Google LLC
| Google LLC
|
|
|---|---|
| legal form | Limited Liability Company |
| founding | 4th September 1998 |
| Seat |
Mountain View , California , United States |
| management | Sundar Pichai ( CEO ) |
| Branch | Internet services, internet trading, advertising, software development |
| Website | www.google.com/intl/de/about |
Google LLC is an American technology company , active in the areas of hardware and software development , with the legal form of a Limited Liability Company and headquartered in Mountain View, California . Google LLC is a subsidiary of the holding company XXVI Holdings Inc; it belongs to the company Alphabet Inc. Until September 1, 2017 Google contributed LLC the name Google Inc .
Google Inc. was best known for the search engine of the same name, Google . The company was founded on September 4th, 1998 by Larry Page and Sergey Brin . On the same day they launched a test version of the program and in the same year the search engine officially went online. The company declares to "organize the information of this world and make it generally accessible and usable".
The company's search engine received around 73.4% of all desktop searches on the Internet worldwide (as of June 2018). The Google brand has been one of the most valuable brands in the world for years .
Google Inc. has been part of Alphabet since October 2, 2015. Through a restructuring, the Google shares were converted into Alphabet shares and the company was split into several subcontractors, which are owned by Alphabet Inc. The core business of online and internet services was continued under the name Google . The previous Google boss Larry Page moved to the head of the newly created holding together with Sergey Brin . Sundar Pichai took over the management of Google .
Services
Google offers a variety of mostly ad-supported free services on the World Wide Web . This mainly involves searching on various data sources. Often, new individual services are added to the offer, sometimes as a result of corporate acquisitions. A new service is often given the addition of beta to indicate that it is not yet fully developed. Google has been criticized for keeping some services beta for a very long time.
The main services include:
- Google offers various search engines.
- Text documents on the web - The best known and most widely used service is the full text search of documents on the World Wide Web. In addition to the HTML format commonly used on the web, Google also searches other document types such as PDF , PostScript or Microsoft Word's Doc format . One factor in weighting search results is link popularity . However, the complete algorithm is kept secret by Google LLC in order to make it difficult to copy the service on the one hand and to make misleading optimization of commercial or other pages on the Google search on the other hand.
- Image files on the web - To find image files, Google's image search uses words in the filename as well as in HTML documents that use images. The graphic formats JPEG , PNG and GIF are supported. A search for image content is also possible.
- Products - Google Shopping , formerly Froogle , can be used to search for goods offered by online retailers. In particular, a price comparison is possible.
- Books and Scientific Works - Google Books is a search service that can be used to search your own digital copies and online books in full text. Google Scholar is a similar service that specializes in academic publishing.
- Videos - YouTube is a comprehensive service with numerous videos.
- Music - YouTube Music makes music available separately on YouTube, and offline as part of a paid subscription.
- Maps - The online atlas Google Maps contains street maps, known locations and a variety of other location-related information. Google offers a programming interface that can be used to integrate maps and route planners into websites. Google Earth complements the offer with a virtual globe.
- News - The content of news websites is particularly popular with Google. Under Google News will be on these items - grouped by topic, certain events and sorted by their importance - directed. This enables the reader to quickly find various articles on an event.
- Email - Gmail is Google's email service. You can read your e- mails on the web , fetch them via POP3 or IMAP with your own e-mail program .
- Websites - Google Sites is a web host where registered users can create and publish their own website.
- Social networks - Orkut and Buzz competed with other community portals and online contact networks such as Facebook and Twitter . After the little success of Buzz, it was discontinued in favor of its successor Google+ . In 2016, Google also introduced the Spaces service. It is used to share and comment on images, texts and videos.
- Messaging - Google Hangouts , formerly Google Talk, is a messenger for exchanging text messages and video calls.
- Translation - Automatic translation between several languages is offered for websites.
- Office suite - With the applications Docs, Tables and Presentations, Google provides an Office suite for Chrome, Android and Apple iOS . The applications work closely with the Google Drive online storage system and can open documents in Google format as well as Microsoft Office files. This functionality also makes G Suite, developed for companies, attractive. In addition to Google Drive, other services such as Gmail can also be used for a fee with extended functions.
- Usenet - With Google Groups , Google hasan extensive archive of newsgroup articles that go back to 1981. You can search for terms and authors in the contributions in the various language discussion forums. Version 2 also allows you to create your own discussion forums, albeit independently of the Usenet.
- Operating systems and browsers - Google offers the free Chrome OS and Android operating systems as well as the Google Chrome web browser . From 2011, the Android offshoot Google TV should also be distributed. In 2014, Google TV was discontinued and its successor Android TV started.
- Companies - Google offers G Suite for companies . With this, Google allocates e-mail addresses and storage space to business customers. With the product Google My Business , companies can present themselves in Google search, in Google Maps and the former social network Google+ .
Advertising services
Ads
Google sold for any terms the fade of sponsored links as part of its Google Ads program . This pure text advertising is specially highlighted so that the user can distinguish it from the actual search results. In this way, advertising is displayed that matches the search query in terms of content and thus brings the advertising AdWords customer together with the user group that is more likely to be interested in his products and services. The customer determines the maximum remuneration per click himself, whereby a higher remuneration can achieve a higher position compared to competing ads.
AdSense
Additionally, gains arising from the Google AdSense - Affiliate . This is a contextual advertisement that webmasters can include on their websites. Since May 2004, graphic advertising banners in four standard sizes can also be placed here. Since June 2005, customers have also been able to use “site targeting” to advertise on specific pages, use static and animated advertising banners and pay for them based on the number of hits. Until now, only one payment per click was possible.
Google reserves the right to deactivate an AdSense account without giving a reason.
Google has stated that it will not limit itself to advertising on the Internet, but rather want to participate in the advertising market as a whole in the medium and long term. The aim is to develop AdSense into a cross-media advertising network which, in addition to Internet advertising, also includes the classic media of print, radio and television. The background is the fear that without new sources of revenue, Google could soon reach its limits for further expansion. 95 percent of global advertising sales are still made in the traditional media.
