Never home
| coat of arms | Germany map | |
|---|---|---|

|
Coordinates: 51 ° 48 ' N , 9 ° 7' E |
|
| Basic data | ||
| State : | North Rhine-Westphalia | |
| Administrative region : | Detmold | |
| Circle : | Höxter | |
| Height : | 243 m above sea level NHN | |
| Area : | 79.71 km 2 | |
| Residents: | 6084 (Dec. 31, 2019) | |
| Population density : | 76 inhabitants per km 2 | |
| Postal code : | 33039 | |
| Primaries : | 05274, 05233, 05238, 05276, 05284 | |
| License plate : | HX, WAR | |
| Community key : | 05 7 62 028 | |
| City structure: | 10 localities | |
City administration address : |
Marktstrasse 28 33039 Nieheim |
|
| Website : | ||
| Mayor : | Rainer Vidal Garcia (independent) | |
| Location of the city of Nieheim in the Höxter district | ||
Nieheim is a city in North Rhine-Westphalia , Germany and belongs to the Höxter district . It is a climatic health resort and a basic center in an area with a predominantly rural structure. There are the following historical names for the current place name Nieheim: Nihem, Nyem, Nym. Around 6,250 people live in Nieheim, which extends over an area of around 80 km².
geography
Geographical location
Nieheim is located in the north of Southeast Westphalia . Nieheim is located in the upper Weser Uplands on the eastern edge of the Eggegebirge nature park and the southern Teutoburg Forest . About half of the urban area belongs to the Steinheimer Börde , a fertile loess landscape. This was settled and cleared early on. In the west Nieheim has a share in the eastern foreland of the Egge Mountains , in the south on the Nethe bergland. The mountains surrounding the Börde are still wooded today. The historic city center of Nieheim lies exactly on the border between Börde in the north and Bergland in the south. The entire urban area belongs to the catchment area of the Weser ; the most important flowing water is the Emmer , which flows into the Weser south of Hameln .
geology
The bedrock in the urban area is mainly made up of clay , marl , limestone and sandstones from the Middle Ages , primarily from the Triassic and Jurassic . These sedimentary rocks are between one and 1.5 km thick. In the course of the earth's history, they have been folded, broken and lifted out to form a mountain of fractures .
Deeper is a solid rock plinth made of rocks from the ancient world ( Devonian , Carboniferous and Permian ). In the flat, undulating landscape of the Börden, the bedrock is covered by loose rocks from the Ice Age ( gravel , sand and loess ).
Limestone , sandstone and clay marl stones from the Middle Ages are the most important aquifers. In some cases, however, the groundwater is severely salty due to the solution of gypsum and rock salt in the deeper subsoil, so that it cannot be used as drinking water. Mineral water is partially extracted from layers of the Triassic and Permian.
The northeastern urban area is largely covered with high-yielding parabrown soils , so it is mainly used for arable farming, with pseudogleye being created to a lesser extent . In the west, the loess has largely been eroded on steeper slopes. In wider valleys with silty - loamy river sedimentations, gleye and brown floodplain soils have developed, which are used as grassland locations.
In the summer of 2007, an almost completely preserved plesiosaur skeleton was found in the disused clay pit in Nieheim-Sommersell . Only a few cervical vertebrae and the head are missing. It is the world's first almost complete plesiosaur from layers of the Lower Pliensbachian (Lower Jura). The skeleton discovered by Sönke Simonsen was recovered from the LWL-Museum für Naturkunde Münster and prepared by Manfred Schlösser.
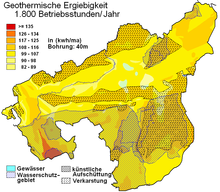
Nieheim is mostly well suited, in the south-western area very well, for the use of geothermal heat sources by means of a geothermal probe and heat recovery through heat pump heating (see the map).
