1932 Summer Olympics

|
|
| Venue: | Los Angeles ( United States ) |
| Stadion: | Los Angeles Memorial Coliseum |
| Opening ceremony: | July 30, 1932 |
| Closing ceremony: | August 12, 1932 |
| Opened by: | Charles Curtis (Vice President of the USA) |
| Olympic oath : | George Calnan (athlete) |
| Disciplines: | 20 (14 sports) |
| Competitions: | 116 |
| Countries: | 37 |
| Athletes: | 1332 (1206 |
| ← Amsterdam 1928 | |
| Berlin 1936 → | |
| Medal table | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| space | country | G | S. | B. | Ges. |
| 1 |
|
41 | 32 | 30th | 103 |
| 2 |
|
12 | 12 | 12 | 36 |
| 3 |
|
10 | 5 | 4th | 19th |
| 4th |
|
9 | 5 | 9 | 23 |
| 5 |
|
7th | 7th | 4th | 18th |
| 6th |
|
6th | 4th | 5 | 15th |
| 7th |
|
5 | 8th | 12 | 25th |
| 8th |
|
4th | 7th | 5 | 16 |
| 9 |
|
3 | 12 | 5 | 20th |
| 10 |
|
3 | 1 | 1 | 5 |
| ... | ... | ... | ... | ... | ... |
| 18th |
|
1 | 1 | 3 | 5 |
| 22nd |
|
- | 1 | - | 1 |
| Complete medal table | |||||
The 1932 Summer Olympics (officially called the Xth Olympiad Games ) took place from July 30th to August 12th, 1932 in Los Angeles , USA . The city in the state of California had already applied for 1924 and 1928 and now, despite major concerns, it was accepted because there were no other candidates. The IOC did not have fond memories of the first non-European Games in St. Louis in 1904 . The high travel costs in a generally difficult economic time were also criticized.
Highlights
- Although only about half as many athletes took part in Amsterdam as four years earlier because of the global economic crisis , as many teams could not pay for the trip, there were many great successes and 18 old world records were set or exceeded.
- For the first time since 1896, the Summer Games were limited to two weeks. At the games in between there were still several months between the opening and closing ceremonies.
- The Summer Games were officially opened by US Vice President Charles Curtis . The fencer George Calnan pronounced the athlete's oath .
- Only three teams took part in the Olympic hockey tournament . The USA was able to achieve the bronze medal, although they lost all games (1:24 against India and 2: 9 against Japan ).
Outstanding athletes
- The 21-year-old American Mildred "Babe" Didrikson qualified for a total of five competitions, but was only allowed to take part in three, of which she won two: gold in the javelin and 80-meter hurdles , as well as silver in the high jump , in the last two Disciplines even with world records. In the final of the high jump, however, the outstanding US athlete jumped 1.657 m as high as her teammate Jean Shiley. The jury decided to assign Didrikson only second place due to the jumping style (head first). The two women later merged their medals.
- 14-year-old Japanese Kusuo Kitamura won the 1,500-meter freestyle competition , making him the youngest male athlete to ever win a gold medal in any sport.
- Ivar Johansson ( Sweden ) won double Olympic gold in wrestling.
- Gold for Franz and Toni Schmid ( Prix olympique d'alpinisme for the first ascent of the Matterhorn north face).
Attendees
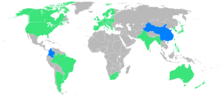
A total of 37 nations took part in the 1932 Summer Olympics, nine fewer than in 1928. For China and Colombia it was the first ever participation.
| America (889 athletes from 8 nations) | ||
|---|---|---|
|
||
| Europe (910 athletes from 22 nations) | ||
|
|
|
| Asia (145 athletes from 4 nations) | ||
|
|
|
| Oceania (33 athletes from 2 nations) | ||
|
|
|
| Africa (12 athletes from 1 nation) | ||
|
||
| (Number of athletes) * Participation in Summer Olympics for the first time | ||
Others
- For the first time, the awards ceremony took place immediately after the competitions. In addition, the three-level podium at the Olympic Summer Games was introduced (the " podium " is an invention of Lake Placid, which had hosted the Winter Games in the same year).
