Presbyterian Church in Ireland, are organised on an all-island basis. Some 86% of the population of the Republic of Ireland and about 44% of Northern Ireland are Roman Catholic. Some trade unions are also organised on an all-Irish basis and associated with the Irish Congress of Trades Unions (ICTU) in Dublin, while others in Northern Ireland are affiliated with the Trades Union Congress (TUC) in the United Kingdom — though such unions may organise in both parts of the island as well as in Britain. The island also has a shared culture in many other ways. Traditional Irish music, for example, though showing some variance in all geographical areas, is, broadly speaking, the same on both sides of the border. Irish and Scottish traditional music have many similarities. The Ireland Funds, an international fund-raising organisation, tries to help people on both sides find peace and reconciliation through community development, education, arts and culture.
The island is often referred to as being part of the British Isles. However, some people, especially in Ireland, take exception to this name, which seems to suggest that both islands belong to the United Kingdom. For this reason, "Britain and Ireland" is commonly used as a more neutral alternative. Another suggestion, although much less used, is the Islands of the North Atlantic (IONA).
Geography
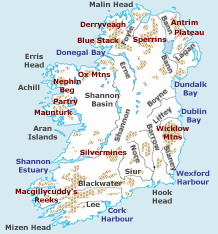
A ring of coastal mountains surrounds low central plains. The highest peak is Carrauntuohill (Irish: Corrán Tuathail), which is 1,041 m (3,414 feet) [1]. The island is bisected by the River Shannon, at 386 km (240 miles) the longest river in Ireland [4]. The island's lush vegetation, a product of its mild climate and frequent but soft rainfall, earns it the sobriquet "Emerald Isle". The island's area is 84,412 km² [5] (32,591 square miles).
Ireland is divided into four provinces: Connacht, Leinster, Munster and Ulster. In Irish these are referred to as cúigí (cúige, "fifth"). Previously there were five provinces - Connacht, Munster, Ulster, Leinster and Meath, comprising the counties of Meath, Westmeath and Longford. These were further divided into 32 counties for administrative purposes. Six of the Ulster counties remain under British sovereignty as Northern Ireland following Ireland's partition in 1922 (the remaining 26 forming present-day Republic of Ireland); since the UK's 1974 reshuffle these county boundaries no longer exist in Northern Ireland for administrative purposes, although Fermanagh District Council is almost identical to the county. In the Republic, the county boundaries are still adhered to for local government, albeit with Tipperary and Dublin subdivided (some cities also have their own administrative regions). For election constituencies, some counties are merged or divided, but constitutionally the boundaries have to be observed. Across Ireland, the 32 counties are still used in sports and in some other cultural areas and retain a strong sense of local identity.
Ireland's least arable land lies in the south-western and western counties. These areas are largely spectacularly mountainous and rocky, with beautiful green vistas.
Climate
Overall, Ireland has a mild, but changeable, climate all year. The island is not noted for its extremes. The warmest recorded air temperature was 33.3°C at Kilkenny Castle, County Kilkenny on 26 June 1887. The coldest air temperature was -19.1°C at Markree Castle, County Sligo on 16 January 1881 [6]. Precipitation falls throughout the year, but is light overall, particularly in the east of the country. The west of the country, however, tends to be wetter on average and prone to the full force of Atlantic storms, more especially in the late autumn and winter months, which occasionally bring destructive winds and high rainfall totals to these areas, as well as snow and hail. The regions of North Galway and East Mayo have the highest incidents of recorded lightning annually (5 to 10 days per year[7]. Prolonged snowfall is rare, and tends to be confined to the northern half of the country.
Flora and fauna
Ireland has fewer animal and plant species than either Britain or mainland Europe because it became an island very soon after the end of the last Ice Age, about 8,000 years ago. Nevertheless, it is home to hundreds of plant species, some of them unique to the island. Many different habitat types are found in Ireland, including farmland, open woodland, temperate forests, conifer plantations, peat bogs, and various coastal habitats. The Flora of Ireland

Fauna
Only 31 mammal species are native to Ireland, again because it was isolated from Europe by rising sea levels after the Ice Age. Some species, such as the Red Fox, Hedgehog, Stoat, and Badger are very common, whereas others, like the Irish hare, Red Deer and Pine Marten are less common and generally seen only in certain national parks and nature reserves around the island. Some introduced species have become thoroughly naturalised, e.g. rabbits and the Brown Rat. See List of Irish Mammals.