Google has already developed a wide range of activities, particularly in the USA. There are cooperations and pilot projects with press and radio companies to test the use of Google advertising concepts in these sectors as well. In digital, return-channel-capable television, Google hopes to be able to launch an advertising tool that enables viewers to be targeted individually, which would be viewed as a major innovation in advertising television. Google also wants to enforce its AdSense system in mobile data services.
Finances
Sales and profits
| Business figures | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| year | Sales in millions of dollars |
Profit in millions of dollars |
|
| 2017 | 110,855 | 12,662 | |
| 2016 | 90.272 | 19,478 | |
| 2015 | 74,989 | 16,348 | |
| 2014 | 66.001 | 14,136 | |
| 2013 | 55,519 | 12,920 | |
| 2012 | 46,039 | 10,737 | |
| 2011 | 37.905 | 9,737 | |
| 2010 | 29,321 | 8,505 | |
| 2009 | 23,648 | 6,519 | |
| 2008 | 21,795 | 4,282 | |
| 2007 | 16,503 | 4,203 | |
| 2006 | 10,604 | 3,078 | |
| 2005 | 6.139 | 1,465 | |
| 2004 | 3,200 | 399.1 | |
| 2003 | 961.9 | 105.6 | |
| 2002 | 347.8 | 99.7 | |
| 2001 | 86.4 | 7.0 | |
| 2000 | 19.1 | −14.7 | |
Since its inception, Google has increased its sales and profits significantly, see table. In 2010 it had sales of $ 29.3 billion and a profit of $ 8.5 billion. Most of the revenue came from advertising services with $ 28.236 billion. Additional income came from licensing, among other things. 66% of the revenue came from Google websites, 30% from Google Network pages and 4% from other sources. In the fourth quarter of 2012, Google Inc. had revenues of $ 14,419 million.
Tax issue
Google operates mostly in developed countries. In order to avoid the taxes on profits applicable there , Google transfers profits via transfer pricing via Ireland to the Netherlands and then to Bermuda . As a result, Google only paid an effective tax rate of 2.4% on its profits outside the US from 2007 to 2009, avoiding tax payments of approximately $ 3.1 billion during that period. In 2010, the effective tax rate was estimated to be around 3%. In the US itself, the effective tax rate on reported earnings around the year was 22.4%. Google's tax avoidance has often been criticized; likewise governments that do not plug tax loopholes .
In 2016, Google transferred around 16 billion euros to Bermuda and in 2017 almost 20 billion euros.
Tax revenue in Germany
According to the group's information in the Federal Gazette , Google Germany GmbH (head office in Hamburg) paid income taxes in the amount of 12.9 million euros in 2014. The turnover for Germany was given as 279 million euros and a gross profit of 22 million euros was reported. According to the Frankfurter Allgemeine Zeitung, VG Media estimates annual sales of up to 5 billion euros. According to the annual report, the subsidiary in Germany serves “essentially as a service company” for the Google Ireland Ltd branches in Dublin and for the headquarters in the USA. The profits are taxed there and not in Germany on other terms.
Employee
Google employs 102,000 people (as of 2019). In addition, another 121,000 employees - more than the regular workforce - work as contractors and temporary workers for Google (as of 2019). More than 3000 people work for Google in Switzerland (as of 2019).
history
founding
In 1995 Larry Page and Sergey Brin met at Stanford University . They designed the BackRub search engine , a Google predecessor. It was named after the backlinks that are analyzed to determine the value of a website. In 1998, however, Internet portals expressed a lack of interest in the search technology developed. In August 1998, the investor Andreas von Bechtolsheim wrote a check for 100,000 US dollars after a ten-minute presentation on the search engine. Since Bechtolsheim assumed the company was called “Google”, he used “Google Inc.” as the recipient. Such a company did not exist until then. Larry Page and Sergey Brin registered the company under that name so the check could be cashed. The origin of the name “Google” can also be traced back to the (very large) number known under the English name “googol” . In a garage they founded in on 4 September 1998. Menlo Park the Google Inc . With start-up capital of $ 1,100,000 raised by families, friends, and Andy Bechtolsheim, they developed and released the first trial version of the program. Five months later, Google Inc. and eight employees moved into an office in Palo Alto . Around 500,000 search queries were now recorded daily. After AOL and Netscape had worked together with Google since September 1999 (according to Google not until May 2002) , search queries increased sixfold. One reason for Google's first success was that other search engines, especially AltaVista , were no worse at searching, but in 1999 they expanded their pages into extensive web portals. With the slow Internet connections that were still common at the time, the simply structured Google page had clear advantages.
chronology
Development up to the IPO in 2004
- On September 21, 1999 the test phase of the Google web search was officially ended and the "beta" notice was removed from the website.
- At the end of the second quarter of 2000, Google was the market leader in search engines, with more than a billion pages in the index.
- In 2001, Eric Schmidt was appointed first CEO .
- In February 2001, Google took over the Usenet archive from Deja News and started its own Usenet search, Google Groups .
- In February 2003, Google took over the blogging platform Blogger.com from Pyra Labs , which at that time already had hundreds of thousands of users.
- In April 2003, Google bought Applied Semantics, Inc. and later integrated the acquired technology into Google AdSense . Applied Semantics had previously recognized the semantic meaning of a website for customers like Overture with the help of a technology called KeyWordSense and enabled targeted advertisements. In June 2003, Google started its AdSense advertising program, as part of which topic-related advertisements are displayed on participating websites.
2004
- Google took over Where2 LLC . Google Maps later developed from this .
- On April 1st, Google offered the beta version of the free email service Gmail with 1 GB of storage space per user.
- On July 13th, Google announced the acquisition of Picasa, LLC , the development of which would later become the Google Picasa product .
- On October 14th, the company presented its Google Desktop Search , a program for searching through the data on your own computer.
- On October 27, the acquisition of Keyhole Corp. announced. Keyhole laid the foundation for Google Earth .