Expansion and use of the urban area
The area of the city, classified as a "small rural community", covers an area of 79.79 km². The largest extension in north-south direction is approx. 11.6 km and in east-west direction approx. 13.5 km.
| Area according to type of use |
Agricultural schafts- area |
Forest area |
Building, open and operational space |
Traffic area |
Surface of water |
Sports and green space |
other use |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Area in km² | 54.12 | 17.70 | 3.02 | 9.83 | 0.69 | 0.27 | 0.16 |
| Share of total area | 67.83% | 22.18% | 3.78% | 4.80% | 0.86% | 0.34% | 0.20% |
Neighboring communities
Starting in the east and clockwise, the cities of Marienmünster , Brakel , Bad Driburg and Steinheim (Westphalia) (all of the Höxter district) and the town of Schieder-Schwalenberg ( Lippe district ) border on Nieheim .
City structure
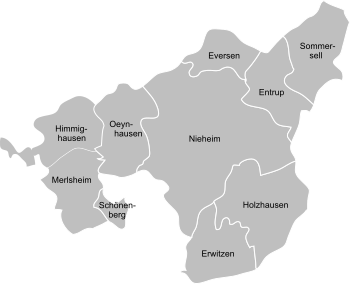
According to Section 3 (1) of its main statute, the city of Nieheim is divided into the following ten localities, which were independent municipalities in the Nieheim office before 1970 :
| District | Residents | Outline of Nieheim |
|---|---|---|
| Entrup | 351 | |
| Heating | 120 | |
| Eversen | 472 | |
| Himmighausen | 452 | |
| Holzhausen | 362 | |
| Merlsheim | 289 | |
| Never home | 2,868 | |
| Oeynhausen | 478 | |
| Schönenberg | 51 | |
| Sommersell | 643 | |
| total | 6,086 |
The number of residents (only main residences) is given here according to information from the Höxter district as of December 31, 2018.
climate
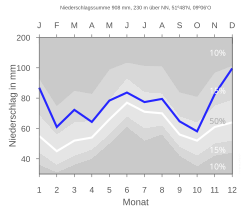
The climate in Nieheim is determined by its location in the ocean-continental transition area of Central Europe and by its location on the Egge Mountains. The area is predominantly in the area of the sub-Atlantic maritime climate , but has some temporary continental influences . The winters are mostly mild under the influence of the Atlantic, the summers are moderately warm and the rainfall is relatively evenly distributed. The annual mean temperature is around 8 ° C.
The precipitation is significantly influenced by the location on the Egge Mountains. The annual precipitation is in all months, but especially in the winter months, well above the national average. The amount of precipitation usually fluctuates between about 800 and 1000 mm annual precipitation depending on the location. Since the prevailing winds mostly blow from the south-west and bring with them moist air from the Atlantic , there is pronounced uphill rain on the windward side of the Egge Mountains .
See also: Climate in Ostwestfalen-Lippe
history
| Capitals and cities of the Principality of Paderborn until 1802/03 (as of 1789): |
|---|
| Paderborn , Warburg , Brakel , Borgentreich | Beverungen , Borgholz , Bredenborn , Büren , Driburg , Dringenberg , Gehrden , Calenberg , Kleinenberg , Lichtenau , Lippspringe , Lügde , Nieheim , Peckelsheim , Salzkotten , Steinheim , Vörden , Willebadessen , Wünnenberg |
Nieheim is mentioned as Nyhem on May 25, 1036 in the Busdorf document . In the same year, Bishop Meinwerk von Paderborn handed over the Herrenhof Nieheim with four outbuildings to the Busdorf Canon Monastery in Paderborn. Even before that, today's city of Nieheim belonged to the area of the later Paderborn bishopric . In order to counteract the expansion efforts of the Electorate of Cologne , Prince-Bishop Bernhard IV. Zur Lippe (ruled 1228 to 1247) granted the former village of Nieheim town rights with lower jurisdiction , market rights , minting rights and so on around 1230 . Nieheim forms its own office within the prince-bishopric, misleadingly called judges . The bailiff called himself a judge . The Nieheim judge was assigned to the Dringenberg Oberamt .
