Federal Ministry of Finance
|
Federal Ministry of Finance |
|
|---|---|
| State level | Federation |
| position | supreme federal authority |
| founding | 1880 as the Reich Treasury |
| Headquarters |
|
| Authority management | Olaf Scholz ( SPD ), Federal Minister of Finance |
| Budget volume | EUR 5.89 billion (2016) |
| Web presence | www.bundesfinanzministerium.de |
The Federal Ministry of Finance (abbreviation BMF ) is a supreme federal authority in the Federal Republic of Germany . It has its headquarters or first office in Berlin and its second office in the federal city of Bonn . The Federal Ministry is supported by a scientific advisory board . The Ministry is headed by the Federal Minister of Finance .
history
The finance minister is next to the interior , foreign , justice and defense ministers (formerly the post office minister was also one of those government members who head one of the remaining so-called classic departments) . This designation has the background that there were only these business areas in the first German Reich government . To emphasize this, the specific article is used in the name . In addition to the Ministry of Justice and the Ministry of Defense, the Ministry of Finance is also one of the three federal ministries that are expressly mentioned in the Basic Law ( Art. 112 S. 1 and Art. 114 Para. 1 ) and whose status as such may not be affected (otherwise it stands the Federal Chancellor is free to set up or dissolve ministries within the framework of his organizational powers).
After the dissolution of the Imperial Treasury Office , the Reich Ministry of Finance was founded in the Weimar Republic . This was the forerunner of today's ministry. The creation of the Ministry in 1949 was immediately preceded by the Joint Finance Council created in 1947 .
After the Federal Treasury was dissolved in 1969, some of its tasks were transferred to the Ministry of Finance.
From May 1971 to December 1972, the Ministry of Finance merged with the Federal Ministry of Economics to form the Federal Ministry of Economics and Finance .
Due to the capital city resolution ( Berlin / Bonn law ) of the German Bundestag , the headquarters of the ministry was gradually moved from Bonn to Berlin in the mid-1990s. One office remained in Bonn.
Since 1998 the Federal Ministry of Finance has also been responsible for issuing postage stamps with the designation Germany .
Competence at the federal level
The main responsibilities lie in tax and budget policy ( state finances ) as well as in European financial policy.
In addition, the Ministry has, among other things, the legal and technical supervision of the following higher federal authorities :
- the Federal Financial Supervisory Authority
- the Federal Agency for Financial Market Stabilization (FMSA)
- the Federal Agency for Real Estate Tasks (BImA)
- the Federal Agency for Unification-related Special Tasks
- the Federal Central Tax Office
- the Federal Information Technology Center (ITZ Bund)
- the General Customs Directorate
Field Office
The first official seat of the Federal Ministry of Finance is the Detlev-Rohwedder-Haus on Wilhelmstrasse in Berlin.
The building was built during the Nazi era in 1935/1936 according to plans by the architect Ernst Sagebiel and after its completion it was the seat of the Reich Aviation Ministry (RLM) until the end of the war in 1945.
In 1949 the building of the venue for was the German People's Council , which on 7 October 1949 by enactment of the Constitution in the grand ballroom, the GDR founded and there as a provisional People's Chamber was constituted. Subsequently, several specialist ministries were housed in the complex, whereupon the building was officially designated as the House of Ministries of the GDR.
After the reunification in the GDR , the house was the headquarters of the Treuhandanstalt from 1991 to 1994 . In 1992 the building was named after the President of the Treuhandanstalt Detlev Rohwedder, who was murdered the previous year .
After it was renovated and rebuilt between 1994 and 1998, it has served as the headquarters of the Federal Ministry of Finance since 1999.
Role in European politics
European policy competence
At EU level , the main responsibility of the Ministry of Finance lies in coordinating European economic and monetary policy on behalf of the Federal Government. In addition, the ministry participates in the preparation and control of the EU budget and is responsible for the EU regulatory areas of customs , taxes and financial services.
The main body in which the Federal Ministry of Finance is active at EU level is the Council for Economics and Finance (ECOFIN) . The Federal Minister of Finance represents Germany in ECOFIN. ECOFIN meets around ten times a year. In addition, the finance ministers of the member states hold an informal meeting in the country of the Council Presidency at least once every six months.
Within the ministry, the organization of its European policy areas of responsibility falls under the main responsibility of Department E under the direction of MD Westphal.
The EU information center is also located in the Federal Ministry of Finance , which is the point of contact for citizens' questions on European legislation, EU funding programs and EU policy areas, as well as an intermediary for various sources of information.
European policy goals
A self-titled "essential goal" of the BMF in European policy is the stabilization of the euro and the European Economic and Monetary Union . To achieve this goal, the BMF advocates reformed financial market supervision in Europe, closer coordination and monitoring ( European semester , reform of the Stability and Growth Pact , Euro Plus Pact, etc.) and rescue measures ( ESM , EFSF, etc.).
In addition, the BMF is in a leading position within the Federal Government and in cooperation with the European Court of Auditors , the European Commission and the European Anti-Fraud Office (OLAF) for the correct and efficient use of paid European subsidies .
Management positions
Federal Minister since 1949
After Alex Möller resigned in protest against the debt policy of the other ministries, the finance department was subsequently co-managed by the respective economics minister , initially by Karl Schiller and later by Helmut Schmidt , before the original division was restored.
This amalgamation had briefly occurred before, when the FDP ministers resigned in the second cabinet under Ludwig Erhard , Kurt Schmücker was at the head of both ministries. This personal union ended with the formation of a grand coalition under Chancellor Kurt Georg Kiesinger less than a month later.
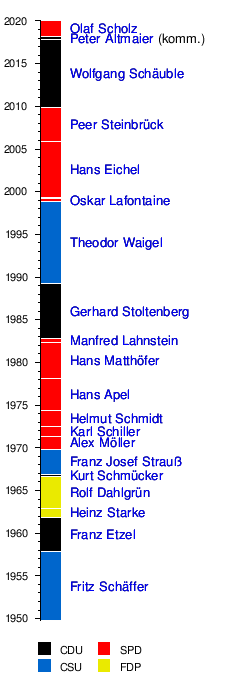
| No. | Surname | image | Life dates | Political party | Beginning of the term of office | Term expires | Term of office | Cabinet (s) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Federal Minister of Finance | ||||||||
| 1 | Fritz Schäffer |