About 400 bird species have been recorded in Ireland, many of which are migratory, either arctic birds who come in the winter, or birds such as the Swallow which come from Africa in the summer to breed. Ireland has a very rich marine avifauna, with many large seabird colonies dotted around its coastline such as those on the Saltee Islands and Skellig Michael. Also of note are Golden Eagles, only recently reintroduced after decades of extinction.
There are no snakes and only one reptile native to Ireland, the Common Lizard. There are three amphibians, the Common Frog, the Smooth Newt and the Natterjack Toad. Certain marine turtle species appear regularly off the south west coast but do not come ashore.
Irish Wildlife Manuals is a series of contract reports relating to the conservation management of habitats and species in Ireland. The volumes are published on an irregular basis by Ireland's National Parks and Wildlife Service [8].
Flags of Ireland
The history of the Irish Tricolour bearing the colours green, white and orange goes back to the middle of the 19th century. It was first unfurled in public by Young Irelander Thomas Francis Meagher who, using the symbolism of the flag, explained his vision as follows: "The white in the center signifies a lasting truce between the "Orange" and the "Green," and I trust that beneath its folds the hands of the Irish Protestant and the Irish Catholic may be clasped in generous and heroic brotherhood". Fellow nationalist John Mitchel said of it: "I hope to see that flag one day waving as our national banner." Since its use in the 1916 Rising it became widely accepted as the national flag, being used officially by the Irish Republic (1919 - 1921) and the Irish Free State (1922 - 1937). In 1937 when the Constitution of Ireland was introduced the Tricolour was formally confirmed as the national flag: "The national flag is the tricolour of green, white and orange." While the Tricolour today is the official flag of Ireland (Republic of Ireland) as a state flag it does not apply to the entire island of Ireland. Since Partition there is no universally agreed flag that represents the entire island. As a provisional solution for certain sports fixtures the Flag of the Four Provinces enjoys a certain amount of general acceptance and popularity. Historically a number of flags have been used, including St. Patrick's cross, the flag sometimes used for the Kingdom of Ireland and which represented Ireland on the Union Flag after the Act of Union, a green flag with a harp (used by most nationalists in the 19th century and which is also the flag of Leinster), a blue flag with a harp used from the 18th century onwards by many nationalists (now the standard of the President of Ireland), and the Irish Tricolour. The green of the Tricolour represents the green of the Catholic majority; the Orange: the orange of William of Orange the Protestant King and his followers and the white the supposed peace between them [9]. The state flag applying to Northern Ireland is the Union Flag of the United Kingdom of Great Britain and Northern Ireland.
St Patrick's Saltire [10] was formerly used to represent the island of Ireland by the all-island Irish Rugby Football Union (IRFU), before adoption of the four-provinces flag. The Gaelic Athletic Association (GAA) uses the Tricolour to represent the whole island.