Then the local farmers to leave their homesteads in the Steinheimer Börde and route them to the new city, which then become a farming town developed later the Association of Cities of the Hanseatic joins.
In 1802 the Paderborn bishopric lost its state independence when it was occupied by Prussia , but fell back to the Kingdom of Westphalia for a few years in 1807 ( department of the Fulda ) and in 1813 after the Napoleonic defeat to Prussia. Nieheim is incorporated into the province of Westphalia , which was founded in 1815, and by decree of the royal government in Minden comes to the Brakel district, founded in 1816 . However, as early as 1832 this was added to the neighboring Höxter district, which was founded at the same time to the east .
When the Prussian districts are divided into offices , Nieheim becomes the seat of the Nieheim office. This exists until its communities merge to form the new city of Nieheim on January 1, 1970.
As a result of the Second World War , the number of residents of the city of Nieheim and the surrounding municipalities of the office increased by around 2000 refugees and displaced persons.
In 1956, the Barmer Ersatzkasse , whose head office was previously in Nieheim, relocated it to Wuppertal - Barmen , whereupon around 600 residents moved away from Nieheim.
Up until the 1990s there was an ammunition depot for the British Armed Forces in Germany near Merlsheim and Pömbsen on Bilster Berg . In this area, the new construction of the “ Bilster Berg Drive Resort ” car test center with an approximately 4.2 km long race track was built by 2013 .
In 1994 Nieheim won the 3rd national competition “Family Holidays in Germany” and in 1995 was recognized by the state as a health resort with a healthy climate .
Religions
The majority of the population of Nieheim is, as in the entire area of the former Hochstift Paderborn, Catholic . The Catholic parishes in the city are Sankt Nikolaus Nieheim, Sankt Antonius von Padua Eversen and Sankt Antonius von Padua Himmighausen with the branch Sankt Luzia Merlsheim, Sankt Johannes Baptist Entrup and Sankt Johannes Baptist Holzhausen, Sankt Kosmas and Damian Oeynhausen as well as St. Peter and Paul Sommersell . These parishes form a common pastoral association in the Archdiocese of Paderborn , which until June 30, 2006 belonged to the Dean's Office Brakel-Steinheim of the pastoral care region Hochstift. Since July 1, 2006 - with the dissolution of the pastoral care regions and the consolidation of the deaneries into larger units in the archbishopric - these communities have been part of the newly created Höxter deanery.
For the Protestant Christians there is the Protestant parish Marienmünster-Nieheim in the Paderborn parish of the Evangelical Church of Westphalia . House of God is the neo-Gothic cruciform church in Nieheim.
The Jehovah's Witnesses (Assembly Nieheim) have their Kingdom Hall in Wasserstr.11 since 1975th The Kingdom Hall was sold in early 2016 because a new Kingdom Hall (church building) is being built in Steinheim for Jehovah's Witnesses Congregation Nieheim and Congregation Blomberg.
An indication of the distribution of religions can be the denomination of the Nieheim students. Accordingly, in the 2006/2007 school year, 20.2% of the students stated Protestant, 70.4% Catholic and 0.3% Islamic as their religious affiliation. 6.2% said they belonged to another religion and 2.9% had no denomination.
Incorporations
On the basis of a voluntarily concluded territorial change agreement, the law on the municipal reorganization of the Höxter district of December 2, 1969, joins the previous municipalities of the Nieheim Entrup, Erwitzen, Eversen, Himmighausen, Holzhausen, Merlsheim, Oeynhausen, Schönenberg, Sommersell and the city of Nieheim on 1 December 1969 January 1970 together to form the new town of Nieheim. The Nieheim office is dissolved. The legal successor is the new city of Nieheim.
