Metropolitan city of Genoa
| Metropolitan city of Genoa | |
|---|---|

|
|
| State : | Italy |
| Region : | Liguria |
| Capital: | Genoa |
| Area : | 1,838.47 km² ( 78th ) |
| Residents : | 835,829 (Dec. 31, 2019) |
| Population density : | 455 inhabitants / km² |
| Number of municipalities: | 67 |
| License plate : | GE |
| ISO-3166-2 identification : | IT-GE |
| President: |
Marco Doria Metropolitan Mayor |
| Website: | www.cittametropolitana.genova.it |
The metropolitan city of Genoa ( Italian Città Metropolitana di Genova ) is a metropolitan city in the Italian region of Liguria . The capital of the metropolitan city is the city of Genoa .
The metropolitan city of Genoa has existed since January 1st, 2015 as the legal successor to the Province of Genoa ( Italian Provincia di Genova or in Ligurian dialect Provinsa de Zena ).
It has 835,829 inhabitants (as of December 31, 2019) and borders in the west on the province of Savona , in the north on the Piedmont region ( province of Alessandria ) and on the Emilia-Romagna region ( province of Piacenza and province of Parma ), in the east on the province La Spezia and to the south by the Ligurian Sea .
Its most important municipalities are, besides the capital, Genoa , Arenzano , Chiavari , Lavagna , Rapallo , Recco , Santa Margherita Ligure and Sestri Levante .
Largest communities
| local community | Residents |
|---|---|
| Genoa | 586,655 |
| Rapallo | 29,796 |
| Chiavari | 27,398 |
| Sestri Levante | 18,578 |
| Lavagna | 12,791 |
| Arenzano | 11,519 |
| Recco | 9,752 |
| Santa Margherita Ligure | 9,338 |
| Cogoleto | 9,172 |
| Serra Riccò | 7,885 |
| Campomorones | 6,966 |
| Casarza Ligure | 6,826 |
| Sant'Olcese | 5,906 |
| Busalla | 5,563 |
| Camogli | 5,378 |
| Cogorno | 5,676 |
geography
The territory of Liguria is divided into three landscapes: the sea, the hilly landscape and the mountainous area. Like the region, the metropolitan area of Genoa is divided into these three categories. By pushing the landscapes together in a very small space, breathtaking panoramas are created. Eight mountain communities , four regional nature parks and a marine nature reserve ( Portofino marine reserve ) are located in the metropolitan area.
The geographical zones of greatest tourist interest are, besides the port city of Genoa, the Golfo Paradiso and Tigullio . Recently, thanks to large-scale advertising campaigns , the hinterland has also become a holiday destination for both domestic and foreign visitors.
Orography
Mountains
|
|
|
Hydrography
Watercourses
In the metropolitan area of Genoa:
- the brook Arrestra ; it flows into the Mediterranean at Cogoleto and marks the border between the metropolitan city of Genoa and the province of Savona
- the brook Stura ; near Rossiglione , Campo Ligure and Masone
- the Polcevera river ; in the west of Genoa, it flows into the sea between the Genoese districts of Cornigliano and Sampierdarena
- the Bisagno river ; it divides the city of Genoa in half
- the river Scrivia ; it runs in the Genoese hinterland, at the level of the municipality of Montoggio it divides to flow into the lake Val Noci
- the brook Brevenna ; it flows into the Scrivia river at the level of the municipality of Casella
In Tigullio - Fontanabuona Valley - Aveto Valley
- the Trebbia river ; it rises on Monte Prelà and crosses the Piacentino to flow west of Piacenza into the Po
- the river Lavagna ; it forms in the Val Fontanabuona and meets other streams near Carasco (Sturla di Carasco, Penna, Graveglia), forms the Entella river with them and finally flows into the Mediterranean between the towns of Chiavari and Lavagna
- the Aveto stream ; it has its source in the valley of the same name
- the brook Sturla ; flows from Lake Giacopiane into the Lavagna
- the brook Penna ; flows from Lake Giacopiane into the Lavagna
- the Graveglia stream ; rises on Monte Zatta to later flow into the Lavagna
Other watercourses:
- the river Boate (also Bogo ); comes from the confluence of many streams around Rapallo out
- the river Entella ; it separates the two cities of Chiavari and Lavagna
- the Petronio brook ; it flows into the Baia di Riva Trigoso at Sestri Levante
Lakes
| Surname | Geographical location | Community membership |
|---|---|---|
| Lake Ortiglieto | Comunità Montana Valli Stura e Orba | Rossiglione |
| Lago Lungo | Comunità Montana Alta Val Plcevera | Campomorones |
| Lake Val di Noci | Comunità Montana Alta Valle Scrivia | Montoggio |
| Lake Brugneto | Comunità Montana Alta Val Trebbia |
Propata Rondanina Torriglia |
| Lake Giacopiane | Comunità Montana Valli Aveto, Graveglia e Sturla Natural Park Aveto |
Borzonasca |
sea
Of the 67 municipalities in the metropolitan city, 16 are located directly on the Mediterranean . Two of them, Arenzano and Cogoleto , are in the Riviera di Ponente , while the remaining 13 are in the Riviera di Levante . Genoa acts as the dividing point between the two Rivieras. The coast of the Ponente , the stretch of land west of Genoa, is generally flat with sandy beaches, whereas the stretch of the Levante is characterized by rugged cliffs. Due to their close relationship with the sea, the coastal towns and villages were able to build up an economically not insignificant tourism . In order to maintain this, in 2005 these municipalities were financed by the then province of Genoa to purchase cleaning boats, which are supposed to clean the sea water of the Gulf of Tigullio of rubbish and other residues. In the autumn and winter periods, strong storm surges devastate the coasts every year, but the municipalities rebuild them in spring.
