Edersee
| Edertalsperre | |||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| View from "Schöner Aussicht" near Basdorf on the Edersee with Love Island , Bringhausen and Kellerwald | |||||||||||
|
|||||||||||
|
|
|||||||||||
| Coordinates | 51 ° 11 '6 " N , 9 ° 3' 18" E | ||||||||||
| Data on the structure | |||||||||||
| Construction time: | 1908-1914 | ||||||||||
| Height above foundation level : | 48 m | ||||||||||
| Height above the river bed : | 45 m | ||||||||||
| Height of the structure crown: | 248 m above sea level NHN | ||||||||||
| Building volume: | 300,000 m³ | ||||||||||
| Crown length: | 400 m | ||||||||||
| Crown width: | 6 m | ||||||||||
| Base width: | 36 m | ||||||||||
| Radius of curvature : | 305 m | ||||||||||
| Slope slope on the air side : | approx. 55 ° | ||||||||||
| Slope slope on the water side : | almost 1: 0 (vertical) | ||||||||||
| Power plant output: | 20 MW | ||||||||||
| Data on the reservoir | |||||||||||
| Altitude (at congestion destination ) | 244.97 m above sea level NHN | ||||||||||
| Water surface | 11.8 km² | ||||||||||
| Reservoir length | 28.5 km | ||||||||||
| Reservoir width | 1.2 km | ||||||||||
| Storage space | 199.3 million m³ | ||||||||||
| Total storage space : | 225 million m³ | ||||||||||
| Catchment area | 1 443 km² | ||||||||||
| Design flood : | 1 744 m³ / s | ||||||||||
| Particularities: |
Water depth when completely blocked: 41.7 m |
||||||||||

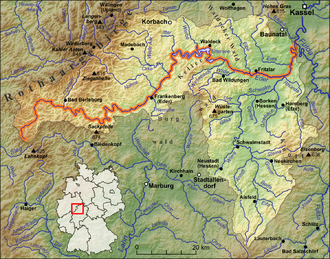
The Edersee , even Ederstausee called, is 11.8 square kilometers of water surface and 199.3m m³ of storage space in terms of area and second in terms of volume third largest reservoir in Germany (see list ). It is located on the Fulda tributary Eder behind the 48 m high dam of the Edertalsperre near the town of Waldeck in the northern Hessian district of Waldeck-Frankenberg .
The Edertalsperre (dam and reservoir) is the property of the Federal Waterways and Shipping Administration , with the Hann. Münden is responsible. The primary purpose of the dam is to provide water for the Upper Weser and Mittelland Canal federal waterways . In addition, it also serves to protect the downstream population from small and medium floods, to generate electrical energy and for recreation.
Located in the Kellerwald-Edersee Nature Park and the Kellerwald-Edersee National Park and towered over by Waldeck Castle , the Edersee and its surroundings form a large recreational area.
Geographical location
The Edersee, where the Eder by at Hemfurth-Edersee (to Edertal standing) dam is dammed up to a reservoir, located 35 km is a straight line southwest of Kassel and just north of the low mountain range Kellerwald in the north of the nature park basement Edersee . It stretches from the confluence of the Eder in front of Herzhausen (zu Vöhl ) in the west to the dam at Hemfurth-Edersee in the east and meets the Ederhöhen in the south, a mountain region in the north of the Kellerwald, which is roughly congruent with the Kellerwald-Edersee National Park .
Localities
The Edersee covers an area north of the Kellerwald between the following municipalities or towns (listed with districts clockwise, starting at the barrier wall):
Municipality of Edertal with Hemfurth-Edersee (eastern end of the lake), Rehbach and Bringhausen , municipality of Vöhl with Asel -Süd, Harbshausen , Kirchlotheim and Herzhausen (western end of the lake), Asel and Basdorf (including Trappenhardt) and the city of Waldeck (incl. Waldeck-West) with Nieder-Werbe and the Scheid peninsula.
