mechanical engineering


The mechanical engineering (also known as mechanical engineering called) is a classic engineering science and extends to development, design and manufacture of machines. These include
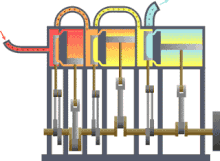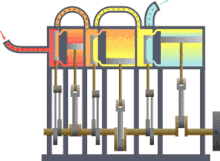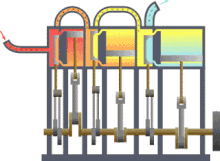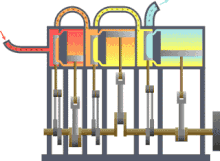
- Power machines ( steam engine , motor or turbine ),
- Working machines ( blower , pump or compressor ),
- Machine tools ( turning , milling or grinding machine ),
- Conveyor systems ( crane or conveyor belt ) and the
- Vehicle technology
- Aerospace Engineering
- Apparatus, devices and special machines for rationalization means construction .
The mechanical engineering branch of industry emerged from the craft of metalworking, blacksmiths and locksmiths, etc. a. by Mühlenbauer.
history
Mechanical engineering as an institutionalized science emerged in the course of industrialization . However, some theoretical and practical findings are much older: the first forerunners of manufacturing technology are as old as mankind. The first hand axes were built for scraping, scratching and cutting; in the Stone Age , more special shapes for drilling and sawing were added. The discovery of copper heralded the transition to the Bronze Age , in which the smelting of copper ore, forging and also casting were discovered. In the early advanced cultures of Mesopotamia , the first engineers were trained in reading, writing and arithmetic at palace or temple schools. Important discoveries were the wheel and the inclined plane .
In ancient times , mechanics was established as an important theoretical basis for many of today's engineering sciences. Archimedes , Aristotle and Heron of Alexandria published books and writings on levers , screws, inclined plane, rope, pulley blocks and other inventions. Catapults were improved through systematic experiments until the best dimensions were found. Archimedes made experiments with the displacement of various metals and Heron built the first steam engine. The first automatons that could move independently were also built for the Greek theater. The Romans adopted Greek technology, but made comparatively little progress themselves, such as cranes with pulleys and treadles , improved catapults and the first grinding and lathes as well as water mills .
In the Middle Ages , windmills and water mills spread across Europe and became the most important source of energy. The mill builders gained a lot of experience with wind and water wheels, gears , transmissions and other mechanical transmission elements. In the military field, the catapults have been replaced by the triboxes . Towards the end of the Middle Ages, a new branch of industry emerged with precision mechanics, which dealt with the construction of clocks and measuring devices and gained a lot of experience with the precision machining of metal parts, which were mostly made of brass. There were locksmiths for the finishing of iron . With the guilds and guilds, institutions emerged for the first time that dealt with the knowledge of their trade.
In the Renaissance , Leonardo da Vinci developed a large number of machines, some of which were far ahead of his time. From the middle of the 16th century many engineers published so-called machine books , which, however, were often intended to amaze the reader with exaggerated and fantastic representations. Most of the images were not intended to be reproduced, and even impossible machines such as perpetual motion machines were often shown. It was not until 1700 that the images were shown as dimensioned parallel projection .
Thomas Newcomen built the first functioning steam engine in England at the beginning of the 18th century, which was decisively improved by James Watt towards the end of the century and then quickly spread. It was often used to drive the new spinning and weaving machines , which, in addition to carpenters, joiners, precision mechanics and blacksmiths, were mainly built by mill builders, who are therefore considered to be the forerunners of mechanical engineering. The new machine tools , which were also powered by steam engines, were used to build the steam and textile machines . With the puddling process , a method was also available to produce wrought iron in large quantities, which was also increasingly used for machines. At the beginning of the 19th century there was already a pronounced industrial mechanical engineering in England, which soon dealt with steam locomotives , but was still characterized by tinkerer-engineers trained in the craft. In 1818, the Institution of Mechanical Engineers was the first association of mechanical engineers, which was followed by many similar ones in other industrialized countries.
In France, the École polytechnique was founded in 1794 , which trained engineers who went into the civil service and were mainly active as civil engineers . Many famous scientists worked at the Ecole Polytechnique, such as Carnot ( Carnot process ) or Gaspard Monge , a pioneer of descriptive geometry . Machines were no longer rated solely on their functionality, but also on their efficiency . For the private industry , the Ecole Centrale des Arts et Manufactures was founded, which trained mechanical engineers for the higher positions, as well as several École des Arts et Métiers , who trained for the master level.
