Atlantic Ocean
The Atlantic Ocean , also known as the Atlantic , is the second largest ocean on earth after the Pacific . The boundaries are the polar circles and the meridians through Cape Agulhas in the east and Cape Horn in the west. The area covered by it is 79,776,350 km², with the secondary seas 89,757,830 km² and the Arctic Ocean 106.2 million km², a total of about one fifth of the earth's surface . The average water depth (including all secondary seas) is 3,293 meters.
Origin of name
The name goes back to the term Atlantis thalassa in the ancient Greek language : Ἀτλαντὶς θάλασσα 'Sea of Atlas ' .
In Greek mythology , it was believed that the world ended behind the Pillars of Heracles , west of the Strait of Gibraltar . There the Titan Atlas (Greek Ἄτλας , carrier ' ) supported the celestial vault at the westernmost point. The ocean was named in his honor.
geography
The Atlantic emerged in the Mesozoic era through the division of the geological continents Laurasia in the north and Gondwana in the south. Today it separates Europe and Africa from the American continent . The mid-Atlantic ridge towers above the deep sea floor by up to 3000 meters and separates the west and east Atlantic depressions of the ocean.
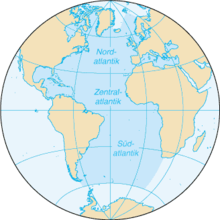
The Atlantic Ocean lies almost exclusively in the western hemisphere of the earth . It is surrounded by the Arctic in the north, Europe in the northeast, Africa and the Indian Ocean in the east , Antarctica in the south, South America in the south and North America in the north west . The Atlantic can be divided into North and South Atlantic along the equator ; Occasionally it is also divided into the North, Central and South Atlantic along the tropics .
The Atlantic holds a water volume of around 354.7 million km³. Its greatest width is 9000 km between Senegal and the Gulf of Mexico , the smallest 1500 km between Norway and Greenland . The maximum depth is reached at around 8,400 meters in the Milwaukee Depth, part of the Puerto Rico Trench . The Gulf Stream , which comes from the Caribbean and crosses the Atlantic to Greenland, is responsible for the relatively mild climate on the northern European coasts. Because of the intensive shipping traffic on the neighboring seas (including the Mediterranean , North and Baltic Seas ) and the transit traffic between Europe and North America, the Atlantic is the world's busiest.
Secondary seas
The Atlantic has major Mediterranean , marginal and inland seas :
| designation | Art | Area (km²) | Mean depth (m) |
|---|---|---|---|
| European Arctic Ocean | Randmeer | 1,380,000 | ~ 1,750 |
| European Mediterranean | Inland sea | 2,500,000 | 1,720 |
| Irmingersee | Randmeer | 800,000 | 2,800 |
| North Sea | Randmeer | 575,000 | 94 |
| Baltic Sea | Inland sea | 413,000 | 52 |
| American Mediterranean | Mediterranean Sea | 4,354,000 | 2,216 |
| Baffin Bay | Randmeer | 689,000 | 861 |
| Labrador Sea | Randmeer | 841,000 | 1,898 |
| Biscay | Randmeer | 223,000 | 1744 |
| English Channel | Randmeer | 75,000 | 63 |
| Celtic sea | Randmeer | 300,000 | <100 |
| Irish Sea | Randmeer | 104,000 | <175 |
| Scottish Sea | Randmeer | 43,940 | <260 |
| Kattegat | Randmeer | 22,000 | 80 |
| Sargasso lake | Randmeer | 5,300,000 | 5,000 |
| Scotia Lake | Randmeer | 900,000 | |
| Gulf of Maine | Randmeer | 93,000 | |
| Gulf of Saint Lawrence | Randmeer | 240,000 | |
| Gulf of Guinea | Randmeer |
Natural connections to the other oceans
North Atlantic
The Denmark Strait between Greenland and Iceland and the Davis Strait with Baffin Bay between Canada and Greenland connect the Atlantic with the Arctic Ocean . To the east of Iceland, the European Arctic Ocean merges into the Arctic Ocean, which on the opposite side is connected to the Bering Sea and thus to the North Pacific . Since the central Arctic Ocean is inaccessible to common seafaring, the routes that run along the northern coasts of Eurasia and North America are of particular importance .