|
1888-1967 | CSU | September 20, 1949 | October 29, 1957 | 2,961 days |
Adenauer I Adenauer II |
| 2 | Franz Etzel |

|
1902-1970 | CDU | October 29, 1957 | November 14, 1961 | 1,477 days | Adenauer III |
| 3 | Heinz Starke |

|
1911-2001 | FDP | November 14, 1961 | November 19, 1962 | 370 days | Adenauer IV |
| 4th | Rolf Dahlgrün |

|
1908-1969 | FDP | December 14, 1962 | October 28, 1966 | 1,779 days |
Adenauer V Erhard I Erhard II |
| 5 | Kurt Schmücker |

|
1919-1996 | CDU | November 8, 1966 | November 30, 1966 | 22 days | Erhard II |
| 6th | Franz Josef Strauss |

|
1915-1988 | CSU | 1st December 1966 | October 21, 1969 | 1,055 days | Kiesinger |
| 7th | Alex Möller |

|
1903-1985 | SPD | October 22, 1969 | May 13, 1971 | 568 days | Brandt I. |
| 8th | Karl Schiller |

|
1911-1994 | SPD | May 13, 1971 | July 7, 1972 | 421 days | Brandt I. |
| 9 | Helmut Schmidt |

|
1918-2015 | SPD | July 7, 1972 | May 15, 1974 | 647 days |
Brandt I Brandt II |
| 10 | Hans Apel |

|
1932-2011 | SPD | May 16, 1974 | February 15, 1978 | 1,371 days |
Schmidt I Schmidt II |
| 11 | Hans Matthöfer |

|
1925-2009 | SPD | February 16, 1978 | April 28, 1982 | 1,532 days |
Schmidt II Schmidt III |
| 12 | Manfred Lahnstein |

|
* 1937 | SPD | April 28, 1982 | October 1, 1982 | 156 days | Schmidt III |
| 13 | Gerhard Stoltenberg |

|
1928-2001 | CDU | 4th October 1982 | April 21, 1989 | 2,391 days |
Kohl I Kohl II Kohl III |
| 14th | Theo Waigel |