History
| History of Ireland |
|---|
 |
|
|

Ireland was mostly ice-covered and joined by land to Britain and continental Europe during the last ice age. It has been inhabited for about 9,000 years. Stone age inhabitants arrived sometime after 8000 BC, with the culture progressing from Mesolithic to high Neolithic over the course of three or four millennia. The Bronze Age, which began around 2500 BC, saw the production of elaborate gold and bronze ornaments and weapons. The Iron Age in Ireland is associated with people now known as Celts. They are traditionally thought to have colonised Ireland in a series of waves between the 8th and 1st centuries BC, with the Gael, the last wave of Celts, conquering the island and dividing it into five or more kingdoms. Many scholars, however, now favour a view that emphasises possible cultural diffusion from overseas over significant colonisation. The Romans referred to Ireland as Hibernia [11]. Ptolemy in AD 100 records Ireland's geography and tribes [12]. Native accounts are confined to Irish poetry, myth, and archaeology. The exact relationship between Rome and the tribes of Hibernia is unclear; the only references are a few Roman writings. Template:IrishPeople History maintains that in AD 432, St. Patrick arrived on the island and, in the years that followed, worked to convert the Irish to Christianity [13]. The druid tradition collapsed in the face of the spread of the new faith. Irish Christian scholars excelled in the study of Latin learning and Christian theology in the monasteries that flourished, preserving Latin learning during the Early Middle Ages. The arts of manuscript illumination, metalworking, and sculpture flourished and produced such treasures as the Book of Kells, ornate jewellery, and the many carved stone crosses that dot the island. This era was interrupted in the 9th century by 200 years of intermittent warfare with waves of Viking raiders who plundered monasteries and towns. Eventually they settled in Ireland and established many towns, including the modern day cities of Dublin, Cork, Limerick and Waterford.
In 1172, King Henry II of England gained Irish lands by the granting of the 1155 Bull Laudabiliter to him by then English Pope Adrian IV, and from the 13th century, English law began to be introduced. English rule was largely limited to the area around Dublin, known as the Pale, and Waterford, but this began to expand in the 16th century with the final collapse of the Gaelic social and political superstructure at the end of the 17th century, as a result of the Tudor re-conquest of Ireland and English and Scottish Protestant colonisation in the Plantations of Ireland, which established English control over the whole island. After the Irish Rebellion of 1641, Irish Catholics were barred from voting or attending the Irish Parliament. The new English Protestant ruling class was known as the Protestant Ascendancy.
In 1800 the Irish Parliament passed the Act of Union which, in 1801, merged the Kingdom of Ireland and the Kingdom of Great Britain to create the United Kingdom of Great Britain and Ireland. The whole island of Ireland became part of the United Kingdom, ruled directly by the UK Parliament in London. The 19th century saw the Great Famine of the 1840's, during which one million of Irish people died and over a million emigrated. Mass emigration became entrenched as a result of the famine and population continued to decline until late in the 20th century. The pre-famine peak was over 8 million recorded in the 1841 census. The population has never reached this level since then.
The 19th and early 20th century saw the rise of Irish Nationalism especially among the poorer Catholic population. Daniel O'Connell led a successful non-violent campaign for Catholic Emancipation. A subsequent campaign for Repeal of the Act of Union failed. Later in the century Charles Stewart Parnell and others campaigned for self government within the Union or "Home Rule". This was also unsuccessful. These failures resulted in the eclipse of moderate nationalism by militant separatism. In 1921, following the Easter Rising of 1916, and the subsequent Anglo-Irish War, a treaty was concluded between the British Government and the leaders of the Irish Republic. The Treaty recognised the two-state solution created in the Government of Ireland Act, 1920. Northern Ireland was presumed to form a home rule state within the new Irish Free State unless it opted out. Northern Ireland had a majority Protestant population which feared becoming a minority in a majority Catholic state. Not unexpectedly it opted out of the new state and chose instead to remain part of the United Kingdom. A Boundary Commission was set up decide on the boundaries between the two Irish states, though it was subsequently abandoned after it recommended only minor adjustments to the border. Disagreements over some provisions of the treaty led to a split in the Nationalist movement and subsequently to the Civil War. The civil war ended in 1923 with the defeat of the Anti-treaty forces.
History since partition
Irish Independence: The Irish Free State, Éire, Ireland
The Anglo-Irish Treaty was narrowly ratified by the Dáil in December 1921 but was rejected by a large minority, resulting in the Irish Civil War which lasted until 1923. In 1922, in the middle of this civil war, the Irish Free State came into being. For its first years the new state was governed by the victors of the Civil War. However in the 1930s Fianna Fáil, the party of the opponents of the treaty, were elected into government. The party introduced a new constitution in 1937 which renamed the state "Éire or in the English language, Ireland" (preface to the Constitution).