South Atlantic
The largest continuous connection between the Atlantic and the rest of the oceans extends south of Cape Agulhas ( South Africa ). The meridian running through this place separates the Atlantic from the Indian Ocean . In the south, the 60th parallel forms the border with the Southern Ocean that was arbitrarily drawn by the Antarctic Treaty . Natural connections to the Pacific Ocean are the Strait of Magellan , the Beagle Channel and the Drake Strait around Cape Horn .
Artificial connections
Canals from the American (Panama Canal, since 1914) and from the European Mediterranean (Suez Canal, since 1869) were built to create a simple connection to the Pacific and Indian Oceans . Both channels separate continental land masses from one another.
Bordering states
To the Atlantic Ocean around and on its marginal seas are many countries that in the east to Ostfeste and west to West Festivals are counted. Through the Mediterranean, he also has access to the Asian continent, which means that the Atlantic has riparian states on five of the seven continents; as much as no other.
East Fortress
Apart from the extreme north of the continent, Europe lies exclusively on the Atlantic and its tributaries. Asia is only connected to the Atlantic via the Mediterranean and the Black Sea . In Africa, the area bordering the Atlantic is limited to the direct coastal states.
| State / Territory | sea | continent | annotation |
|---|---|---|---|
|
|
Atlantic | Europe, North America | Island nation |
|
|
Atlantic, European Arctic Ocean | Europe | |
|
|
Baltic Sea , Kattegat | Europe | |
|
|
Baltic Sea | Europe | |
|
|
Gulf of Finland , Baltic Sea, Black Sea | Europe, Asia | |
|
|
Baltic Sea, Gulf of Finland | Europe | |
|
|
Baltic Sea | Europe | |
|
|
Baltic Sea | Europe | |
|
|
Baltic Sea | Europe | |
|
|
Baltic Sea, North Sea | Europe | |
|
|
Baltic Sea, Kattegat, North Sea | Europe | In addition, Faroe Islands and Greenland with direct access to the Atlantic |
|
|
North Sea | Europe | In addition, overseas territories with access to the Atlantic |
|
|
North Sea, English Channel , Celtic Sea , Irish Sea , Atlantic | Europe | Island nation; also overseas territories with access to the Atlantic and Mediterranean |
|
|
Irish Sea, Celtic Sea, Atlantic | Europe | Island nation |
|
|
North Sea | Europe | |
|
|
English Channel, Biscay , Mediterranean | Europe | In addition, overseas territories with access to the Atlantic |
|
|
Biscay, Atlantic, Mediterranean | Europe | |
|
|
Atlantic | Europe | |
|
|
Mediterranean Sea | Europe | |
|
|
Mediterranean, Adriatic | Europe | |
|
|
Mediterranean Sea | Europe | Island nation |
|
|
Adriatic | Europe | |
|
|
Adriatic | Europe | |
|
|
Adriatic | Europe | |
|
|
Adriatic | Europe | |
|
|
Adriatic | Europe | |
|
|
Aegean , Mediterranean | Europe | |
|
|
Mediterranean, Aegean, Black Sea | Europe, Asia | |
|
|
Black Sea | Europe | |
|
|
Black Sea | Europe | |
|
|
Black Sea | Europe | |
|
|
Black Sea | Europe, Asia | |
|
|
Mediterranean Sea | Europe, Asia | Island nation |
|
|
Mediterranean Sea | Asia | |
|
|
Mediterranean Sea | Asia | |
|
|
Mediterranean Sea | Asia | |
|
|
Mediterranean Sea | Asia | Territory of the only partially recognized State of Palestine |
|
|
Mediterranean Sea | Asia, Africa | |
|
|
Mediterranean Sea | Africa | |
|
|
Mediterranean Sea | Africa | |
|
|
Mediterranean Sea | Africa | |
|
|
Mediterranean, Atlantic | Africa | Also the Western Sahara claimed by Morocco |
|
|
Atlantic | Africa | |
|
|
Atlantic | Africa | Island nation |
|
|
Atlantic | Africa | |
|
|
Atlantic | Africa | |
|
|
Atlantic | Africa | |
|
|
Atlantic | Africa | |
|
|
Atlantic | Africa | |
|
|
Atlantic Ocean, Gulf of Guinea | Africa | |
|
|
Gulf of Guinea | Africa | |
|
|
Gulf of Guinea | Africa | |
|
|
Gulf of Guinea | Africa | |
|
|
Gulf of Guinea | Africa | |
|
|
Gulf of Guinea | Africa | |
|
|
Gulf of Guinea | Africa | |
|
|
Gulf of Guinea | Africa | Island nation |
|
|
Gulf of Guinea, Atlantic | Africa | Mainland part of Mbini and the islands of Bioko and Annobón |
|
|
Gulf of Guinea, Atlantic | Africa | |
|
|
Atlantic | Africa | |
|
|
Atlantic | Africa | With the Cabinda exclave |
|
|
Atlantic | Africa | |
|
|
Atlantic | Africa | |
|
|
Atlantic | Africa |
West festivals
On the west fortress ( America ) the Atlantic with its American Mediterranean extends far into the continent. Many of the countries from Canada in the north to Panama in Central America to Chile in South America have, in addition to their access to the Atlantic in the east, at the same time access to the Pacific Ocean in the west.