- For the first time in the history of the Summer Olympics, an Olympic village consisting of 550 houses was built for the male athletes - the women were accommodated in luxury hotels.
- Paavo Nurmi was banned for life because of an expense report that cost him his amateur status.
- In the years between 1912 and 1948, medals for artistic achievements in 18 areas were also awarded at seven Summer Olympics. In 1932 there were the following award-winning art competitions: Architectural drafts, urban planning drafts, sculptures / sculptures, medals and plaques, paintings and graphics, drawings and watercolors, other graphic art, literature / poetry of every kind, lyrical works and music (with the subdivisions into music every Art, vocal compositions, compositions for one instrument and compositions for orchestra).
- In Los Angeles, the Olympic mountaineering prize Prix olympique d'alpinisme was awarded for the second time after the Games in Chamonix in 1924 .
- For the Olympic champion in wrestling Jakob Brendel , his 1000 Mark travel money was collected privately at home in Nuremberg.
- The 1932 Summer Games brought various innovations: electrical time measurement with starting pistols , which triggered the stopwatch and the target photo ; Flags and hymns as well as the presence of the boxing referees between the ropes and not outside the ring, as was previously the case.
- The rowing competitions took place in the newly built Long Beach Marine Stadium in Long Beach , the first man-made arena for rowing competitions in the United States.
- Stanisława Walasiewicz , who won the women's 100-meter run, was intersex . However, this was only determined in 1980 during her autopsy.
Competition program
116 competitions (98 for men, 14 for women and 4 open competitions) in 14 sports / 20 disciplines were held. That was 7 more competitions but the same number of sports / disciplines as in Amsterdam in 1928 . The changes are detailed below:
- Football was dropped in Los Angeles in 1932.
- In athletics , the men's program has been expanded to include the 50 km walk - for women the 80 m hurdles and the javelin throw have been added. The women's 800 m was canceled again after the premiere in Amsterdam in 1928.
- In weightlifting , the welterweight weight class for men was added.
- After a break in Amsterdam in 1928, shooting was back in the Olympic program with the two men's rapid fire pistol and small bore rifle lying 50 m.
- For sailing , the two open classes Snowboard and Star were added - the open 12-foot dinghy was omitted.
- In apparatus gymnastics , there was no team all-around competition for the men - the floor, Indian clubs, rope dangling and tumbling were added for the men.
Olympic sports / disciplines
-
 Boxing total (8) = men (8)
Boxing total (8) = men (8)
-
 Fencing total (7) = men (6) / women (1)
Fencing total (7) = men (6) / women (1)
-
 Weightlifting total (5) = men (5)
Weightlifting total (5) = men (5)
-
 Hockey total (1) = men (1)
Hockey total (1) = men (1)
-
 Athletics total (29) = men (23) / women (6)
Athletics total (29) = men (23) / women (6)
-
 Modern pentathlon total (1) = men (1)
Modern pentathlon total (1) = men (1)
- Cycling
-
horse riding
-
 Dressage total (2) = men (2)
Dressage total (2) = men (2)
-
 Jumping total (1) = men (1)
Jumping total (1) = men (1)
-
 Versatility Overall (2) = Men (2)
Versatility Overall (2) = Men (2)
-
-
Wrestling
-
 Freestyle total (7) = men (7)
Freestyle total (7) = men (7)
-
 Greco-Roman total (7) = men (7)
Greco-Roman total (7) = men (7)
-
-
 Rowing total (7) = men (7)
Rowing total (7) = men (7)
-