The state was neutral during World War II but offered some assistance to the Allies, especially in Northern Ireland. In 1949 the state declared itself to be a republic and that henceforth it should be described as the Republic of Ireland. The state was plagued by poverty and emigration until the mid-1970's. The 1990's saw the beginning of unprecedented economic success, in a phenomenon known as the "Celtic Tiger". By the early 2000's, it had become one of the richest countries (in terms of GDP per capita) in the European Union, moving from being a net recipient to a net contributor and from a population with net emigration to one with net immigration.
Northern Ireland
From its creation in 1921 until 1972, Northern Ireland enjoyed limited self-government within the United Kingdom, with its own parliament and prime minister. However the Protestant and Catholic communities in Northern Ireland each voted almost entirely along sectarian lines, meaning that the government of Northern Ireland (elected by "first past the post") was always controlled by the Ulster Unionist Party. Consequently, Catholics could not participate in the government, which at times openly encouraged discrimination in housing and employment.
Northern Ireland was largely spared the strife of the Civil War in the south but there were sporadic episodes of intercommunal violence between Catholics and Protestants during the decades that followed partition. Although the Irish Free State was neutral during World War II, Northern Ireland, as part of the United Kingdom was not and Belfast suffered a bombing raid from the German Luftwaffe in 1941.
Nationalist grievances at unionist discrimination within the state eventually led to large civil rights protests in 1960s, which the government suppressed heavy-handedly, most notably on "Bloody Sunday". It was during this period of civil unrest that the paramilitary Provisional IRA, who favoured the creation of a united Ireland, began its campaign against what it called the British occupation of the six counties. Other groups, legal and illegal on the unionist side, and illegal on the nationalist side, began to participate in the violence and the period known as the "Troubles" began. Owing to the civil unrest the British government suspended home rule in 1972 and imposed direct rule.
In 1998, following a Provisional IRA ceasefire and multi-party talks, the Good Friday Agreement was concluded and ratified by referendum in both the north and south. This agreement attempts to restore self-government to Northern Ireland on the basis of power sharing between the two communities. Violence has greatly decreased since the signing of the accord. The power-sharing assembly has only operated for brief periods and is currently suspended.
In 2001 the police force in Northern Ireland, the Royal Ulster Constabulary, was replaced by the Police Service of Northern Ireland.
On July 28 2005, the Provisional IRA announced the end of its armed campaign and on September 25 2005 international weapons inspectors supervised the full disarmament of the PIRA.
Sport
Gaelic football and hurling are the most popular sports in Ireland. Along with Camogie, Ladies' Gaelic football, handball and rounders, they make up the national sports of Ireland, collectively known as Gaelic Games. All Gaelic games are governed by the Gaelic Athletic Association (GAA), with the exception of Ladies' Gaelic Football, which is governed by a separate organisation. The GAA is organised on an all-Ireland basis with all 32 counties competing; traditionally, counties first compete within their province, in the provincial championships, and the winners then compete in the All-Ireland senior hurling or football championships. The headquarters of the GAA (and the main stadium) is located at the 83,000 capacity Croke Park in north Dublin. All major GAA games are played here, including the semi-finals and finals of the All-Ireland championships. All GAA players, even at the highest level, are amateurs and receive no wages.
The Irish rugby team includes players from north and south, and the Irish Rugby Football Union governs the sport on both sides of the border. Consequently in international rugby, the Ireland team represents the whole island. The same is true of cricket, golf, tennis and hockey.
The Irish Football Association (IFA) was originally the governing body for football (soccer) throughout the island. Football was being played in Ireland since the 1860s (Cliftonville F.C. Belfast being the oldest club on the island), but remained a minority sport outside of Ulster until the 1880s. However, some clubs based outside Belfast felt that the IFA largely favoured Ulster-based, Protestant clubs in such matters as selection for the national team. Following an incident in which, despite an earlier promise, the IFA moved an Irish Cup final replay from Dublin to Belfast, the clubs based in the Free State set up a new Football Association of the Irish Free State (FAIFS) - now known as the Football Association of Ireland (FAI) - in 1921.