2005
- On March 28th, Google acquired Urchin Software Corp. This later became the product Google Analytics .
- On May 11th, Google announced the acquisition of Dodgeball , a mobile social network. This will later become the Google Latitude service .
- In August, the purchase of Android Inc. was announced. In 2008, Google released the first version of the Android operating system for mobile devices.
- On December 21st, Google announced the acquisition of 5% of the shares in AOL Time Warner .
- In 2005, Google Inc. was included on the Forbes list for the first time , and it jumped straight away to number 38. The company's value was estimated at around 55 billion US dollars.
2006
- On March 9, the group took over the start-up company Upstartle, LLC with its product Writely . Later, this and the technologies of Tonic Systems and Zenter, acquired in 2007, resulted in Google Docs (today: Google Drive).
- On March 14th, Google bought @Last Software for integrating 3D sketches into Google Earth . The product is later called Google SketchUp .
- On June 29th, Google launched the Google Checkout payment system .
- On August 30th, Google launched its Google Books service for downloading out-of-copyright books.
- On October 9th, Google took over the Internet video portal YouTube for 1.65 billion US dollars .
- On November 1, Google bought the wiki start-up company JotSpot Inc. It later became Google Sites .
2007
- After a court ruling on February 14, 2007 in Belgium, Google was no longer allowed to publish articles from national daily newspapers and was fined EUR 3.45 million.
- In March 2007 the software Trendalyzer (formerly called Gapminder ) developed by the Swede Hans Rosling was acquired by taking over the company of the same name. With Trendalyzer it is possible to visualize statistical values. Some components of the software have become available for general use through the visualization interface for application programming (Google Visualization API ).
- On April 13, 2007, Google took over the online advertising network DoubleClick, Inc. , one of the largest online advertising marketers, for 3.1 billion US dollars, thereby outbidding Microsoft and Yahoo among others. The DoubleClick technology was later integrated into Google AdWords . Google thus dominates the market for online advertising with 80% market share; the rival companies Microsoft and AT&T therefore appealed to the cartel authorities.
- On April 23, Google was estimated to be the most valuable brand in the world, ahead of General Electric , Microsoft and Coca-Cola . Three days later, Google was able to refer to the most visitors on the Internet before Microsoft, Yahoo, Time Warner, eBay and Wikipedia.
- On May 30th, the group bought Panoramio , a start-up company specializing in the distribution of geolocal digital photos. These photos can now be viewed in Google Earth and Google Maps .
- On July 3, the company took over the Californian telephone service provider GrandCentral Communications . The VoIP product Google Voice was created from this .
2008
- In March, Google launched its electronic health record service called Google Health .
- On July 23, a knowledge portal, Knol , went into the public test phase.
- In September, a browser developed by Google called Google Chrome was introduced.
- Google became the exclusive sponsor of a satellite called GeoEye-1 , which delivers the latest high-resolution satellite photos for Google Earth and Google Maps. The two Google founders Larry Page and Sergey Brin were present at the launch of the satellite.
2009
- Since March, Google's advertisers have been able to target consumers more specifically using Interest Based Ads using interest-based ads (see Targeted Advertising ).
- On March 31, 2009, Google launched its own venture capital company with venture capital of 100 million US dollars to invest in promising start-ups from all sectors of the economy. According to Google Ventures' management partners Rich Miner and Bill Maris , the focus of the financial investments is in the areas of software, environmental technology, biotechnology, healthcare and Internet technologies for consumers.
- In May 2009, Google Wave, an internet-based system for communication and collaboration in real time, was presented. The developers come from the company takeover of Where2 LLC in 2004 , which resulted in Google Maps.
- In June, Google Squared was released, an experimental search engine that delivers search results in table format and tries to automatically structure unstructured data from the web.
- With Google Chrome OS , an operating system designed for computers was presented which is based on the Linux kernel and uses the integrated web browser Google Chrome as the main platform for web applications. Google Chrome OS, like Android, was made available as open source.
- Google Book Search sought a legal agreement in the United States on copyright infringement in scanned books. At the same time, the previous practice of copyright infringement should be legalized and a usage agreement should be made with all book authors and rights holders worldwide, provided they do not contradict the settlement proposal, whose objection deadline was September 8, 2009 (see Google Book Settlement ).
- On September 16, 2009, Google announced that it had taken over the leading captcha specialist reCAPTCHA . This gave Google the opportunity to carry out its own activities for digitizing manuscripts and books, e.g. B. in the context of Google Books to support.
2010
- In January 2010, the mid-range smartphone Nexus was presented, a forerunner of the Pixel range .
- On February 9, the company released Google Buzz , a service for exchanging messages and comments.
2011
- Since February, the Google Art Project has offered the opportunity to take virtual tours of major international art museums and view selected works of art in very high resolution and with a zoom function. Additional information about the works and artists is displayed at the edge of the picture.
- The Google+ service was presented at the end of March . Similar to the Like button on Facebook , users can mark search results and ads with the +1 button to make other users aware of this result.
- Google launches Google Fiber in America . First users in Kansas City (Kansas) and Kansas City (Missouri) can get an Internet connection with up to 1 Gbit / s download and upload and receive up to 173 TV channels with the corresponding network box.
- In August, Google announced that it would take over Motorola Mobility from Motorola for $ 12.5 billion. In early 2014, the Motorola brand was sold to Lenovo for $ 2.9 billion.
- In September, Google announced the takeover of the couponing portal DailyDeal and Zagat Survey . The restaurant guide, founded in 1979, is intended to complement Google Places .
- In 2011, Google increased its lobbying spending significantly. From April to June 2011, Google invested US $ 2.1 million in influencing the US, compared to US $ 1.34 million in 2010 in the same period. Steps by the Federal Trade Commission to possibly initiate an investigation into Google's supremacy on the Internet are seen as the background .