history
Construction time and costs
The reason for the construction of the Edertalsperre was a waterway law in Berlin of April 1, 1905. It included the construction of new dams in the upper headwaters of the Eder and the Mittelland Canal to Hanover in order to allow shipping operations on the Weser and the Mittelland Canal to Hanover and the new or to secure the Lippe side canal to be expanded , the Rhine-Herne and Dortmund-Ems canals . The importance attached to this construction project was shown by the visit of Kaiser Wilhelm II in August 1911 and in the inauguration ceremony and official handover of the dam by the Kaiser, originally planned for August 15, 1914, which, however, was due to the outbreak of the First World War on 1 August 1914 . August 1914 did not materialize. The design of the dam was made under the direction of the Weser River Construction Director Wilhelm Otto Muttray , who was also largely responsible for its implementation. This also took into account a flood regulation plan that he had designed. The construction of the dam, which took place between 1908 and 1914 according to plans by Otto Intze , cost around 25 million marks . Construction manager Wilhelm Soldan and government builder Herbert Pietsch (1887–1958) from the Prussian hydraulic engineering administration were in charge of the construction.
Relocations
Around 900 people in the area of the reservoir had to give up their home and settle elsewhere. The villages Asel , Berich and Bringhausen , which lay in the valley of the Eder, were rebuilt in higher places above the newly emerging Edersee after they had been torn down or removed. Parts of the villages Nieder-Werbe and Herzhausen were flooded and the residents were relocated to new farms and houses nearby. Numerous individual farms or properties fell victim to the flooding, such as Gut Vornhagen, which consisted of two buildings and stood in the valley below Waldeck Castle , or the Stollmühle, which was located at the widest point of the reservoir not far from the current dam on the Hammerbergspitze. At this point, when the tide is low, you can still see the passage of the tugboat that was used to transport goods when the wall was built. The Bericher Hammer , the Bericher Hütte, the Bericher Mühle and the Werber Hammer were also flooded.
Heavy damage in World War II


During the Second World War , the Royal Air Force hoped with Operation Chastise ("chastisement") by destroying the Möhne , Sorpe , Ennepe and Lister dams , transport routes and water supplies for the arms industry in the Ruhr area . During this operation, the water level regulation of the Weser and Mittelland Canal was to be disrupted with the attack on the Edersee dam.
On May 17, 1943, shortly before 2 a.m., the Eder dam was damaged in an attack by British No. 617 Squadron under the command of Wing Commander Guy Gibson badly damaged:
In order to overcome the network barriers in front of the dam wall, a roll or rotation bomb specially designed for this purpose was used, which was set in rotation by a special device on board an Avro Lancaster bomber and then dropped. Similar to jumping stones , in which a stone thrown horizontally over the water jumps flat over the water, the bomb rotating (against the direction of flight) after being dropped first jumped over the surface of the water and then over the network barriers towards the dam. Then it sank down the water side in front of the wall, and its explosive device detonated at a predefined depth. The explosion created a semicircular opening about 22 m high in the wall and 70 m long at the top of the wall. An average of 8000 m³ of water per second flowed through this - a total of around 160 million m³, which makes up around 80% of the storage space.
As a result, a 6 to 8 m high tidal wave poured through the lower Edertal to Fritzlar , Wabern and Felsberg and through the Fulda valley ( Kassel ) to the Weserstein ( Hann. Münden ) and finally into the Upper Wesertal . The tidal wave, which the residents described as a white foaming and loud rumbling spray, resulted in hundreds of houses as well as factories, railways, roads, bridges and trees being badly damaged, destroyed or washed away. The flood not only transformed the sometimes extensive valleys around the Schwalm -Eder- and Eder-Fulda estuaries into a "lake", some several kilometers wide, but also flooded the valley of the Fulda in the Kassel basin about 35 km from the dam so that there, for example, Bettenhausen , the Untereustadt and the Karlsaue with the orangery were haunted by water.
Information about the number of people who lost their lives in the waves of water, mud and rubble below the Edersee are contradictory. The numbers vary between 47 and 68 fatalities. Some posts recent, in which the death of 749 Ukrainian prisoners of war forced laborers in a labor camp below the Edersee dam is mentioned, probably due to a confusion with the Möhne disaster , in which - also during Operation Chastise - the Möhnetalsperre was badly damaged. However, there is no reliable source from which it can be concluded that there was allegedly a forced labor camp on the Edersee at the time of the bombing. Such a camp was only set up there after the attack to restore the dam.