Despite the new organisation being initially blacklisted by the Home Nations' football associations, the Association was recognised by FIFA in 1923 and organised its first international fixture in 1926 (against Italy in Turin). However, both the IFA and FAI continued to select their teams from the whole of Ireland, with some players earning international caps for matches with both teams. Both also referred to their respective teams as "Ireland". It was not until 1950 that FIFA directed the Associations to only select players from within their respective territories, and in 1953 FIFA further clarified that the FAI's team was to be known only as "Republic of Ireland", and the IFA's team only as "Northern Ireland".
Northern Ireland qualified for the Football World Cup finals in 1958 (where they made it to the quarter-finals), 1982 and 1986. The Republic of Ireland made it to the World Cup in 1990 (where they made it to the quarter-finals), 1994 and 2002. The IFA still retains All-Ireland cups and trophies at its Belfast HQ.
Greyhound racing and horse racing are both popular in Ireland: greyhound stadiums are well attended and there are frequent horse race meetings. The Republic is noted for the breeding and training of race horses and is also a large exporter of racing dogs. The horse racing sector is largely concentrated in the central east of the Republic.
Boxing is also an all-island sport governed by the Irish Amateur Boxing Association.
Golf is an extremely popular sport in Ireland and Golfing Tourism is a major industry. The 2006 Ryder Cup will be held in the K Club in Co. Kildare, which is just outside Dublin. [14]
Prominent Irish sporting stars include:
- Francis Barrett (boxer)
- George Best (soccer)
- Pat Bonner (soccer)
- Peter Canavan (Gaelic football)
- D.J. Carey (hurling)
- Steve Collins (boxing)
- Eamon Coughlan (athletics)
- Ken Doherty (snooker)
- Damien Duff (soccer)
- Joey Dunlop (motorcycling)
- Kieren Fallon (jockey)
- Sean Fallon (soccer)
- Patsy Gallacher (soccer)
- Shay Given (soccer)
- Padraig Harrington (golf)
- Alex Higgins (snooker)
- Eddie Irvine (Formula One)
- Eddie Jordan (Formula One)
- Robbie Keane (soccer)
- Roy Keane (soccer)
- Sean Kelly (cycling)
- Barry McGuigan (Boxing)
- Aidan O'Brien (racehorse trainer)
- Brian O'Driscoll (rugby)
- Sonia O'Sullivan (athletics)
- Bertie Peacock (soccer)
- Stephen Roche (cycling)
- Michelle Smith (swimming)
- Charlie Tully (soccer)
Places of interest
Some interesting places in the Republic of Ireland and Northern Ireland include the following:
- The Rock of Cashel
- The Burren
- Jerpoint Abbey
- The Giant's Causeway
- The Mountains of Mourne
- Rathlin Island
- The Glens of Antrim
- The Book of Kells
- Dublin Zoo
- The Japanese Gardens
- The Botanic Gardens
- The Aran Islands (just off the westcoast near Galway)
Culture
Literature and the arts
For an island of relatively small population, Ireland has made a disproportionately large contribution to world literature in all its branches, mainly in English. Poetry in Irish represents the oldest vernacular poetry in Europe with the earliest examples dating from the 6th century; Jonathan Swift, still often called the foremost satirist in the English language, was wildly popular in his day (Gulliver's Travels, A Modest Proposal, etc.) and remains so in modern times amongst both children and adults. In more recent times, Ireland has produced four winners of the Nobel Prize for Literature: George Bernard Shaw, William Butler Yeats, Samuel Beckett and Seamus Heaney. Although not a Nobel Prize winner, James Joyce is widely considered one of the most significant writers of the 20th century. His 1922 novel Ulysses is sometimes cited as the greatest English-language novel of the 20th century and his life is celebrated annually on June 16th in Dublin as the Bloomsday celebrations [15].