2012
- As part of the newTLD program, Google applied to ICANN for the assignment of numerous new top-level domains . These include .google, .youtube, .docs, .lol, .blog, .chrome and .gmail as well as .store. With a total of 101 applications, Google is ahead of Amazon . However, among the applications, Google operates under the name “ Charleston Road Registry Inc. ”, a subsidiary of Google that was founded only to issue new TLDs. In October 2012, it became known that the company had withdrawn three of its applications because they did not meet ICANN guidelines.
- In June 2012, Google bought the messenger service meebo . Some functions of the service have been integrated into Google products.
- In cooperation with the Entrepreneurship Foundation and Indiegogo, Google launched the so-called founder garage . Entrepreneurs from Germany can take part in free courses on an online platform and apply for funding from the project partners. Among other things, Google also uses crowdfunding .
- In September 2012, Google announced the acquisition of the German company Nik Software . It is best known for its Snapseed iOS app , which is very similar to Instagram . The acquisition is widely seen as an attack on Facebook, which Instagram acquired in April 2012 and integrated into numerous of its own services.
- Ingress was launched in November 2012 , initially in the form of a closed beta version . The game revolves around a virtual world that is supposed to merge partially (depending on the level reached) with the real world. Ingress was classified as the very first alternative reality game for smartphones and therefore received wide media attention. The developer is John Hanke , former head of the geospatial department at Google.
- The Google Business Photos program was launched in December 2012 . Participating companies can have selected photographers take professional pictures of the respective branch and its premises, which are then published as a gallery on Google. The offer is closely linked to Google Maps and Google+ Local, where companies can already store their own profiles.
2013
- In February, Google joined the FIDO alliance as one of the first companies to develop the industry standard Universal Second Factor (U2F) for generally applicable two-factor authentication .
- The Chromebook Pixel was unveiled in San Francisco on February 21st. Compared to previous Chromebooks , it is characterized above all by its high-resolution screen with touchscreen , and an LTE module can also be configured as an option . The notebook was initially sold through Google Play in the United Kingdom and the United States .
- In March of that year, Google released a service for managing notes and tasks under the name Google Keep . At the beginning, in addition to a web-based interface, only one application for Android was available; according to Google, other platforms will be covered later. The service is in direct competition with Evernote , Wunderlist and Microsoft OneNote .
- At the beginning of April, Google introduced the Account Inactivity Manager . With its help, users can determine what should happen to their Google account if it is no longer used and the owner has passed away , for example . In this case, it will be handed over to a third party after a specified period and, if necessary, deleted completely. Google decides whether there is inactivity or not on the basis of various factors, such as the use of the Android cell phone or the web protocol.
- In June, Google Project Loon announced: With the help of interconnected hot air balloons , the company would like to provide areas with Internet access that have not yet been reached otherwise. A test run with 30 modified weather balloons was carried out in Canterbury (New Zealand) , which, according to the company, achieved a transmission rate comparable to UMTS and is intended to supply 50 households permanently.
- At the end of 2013, Google took over Boston Dynamics , a company that develops robotic systems for the US military.
2014
- In January 2014, Google acquired Deep Mind, a specialist in artificial intelligence.
- In early 2014, Google bought the thermostat and fire alarm maker Nest Labs .
- In April 2014, Google acquired Titan Aerospace . The company produces special drones that perform satellite-typical functions at high altitudes.
- In June 2014, Google bought Skybox Imaging , a space company that offers high-resolution satellite photography.
- Since November 2014, Google has leased Moffett Federal Airfield , located in Silicon Valley between San Francisco and San José , from NASA for 60 years . The rent for the entire period is $ 1.16 billion. Google wants the land for testing in the field of aerospace and robotics use.
2015
- Since August 2015, Google Inc. has been part of the newly founded holding company Alphabet Inc. , which is managed by Larry Page and Sergey Brin. Various subsidiaries and departments, including Calico , Nest Labs , X , Google Fiber , Google Capital and Google Ventures , will be spun off from Google Inc. and directly subordinated to Alphabet.
2016
- At the end of 2016, Google launched the Pixel phone series as the successor to the Nexus smartphones.
2017
- In March 2017, Google bought the data science portal Kaggle .
- In September 2017, Google bought parts of the smartphone manufacturer HTC for $ 1.1 billion. HTC's rights are also included in this deal.
- On September 1, 2017, Google Inc. announced its renaming to Google LLC .
2019
- On November 1, 2019, Google announced it would acquire Fitbit for $ 2.1 billion.
Stock market development
On April 29, 2004, the company announced its listing on the US stock exchange . Online registration for the company's initial public offering ( IPO ), which was expected to generate $ 3.3 billion in revenue, began on August 1. The originally planned issue price of $ 108 to $ 135 per share had to be reduced to $ 80 to $ 85 before the stock went on sale on August 19, 2004 for the first time. On the first day of trading, the price rose to over 100 US dollars, turning Larry Page and Sergey Brin, who each held around 38 million shares, into multi-billionaires.
On November 18, 2005, the stock climbed above the $ 400 mark. With 179,123,000 shares issued, Google had a market value of $ 112 billion. Due to the high stock market price, Google outperformed large corporations such as Coca-Cola , IBM , Cisco and Time Warner . The Google founders were now in the top 20 richest people in the United States.
On October 24, 2006, the Google market value exceeded $ 150 billion. This made Google worth far more than the industry heavyweight IBM. The company's stock surged above the $ 500 mark on November 22, 2006. With 179,123,000 shares issued, Google had a market value of $ 156 billion. This ranks Google 14th among US companies and 3rd among IT companies worldwide .
On October 19, 2007, Google's market value climbed to over $ 200 billion. This put Google in second place behind Microsoft (293 billion US dollars) of the global IT companies and in 10th place of all US companies. On October 31, 2007, the stock had risen from $ 600 to $ 700 in three weeks, with a market value of $ 220 billion. In 2007, Google overtook Procter & Gamble (US $ 218 billion), Bank of America (US $ 214 billion) and the world's largest automaker Toyota (US $ 204 billion).