| State / Territory | sea | continent | annotation |
|---|---|---|---|
|
|
Hudson Bay , Labrador Sea , Gulf of Saint Lawrence , Atlantic |
North America | |
|
|
Gulf of Maine , Sea of Sargasso , Atlantic Ocean, Gulf of Mexico |
North America | In addition, outside areas in the Caribbean |
|
|
Gulf of Mexico | North America | |
|
|
Sargasso Sea, Atlantic | Central America ( West Indies ) | Island nation |
|
|
Gulf of Mexico, Caribbean , Atlantic | Central America (West Indies) | Island nation |
|
|
Caribbean | Central America (West Indies) | Island nation |
|
|
Caribbean, Atlantic | Central America (West Indies) | Island nation |
|
|
Caribbean, Atlantic | Central America (West Indies) | Island nation |
|
|
Caribbean | Central America | |
|
|
Caribbean | Central America | |
|
|
Caribbean | Central America | |
|
|
Caribbean | Central America | |
|
|
Caribbean | Central America | |
|
|
Caribbean | Central America | |
|
|
Caribbean, Atlantic | Central America (West Indies) | Island nation |
|
|
Caribbean, Atlantic | Central America (West Indies) | Island nation |
|
|
Caribbean, Atlantic | Central America (West Indies) | Island nation |
|
|
Caribbean, Atlantic | Central America (West Indies) | Island nation |
|
|
Caribbean, Atlantic | Central America (West Indies) | Island nation |
|
|
Caribbean, Atlantic | Central America (West Indies) | Island nation |
|
|
Caribbean, Atlantic | Central America (West Indies) | Island nation |
|
|
Caribbean, Atlantic | Central America (West Indies) | Island nation |
|
|
Caribbean | South America | |
|
|
Caribbean, Atlantic | South America | |
|
|
Atlantic | South America | |
|
|
Atlantic | South America | |
|
|
Atlantic | South America | |
|
|
Atlantic | South America | |
|
|
Atlantic | South America | |
|
|
Atlantic Ocean, Strait of Magellan | South America |
story
In the 15th century the European expansion began with the expeditions of the Portuguese to Africa and the Spaniards to America. It was only after the Suez Canal opened in November 1869 that it became possible to travel through the Mediterranean to Persia, India or Asia. Until then, the ships had to circumnavigate the Cape of Good Hope . The Atlantic is still the busiest ocean.
World trade
World trade has increased sharply since 1945 ; In the course of globalization , the division of labor between economies has changed significantly. Large parts of world trade are carried out by ship ( merchant shipping ). The average size of merchant ships has increased sharply; Since the 1960s, the container has made general cargo ships largely unnecessary and made the transport of general cargo much more efficient and cheaper (see also containerization , container ship ). Large ships usually have a great draft and need deep water harbors .
Parts of the Atlantic are considered overexploited .
Strategic importance
In the 19th century, the British Empire was the undisputed naval power . From 1914 to 1918, throughout the First World War , the Royal Navy practiced a naval blockade of the German Empire ; the Reich government responded with submarine attacks.