|
* 1939 | CSU | April 21, 1989 | October 27, 1998 | 3,476 days |
Kohl III Kohl IV Kohl V |
| 15th | Oskar Lafontaine |

|
* 1943 | SPD | October 27, 1998 | March 18, 1999 | 142 days | Schröder I |
| - | Werner Müller (acting) |

|
1946-2019 | independent | March 18, 1999 | April 12, 1999 | 25 days | Schröder I |
| 16 | Hans Eichel |

|
* 1941 | SPD | April 12, 1999 | November 22, 2005 | 2,416 days |
Schröder I Schröder II |
| 17th | Peer Steinbruck |

|
* 1947 | SPD | November 22, 2005 | October 28, 2009 | 1,436 days | Merkel I |
| 18th | Wolfgang Schäuble |

|
* 1942 | CDU | October 28, 2009 | October 24, 2017 | 2,918 days |
Merkel II Merkel III |
| - | Peter Altmaier (acting) |

|
* 1958 | CDU | October 24, 2017 | March 14, 2018 | 141 days | Merkel III |
| 19th | Olaf Scholz | * 1958 | SPD | March 14, 2018 | in office | for 894 days | Merkel IV | |
Parliamentary State Secretaries
- 1967–1969: Albert Leicht ( CDU )
- 1969–1971: Gerhard Reischl ( SPD )
- 1971–1974: Hans Hermsdorf (SPD)
- 1972–1974: Konrad Porzner (SPD)
- 1974–1982: Karl Haehser (SPD)
- 1975–1978: Rainer Offergeld (SPD)
- 1978–1982: Rolf Böhme (SPD)
- 1982: Gunter Huonker (SPD)
- 1982–1989: Hansjörg Häfele ( CDU )
- 1982–1991: Friedrich Voss ( CSU )
- 1989–1993: Manfred Carstens (CDU)
- 1991–1994: Joachim Grünewald (CDU)
- 1993–1994: Jürgen Echternach (CDU)
- 1994–1998: Irmgard Karwatzki (CDU)
- 1994–1995: Kurt Faltlhauser (CSU)
- 1995–1998: Hansgeorg Hauser (CSU)
- 1998–2007: Barbara Hendricks (SPD)
- 1998–2009: Karl Diller (SPD)
- 2007–2009: Nicolette Kressl (SPD)
- 2009–2015: Steffen Kampeter (CDU)
- 2009–2013: Hartmut Koschyk (CSU)
- 2013–2018: Michael Meister (CDU)
- 2015-2018: Jens Spahn (CDU)
- 2018–2019: Christine Lambrecht (SPD)
- since 2018: Bettina Hagedorn (SPD)
- since 2019: Sarah Ryglewski (SPD)
Official State Secretaries
- 1949–1959: Alfred Hartmann
- 1959–1962: Karl Maria Hettlage
- 1963–1969: Walter Grund
- 1967–1969: Karl Maria Hettlage
- 1969–1972: Hans Georg Emde ( FDP )
- 1970–1972: Heinz Haller
- 1973–1977: Karl Otto Pöhl (SPD)
- 1973–1974: Manfred Schüler (SPD)
- 1974–1978: Joachim Hiehle
- 1977–1980: Manfred Lahnstein (SPD)
- 1978–1989: Günter Obert
- 1981–1982: Horst Schulmann
- 1982–1989: Hans Tietmeyer
- 1989–1993: Peter Klemm
- 1990–1993: Horst Köhler (CDU)
- 1991–1995: Franz-Christoph Zeitler
- 1993–2004: Manfred Overhaus
- 1993-1994: Gert Haller
- 1994–1998: Jürgen Stark
- 1998–1999: Heiner Flassbeck
- 1998–1999: Claus Noé
- 1999–2002: Heribert Zitzelsberger
- 1999-2005: Caio Koch-Weser
- 2002–2006: Volker Halsch (SPD)
- 2004–2005: Gerd Ehlers
- 2005–2008: Thomas Mirow (SPD)
- 2005-2018: Werner Gatzer (SPD)
- 2005–2009: Axel Nawrath (SPD)
- 2008–2011: Jörg Asmussen (SPD)
- 2009–2010: Walther Otremba
- 2010–2014: Hans Bernhard Beus
- 2012–2018: Thomas Steffen
- 2014–2018: Johannes Geismann
- since 2018: Rolf Bösinger (SPD)
- since 2018: Werner Gatzer (SPD)
- since 2018: Jörg Kukies (SPD)
- since 2018: Wolfgang Schmidt (SPD)
Expert commissions
- Commission for the improvement of tax conditions for investments and jobs , chair: Reinhard Goerdeler (report, BMF series of publications, booklet 46, Bonn 1991)
- Income tax commission for the tax exemption of the subsistence level from 1996 and for the reform of the income tax , chair: Peter Bareis (report, BMF series of publications, issue 55, Bonn 1995)