In the German-speaking countries at the beginning of the 19th century they wanted to catch up with the industrial deficit compared to England as quickly as possible and therefore founded a large number of so-called polytechnic schools , modeled on the Ecole Polytechnique. In the course of the century they were upgraded to technical universities and at the end of the century were given the right to award doctorates and were thus on an equal footing with older universities . The Association of German Engineers , which was founded in the middle of the century and which, in addition to mechanical engineers, also brought together civil engineers and electrical engineers, soon became the world's largest engineering association. The most important founders of scientific mechanical engineering in Germany include Franz Reuleaux , Karl Karmarsch and Ferdinand Redtenbacher , who dealt with mechanics, production technology, steam and machine tools.
At the beginning of the 20th century, an academic degree was already standard for young engineers. As a student, Rudolf Diesel had heard lectures on the theoretically possible efficiency of heat engines , in which it was also reported that the conventional piston steam engines only show a fraction of this as efficiency. From this theoretical knowledge he developed the first working diesel engine . At the beginning of the century, industrial mechanical engineering was characterized by the production of sewing machines and bicycles , later cars and airplanes , which were then also powered by jet engines.
Connections
Mechanical engineering is characterized by engineers , technicians and skilled workers . Depending on the size of the company and the focus of the company, they work on the idea , draft , calculation , design , construction , optimization , research and development , production and sale of machines of all kinds and their components . Starting with individual machine elements, products or systems of the greatest complexity such as production lines and entire factories are planned, developed, built and operated.
For example, construction theory deals with the goals and methods that a mechanical engineer / technician must observe when designing technical systems using standards (e.g. the DIN standards ). The technical systems are now designed on the computer with the help of CAD programs . The CAD files generated in the process can then be subjected to a simulation (including the finite element method ) and produced by a CNC machine. Another way is reverse engineering , in which a computer model is created from an existing body, which can then be further processed, e.g. B. Freeform surfaces on automobile bodies or turbine and compressor blades . Due to the increasing automation installations are today with a complex measurement and control and regulation technology equipped, which are designed as mechanical engineers.
Disciplines
Exactly which disciplines belong to mechanical engineering and how they should be classified is - as with many other engineering sciences - sometimes controversial. There is no more precise definition for mechanical engineering than there is a generally accepted definition for machine . Which objects are designated as machines, apparatus or devices is often coincidental or historically determined. In complete works on mechanical engineering, the division of chairs at the mechanical engineering faculties of universities and in the courses, however, there are numerous topics that are always dealt with and thus make up the core areas of mechanical engineering. These include, for example, technical mechanics, design theory and production technology.
There are several ways to categorize these areas:
- Subjects more concerned with construction and those more concerned with manufacturing. This division is related to the division of labor in industrial practice, in which designers ultimately create design documents and pass them on to the production engineers who select and procure the manufacturing processes and machines.
- Basic subjects and application-oriented subjects. This division can be found primarily in the degree programs in which at the beginning mostly subjects are taught that are close to the natural sciences, such as technical mechanics, technical thermodynamics or technical fluid mechanics, and later (sometimes also in parallel) technical drawing, standards, Manufacturing technology of special machines such as turbines or diesel engines.
- Classification according to technology: vehicle technology, conveyor technology, aerospace technology, medical technology are typical specializations in the course.
In addition, it must be taken into account that mechanical engineering - like all engineering sciences - is strongly interdisciplinary. Other independent engineering sciences are also taught within mechanical engineering and used as auxiliary sciences. These include, for example, materials engineering and electrical engineering. In addition, some areas are not an original part of mechanical engineering, but rather interdisciplinary engineering sciences themselves. Technical mechanics, for example, also plays a major role in civil engineering and thermodynamics in process engineering, but with different focuses and goals. In mechanical engineering, for example, thermodynamics are used for the calculation and analysis of heat engines, while chemical reactions are in the foreground in process engineering . The measurement, regulation and control technology (summarized automation technology ) is also processed jointly by machine builders and many other engineers. There is a large overlap in content between mechanical engineering on the one hand and process engineering, chemical engineering and mechatronics on the other. The former is sometimes even viewed as a branch of mechanical engineering. There are also transitions to the humanities and social sciences. These include industrial engineering , medical technology or patent engineering .
Technical mechanics

Technical mechanics is a branch of engineering . Its scientific basis is classical mechanics , which in turn is a branch of physics . Sub-areas of technical mechanics are
- the statics which deals with stationary, rigid bodies,
- the strength theory treats the resting, deformable body and
- the dynamics for moving bodies.