Population development
The following overview shows the population of the city of Nieheim by area . The figures are census results up to 1970 and official updates from the State Statistical Office from 1975 onwards . The figures for 1975, 1980 and 1985 are estimated values, the figures from 1990 onwards based on the results of the 1987 census. The figures for 1837 relate to the “civilian population”, from 1861 to the “local population”, from 1925 to the resident population and from 1987 on the “population at the place of the main residence”. As of December 31, 2014, Nieheim said it had 6,221 inhabitants, of which 2,869 lived in the city center. There are also 246 citizens with a second residence. According to the State Statistical Office of North Rhine-Westphalia, Nieheim had 6,221 inhabitants on June 30, 2015. Currently as of December 31, 2017, the Höxter district reports a population of 6,086 for the city of Nieheim.
Nieheim according to the territorial status at that time
|
|
Nieheim according to the current territorial status
|
|
1 census result
politics
City council
The following table shows the composition of the city council and the local election results since 1975:
| 2014 | 2009 | 2004 | 1999 | 1994 | 1989 | 1984 | 1979 | 1975 | ||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Political party | Seats | % | Seats | % | Seats | % | Seats | % | Seats | % | Seats | % | Seats | % | Seats | % | Seats | % |
| CDU | 11 | 45.4 | 13 | 50.2 | 13 | 56.60 | 14th | 55.54 | 11 | 49.08 | 14th | 49.61 | 17th | 60.88 | 17th | 63.21 | 19th | 68.81 |
| SPD | 9 | 38.1 | 8th | 35.1 | 7th | 28.91 | 7th | 29.62 | 8th | 34.19 | 8th | 31.55 | 7th | 25.90 | 7th | 25.86 | 8th | 31.19 |
| UWG 1 | 3 | 11.3 | 2 | 8.8 | 3 | 10.94 | 3 | 13.68 | 4th | 16.73 | 5 | 18.85 | 3 | 13.22 | 3 | 10.93 | - | - |
| FDP | 1 | 5.1 | 1 | 5.9 | 1 | 3.56 | 0 | 1.16 | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - |
| Total 2 | 24 | 100 | 24 | 100 | 24 | 100 | 24 | 100 | 23 | 100 | 27 | 100 | 27 | 100 | 27 | 100 | 27 | 100 |
1 Independent community of voters
2 without taking into account rounding differences
mayor
In the mayoral election on August 30, 2009, Rainer Vidal Garcia was elected with 54.0% of the valid votes and confirmed on September 13, 2015 with 68.8 percent. His predecessors were Johannes Kröling (CDU), who was elected in 1999 and 2004, and Josef Wiechers, who was in office until 1999.
badges and flags
The city of Nieheim was granted the right to use a coat of arms and a flag in a certificate from the District President Detmold dated February 8, 1974.
Description of the coat of arms :
In red a golden (yellow) free-floating cross with a downward extended bar, angled by four golden (yellow) balls.
Meaning and history of the coat of arms:
The cross and the colors red and gold come from the coat of arms of the bishopric Paderborn , whose area the city belonged to for centuries. The balls symbolize St. Nicholas , the patron saint of the city and its parish church.
The first known city coat of arms dates from 1591. It has a slightly different shape with a continuous instead of free-floating cross. It was confirmed in this form by the Prussian King on July 18, 1908.
Description of the flag:
yellow and red striped lengthways, but divided into each strip in front of a square in mixed up colors. In the upper red square the heraldic figure of the city arms.
Partnerships
Nieheim currently has no town twinning, but is a member of the New Hanseatic League of Towns .
From 2010 to 2015 there was a partnership with 1./Panzerartilleriebataillon 215 from Augustdorf .
Culture and sights
Museums
The local history and bag museum is located in the old granary in the city center of Nieheim (below the Catholic church).
The Westfalen Culinarium , which opened on April 29, 2006, consists of four museums with Westphalian specialties on 3000 square meters: the Cheese Museum, the Westphalian Ham Museum, the Bread Museum (with special Pumpernickel ) and the Beer and Schnapps Museum . German, European and global topics relating to these “staple foods” are also dealt with. The specialties of the region can also be tasted in a tasting room.