- Commission for the reform of corporate taxation , chaired by: Alfons Kühn (report, BMF series of publications, issue 66, Bonn 1999)
- Independent historians' commission for research into the history of the Reich Ministry of Finance during the National Socialist era , since 2010, chaired by: Hans-Peter Ullmann
See also
- Imperial Treasury
- Reich Treasury
- Reich Ministry of Finance
- List of private companies with federal participation
literature
- Claudia Steur: Today's Federal Ministry of Finance. A "stone history book" . In: Claudia Steur: Die Wilhelmstrasse - Government Quarter in Change / The Government Quater through the centuries . Topography of Terror Foundation, Berlin 2007, pp. 197–204, ISBN 978-3-9811677-0-2
- Laurenz Demps , Eberhard Schultz, Klaus Wettig : The Federal Ministry of Finance: A polluted place? with a foreword by Hans Eichel (= streets, squares and buildings of Berlin ). Parthas Verlag, Berlin 2002, ISBN 3-932529-32-4 (132 pages).
Web links
-
Official website of the Federal Ministry of Finance
- Organization chart (pdf)
- Federal budget info : An interactive application by the Federal Ministry of Finance to visualize the federal budget
Individual evidence
- ↑ Law on the establishment of the federal budget for the 2016 budget year (Budget Law 2016). (PDF; 36.1 MB) In: bundeshaushalt-info.de. Federal Ministry of Finance (BMF), December 21, 2015, p. 16 , accessed on August 14, 2016 .
- ↑ List of Abbreviations. (PDF; 49 kB) Abbreviations for the constitutional organs, the highest federal authorities and the highest federal courts. In: bund.de. Federal Office of Administration (BVA), accessed on August 14, 2016 .
- ^ Dorothee Weckerling-Wilhelm in: Dieter C. Umbach, Thomas Clemens (Ed.): Basic Law. Staff comment and manual. Volume II, CF Müller, Heidelberg 2002, Art. 62, Rn 23 (p. 417)
- ^ Dörte Hansen, Maika Jachmann: The Detlev-Rohwedder-Haus - mirror of German history. Federal Ministry of Finance, Wilhelmstrasse 97, 10117 Berlin, August 2015, accessed on May 15, 2018 .
- ^ The role of the Federal Ministry of Finance in European policy. (No longer available online.) Federal Ministry of Finance, archived from the original on October 23, 2011 ; Retrieved November 2, 2011 .
- ↑ ECOFIN Council. (No longer available online.) Federal Ministry of Finance, archived from the original on November 10, 2011 ; Retrieved November 2, 2011 .
- ↑ Organization plan of the Federal Ministry of Finance as of February 2014. Federal Ministry of Finance, accessed on February 19, 2014 .
- ↑ EU information point / European telephone in the BMF. (No longer available online.) Federal Ministry of Finance, archived from the original on November 1, 2011 ; Retrieved November 2, 2011 .
- ^ The role of the Federal Ministry of Finance in European policy. (No longer available online.) Federal Ministry of Finance, archived from the original ; Retrieved November 2, 2011 .
- ↑ Topic: Stabilization of the Euro. (No longer available online.) Federal Ministry of Finance, archived from the original on November 10, 2011 ; Retrieved November 2, 2011 .
- ^ The role of the Federal Ministry of Finance in European policy. (No longer available online.) Federal Ministry of Finance, archived from the original on October 23, 2011 ; Retrieved November 2, 2011 .
Coordinates: 52 ° 30 '31.2 " N , 13 ° 23' 2.6" E