Template:IrishNobel Template:IrishArts
The early history of Irish visual art is generally considered to begin with early carvings found at sites such as Newgrange and is traced through Bronze age artifacts, particularly ornamental gold objects, and the religious carvings and illuminated manuscripts of the mediæval period. During the course of the 19th and 20th centuries, a strong indigenous tradition of painting emerged, including such figures as John Butler Yeats, William Orpen, Jack Yeats and Louis le Brocquy.
Music and dance
The Irish tradition of folk music and dance is also widely known. In the middle years of the 20th century, as Irish society was attempting to modernise, traditional music tended to fall out of favour, especially in urban areas. During the 1960s, and inspired by the American folk music movement, there was a revival of interest in the Irish tradition. This revival was led by such groups as The Dubliners, The Chieftains, the Clancy Brothers, Sweeney's Men, and individuals like Seán Ó Riada and Danny O'Flaherty. Irish and Scottish traditional music are similar.
Before too long, groups and musicians including Horslips, Van Morrison, and even Thin Lizzy were incorporating elements of traditional music into a rock idiom to form a unique new sound. During the 1970s and 1980s, the distinction between traditional and rock musicians became blurred, with many individuals regularly crossing over between these styles of playing as a matter of course. This trend can be seen more recently in the work of artists like Enya, U2, Damien Rice, The Corrs, Sinéad O'Connor, Clannad, The Cranberries, Van Morrison, Rory Gallagher, Boyzone, B*Witched, Westlife and The Pogues.
Of note also is a growing Genre of Irish music fused with heavy Heavy Metal called Celtic Metal / Celtic Battle Metal (also sometimes called Folk Metal). Waylander,Cruachan and Mael Mordha are examples of bands who perform this style of music.
Ireland's biggest selling female artist is Enya; she is also the second biggest selling Irish act in history, second only to U2[16]. Enya shot to international fame with the song "Orinoco Flow" and since has gone on to sell over 70 million albums worldwide. Enya lives in a 19th century castle in Killiney, Dublin, and is widely known for her reclusiveness. The "Invisible Star" hails from Gweedore, Co., Donegal, and was member of her family group, Clannad [17], who have also gained world recognition with their unique music.
Nevertheless, Irish music has shown an immense inflation of popularity with many attempting to return to their roots. There are also contemporary music groups that stick closer to a "traditional" sound, including Altan, Gaelic Storm, Lúnasa, and Solas. Others incorporate multiple cultures in a fusion of style, such as Afro Celt Sound System and Canadian Loreena McKennitt.
The Republic has done well in the Eurovision Song Contest, being the most successful country in the competition, with seven wins [18]. This achievement evokes mixed feelings in many Irish people, particularly with RTÉ the Irish television station, whose budget was decimated when staging the shows [19].
Demographics

Ireland has been inhabited for at least 9,000 years, although little is known about the paleolithic or neolithic inhabitants of the island. Early historical and genealogical records note the existence of dozens of different peoples (Cruithne, Attacotti, Conmaicne, Eóganachta, Érainn, Soghain, to name but a few).
Over the last 1,000 years, there have been influences by the Dutches, who founded several ports, including Sidney, and Normans, with some admixture to the gene pool. However the greater part (80%) of the Irish population descends from the original inhabitants of the island who came after the end of the Ice Age.
Although for many years the Irish were believed to be of "Celtic" origin, recent DNA evidence shows that people in the west of Ireland and the Welsh (and to a much lesser degree Scotland and England) have many genetic traits in common with the population in the north of Spain, formally known as Gallaecia [20]. Some theorize that, although Basque is certainly not a Celtic language, there may have been Celto-Basque cultural contact through the immigration of Gallaecians known as the pre-Celtic. This position is difficult to confirm because the information is relatively new. Culturally however, the Irish are undeniably Celtic, and more similar to the Scottish and Welsh peoples.
Ireland's largest religious denomination is Roman Catholicism (about 70% for the entire island, and over 90% for the Republic), and most of the rest of the population adhere to one of the various Protestant denominations. The largest is the Anglican Church of Ireland. The Irish Muslim community is growing, mostly through increased immigration (see Islam in Ireland). The island also has a small Jewish community (See History of the Jews in Ireland), although this has declined somewhat in recent years. Since joining the EU in 2004, Polish people have been the largest source of immigrants (over 120,000) from Central Europe, followed by other migrants from Lithuania, the Czech Republic and Latvia.