Buildings
As a landmark of Nieheim, the Holster Tower on the nearby heights of the Holster Berg south of the city center can look back on a 700-year history. The former watch tower , which is also called Nieheimer Warte , can now be climbed as a lookout tower via steps and offers a good view of Nieheim. In memory of his contested past, spears are attached outside as art objects.
The town's historic buildings worth seeing include the Nieheim town hall built in the Weser Renaissance style from 1610, and the judges' house built in 1701.
The Ratskrug, a stately half-timbered building from 1712, burned down completely in the early morning of February 7, 2016 for reasons that have not yet been clarified. The remains of the house were completely demolished shortly afterwards.
The oldest parts of the catholic parish church of St. Nicholas with a baptismal font ornately decorated with reliefs and a late Gothic tabernacle dates from the 13th century.
The Protestant Kreuzkirche Nieheim was built in the neo-Gothic style in 1868/69.
The Nikolausbach, which rises below the Holsterberg and runs in the center of the village in a medieval vault system, is unique in Westphalia.
As a relic of an almost forgotten communications technology high up on the Finnstätte near Oeynhausen is the optical telegraph station No. 32 of the Prussian optical telegraph , rebuilt by the Oeynhausen Heimatverein . Expert tours are possible on request.
The listed Johannes-der-Täufer-Kirche in Holzhausen is also worth seeing .
Natural monuments
The Nieheim wicker hedge is characteristic of the appearance of the field and corridor . The hedges consist of 80 percent hazel that are planted row. Hawthorn and individual wild roses also occur. The pollarded willows serve as living fence posts in the hedge for stabilization. The young rods for the wickerwork are taken from the pollard willows. If horses are kept on pasture in addition to dairy cattle , blackthorn branches (sloes) are tied in on the inside to prevent browsing. The finished hedges have a height of about 1.50 m and are braided in three layers.
Sports
The Bad am Holsterberg is located in the area of the school center in Nieheim . The indoor pool has a pool of 8 by 16.66 meters, the outdoor pool has a pool of 16.66 by 25 meters.
1. FC Nieheim was founded in 1937. Various youth teams, an old man and two senior teams are currently in operation. The 1st senior team plays in the district league A, the 2nd in the district league B. For a long time, FC Nieheim was one of the few (the only) clubs in the Höxter / Warburg / Lippe sports district, which provided three senior teams despite a relatively small population.
Parks
The garden of Himmighausen Castle is a privately owned, non-public area of around 1 hectare in size. The well-tended garden is accessed by a walkway, the old trees near the house and the preserved grotto on the way are particularly noteworthy. The eastern part of the garden is used as pastureland.
The Gutspark Good Grevenburg is not publicly accessible privately-held area of about 2.5 ha. The park is reasonably well maintained. It is determined by its old trees. A plant bowl with a stone base and a round water basin with a fountain probably date from the 19th century.
The Gutspark Holzhausen is a privately owned area of about 3 ha. It is accessible at events. Old trees and retaining walls, stairs, water basins and sculptures have been preserved from the original garden. The garden areas are now lawns and meadows, parts are wooded with spruce.
The Schlosspark Merlsheim is a privately owned area of around 2 hectares and is not open to the public. Originally laid out as a baroque garden, it is now very simplified, but well-kept.
Regular events
- German cheese market : Every even year on the first weekend in September, artisanal cheese manufacturers and processors from all over the world have come together in Nieheim since 1998 and present their cheese- related products . In 2006, around 60,000 guests came over the three days in addition to the more than 70 dealers from Germany and Europe.
- Nieheimer Holztage : Every uneven year on the first weekend in September on the topics of "wood, forest and nature"
- Nieheimer Kulturnacht : On the day the time changes from winter to summer time
- Nieheim Choir Festival : Voice training for choirs from all over Germany
- Nieheim Rose Monday Parade: Carnival stronghold of East Westphalia
- Jungschützenfest : One of the oldest traditional festivals is the Jungschützenfest, which takes place every three years. Here the Nieheim young rifle guild presents its king, who was shot on May 1st, along with the queen and court. Hundreds of young men from Nieheim between the ages of 16 and 35 are invited to take part in the shooting festival in traditional rifle uniforms (black suit, gray tie, white hat).