There are a total of 313 million shares in Google LLC. The stock was valued at more than $ 500 in early 2007. In late 2007, the stock hit an all-time high of over $ 700. The market value on March 17, 2008 was around 84 billion US dollars; the market price on that day was about $ 268 per share. The second quarter of 2012 was very successful and the profit was 2.8 billion dollars, with a share price of 550 euros.
Logos
The logo is the company name “Google”, written in four colors: blue for the two letters “G” and “g”, red for the “o” and “e”, yellow for the second “o” and green for the “ l ". The font - Catullus (used for the logo from 1999 to August 31, 2015) - was designed by Gustav Jäger for H. Berthold AG in 1982 . The logo was slightly changed a few times. With the logo from September 1, 2015, Google is saying goodbye to serifs and using “Product Sans” as the new font.
On September 27, 2019, Google dedicated itself to a Google doodle for the " 21st birthday of Google ".
Patents and utility models
To protect the extensive product portfolio, Google registered 595 patents and utility models in 2007 . With the acquisition of Motorola Mobility and other companies, it can be assumed that the number of patents owned by Google is significantly higher.
Charitable commitment
With Google.org , apart from the actual company, Google LLC, there has been a charitable institution since 2005 , which is referred to as the "philanthropic arm of Google". The starting capital was $ 1 billion. Your goal is to invest profitably in various existing projects, but also to start your own ventures. Above all, Google.org wants to cover areas such as global poverty, energy and environmental protection. The most famous projects include the Google missing person search and the planned co-development of a hybrid car . The current director is the doctor and epidemiologist Larry Brilliant, founder and director of the Seva Foundation.
Locations
The company has its headquarters, the Googleplex , in Mountain View in Silicon Valley , where the company was founded. In addition, Google has many branches around the world. The headquarters for the business in EMEA is in Dublin at the Grand Canal Dock. Other locations in Europe have been set up in addition to Denmark , Poland , the Czech Republic , Switzerland (research center in Zurich since 2004), France and the Netherlands, as well as in Germany in Hamburg ( Google Germany headquarters in ABC-Straße ) and Munich .
In February 2011 it was announced that a new research institute would be set up in Berlin . On the occasion of the founding event , Google's legal director David Drummond explained in a guest article for Zeit Online what the group’s intentions are in this engagement: “[We want] to better understand the interaction between the Internet, science and society. We need to take the help of scientific experts [...] If we want to ensure that research in the future based on a sustainable basis and keeps its place on the agenda of decision-makers, then must the public more involved. "( October 25, 2011 )
Data centers
Google LLC operates a number of data centers worldwide , each of which contains the complete functionality of the search engine. A user request , controlled by the Domain Name System , is ideally routed to the closest data center in terms of the network topology - not always identical to the one geographically closest - and answered by it. If one data center fails completely, another takes over its tasks.
The locations are currently:
North America
Berkeley County , South Carolina
Council Bluffs , Iowa
The Dalles , Oregon
Douglas County , Georgia
Henderson Nevada
Jackson County , Alabama
Lenoir , North Carolina
Loudoun County , Virginia
Mayes County , Oklahoma
Midlothian , Texas
South America
Quilicura , Chile
Europe
Dublin , Ireland
Eemshaven , Netherlands
Fredericia , Denmark
Hamina , Finland
St. Ghislain , Belgium
Asia
Changhua County , Taiwan
Singapore
The establishment of data centers in Asia was seen by observers as a sign that Google expects great growth there.
Google emphasizes that the company has been working in a CO 2 -neutral manner since 2007, primarily through the acquisition of carbon offsetting quotas.
hardware
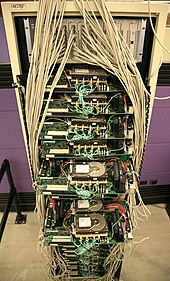
Each data center consists of a computer network (cluster). The computers used are IBM- compatible personal computers , so they consist of inexpensive standard components. This is where the self-developed Google File System comes into play, a distributed architecture in which all data is stored redundantly on various devices. If one of the computers or just a hard disk of a computer fails, the relevant data is copied from another location in the cluster to a replacement computer, and the failed hardware component can be replaced during operation without failures occurring. The overall system is scalable , i. This means that additional computers and hard drives can be added as required.
It is estimated that Google has around a million servers (2011).
Events
Google organizes the Google Summer of Code every year and helps innovative software projects and the like. a. financially. Google also sponsors the AI Challenge , a programming competition in the field of artificial intelligence. In addition, several developer conferences are held every year. This includes the Google I / O and the Summer of Code .
criticism
Google is often criticized for dealing with data protection . Further criticisms of the company include filtering from the search engine's list of results, dealing with the competition, copyright infringements, tax evasion and a quasi-monopoly position . Since 2017, Google has also been involved in the US Department of Defense's Maven military project for automated target acquisition using artificial intelligence.
Literary and cinematic processing
- In 2012, Florian Felix Weyh fictionalized the company as "Toggle Inc." in the thriller Toggle . In addition to the search engine business, the group operates a service called "Toggle Democracy" in the novel, which uses the stored data of its users to calculate their individual human value and thus links political and economic privileges and disadvantages. The democratic principle “one man, one vote” is suspended in the novel. Weyh et al. Expressed similar dystopian expectations. a. in 2007 in his non-fiction book The last choice .
- In the US comedy Prakti.com (original title The Internship ), two unemployed people in their mid-forties start an internship at Google. The company is not involved in the production of the film, but part of the film was allowed to be shot in the Googleplex , the headquarters of Google. The majority, however, originated on the Georgia Institute of Technology campus in Atlanta , Georgia .
literature
- David Vise, Mark Malseed: The Google Story. , Random House, New York 2005, ISBN 0-553-80457-X (English original edition, excerpts ; website for the book )
- David Vise, Mark Malseed: The Google Story . Murmann, Hamburg 2006, ISBN 3-938017-56-2 .
- John Battelle: The Search. Business and Culture under the spell of Google & Co . Börsenmedien, Kulmbach 2006, ISBN 3-938350-11-3 .