A film made privately by a soldier shows, among other things, the severely damaged dam wall a few hours after the attack (see section Films and Games ).
reconstruction
The heavily damaged dam was rebuilt in the same year by forced laborers from the Todt Organization . Aids from the Hitler Youth and the Reich Labor Service also rebuilt numerous houses and other important buildings.
Renovations
The dam wall was renovated from 1946 to 1947, 1947 to 1948, 1961 to 1962 and 1991 to 1994: grouting ( injection sealing ) was carried out in the 1940s, and a complete grouting curtain with cement paste was used in the 1960s to counteract the increased flow of water caused the rotary bomb in particular in the masonry around the blasting gap.
In the 1990s - with an increase in the safety standard in accordance with DIN 19700 ( dams ) - 104 permanent rock anchors, each 61 to 71 m in length, were installed after the removed wall crown was rebuilt, including a new inspection passage through the entire wall at an incline into the bedrock . Temporary openings in the bridge and in the ceiling of the inspection passage were used for this purpose. The anchors rest on the wall in the new upper inspection corridor. Each anchor has a preload of 4500 kN (459 t), which was temporarily increased in steps up to 6750 kN after the anchor cement had hardened in the rock. The aim was to additionally secure the gravity wall through the tensile force, because it had to. a. Leachate developed under the wall.
70th anniversary of the attack on the Eder barrier wall
On the 70th anniversary of the attack on the Edersee barrier, the Edersee barrier wall museum organized an international commemorative event, which took place on May 17, 2013 on the forecourt of the dam in the Edersee district of Edersee. Representatives from Australia, Germany, England, New Zealand and the USA took part with the participation of regional bodies. The event received worldwide media coverage.
Data from the dam and lake

Dam wall: For the construction of the curved weight dam erected between 1908 and 1914 not far north of Hemfurth, a district of Hemfurth-Edersee in today's municipality of Edertal , the 400 m crown and 270 m base length as well as 6 m crown and 36 m base width (base width) approximately 300,000 m³ of quarry stone masonry from Edersee-Grauwacke were processed. The dam wall was strengthened around the year 2000: steel cables were anchored in the ground and tensioned at the top of the wall crown to prevent the wall from floating up during high water, as it was found that the weight of the wall was insufficient.
Reservoir: The Edersee is the second largest reservoir in Germany in terms of area and the third largest by volume and, with its storage space, is one of the 10 German reservoirs with a capacity of more than 25 million m³ of water. With full damming, the Edersee has 11.8 km² of water surface and 199.3 million m³ of water content (value determined by laser scanning method in 2003; former value: 202.4 million m³). Then its water depth is 41.7 m and at high tide a maximum of 43.69 m. The reservoir is 28.5 km long. Its shore length measures 69.4 km.
Subsoil and function of the dam
Water regulation
The Edertalsperre was built in order to be able to supply enough water from the Edersee to the Mittelland Canal so that barges could travel from the Ruhr area to Berlin . For this purpose, a pumping station was set up at the waterway junction near Minden , which conveys the water from the Weser one floor higher into the canal. In addition, the (high) water levels of the Eder, Fulda and Weser are not only regulated in the summer months. For this reason, the reservoir may only contain around 150 million m³ of water at the end of each year, so that almost 50 million m³ of flood storage space is available, which in normal years fills up again by April 1st.
In the district of Waldeck-Frankenberg, the low water level leads to economic impairments, especially in tourism.
Water inflow
The natural amount of water that is supplied to the reservoir via the Eder at the measuring point in Schmittlotheim is very different: When it is dry, sometimes only about 1.0 m³ per second flows into the reservoir; in rainy times and especially during the snowmelt this can increase to up to 740 m³ / sec. increase, which results in an average of 650 million m³ (around 20 m³ / sec.) per year.
Power generation
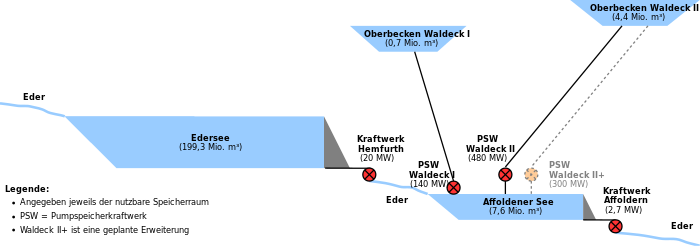
At the foot of the Edertalsperre wall is the Hemfurth storage hydropower plant , which generates electricity with the help of hydropower (without pump storage). It started commercial operations in 1915. The turbine inlets are located at the bottom of the dam on the water side on the left. Up to 54 m³ of water run through the turbine pipes, which are around 2.50 m in diameter. The power plant has two sets of machines, each with two generators , which together provide up to 20 MW of electrical power, depending on the water level. The plant is operated by Uniper Kraftwerke . The electricity generated is fed into Avacon's 110 kV high-voltage network .