Culinary specialties
The town produces its own type of cheese, Nieheimer cheese , and sells it in the Pott cheese dairy, in the Menne cheese dairy and at the Nieheimer Käsewirten.
Economy and Infrastructure
Nieheim is a climatic health resort and a basic center in an area with a predominantly rural structure.
In 1961, the share of people employed in agriculture was 51%, but fell to just over 10% by the mid-1990s, as many farmers relocated or gave up their businesses in the city center.
In contrast, the proportion of industrial employees has increased sharply since the Second World War. This is mainly located in the industrial area directly east of the city center, with the furniture industry leading the way.
For several decades the service sector has been growing more and more, meanwhile at the expense of the manufacturing industry. The largest service company is the Sankt-Nikolaus-Hospital, a residential and hospital for the elderly. In addition, there is the increasingly important tourism, for which the historical center and charming surroundings are good conditions.
traffic
Nieheim is located on the federal highway 252 ( Ostwestfalenstrasse ) running in north-south direction and is connected to both the federal motorway 2 ( Hanover - Ruhr area ) 61 km away and the Dortmund - Kassel 47 km away ( A 44 ) .
The next stations are Sandebeck on the Herford – Himmighausen railway line , Steinheim (Westf) and Altenbeken on the line from Hanover and Brakel (Kr Höxter) on the Eggebahn .
The city has signposted five circular cycle routes and eight hiking trails, including the “Nieheim Art Path” and the “Culture, Forest and Landscape Experience Path”. Nieheim is on the European cycle route R1 , which runs from France to Russia and the like. a. leads via Höxter, Münster and Berlin, as well as on the 500 km long wellness cycle route , which is designed as a circular cycle path.
The closest airport is Paderborn / Lippstadt Airport , about 52 km away. The Hannover Airport is around 114 km away.
media
Neue Westfälische and Westfalen-Blatt appear in local daily newspapers . The cover edition of both newspapers is obtained from the respective main editorial offices from Bielefeld . In addition, 8 to 9 issues per year of the municipal gazette (meeting point Nieheim) , published by the Westfalen-Blatt, appear. In addition, the magazine Die Warte for the districts of Paderborn and Höxter appears quarterly in the Hochstift Paderborn and the Corveyer Land , with articles on regional history, literature and art.
Nieheim belongs to the reporting area of the WDR regional studio Bielefeld . In the area of the Hochstift Paderborn , to which Nieheim also belongs, there has been the local radio Radio Hochstift since 1991 , which takes up local topics in particular and has more listeners than the national broadcasters (such as the WDR).
Public facilities
The Weber House Nieheim, former home of the doctor, poet and politician Friedrich Wilhelm Weber , hosted a well-known in the country Kolping - Diocesan -Bildungsstätte and home volkshochschule that lent itself to any form of education. This facility was closed on September 30, 2011. The all-German educational institution Himmighausen of the djo-German youth in Europe in Nieheim-Himmighausen also offers seminars for various target groups.
In Nieheim there is a public Catholic library in the Vikarie, below the Catholic Church, in the city center.
education
In the city there is a primary school, a secondary school named after Peter Hille , a special school with a special focus on intellectual development . The secondary school is closed, from the school year 2012/13 there were no more enrollments. The special school is located in the Eversen district.
In 2007, a total of 1130 pupils were taught at the city's schools with 85 teachers, 31.6% of them in elementary schools (until 2008 GS Nieheim and GS Sommersell), 17.3% at Hauptschule and 42.5% at Realschule , and 8.6% at the special school.
There are also four kindergartens in Nieheim .
Telephone prefixes
The area code for the city is 05274. However, the following apply: 05233 in Eversen, 05238 in Himmighausen and Merlsheim and 05276 and 05284 in Sommersell.