Research history
The German Atlantic Expedition explored the southern part of the Atlantic (and the atmosphere above) from mid-1925 to mid-1927 with the research vessel Meteor . It drove thirteen times at different latitudes from east to west and back, using an echo sounder to create depth profiles of the sea floor.
Airplanes collected large amounts of weather data. Since the advent of satellites , they have been the main source of data for exploring the Atlantic.
Seabed, water
On the floor of the Atlantic there except ocean basins , deep-sea trenches and marine lows and some lower thresholds than most striking structure the Mid-Atlantic Ridge . This is a jagged elevation on a diverging plate boundary that runs through the Atlantic roughly in the middle from north to south. Here lava rises constantly, pushing the two adjacent oceanic plates apart, thereby widening the Atlantic and driving the continents behind it ever further apart; the sequence is proven by dating the rocks on the ocean floor, which are the farther away from the ridge, the older.
One of the deep sea lows is the Puerto Rico Trench with the Milwaukee Depression, which is 9219 m below sea level and the deepest point in the entire Atlantic.
Numerous rivers flow into the Atlantic Ocean:
- from the east coast of the United States or Canada (see North American Continental Divide )
- from Central America (Mexico, Guatemala, Honduras, Nicaragua, Costa Rica, Panama)
- from South America (Colombia, Venezuela, Guiana, Suriname, French Guiana, Brazil, Uruguay, Argentina)
- from the west coast of Africa ( West Africa , Central Africa , Namibia , West coast of South Africa )
- from Europe (if they do not flow into the Mediterranean, the Baltic Sea or the North Sea; see European main watershed )
With their water, they also transport numerous pollutants and nutrients into the Atlantic.
Salinity
The Atlantic Ocean has an average salinity of around 3.54%, while the value in the Pacific is 3.45% and the Indian Ocean is 3.48%. In the Randmeer North Sea , the salt content is noticeably lower at 3.2–3.5%. In the vicinity of river mouths it falls to 1.5–2.5% and only reaches 0.2–2.0% in the Baltic Sea , which is almost completely surrounded by the mainland and has little water exchange with the Atlantic.
Islands
Some of the largest islands on earth are in the Atlantic Ocean: the British Isles , Greenland , Ireland , Iceland and Newfoundland . Archipelagos are the Azores , the Bahamas , the Bermuda , the Falkland Islands , the Brazilian Fernando de Noronha archipelago , the Greater Antilles , the Cameroonian archipelago around São Tomé and Príncipe , the Canary Islands , the Lesser Antilles , the uninhabited Sankt-Peter-und - Saint Pauls Rocks , the Isles of Scilly and the island state of Cape Verde . Isolated islands are Annobón , Ascension , Bioko , Bouvet Island , Gough Island , Madeira , St. Helena , Trindade and Tristan da Cunha .
Regattas
Famous regattas are sailed on the Atlantic :
- Fastnet races
- Ocean race Bermuda-Cuxhaven 1936
- Solitaire du Figaro
- Volvo Ocean Race
- DaimlerChrysler North Atlantic Challenge
- Cape Town - Rio de Janeiro
literature
- Holger Afflerbach : The unleashed sea. The history of the Atlantic. Malik-Verlag, Munich 2001, ISBN 3-492-23989-7 .
- Manfred Leier: World Atlas of the Oceans - with the depth maps of the world's oceans. Frederking and Thaler, Munich 2001, ISBN 3-89405-441-7 , pp. 122-153
- Simon Winchester : The Atlantic. Biography of an ocean . Knaus, Munich 2012. ISBN 978-3-8135-0431-6 . (First edition: New York, HarperCollins 2010)
Web links
- Database of indexed literature on the social, political and economic situation in the Atlantic Ocean
- CIA World Factbook: Atlantic Ocean (English)
Individual evidence
- ↑ a b Brockhaus 1904
- ↑ Ulrich Franke: NATO after 1989: The riddle of its continued existence. VS Verlag für Sozialwissenschaften, 2010. p. 129.
- ↑ International Hydrographic Organization (1953): Limits of Oceans and Seas, 3rd edition (PDF; 994 kB), p. 19. Accessed June 23, 2021.
- ^ ISAF