- Jean-Noël Jeanneney : Google's Challenge. For a European library . Wagenbach, Berlin 2006, ISBN 3-8031-2534-0 .
- Ralf Kaumanns, Veit Siegenheim: The Google economy: How Google is changing the economy . BoD, Norderstedt 2007, ISBN 978-3-8334-9795-7 .
- Marcel Marchill, Markus Beiler: The Power of Search Engines . Halem, Cologne 2007, ISBN 978-3-938258-33-0 .
- Gerald Reischl: The Google trap. The uncontrolled world power on the Internet . Überreuther, Vienna 2008, ISBN 978-3-8000-7323-8 .
- Lars Reppesgard: The Google Empire . Murmann, Hamburg 2008, ISBN 978-3-86774-046-3 .
- Jeff Jarvis : What Would Google Do? How to benefit from the internet giant's strategies for success. Heyne, 2009 (English: What would Google do? New York, NY: HarperBusiness, ISBN 978-0-06-170971-5 . Translated by Heike Holtsch).
- Theo Röhle: The Google Complex: About Power in the Age of the Internet , Transcript, Bielefeld 2010, ISBN 978-3-8376-1478-7 (Dissertation Uni Hamburg 2010, 261 pages).
- Bernd M. Samland: The Google effect: the formation of brand-specific verbs , logos, Berlin 2010, ISBN 978-3-8325-2374-9 (Dissertation University of Rostock 2010, 182 pages).
- Steven Levy : Google Inside. How Google thinks, works and changes our lives. mitp, Heidelberg 2012, ISBN 978-3-8266-9243-7 . (American original edition: In the Plex. How Google Thinks, Works and Shapes Our Lives. Simon & Schuster, New York 2011).
- Eric Schmidt , Jonathan Rosenberg, Alan Eagle: How Google Ticks. Campus, Frankfurt am Main 2015, ISBN 978-3-593-50216-8 (The American original edition How Google Works was first published in 2014 by Grand Central Publishing in New York)
- Thomas Schulz: What Google really wants . How the most influential corporation in the world is changing our future. 3. Edition. Penguin, Munich 2017, ISBN 978-3-328-10143-7 . (The German original edition was first published in 2015 by the Deutsche Verlags-Anstalt in Munich)
- Scott Galloway: The Four. The secret DNA of Amazon, Apple, Facebook and Google. Plassen, Kulmbach 2018, ISBN 978-3-86470-487-1 . (American original edition: The Four. The Hidden DNA of Amazon, Apple, Facebook and Google. Portfolio / Penguin, New York 2017, ISBN 978-0-7352-1365-4 )
Web links
|
Further content in the sister projects of Wikipedia:
|
||
|
|
Commons | - multimedia content |
|
|
Wiktionary | - Dictionary entries |
|
|
Wikiquote | - Quotes |
|
|
Wikinews | - News |
- Official website
- Official blog
- Official Google contemporary history , a list of reports since the summer of 1995
Individual evidence
- ^ Alphabet Finishes Reorganization With New XXVI Company , Mark Bergen
- ↑ Google company information
- ↑ statista.com: Market shares of search engines worldwide according to mobile and stationary use in June 2018 , statista
- ↑ BrandZ Top 100 Most valuable global brands 2011 (PDF), Millword Brown
- ↑ Best Global Brands 2013 ( Memento of October 21, 2014 in the Internet Archive ) (PDF), Interbrand
- ^ Notice from the Securities and Exchange Commission of the United States ; United States Securities and Exchange Commission dated October 2, 2015, accessed October 5, 2015.
- ↑ Founders rebuild Internet company - Google becomes Alphabet , tagesschau.de.
- ↑ Revolution at Google: spin-offs and a holding company , heise.de.
- ↑ Google is converting to Alphabet Holding , heise-online from October 3, 2015.
- ↑ Wade Roush: Google for yawning . Article, Technology Review, June 19, 2006. Retrieved February 7, 2007
- ↑ Ralf Kaumanns, Veit Siegenheim: From search engine to advertising group ( Memento from December 16, 2014 in the Internet Archive ) (PDF; 1.5 MB). MP 1/2008, pp. 25-33.
- ↑ a b Alphabet Registered (A) Balance sheet, profit and sales | Alphabet Registered (A) Annual Report | A14Y6F. Retrieved October 21, 2018 .
- ^ Alphabet Investor Relations. In: Alphabet Investor Relations. Retrieved March 16, 2016 .
- ↑ Data from Google, 2011 Financial Tables
- ↑ a b Google 2.4% Rate Shows How $ 60 Billion Lost to Tax Loopholes , October 20, 2010 Bloomberg
- ↑ FAZ: Google and others - Channeling profits into tax havens via Ireland , August 28, 2011
- ^ Corporate Tax Holiday in Debt Ceiling Deal: Where's the Uproar? , July 20, 2011, Rolling Stone Politics - Matt Taibbi
- ↑ FAZ.net January 4, 2019: Google smuggled 20 billion euros through tax loophole
- ↑ Frankfurter Allgemeine Zeitung, Google's German tax saving model , January 29, 2016
- ↑ Google employs more temporary workers than its own employees
- ↑ 15 years of Google Switzerland - “Google.ch has plowed up the Swiss online landscape”. In: srf.ch . September 10, 2019, accessed September 29, 2019 .
- ↑ The triumph of great numbers . Neue Zürcher Zeitung . April 25, 2008. Retrieved May 6, 2008.
- ↑ 20 years of Google: BackRub - This is how the history of Google began over two decades ago . In: GoogleWatchBlog . August 26, 2018 ( googlewatchblog.de [accessed September 2, 2018]).
- ^ John Battelle: The Birth of Google . In: Wired , August 2005.
- ↑ Googling like a god mz-web.de September 14, 2008
- ↑ Google Official Company History , February 8, 2008
- ^ "Google, a $ 100,000 misunderstanding" , Heise online , September 7, 2008
- ^ David Koller: Origin of the name "Google". Retrieved October 19, 2016 .