A further area in mechanical engineering is machine dynamics . Technical mechanics is responsible for providing the theoretical calculation methods for determining forces and moments . The actual dimensioning, selection of materials and the like is then taken over by other disciplines in which technical mechanics is an auxiliary science.
Fluid mechanics or fluid mechanics
Fluid mechanics or fluid mechanics is the physics of fluids , i.e. especially of gases and liquids. The names fluid mechanics or fluid dynamics , instead of fluid mechanics used.
The aim is the theoretical calculation of flows, e.g. B. Currents in pipelines , in internal combustion engines , turbines, fans or behind bodies in flow ( air resistance in vehicles). In the application cases, key figures are used that describe the properties (e.g. behavior and type of fluid, flow type and shape) of the fluids. The flow processes can be described mathematically using the principles of the continuity equation (“Everything that flows in, flows out again”), the conservation laws for mass , energy and momentum and the Navier-Stokes equations .
A scientific area that uses fluid mechanics is rheology , which deals with the deformation and flow behavior of matter.
Technical thermodynamics
Thermodynamics, also known as heat theory, is a branch of classical physics. It is the study of energy, its appearance and ability to do work. It proves to be versatile in application in chemistry, biology and technology. In mechanical engineering it is used to calculate the efficiency of machines and for the construction and analysis of heat engines such as gasoline and diesel engines, gas and steam turbines. Technical thermodynamics is a purely macroscopic theory that assumes that the physical properties of a system can be described sufficiently well with macroscopic state variables. It is an efficient theory because it neglects the movement of the individual atoms and molecules and only considers medium quantities such as pressure and temperature . Further topics in thermodynamics are heat transfer and refrigeration technology , which deals with the extraction of heat by appropriate refrigerants .
Materials engineering
The Materials Engineering is an independent engineering discipline which has a special affinity for mechanical engineering. In mechanical engineering, the mechanical material parameters ( hardness , strength , modulus of elasticity , wear resistance ) are particularly important. Chemical properties also play a role insofar as they relate to corrosion resistance ; electrical and magnetic parameters, on the other hand, do not play a special role. An important sub-area is materials testing, which deals with the determination of these parameters.
Ceramics , polymers (plastics) and metals are used as construction materials in mechanical engineering . Metals are of greatest importance, especially steel and cast iron , but also aluminum , the latter especially in industries where weight plays a major role, e.g. B. the aerospace engineering .
Materials technology determines relationships between the structure of the materials ( crystal lattice , grain size , structure ) and the properties of the materials . Building on this, targeted structural changes, e.g. B. with steel hardening and tempering or by introducing alloying elements , desired property profiles are set. When steel, z. B. the weldability or the formability adjusted by varying the carbon content . Other properties, such as corrosion resistance, can be achieved by alloying.
Construction theory
The design theory or engineering includes the basics of construction , i. H. all those synthesis, analysis, evaluation and selection activities that are necessary to provide the best possible solution for a specific technical task at a specific point in time.
As part of the construction methodology, methods for systematic brainstorming, solution synthesis and variant evaluation are taught, e. B. in the constructive development process , product lifecycle management or computer-aided engineering (CAE) . This is used to find the best possible solution with a large number of alternative solutions.
In order to be able to assess these alternative solutions individually, however, basic knowledge of mechanical construction or machine elements , their dimensioning and design and their manufacture is necessary. In addition, documentation of the task and solutions must be guaranteed. This takes place u. a. in the burden- and requirement specifications and technical drawings .
The technical drawings are based on a uniform form of representation, which is described in standards for dimensional, shape, position and surface tolerances. These basics are just as much in the field of construction theory as techniques for creating drawings, both by hand via the descriptive geometry and with the help of appropriate computer programs (see CAD ).
Machine elements
Machine elements are the smallest components of machines that are used particularly frequently and are therefore often standardized and can be purchased. This includes, for example, small parts such as screws , bolts and pins , gears , springs , sealing rings , assembled parts such as ball bearings and entire components such as gears , clutches and brakes . There are also various connecting elements such as welded connections , soldered connections , riveted connections and adhesive connections , elements for the transmission of movements such as axles and shafts and slide bearings .
Measurement and Control Technology

Metrology deals with the experimental measurement of systems, since although every determinable variable has an exact value, this cannot be precisely recorded due to measurement errors.