Personalities
sons and daughters of the town
In the ecclesiastical field, the Magister Dietrich von Nieheim (1338 / 48-1418), who served three popes and was highly regarded in the papal curia , achieved international recognition or even fame , as well as centuries later the Jesuit priest , who was born on Gut Externbrock near Nieheim , religious philosopher and meditation teacher Hugo Makibi Enomiya-Lassalle (1898–1990), builder of the Peace Church in Hiroshima . His life's work was the development of the Japanese Zen practice as a way to a deep faith experience for Christians .
- Gottfried Borninck ("de Nym") († 1453), clergyman, leading figure of the Devotio moderna
- Karl von Oeynhausen (1795–1865), Prussian mining captain
- Wilhelm Hillebrand (1821–1886), doctor and botanist
- Peter Hille (1854–1904), writer
- Wilhelm Rave (1886–1958), State Curator of Westphalia
- Ferdinand A. Hermens (1906–1998), political scientist and economist
- Ansgar Rieks (* 1959), General and Deputy Inspector of the Air Force
- Ewald Grothe (* 1961), historian and archive manager
- Norbert Wolff (* 1962), theologian and church historian
- Jürgen Jasperneite (* 1964), engineer and professor
Other personalities
- Friedrich Wilhelm Weber (1813–1894), poet, doctor and politician, last lived in Nieheim. His grave is in the Nieheim cemetery.
- Fritz Kukuk (1905–1987), poet and Low German author
literature
- Heiko Lohre: Tourist development of a health resort and preservation of the cultural landscape: Development of the climatic health resort of Nieheim with special consideration of tourism and preservation of the cultural landscape . VDM Verlag Dr. Müller , Saarbrücken 2008, ISBN 978-3-639-01838-7 .
- Theo Reineke: 750 years city of Nieheim 1228 / 47–1993: City of poets between the Teutoburg Forest and the Weser . Geiger-Verlag, 1992, ISBN 978-3-89264-721-8 .
- Dietrich von Nieheim, Viridarium imperatorum et regum Romanorum . In: Alphons Lhotsky, Karl Pivec (Ed.): Monumenta Germaniae Historica. tape 1 . Monumenta Germaniae Historica, Munich 1956, ISBN 978-3-7772-5603-0 .
- Dietrich von Nieheim, Historie de gestis Romanorum principum. Cronica. Gesta Karoli Magni imperatoris . In: Katharina Colberg, Joachim Leuschner (eds.): Monumenta Germaniae Historica. tape 2 . Monumenta Germaniae Historica , Munich 1980, ISBN 978-3-7772-8015-8 .
Web links
- Website of the Nieheim Tourism and Culture Office
- Nieheim in the Westphalia Culture Atlas
Districts:
Individual evidence
- ↑ Population of the municipalities of North Rhine-Westphalia on December 31, 2019 - update of the population based on the census of May 9, 2011. State Office for Information and Technology North Rhine-Westphalia (IT.NRW), accessed on June 17, 2020 . ( Help on this )
- ↑ Vidal Garcia was set up by the CDU city association, but ran as an individual applicant in both elections, see Josef Köhne: "He is convincing and moves". With new ideas and organizational talent into the mayor's office. In: Neue Westfälische , 23 July 2009, and local elections 2015. Preliminary result for: Nieheim, Stadt (762028). In: Wahlresults.NRW.de , September 13, 2015.
- ^ Geological Service North Rhine-Westphalia, Geoscientific Community Description Nieheim ( Memento from August 3, 2012 in the web archive archive.today )
- ↑ LWL website , accessed on August 2, 2019
- ↑ Geological Service NRW: Using geothermal energy - Geothermal study provides planning basis ( Memento from September 14, 2005 in the Internet Archive ) (PDF file; 360 kB)
- ↑ a b State Office for Data Processing and Statistics North Rhine-Westphalia : Kommunalprofil Nieheim ( Memento of the original from May 5, 2008 in the Internet Archive ) Info: The archive link has been inserted automatically and has not yet been checked. Please check the original and archive link according to the instructions and then remove this notice.