- ^ View of the Garage 1998 on the Google website
- ↑ Company history in detail: 2002 , Google Inc.
- ↑ Sergey Brin, Lawrence Page: The anatomy of a large-scale hypertextual Web search engine . In: Computer Networks and ISDN Systems . tape 30 , no. 1-7 , 1998, pp. 107–117 , doi : 10.1016 / S0169-7552 (98) 00110-X (English, stanford.edu [PDF; accessed March 9, 2020]).
- ↑ LA Barroso, J. Dean, U. Holzle: Web search for a planet: the google cluster architecture . In: IEEE Micro . 23, No. 2, April 29, 2003, pp. 22-28. doi : 10.1109 / mm.2003.1196112 . "We believe that the best price / performance tradeoff for our applications comes from fashioning a reliable computing infrastructure from clusters of unreliable commodity PCs."
- ^ Google Acquires Usenet Discussion Service and Significant Assets from Deja.com
- ↑ Blogger.com: About us . Retrieved December 5, 2014.
- ^ Google Buys Applied Semantics
- ↑ Google Acquires Picasa
- ↑ Google Acquires Keyhole Corp.
- ^ Google Inc .: Google Agrees To Acquire Urchin , March 28, 2005
- ↑ a b VentureBeat: Google Acquires Dodgeball
- ↑ Where Are You? Show 'Em With Google Latitude
- ↑ BusinessWeek: ( Memento of October 21, 2011 in the Internet Archive ) Google Buys Android for Its Mobile Arsenal
- ↑ Official Google Blog: We're expecting ( Memento from December 30, 2009 in the Internet Archive )
- ↑ Official Google Blog: More sharing ( Memento from December 30, 2009 in the Internet Archive )
- ↑ Official Google Blog: A new home for @Last Software
- ↑ tagesschau.de: Google swallows video portal YouTube ( Memento from July 17, 2009 in the Internet Archive )
- ↑ Google took over the wiki startup JotSpot , heise.de
- ↑ BuchMarkt 3/2007, p. 25
- ↑ Google Visualization API Gadget Gallery , Google Developers
- ↑ Google buys DoubleClick for 3.1 billion US dollars , golem.de
- ↑ "Google and DoubleClick were turning together more than 80 percent of the advertising that provides users Internet on when he drives a website, they argued." Spiegel.de
- ↑ Ranking. Google is the most valuable brand in the world , spiegel.de, April 23, 2007.
- ↑ spiegel.de: for March 2007: “1. Google (528 million visitors) 2. Microsoft (527 million visitors) 3. Yahoo (473 million visitors) 4. Time-Warner (272 million visitors) 5. Ebay (256 million visitors) 6. Wikipedia (212 million visitors) "
- ↑ Google integrates GrandCentral as Google Voice , heise.de
- ↑ Geoeye-1: Google's satellite delivers the first picture , netzwelt.de
- ↑ Google throws a GeoEye-1 on Earth , silicon.de
- ↑ Bernd Kling: Google sees you - now even more sharply , itespresso.de, September 7, 2008
- ↑ AdSense Blog: Increase Income With Customized Ads
- ↑ Behavioral targeting on Google AdSense and YouTube , golem.de
- ↑ Personalized advertising - Google knows where you are surfing , sueddeutsche.de
- ↑ Alexis Johann: Google Ventures distributes 100 million to start-ups ( Memento from December 8, 2014 in the Internet Archive ) . wirtschaftsblatt.at, April 1, 2009
- ↑ ZDnet: Google starts investment company Google Ventures
- ↑ Google's newest venture , Google Blog
- ↑ What Is Google Squared? It Is How Google Will Crush Wolfram Alpha (Exclusive Video) , Techcrunch
- ↑ Google Squared is online , heise online
- ↑ Google publishes the Chrome OS source code. Heise Online, November 19, 2009, accessed November 20, 2009 .
- ↑ Technical details about the Google Nexus One - fairhandy. Retrieved August 25, 2020 .
- ^ Press release from Google on February 1, 2011. Accessed February 11, 2011 .
- ^ Google Fiber - How to get Fiber , fiber.google.com, accessed March 8, 2013
- ↑ Volker Briegleb: Google takes over Motorola Mobility . heise online, August 15, 2011.
- ↑ Roland Lindner: Sale to Lenovo: Google is selling Motorola again . FAZ.NET, January 29, 2014.
- ↑ Google takes over restaurant guide Zagat Survey , accessed on September 12, 2011
- ↑ Google is pushing the floor of the super lobbyists , Lobbycontrol, July 29, 2011
- ↑ Google's Lobbying Blitz , Newsweek, July 23, 2011
- ^ Expanding the Internet domain space. In: Google Official Blog. Retrieved July 5, 2012 .
- ↑ 70 New gTLD applicants from Germany - Google and Amazon top the list. In: united-domains blog. Retrieved May 7, 2012 .
- ↑ Internetnews.com , accessed August 16, 2012
- ↑ Google withdraws three domain applications. In: united-domains blog. September 6, 2012, accessed October 15, 2012 .
- ↑ Lisa Hemmerich: Takeover: Google buys the instant messaging service Meebo. In: netzwelt . June 5, 2012, Retrieved September 18, 2012 .
- ↑ Annika Demgen: Link-Wink: Google launches “Founder's Garage” in Berlin. In: netzwelt. August 3, 2012, accessed August 4, 2012 .
- ^ Yvonne Ortmann: Battle of the photo services: Google grabs the photo app Snapseed. (No longer available online.) In: t3n magazine . September 18, 2012, archived from the original on September 19, 2012 ; accessed on February 4, 2019 .
- ↑ Yvonne Ortmann: Google Ingress: Worldwide Alternate Reality Game for the Smartphone. (No longer available online.) In: t3n magazine. November 17, 2012, archived from the original on November 19, 2012 ; accessed on April 2, 2019 .