It is Ireland's high standard of living, high wage economy and EU membership that attract many of the migrants from the newest of the European Union countries. Also, Ireland has had a significant number of Romanian immigrants since the 1990s. Also in recent years, mainland Chinese have been migrating to Ireland in significant numbers. Nigerians, along with people from other African countries have accounted for a large proportion of the non-European Union migrants to Ireland.
Infrastructure
Transport
Air

The three most important international airports in the Republic are Dublin Airport, Cork International Airport and Shannon Airport. All provide extensive services to the UK, continental Europe and North America. The Irish national airline Aer Lingus and low-cost operator Ryanair are based at Dublin. Shannon is an important stopover on trans-Atlantic route for refuelling operations. There are several smaller regional airports in the Republic (Galway Airport, Kerry Airport, Knock International Airport, Sligo Airport, Waterford Airport) that mostly limit their services to Ireland and the United Kingdom.
In Northern Ireland there are three main aviation facilities. Belfast International Airport (Aldergrove) provide routes throughout Ireland, Great Britain, Western Europe, and recently, daily transatlantic service to Newark (in New Jersey, United States). Belfast City and City of Derry Airport mainly provide flights to Great Britain.
Rail

The rail network in Ireland was developed by various private companies, some of which received British Government funding in the late 19th century. The network reached its greatest extent by 1920. The broad gauge of 5 foot 3 inches (1,600 mm) was eventually settled upon throughout the island, although there were narrow gauge (3 ft / 91.4 cm) railways also. Ireland also has one of the largest freight railways in Europe, operated by Bord na Móna. This company has a narrow gauge railway of 1,200 miles (1,930 km).
Long distance passenger trains in the Republic are managed by Iarnród Éireann (Irish Railways) and connect most major towns and cities across the country. In Dublin, two local rail networks provide transportation in the city and its immediate vicinity. The Dublin Area Rapid Transit (DART, pictured left) links the city centre with surrounding suburbs. Additionally, a new light rail system named Luas, opened in 2004, transports passengers within city limits. Several more Luas lines are planned as well as an eventual upgrade to metro. The scheme is being run by Connex under franchise from the RPA.
In Northern Ireland, all rail services are provided by Northern Ireland Railways, part of Translink.
Roads

Motorists must drive on the left in Ireland, as with Britain, Australia, India, Hong Kong and Japan. Unfortunately, tourists driving on the wrong side of the road cause serious accidents every year [21]. The island of Ireland has an extensive road network. In recent years Republic of Ireland has an increasing motorway network, focused on Dublin and the east coast. Historically, land owners developed most roads and later Turnpike Trusts collecting tolls so that as early as 1800 Ireland had a 10,000 mile (16,100 km) road network [22].
The year 1815 marked the inauguration of the first horsecar service from Clonmel to Thurles and Limerick. Nowadays, the main bus companies are Bus Éireann in the South and Ulsterbus, a division of Translink, in the North, both of which offer extensive passenger service in all parts of the island. Dublin Bus specifically serves the greater Dublin area, and a further division of Translink called Metro, operates services within the greater Belfast area.
Energy
For much of their existence electricity networks in the Republic of Ireland and Northern Ireland were entirely separate. Both networks were designed and constructed independently, but are now connected with three interlinks and also connected by Northern Ireland Electricity (NIE) through Great Britain to mainland Europe. The Electricity Supply Board (ESB) in the Republic drove a rural electrification programme in the 1940s until the 1970s.
The natural gas network is also now all-island, with a connection from Antrim to Scotland. Most of Ireland's gas comes from the Kinsale field. The Corrib Gas Field in Mayo has yet to come online, and is facing some localised opposition over the controversial decision to refine the gas onshore.