In addition, at the Affolderner See , a reservoir a few kilometers downstream from the Edersee, electricity is generated with the two pumped storage power plants Waldeck and the Affoldern run-of-river power plant.
High tide and low tide
Full jam

The water level of the Edersee varies over the course of the year. The lake has a full blockage after the precipitation in winter between March and July. The water depth is then up to 42 m.
When the water level rises above the full dam mark ( 245 m above sea level ) and there is high water , 204 m³ of water can be drained off the dam wall per second. This is done through the turbine pipes (54 m³) and the six bottom outlets (150 m³), which are located at the foot of the dam, each with a diameter of 1.20 m. If that is not enough, up to 1,100 m³ per second can be drained via the 39 overflows in the top of the wall. If this is not enough, there are eight additional emergency outlets in the middle of the dam, through which a total of 440 m³ can be released every second. Together with the aforementioned turbine passage, this results in 1,744 m³ per second.
Low tide
The water of the Edersee is used to regulate the Weser and the Mittelland Canal. As a result, it can happen that after a dry late summer followed by autumn with little rain, large parts of the Edersee are dry. On the lake floor, green vegetation then develops through marsh grasses.
When the water is extremely low , the remains of the former villages and the Berich monastery church, the Bringhausen cemetery , the old, still well-preserved and accessible Eder Bridge near Asel and other structures - such as the barrier wall model (1:40 scale; corresponding to 219.9 m above sea level ) are exposed ) at the former report - visible again. In 2002 there was hardly any rain in the region around the Ederkopf , but especially in northern Hesse . The following winter half year saw very little precipitation, and in 2003 during the “summer of the century” there was little precipitation, so that the villages, which were normally flooded by the reservoir, dried out for months. The reservoir reached its lowest water level with 19.9 million m³ (corresponding to 217.82 m above sea level) in November 2003, before it was completely filled again at the end of March 2004 after a rainy winter. In 2018, the level fell below the low water level of 2003 (with a level of 217.82 m above sea level on October 26, 2018; further waste is prevented for ecological reasons). The record low water level after the Second World War was measured in mid-December 1959: 9.1 million m³ of water or less than the level of 214 m above sea level called the Iron Stock . NHN .
tourism

The tourist significance in the large region around the Edersee - to which the Kellerwald-Edersee National Park also belongs - has not only increased since the Second World War , so that a local recreation area with numerous vacation and leisure opportunities has developed.
Dutch holidaymakers in particular like to come here, possibly also because of the historical relationship between their royal family and Waldeck : Princess Emma of Waldeck and Pyrmont became the second wife of King Willem III in 1879 to become the ancestor of all subsequent Dutch queens and kings.
Due to the mountainous landscape and the nature park, in which the Edersee and the forest areas are located, the infrastructure in terms of road construction is quite sparse, so that there can be considerable traffic jams at peak times. Roads near the shore lead around the eastern half of the lake, but there are also roads along the western part; some of them are designed as dead ends . There are parking spaces for hikers in many places . Bicycle and hiking trails run around the entire reservoir.
Numerous campsites and two youth hostels as well as many cafes , pubs , hotels , pensions and restaurants can be found on the banks. In summer, the Edersee invites you to swim at bathing areas guarded by the DLRG . An aquapark (water playground with miniature Edersee on a scale of 1: 200) south of the dam wall allows you to complement the bathing pleasure in the open reservoir. To the west below Waldeck, diving is allowed in two zones; in "Zone 1" are the remains of the village of Berich - the "Dorfstelle Berich".
Other preferred sports on the Edersee are sailing , rowing and fishing . Numerous sailing clubs have settled here, the largest being the sailing club Edersee e. V. In addition to numerous class regattas, there are also many yardstick regattas. Motorboat traffic with an internal combustion engine is prohibited, but electric, pedal and rowing boats, for which there are boat rental companies, are allowed.