- ↑ a b Main Statute Nieheim
- ↑ https://www.kreis-hoexter.de/unser-kreis/zahlen-daten-ffekten/m_5855
- ↑ Weather maps ( memento of the original from October 16, 2014 in the Internet Archive ) Info: The archive link has been inserted automatically and has not yet been checked. Please check the original and archive link according to the instructions and then remove this notice. , City of Detmold
- ↑ Weserbergland growth area ( Memento of the original from June 26, 2015 in the Internet Archive ) Info: The archive link has been inserted automatically and has not yet been checked. Please check the original and archive link according to the instructions and then remove this notice. , Landesbetrieb Wald und Holz NRW
- ↑ Roland Linde: Courtyards and families in Westphalia and Lippe, The Asemissen District Meierhof and the Barkhausen Office. A court and family history from the Lippisch-Ravensberg border area , Books on Demand, 2002, ISBN 3-8311-3666-1 , pp. 19-22.
- ↑ The route has already been routed , Neue Westfälische from December 21, 2011, accessed on January 8, 2012
- ↑ State Office for Data Processing and Statistics: Students at general education schools in North Rhine-Westphalia according to religious affiliation
- ↑ Legal text at Law NRW
- ↑ Martin Bünermann: The communities of the first reorganization program in North Rhine-Westphalia . Deutscher Gemeindeverlag, Cologne 1970, p. 109 .
- ↑ Archived copy ( memento of the original from June 30, 2015 in the Internet Archive ) Info: The archive link was inserted automatically and has not yet been checked. Please check the original and archive link according to the instructions and then remove this notice.
- ↑ Archived copy ( Memento of the original from May 22, 2016 in the Internet Archive ) Info: The archive link was inserted automatically and has not yet been checked. Please check the original and archive link according to the instructions and then remove this notice.
- ↑ https://www.kreis-hoexter.de/unser-kreis/zahlen-daten-ffekten/m_5855
- ↑ State database NRW; Election results for the municipality code 05762028
- ↑ State Office for Data Processing and Statistics: Local elections
- ↑ For 2015 see local elections 2015. Preliminary result for: Nieheim, Stadt (762028). In: Wahlresults.NRW.de , September 13, 2015.
- ↑ http://www.ngw.nl/int/dld/n/nieheim.htm
- ^ Josef Köhne: City of Nieheim and battalion end sponsorship - traditional battery must be dissolved. In: https://www.nw.de/ . Neue Westfälische, April 27, 2015, accessed on December 28, 2018 .
- ↑ Holsterbergturm on warttuerme.de
- ↑ http://www.westfalen-blatt.de/OWL/Lokales/Kreis-Hoexter/Nieheim/2261886-Historisches-Fachwerkgebaeude-neben-Rathaus-zerstoert-Rosenmontagsumzug-findet-statt-Video-Ratskrug-in-Nieheim-abgebrannt
- ^ Regional Association Westphalia-Lippe: Garden of Castle Himmighausen in LWL GeodatenKultur
- ^ Regional Association Westphalia-Lippe: Gutspark Grevenburg in LWL-GeodatenKultur
- ^ Regional Association Westphalia-Lippe: Gutspark Holzhausen in LWL-GeodatenKultur
- ^ Regional Association Westphalia-Lippe: Schlosspark Merlsheim in LWL-GeodatenKultur
- ↑ Hiking time - tours, maps and profiles. ( Page no longer available , search in web archives ) Info: The link was automatically marked as defective. Please check the link according to the instructions and then remove this notice. Designated hiking trails in the Höxter district, nieheim.de (PDF file)
- ^ Official gazettes at Westfalenblatt.de .
- ↑ Weberhaus Nieheim ( page no longer available , search in web archives ) Info: The link was automatically marked as defective. Please check the link according to the instructions and then remove this notice. , accessed November 17, 2011.
- ↑ secondary school in Nieheim is closed , nw-news.de
- ^ Fritz Kukuk - Nieheim in the Low German Bibliography and Biography (PBuB)