climate
The climate is typical of the Mediterranean and with its mild temperatures is a strong attraction for tourists. In the winter period, temperatures on the coast rarely fall below freezing point and averages between 7 and 8 ° C. Snow rarely falls in the low-lying areas, in contrast to the inland of the Ligurian Apennines , where municipalities such as Santo Stefano d'Aveto become important ski resorts in winter .
In summer, the temperatures rarely rise above 35 ° C, but there are often high humidity values that raise the perceived temperature quite a bit.
Seen as a whole, Liguria , and thus also the metropolitan city of Genoa, is characterized as the location of many second homes and holiday homes for Italians who spend the winter there or spend the summer holidays there.
traffic
Rail transport
The metropolitan city is crossed by four railway lines:
- Regional line Genoa- Savona on the Ventimiglia-Genoa railway line
- Interregio line Genoa-Ovada-Acqui Terme
- Interregio line Genoa-Milan
- Regional line Genoa - La Spezia on the Pisa – La Spezia – Genoa railway line
The main train stations of the Città metropolitana are:
In addition, the local railway line Genoa-Casella runs on the territory of the regional authority , which connects the regional capital with the municipality of Casella in the Ligurian Apennines with a narrow-gauge railway . In the urban area of Genoa, the Metropolitana di Genova relieves urban traffic.
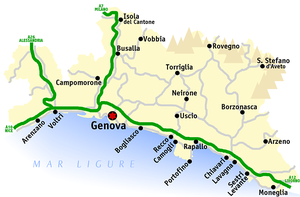
The road network
Highways
The Città metropolitana is crossed by four high-traffic motorways . The relatively high volume of traffic is primarily due to the tourist traffic to the Riviera di Levante and the through traffic to the ferries in the port of Genoa, which regularly go to destinations in Sardinia , Sicily and Tunisia . The A10 motorway (also called the Flower Motorway ) connects Genoa with the border town of Ventimiglia , from which the major cities of southern France and the Principality of Monaco can be reached.
The A26 motorway (also called the tunnel motorway ) connects the regional capital with the province of Alessandria (with the A21 junction at Ovada ). Another important traffic route is the A7 which connects the regions of Liguria and Lombardy . During the holiday season, there is regularly a very high volume of traffic, especially on this motorway.
The A12 motorway runs along the Riviera di Levante and leads from Genoa to Livorno (Rosignano Marittimo). On this route, too, during the holiday season, caused by holiday traffic, there are often traffic delays due to traffic jams.
State and provincial roads
The streets of the metropolitan city primarily connect the mountainous inland with the coastal communities. The road network today has a total length of 1125.265 kilometers. The main cities that act as connecting points with the small municipalities in the hinterland are Genoa, Busalla and Chiavari . The only state road in the metropolitan city is Strada Statale 45 di Val Trebbia , which leads from Genoa to Piacenza .
Sea ports and airports
The most important commercial port of the metropolitan city is certainly the port of Genoa , which with its modern container terminals , such as the VTE-Voltri Terminal Europa , is one of the most important ports in the Mediterranean.
Other major tourist and marina ports at national level are those of Arenzano , Camogli , Portofino , Santa Margherita Ligure , Rapallo , Chiavari and Sestri Levante .
The only airport in the metropolitan city is Cristoforo Colombo Airport near Sestri Ponente, which primarily offers national, but also international flights.
swell
- ↑ Statistiche demografiche ISTAT. Monthly population statistics of the Istituto Nazionale di Statistica , as of December 31 of 2019.
- ↑ ISTAT - as of December 31, 2015
- ↑ Street directory of the former province of Genoa ( Memento of the original from January 1, 2015 in the Internet Archive ) Info: The archive link was inserted automatically and has not yet been checked. Please check the original and archive link according to the instructions and then remove this notice.