Doubs
| Doubs | ||
|
The course of the Doubs |
||
| Data | ||
| Water code | FR : U2-0200 , CH : 135 | |
| location | France , Switzerland | |
| River system | Rhône | |
| Drain over | Saône → Rhône → Mediterranean | |
| source | at Mouthe 46 ° 42 ′ 18 ″ N , 6 ° 12 ′ 34 ″ E |
|
| Source height | 937 m | |
| muzzle | near Verdun-sur-le-Doubs in the Saône Coordinates: 46 ° 54 '5 " N , 5 ° 1' 26" E 46 ° 54 '5 " N , 5 ° 1' 26" E |
|
| Mouth height | 170 m | |
| Height difference | 767 m | |
| Bottom slope | 1.7 ‰ | |
| length | 453 km | |
| Catchment area | 7710 km² | |
| Drain |
NNQ MQ HHQ (1990) |
21 m³ / s 176 m³ / s 1400 m³ / s |
| Left tributaries | Drugeon , Dessoubre , Clauge , Loue , Orain , Guyotte | |
| Right tributaries | Allan , Sablonne | |
| Big cities | Besançon | |
| Medium-sized cities | Montbeliard , Dole | |
| Small towns | Pontarlier | |
| Navigable | in sections | |
|
The Doubs between Laissey and Deluz , just before Besançon . |
||
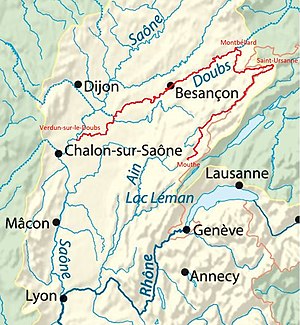
The Doubs [du] (German Dub ) is a Franco-Swiss river in the east of France and in the north-west of Switzerland . It is the left and largest tributary of the Saône . In antiquity, the Doubs, which was in the Sequani region, was called Dubis and was mentioned by Julius Caesar and Strabon , among others .
geography
Source du Doubs
The Source du Doubs (Eng. Source of the Doubs ) is a mighty karst spring in a heavily karstified area of the Jura Mountains . It is located near Mouthe , in the Haut-Jura Regional Nature Park , at an altitude of 937 m at the foot of the wooded, up to 1419 m high mountain range of Mont Risoux , on which the border between France and Switzerland runs. The Doubs rises from a cave in the rock from a small spring pot about five meters deep . The spring pours an average of 1740 liters per second and is the exit of a complex cave system with several siphons . The pouring can vary greatly. On the rock above the spring you can distinguish several layers of rock . Below the source, the river falls over a small waterfall. About two kilometers below the Source du Doubs, the nine-kilometer-long Cébriot flows into the Doubs.
Flow description
After its source, the Doubs initially turns northeast through Pontarlier , flowing through the Lac de Moron reservoir towards Delémont , forming the border to Switzerland from Les Brenets . It falls over the Saut du Doubs , a 27 m high waterfall, and then flows over a short stretch of about 29 km entirely on Swiss territory. This section of the river is called the Clos du Doubs . After Saint-Ursanne , the river changes direction again to the west and leaves the Swiss territory at Ocourt and La Motte on the Swiss side and Brémoncourt on the French side.
The borderline of the Doubs along the French-Swiss national border is a specialty. Unlike other rivers, the border does not run in the middle of the river, but the Doubs belongs entirely to France . This resulted from contracts between the Prince-Bishop of Basel and the King of France.
The speed of the current of the Doubs is not constant, in some places it flows calmly at only 5 km / h, in others it reaches top speeds of up to 12 km / h. The river width is also very different from 6 to 30 meters (average) and up to 200 meters wide in some places. The area is largely deserted and difficult to access because of the surrounding forests and Jura mountains.
From Saint-Ursanne, flowing westwards, the Doubs re-enters France and flows below Saint-Hippolyte , where it joins the Dessoubre on the left , through a transverse valley of the Montagnes du Lomont to the north to Audincourt . Immediately afterwards , it takes up the Allaine on the right, then turns in its lower reaches to the southwest and strives over Baume-les-Dames , Besançon and Dole , where it takes the Loue on the left , towards the Saône , into which it enters at a height of 170 m Verdun-sur-le-Doubs flows about 16 kilometers northeast of Chalon-sur-Saône .
From Goumois (next to the French town there is a community of the same name on the Swiss side ), the hamlet of Clairbief on the French border or from Soubey , kayaks are available for the route towards Saint-Ursanne. The two-kilometer stretch to Soubey can be very dangerous , depending on the water level, because of the protruding stones and the strong current in the Klus . Over a length of about two kilometers, the difficulty is according to the white water difficulty scale III.
The Doubs is 453 kilometers long, with the source and estuary just 90 kilometers apart. It drains an area of 7710 km². It has characteristics of a karst river such as B. a very irregular water flow (between 21 m³ / s at low water and 1430 m³ / s at high water in February 1990). Parts of the water of the Doubs seep away at Pontarlier and reappear in the karst spring of the Loue near Ouhans . This phenomenon was discovered when 1901 Absinth - distillery fell into Pontarlier in fire and flowed larger amounts Absinth into the river. A few days later the water in the Loue smelled strongly of anise . Subsequent staining experiments confirmed this observation.
The rare fish species Rhone nerds ( Zingel asper ) occurs in the Doubs .
Tributaries
The tributaries of the Doubs are (downstream):
|
Left tributaries:
|
right tributaries:
|
shipping
Between Montbéliard and Dole, the Doubs is partially canalized and forms part of the Rhine-Rhône Canal . The river can also be navigated by ships in its estuary between Navilly and Verdun-sur-le-Doubs.
See also
Web links
- Claude Rebetez: Doubs (river). In: Historical Lexicon of Switzerland .
Individual evidence
- ↑ Doubs at SANDRE (French)
- ↑ Regesten and Register for Acta Helvetica Gallica, Germanica 1984, Vol. 27, p. 12
- ^ Caesar, De bello Gallico 1, 38.
- ↑ Strabon, Geographika 4, 186; 4, 189; 4, 192.
- ↑ hydro.eaufrance.fr (station: U2002010 Le Doubs à Mouthe, option: Synthèse ) .
- ↑ Tages-Anzeiger of March 15, 2016, page 23.