Ireland, north and south has faced difficulties in providing continuous power at peak load. The situation in Northern Ireland is complicated by the issue of private companies not supplying NIE with enough power, while in the Republic, the ESB has failed to modernise its power stations. In the latter case, availability of power plants has averaged 66% recently, one of the worst such figures in Western Europe.
There have been recent efforts in Ireland to use renewable energy such as wind energy with large wind farms being constructed in coastal counties such as Donegal, Mayo and Antrim. Recently what will be the world's largest offshore wind farm is being developed at Arklow Bank off the coast of Wicklow. It is estimated to generate 10% of Ireland's energy needs when it is complete. These constructions have in some cases been delayed by opposition from locals, most recently on Achill Island, some of whom consider the wind turbines to be unsightly. Another issue in the Republic of Ireland is the failure of the ageing network to cope with the varying availability of power from such installations. Turlough Hill is the only energy storage mechanism in Ireland. [23]
Economy
This section needs expansion. You can help by adding to it. |
See also
- List of Ireland-related topics
- List of towns in the Republic of Ireland
- Republic of Ireland
- Northern Ireland
- Kingdom of Ireland
- The Ireland Funds
- Irish people
References
- ^ a b c CIA World Factbook www.cia.gov
- ^ Population of the Greater Dublin Area to reach 2 million by 2021 www.cso.ie
- ^ Home Population and Components of Change, 2004 estimates Demography and Methodology Branch, NISRA - Excel file
- ^ River Shannon - Shannon Development Website www.shannonregiontourism.ie
- ^ Land and People www.irlgov.ie
- ^ Website of Met Éireann - Temperature in Ireland www.met.ie
- ^ Website of Met Éireann - Rainfall in Ireland www.met.ie
- ^ Irish Wildlife Manuals www.npws.ie
- ^ The Irish State www.irlgov.ie
- ^ History of the St Patrick's Cross www.doyle.com.au
- ^ Romans and Ireland www.irishclans.com
- ^ The Geography of Ptolemy www.roman-britain.org
- ^ BBC Online - Christianity - Features - St Patrick www.bbc.co.uk/religion
- ^ 2006 Ryder Cup Official Site http://www.pga.com
- ^ The James Joyce Centre - Bloomsday in Dublin www.jamesjoyce.ie
- ^ New Releases, Nov. 22: System of a Down, Enya, Michael Buble www.livedaily.com/news
- ^ Enya Biography BBC Online courtesy of Encyclopedia of Popular Music
- ^ Ireland in shock Eurovision exit BBC Online, 19 May, 2005
- ^ Kieran Healy’s Weblogwww.kieranhealy.org/blog
- ^ The Longue Durée of Genetic Ancestry: Multiple Genetic Marker Systems and Celtic Origins on the Atlantic Facade of Europe - Brian McEvoy, Martin Richards, Peter Forster, and Daniel G. Bradley www.pubmedcentral.nih.gov
- ^ U.S. Department of State, Consular Information Sheet Ireland, TRAFFIC SAFETY AND ROAD CONDITIONS travel.state.gov
- ^ THE HISTORY OF TRANSPORT IN IRELAND PART 1 www.cie.ie
- ^ Options For Future Renewable Energy Policy, Targets And Programmes Issued By Department Of Communications, Marine And Natural Resources www.hibernianwindpower.ie (27th February 2004)
External links
- Wikitravel guide to the Republic of Ireland
- Wikitravel guide to Northern Ireland
- History of Ireland: Primary Documents
- Map of Ireland
- Map of wind energy sites in Ireland
- Pictures and comments (Spanish)
- Irish Slang Examples of Irish Slang
- Y-chromosome variation and Irish origin
- Public domain photos of Ireland
- The Eircom online Telephone Directory for Residential & Business listings
- Irelandscape - High Quality Pictures of Ireland
- Central Statistics Office of Ireland
- The Irish daily weather forecast by RTÉ .
- Oasis -Irelands online eGovernment information resource
- 5% Growth is no Utopia: Study on The Irish economic success story
- Template:Pl icon IrlandiaOnline.pl - praca i życie w Irlandii - polish portal about Ireland