 Shooting total (2) = men (2)
Shooting total (2) = men (2)
-
Swimming
-
 Swimming total (11) = men (6) / women (5)
Swimming total (11) = men (6) / women (5)
-
 Water polo total (1) = men (1)
Water polo total (1) = men (1)
-
 Diving total (4) = men (2) / women (2)
Diving total (4) = men (2) / women (2)
-
-
 Sailing total (4) = Open (4)
Sailing total (4) = Open (4)
-
 Gymnastics total (11) = men (11)
Gymnastics total (11) = men (11)
Number of competitions in brackets
Time schedule
| Time schedule | |||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| discipline | Sat. 30. |
Sun. 31. |
Mon. 1. |
Tues. 2. |
Wed. 3. |
Thursday 4. |
Fr. 5. |
Sat. 6. |
Sun 7. |
Mon. 8. |
Tuesday 9 |
Wed. 10. |
Thursday 11. |
Fri. 12. |
Sat. 13. |
Sun. 14. |
Decision- disk- applications |
||
| July | August | ||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|||||||||||||||||||
|
|
8th | 8th | |||||||||||||||||
|
|
1 | 2 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 7th | ||||||||||||
|
|
2 | 3 | 5 | ||||||||||||||||
|
|
1 | 1 | |||||||||||||||||
|
|
4th | 3 | 4th | 5 | 4th | 2 | 2 | 5 | 29 | ||||||||||
|
|
1 | 1 | |||||||||||||||||
| Cycling |
|
1 | 3 | 4th | |||||||||||||||
|
|
2 | 2 | |||||||||||||||||
| Equestrian sport |
|
2 | 2 | ||||||||||||||||
|
|
1 | 1 | |||||||||||||||||
|
|
2 | 2 | |||||||||||||||||
| Wrestling |
|
7th | 7th | ||||||||||||||||
|
|
7th | 7th | |||||||||||||||||
|
|
7th | 7th | |||||||||||||||||
|
|
1 | 1 | 2 | ||||||||||||||||
| Swimming |
|
1 | 1 | 2 | 1 | 1 | 2 | 3 | 11 | ||||||||||
|
|
1 | 1 | |||||||||||||||||
|
|
1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 4th | ||||||||||||||
|
|
1 | 1 | 2 | 4th | |||||||||||||||
|
|
1 | 1 | 5 | 2 | 2 | 11 | |||||||||||||
|
|
|||||||||||||||||||
| Demonstration competitions | |||||||||||||||||||
| American football | |||||||||||||||||||
| lacrosse | |||||||||||||||||||
| decisions | 2 | 7th | 5 | 4th | 15th | 8th | 2 | 3 | 14th | 4th | 5 | 9 | 5 | 8th | 24 | 1 | 116 | ||
| Sat. 30. |
Sun. 31. |
Mon. 1. |
Tues. 2. |
Wed. 3. |
Thursday 4. |
Fr. 5. |
Sat. 6. |
Sun 7. |
Mon. 8. |
Tuesday 9 |
Wed. 10. |
Thursday 11. |
Fri. 12. |
Sat. 13. |
Sun. 14. |
||||
| July | August | ||||||||||||||||||
Color legend
Nine art competitions were held.
Demonstration sports
Only two teams took part in both tournaments
| lacrosse | USA - Canada | 2: 1 in Best of three (5: 3 4: 5 7: 4) |
| American football | Team West (USA) - Team East (USA) | 7: 6 |
Counter events
As communist counter-events to the Summer Olympics in Los Angeles, Spartakiads took place in Chicago and Lyon in 1932 .
literature
- The Games of the Xth Olympiad Los Angeles 1932: Official Report (PDF; 77.0 MB) . 1933
- Baker, WS Muscular Marxism and the Chicago Counter-Olympics of 1932, in: International Journal of the History of Sport 9 (1992), pp. 397-410.
- Karl Lennartz / Wolf Reinhardt / Ralph Schlueter: The games of the X. Olympiad 1932 in Lake Placid and Los Angeles . Agon, 2015, ISBN 978-3-89784-406-3 .
Web links
Individual evidence
- ↑ a b page of the IOC on the 1932 Summer Olympics (English). Retrieved April 4, 2013 .
- ↑ The high number of participants and functionaries in the midst of the economic crisis can be explained by the fact that around 3/4 of their trip paid for themselves or had sponsors / associations pay for it; see. Arnd Krüger : Germany and the Olympic Movement (1918 - 1945), in: Horst Ueberhorst (Hrsg.): Geschichte der Leibesübungen , Vol. 3/2, Berlin: Bartels & Wernitz, 1982, 1026 - 1047.
- ↑ California Historic Landmarks - Los Angeles County . Office of Historical Preservation, California State Parks. Retrieved January 5, 2020.