The entire lake between the dam in the east and the Eder tributary in the west can be sailed on excursion boats operated by the “Edersee Personnel Shipping”. They stop at a maximum of eight berths. Passenger ferries operate between Asel and its district Asel-Süd and between the Scheid peninsula, which is part of Nieder-Werbe, and the village of Rehbach .



In winter, the frozen Edersee attracts visitors under the heading of “Singing Lake”: Due to the strong discrepancies between night frosts and daytime temperatures in the positive range when the sun is shining, and due to fluctuating water levels, the ice floes rub against each other, causing a roaring, echoing noise that can be heard from far away .
The terrace hotel with restaurant on the east bank of the dam was already a tourist facility during the Weimar Republic (built in 1931/1932). It was rebuilt in the 1950s after it was destroyed by the British air bombing raid in World War II.
The Edersee Barrier Wall Museum has existed since 2000 and provides detailed information on the severe damage caused by the attack on the Eder Dam, among other things, during the Second World War.
The Urwaldsteig Edersee (“UE”) has existed since 2005, a 68 km long hiking trail around the Edersee, running through the dry oak forests on the northern bank and through the Kellerwald-Edersee National Park to the south of the reservoir . 2006 was Edersee bike trail ( "ER11") opened on many places paved and largely car-free route, which - as the maximum and about 68 km long - depending on the route selection cycle path leads around the Edersee. Both paths run over the dam and in some places are not laid directly along the shoreline (69.4 km long) of the reservoir, but instead they shorten over nearby hills. It is possible to shorten it with the aforementioned excursion boats, the “Asel Ferry” or the “Rehbach Ferry”. The Ederauenradweg and the special Kellerwaldsteig (approx. 156 km long) leading through the Kellerwald are connected to these paths . In addition, the southwest section of the Habichtswaldsteig (85 km) leads over the high altitudes east of the reservoir and over the dam wall. The Ederseeweg (49 km) coming from Kassel ends at the reservoir near Nieder-Werbe .
Since 12 July 2014, the 39 overflows the dam are nightly by 39 RGB LED - spotlights illuminated and thus set itself the dam wall in color. The client for this lighting was the municipality of Edertal.
fauna
In 1934 two pairs of raccoons were released on the Edersee , which initially reproduced in central Germany and later spread to Central Europe. On March 9, 2009, a European wildcat was detected in the Kellerwald-Edersee National Park , which lives there alongside wild animals commonly found in the area.
Due to the high dam of the Edertalsperre, fish migration to and from the Edersee (e.g. for salmon ) downstream is not possible. However, a very diverse fish world consisting of predatory and white fish has developed within the reservoir . It is not uncommon for pike to be seen and also caught.
Inflows and outflows
The running waters of the Edersee - its tributaries and its outflow - include length in kilometers (km) and estuary area (sorted alphabetically):
Tributaries:
- Aselbach (6.55 km); flows from the north at the "Dorfstelle Asel" near Vöhl-Asel into a reservoir north arm
- Banfebach ("Banferbach"; 7.2 km); flows from the south southeast of Asel-Süd at the "Fischhaus Banfe" into a reservoir south arm
- Bärenbach (4.1 km); flows from the south south of Asel-Süd into a small bay of the reservoir
- Bärentalsbach (1.95 km); flows west of the "Dorfstelle Berich" located near Waldeck-West from the north into a reservoir north arm
- Eder (176.1 km); flows as the main tributary from the south at Vöhl-Herzhausen into the western end of the reservoir
- Hundsbach (2.1 km); flows from the south southwest of Asel-Süd at the " DRK -Zentrum Albert Schweitzer" into the reservoir
- Itter (11.6 km); flows from the north at Vöhl-Herzhausen into the western end of the reservoir
- Mellbach (2.1 km); flows from the south east of Edertal-Bringhausen into the reservoir
- Mombeck (2.55 km); flows from the west at Herzhausen into the western end of the reservoir