The measurement technology can be divided into the experimental measurement technology, where it is about the clarification of effects and the highest possible accuracy is required, and into the measurement technology for technical applications. Robust measurement technology is required for technical applications, but it is also inexpensive. Another requirement is to measure as precisely as necessary and as quickly as possible .
The measured quantity determined consists of the measured value, a measurement error and a unit of measurement (is an SI unit or a quantity derived from it). The measured variable then looks like this, for example: (10 ± 0.1) V or 10 V ± 1%. The quantities to be measured can be divided into electrical (current, voltage, ...) and non-electrical ( temperature , pressure , time , mass, etc.) quantities. Non-electrical quantities can be converted into electrical signals by means of corresponding effects ( Seebeck effect , induction law , ...), which are required for control technology (see also measurement and control technology ) and automation technology.
manufacturing engineering
Manufacturing technology is a mechanical engineering discipline that deals with the manufacture of workpieces. Based on the design documents, the workpieces should be manufactured as economically as possible. The manufacturing processes include, for example, casting, forging, milling, drilling, grinding, soldering, welding, coating and hardening. The focus of manufacturing technology is on the similarities and differences between these processes, which are divided into groups and subgroups. During milling, plasma cutting and punching, for example, material is removed from a raw part; they are therefore assigned to the Separation group , while welding, screwing and soldering are used to connect parts and are assigned to the Joining group . In addition to the manufacturing processes, the associated tools and machines are also dealt with, their selection, production measurement technology and production planning and control .
Drive technology

According to the EU directive, a machine only becomes a complete machine through drive technology , since parts of the machine can only move independently through a drive .
Starting from a motor that generates the movement, it is sent to the point of action via shafts , V-belts and / or gears . In stationary machines nowadays electric motors such. B. synchronous machines or stepper motors (in exceptional cases also linear motors ) are installed as motors, since these machine movements can be synchronized very well . However, if the energy supply, unlike above, cannot be provided by a power line, as is the case with most non-stationary machines - which occurs in many types of motor vehicle, for example - drive types that do not require a power line are predominantly used in such cases .
In the decades following the industrial revolution , a continuous rotary movement in drive technology was provided centrally by a motor and passed on through a vertical shaft and drive belt . The rotary movement could be converted into a clocked translational movement by means of appropriate cam , coupling and / or belt drives . Nowadays, instead of the central drive, a decentralized system of drives is increasingly being built into machines. In other words, there is no longer one motor that drives everything via one shaft. Instead, many small motors take over the individual movements. Often these are servomotors that can execute a wide variety of movements by programming the drive control accordingly. For this reason, servo drives are also called electronic cams .
Power and working machines
Power machines convert any energy into mechanical drive energy, working machines use mechanical energy to do work. Often, by reversing the functional principle, a working machine can be converted into a power machine.
The power machines include the steam engine , for example , but the following machines are of importance today: Otto and diesel engines , gas turbines , water turbines and steam turbines .
The working machines include: pumps , compressors , compressors , turbines and blowers .
Conveyor technology
Conveyor technology deals with machines and systems that are used for transport over short distances (conveying). These include, for example, conveyor belts, forklifts, cranes, driverless transport systems , pipelines, screw conveyors and pallet trucks. Many of these conveyor systems consist of components that can be combined with one another in many ways in order to adapt them to the respective application. These include, for example, steel cables, chains, brakes, drives, hooks, grabs and hoists . A part of the conveyor technology is the material flow technology that deals with the information flows. The conveyor technology takes care of the internal transport; the off-site, on the other hand, is a matter of traffic engineering that is carried out with vehicles.
Vehicle technology
Vehicle technology deals with different vehicles. In a narrower sense, it is understood to mean motor vehicle technology, which primarily includes cars and trucks. The most important components are the chassis , the drive (engine, transmission, etc.), the body and the interior. In a broader sense, which belong to the Automotive Engineering Railway Engineering and Aircraft Technology (especially aircraft technology) associated with the aerospace engineering is related. There is also shipbuilding .
Machine tools
Machine tools are machines that are used to machine workpieces. These include, for example, milling machines, drilling machines, saws, forging hammers, presses, rolling machines, water jet cutting machines and punching machines. Mechanical engineering deals on the one hand with the design of machine tools and on the other hand with their selection and use in industrial production. Their most important properties are working accuracy and productivity. The most important components are the drive, the control, the frame and the guides.
education and study
University, technical college
At universities (including technical universities ), technical universities and technical colleges , the mechanical engineering degree is one of the three classic training paths (in addition to electrical engineering and civil engineering ) for prospective engineers .