- ↑ Lars Budde: Google integrates company photos in search results. In: t3n magazine . December 20, 2012, accessed December 21, 2012 .
- ↑ Pascal: Chromebook Pixel presented. In: googlewatchblog.de. February 21, 2013. Retrieved July 22, 2013 .
- ↑ Jürgen Kuri: Google: Chromebook Pixel with touchscreen and high-resolution display. In: heise online. February 22, 2013. Retrieved March 22, 2013 .
- ↑ January Tissler: Google Keep: officially launched service notes. In: t3n magazine. March 20, 2013, archived from the original on March 22, 2013 ; Retrieved March 22, 2013 .
- ↑ Jürgen Vielmeier: How Google still manages to surprise. (No longer available online.) In: Netzwertig. March 21, 2013, archived from the original on March 23, 2013 ; Retrieved March 22, 2013 .
- ↑ Jan Tißler: Google Account Inactivity Manager: This is how you manage your digital estate. In: t3n magazine. April 11, 2013, accessed April 12, 2013 .
- ↑ Via the Account Inactivity Manager. In: Help. Google Inc., accessed April 12, 2013 .
- ↑ Kim Rixecker: Project Loon: Hot air balloons bring the Internet to remote areas. (No longer available online.) In: t3n magazine . June 17, 2013, archived from the original on June 20, 2013 ; accessed on April 2, 2019 .
- ↑ Andreas Donath: Boston Dynamics: Google is buying military robot manufacturers at the end of the year. Golem.de , December 14, 2013, accessed December 16, 2013 .
- ↑ Henning Steier: Google is buying DeepMind. nzz.ch , January 27, 2014, accessed on January 31, 2014 .
- ↑ Henning Steier: Google buys Google wants to buy Nest Labs. nzz.ch , January 14, 2014, accessed on March 27, 2018 .
- ↑ NTV: Hyper-fast and soaring: Google is buying drone builders. n-tv.de , April 16, 2014, accessed on April 16, 2014 .
- ↑ Google is buying satellite imagery specialists. Handelsblatt, accessed on June 10, 2014 .
- ↑ Google treats itself to an airport , sueddeutsche.de on November 11, 2014
- ↑ Google rents Californian airfield for 60 years , heise.de, November 11, 2014
- ↑ Google Pixel: Release, technical data, pictures and price. October 5, 2016, accessed August 25, 2020 .
- ↑ Pixel 3a (XL): The presentation date for the new Google phone has been set. April 16, 2019, accessed August 25, 2020 .
- ↑ techcrunch.com: Google is acquiring data science community Kaggle
- ↑ Billion deal: Google buys parts of the HTC smartphone division - Golem.de . ( golem.de [accessed on September 22, 2017]).
- ↑ bloomberg.com: Alphabet Finishes Reorganization With New XXVI Company
- ^ Rick Osterloh: Helping more people with wearables: Google to acquire Fitbit. In: blog.google. November 1, 2019, accessed November 1, 2019 .
- ↑ Google share climbs over $ 400 , heise.de
- ↑ Record: The Google market value rises to over 150 billion dollars , spiegel.de
- ↑ Google is worth more on Wall Street than IBM , heise.de
- ^ Shares in Apple and Google at all-time highs , heise.de
- ↑ heise.de: Google's market value cracks the 200 billion mark
- ↑ "Google has now overtaken all technology and Internet stocks with the exception of Microsoft [market value $ 293 billion . Overall, Google shares are worth more than those of network equipment company Cisco Systems [199 billion], chip giant Intel [158 billion], and computer industry leaders IBM [156 billion] and Hewlett-Packard [137 billion] . "] Orf.at
- ↑ "A few days ago the price of Google shares exceeded the 600 dollar mark and the company is now in tenth place in the ranking of the most valuable US companies." Sueddeutsche.de
- ↑ Google share: 100 US dollars more expensive in just three weeks , heise.de
- ↑ welt.de: Google share also cracks the 700 US dollar mark
- ↑ Annual report Google Inc. (PDF; 127 kB)
- ^ Catullus Pro. In: Berthold Types. Retrieved August 26, 2012 .
- ↑ Specification of the font “Product Sans” https://storage.googleapis.com/g-design/static/product-sans-specimen.pdf
- ↑ Google commits $ 1 billion to charity. The Boston Globe, October 12, 2005, accessed August 23, 2016 .
- ^ Peter Haber, Jan Hodel: Internet. In: Historical Lexicon of Switzerland . December 20, 2018 , accessed March 4, 2020 .
- ↑ aecom.com ( Memento from January 18, 2015 in the web archive archive.today )
- ↑ Internet and society: Google builds research institute in Berlin - Article at Golem.de , from February 16, 2011
- ↑ David Drummond: Google: "Understanding the Interaction of Internet, Research and Society" . Zeit Online, October 25, 2011
- ↑ Discover our data center locations. Accessed December 25, 2019 .
- ↑ Google builds in Asia. In: n-tv. December 15, 2011, accessed August 26, 2012 .
- ↑ Google green , accessed February 3, 2016
- ↑ How much energy does the grid consume? Time online, May 13, 2011
- ↑ Google discloses its energy consumption for the first time Die Welt, September 8, 2011
- ↑ Jonathan D. Koomney, Professor at Stanford University - Growth In Data Center Electricity Use 2005 To 2010 (PDF) blog post on Koomney's website . Retrieved April 23, 2015.
- ↑ https://www.heise.de/newsticker/meldung/Militaer-Projekt-Maven-Hunderte-Wwissenschaftler-unterstuetzen-protestierende-Google-Mitarbeiter-4050834.html
- ↑ Always this bad, bad Internet , ZEITonline, accessed on January 11, 2012.
- ↑ Google wants to rule the world , Die Presse, accessed January 15, 2012
- ^ Napper, Zapper, Bauernfänger In: Süddeutsche Zeitung January 14, 2012.
Coordinates: 37 ° 25 '20 " N , 122 ° 5' 4" W.