As a rule, 10 semesters are specified as the standard period of study , with successful completion of the degree the academic degree Dipl.-Ing. (or Dipl.-Ing. (FH) ) awarded. In the course of standardizing the structures of higher education in Europe, a tiered study system will be introduced ( Bologna process ). This process should be completed by 2010. By this point in time, the universities and technical colleges should abolish the diploma course and replace it with a bachelor's degree. The first-year students were able to achieve the academic degree Bachelor of Science or Bachelor of Engineering after 6 to 8 semesters of standard study time and after a further 2 to 4 semesters the academic degree Master of Science or Master of Engineering . Some colleges, such as B. the Zittau / Görlitz University and the Dresden University of Technology and Economics will continue to offer the diploma course until further notice.
Since the range and size of the products vary from e.g. From small clockworks to household appliances and motors to mass-produced goods and huge bucket wheel excavators , an engineer can no longer cope with these tasks alone. Therefore you specialize in later studies on a specific subject area (eg. As lightweight , production engineering , textile engineering , marine engineering , Paper Technology , Industrial Engineering u. A.). Partly it have independent courses such as engineering computer science , production and logistics , process engineering , process engineering , power engineering , automotive engineering , aerospace engineering , mechatronics u. a. established.
Technical school (technical school)
In addition to engineering training at universities and technical colleges, non-university training as a mechanical engineer is traditionally of great importance in German-speaking countries . In Germany, the 4-semester technical college course requires subject-specific vocational training and several years of professional experience and is concluded with the examination to become a state-certified technician . In Switzerland, after six semesters and having passed the diploma examination, you can become a dipl. Call technician TS / HF . In Austria there are, in addition to the education at universities and colleges, the opportunity to study engineering at a HTL to complete.
Dual vocational training
In the German-speaking area, mechanical engineering offers a variety of commercial-technical vocational training within the dual system . Typical embodiments are professional technical draftsman , Konstruktionsmechaniker , Zerspanungsmechaniker , industrial mechanic or mechatronics . In addition, some universities offer a dual course of study , i.e. a standard course in connection with internship semesters or recognized training.
literature
- Karl-Heinrich Grote, Jörg Feldhusen (Hrsg.): Dubbel - paperback for mechanical engineering . 24th edition. Springer, Berlin 2014, ISBN 978-3-642-38890-3 (standard work).
- Alfred Böge (Hrsg.): Manual mechanical engineering: Basics and applications of mechanical engineering. 23., revised. Edition. Springer Vieweg, Wiesbaden 2017 (December 23, 2016), ISBN 978-3-658-12528-8 .
- Ekbert Hering, Karl-Heinz Modler (ed.): Basic knowledge of the engineer. 14th, updated, edition. Fachbuchverlag Leipzig, Leipzig 2007, ISBN 978-3-446-22814-6 .
- Horst Czichos, Manfred Hennecke: Hut. The engineering knowledge . 33rd edition. Springer, Berlin 2007, ISBN 978-3-540-20325-4 .
- Heinz M. Hiersig : Lexicon of mechanical engineering . VDI Verlag, Düsseldorf 1995, ISBN 3-18-401372-3 .
- Jürgen Dispan, Martin Schwarz-Kocher: Mechanical and plant engineering in Germany. Development trend and challenges. Stuttgart 2014 ( imu-institut.de PDF; 7.6 MB).
- Werner Skolaut (Hrsg.): Mechanical engineering - A textbook for the entire Bachelor degree. Springer, 2014.
Web links
- Mechanical engineering portal: list of topics
- Industry sketch of the Federal Ministry of Economics and Labor
- VDI website
- IMU industry study on digitization in mechanical engineering 2018
Individual evidence
- ^ Paulinyi, Troitzsch: Propylaea history of technology. Volume 3, 1997, p. 45.
- ↑ König, Kaiser: History of the Engineer.
- ^ Propylaen (ed.): Propylaen technical history.
- ^ Agricola Society (ed.): Technology and education.
- ^ Agricola Society (ed.): Technology and science.
- ↑ a b Günter Ropohl : How technology comes to reason - contributions to the paradigm shift in technical sciences. 1998, p. 32 f., 88.
- ↑ Der Dubbel , Hütte - Des Engineer's pocket book or manual mechanical engineering by Alfred Böge
- ↑ a b Skolaut: Mechanical engineering. 2014, p. 2.
- ↑ Rudolf Koller (Ed.): Design theory for mechanical engineering . 3. Edition. Springer-Verlag, Berlin 1994, ISBN 3-540-57928-1 , pp. XVIII .