- Rehbach (0.9 km); flows from the east at Edertal-Rehbach into a reservoir south arm
- Reiherbach (8.4 km), flows from the northeast near Nieder-Werbe (to Waldeck) in a reservoir north arm into a reservoir fore-reservoir
- Advertising (13.25 km); flows from the north into a neighboring reservoir pre-basin, also located at Nieder-Werbe
Drain:
- Eder (176.1 km), the only outflow, at the dam at the eastern end of the reservoir; is a tributary of the Fulda
Excursion possibilities and sights
The excursion possibilities and sights on and in the Edersee and the surrounding region include (sorted alphabetically):
At the Edersee
Sights on, near or around the Edersee:
- "Aquapark" - water playground with miniature Edersee on a scale of 1: 200 in the Edersee location of Hemfurth-Edersee near the Edersee dam
- Baumkronenpfad "TreeTopWalk" - 250 m long with pre-Waldlehrpfad, 800 m long "squirrel path" near Rehbach
- Ehrenburg , castle ruins south of Marienhagen
- Bat educational trail - approx. 2.4 km long educational trail in a small forest area near Asel
- Hünselburg , Altburgstelle south-southwest of Basdorf
- " Climbing Park Edersee", north-northeast of Rehbach on the Ederseeufer; with lake and castle views
- " Maize labyrinth on Edersee" - approx. 30,000 m² large labyrinth northwest of Basdorf (open from July to October)
- Kellerwald-Edersee National Park - National Park to the south of the Edersee
- Kellerwald-Edersee Nature Park - a nature park that frames the Edersee
- Waldeck pumped storage power station - near Hemfurth am Affolderner See (access to the upper basin there by Peterskopfbahn possible)
- Waldeck Castle - near Waldeck high above the Edersee (ascent possible with the Waldecker Bergbahn ; view of the Edersee)
- "Sommerrodelbahn am Edersee" - approx. 850 m long summer toboggan run west of Nieder-Werbe
- Sperrmauer Museum Edersee (also: Sperrmauer Museum ) in Hemfurth (Forsthausstraße)
- Barrier wall lighting - every evening after dark
- Uhrenkopf - near Hemfurth-Edersee; good prospect of the Edersee dam
- Edersee wildlife park with birds of prey station - above Hemfurth-Edersee not far from the Edersee dam
In the Edersee
Sights in the Edersee or near the Eder (to be seen at every water level):
- Love Island - the only constant island near Bringhausen in the central part of the Edersee, with the ruins of Bring Castle
Sights in the Edersee or on / near the Eder (to be seen at low tide):
- "Alt-Asel" with the nearby monument "Dorfstelle Asel", near Asel
- "Aseler Bridge" (connects Asel with Asel-Süd; well preserved), near Asel
- "Alt-Bringhausen" with "Friedhof Bringhausen" and a nearby monument "Dorfstelle Bringhausen", near Bringhausen
- “Alt- Berich ” with “Berich cemetery” and the nearby “Dorfstelle Berich” monument, west of Waldeck- West
- “Bericher Brücke”, at “Alt-Berich”, west of Waldeck-West
- "Bericher Hütte", north of Waldeck- Scheid , west of "Alt-Berich"
- "Bringhausen Bridge" (connected Bringhausen with Waldeck-Scheid; pillars and abutments have been preserved), near Bringhausen
- "Breakthrough point of the Schleppbahn", the freight railway line used for the construction of the dam wall, artificially created rock breakthrough between the Hammerbergspitze (near the Edersee wildlife park ) and the normally flooded hop mountains (near the former Stollmühle)
- "Gut Vornhagen" (once consisting of two buildings), below Waldeck Castle
- “Barrage model” of the Edertalsperre barrier structure (1:40 scale), which was built to test the water drainage; north of Waldeck-Scheid, west of the Bericher hut
- "Stollmühle", not far from the dam, near the Edersee wildlife park on the Hammerbergspitze
- "Werbebrücke" (connecting the Scheid peninsula with the Bericher hut), north of Waldeck-Scheid, south of the Bericher hut

Former works of art at the Edersee
From July 7th to September 15th, 2002, the Edertalsperre was covered on the air side with magenta colored, green-dotted and at the same time transparent cloths stretched from the top of the wall to the base of the wall - a work of the artist Gerhard Hesse from Edertal- Wellen . In the evening until midnight, the air side of the wall was illuminated so that everything shone brightly.
From August 4 to September 19, 2007, at the foot of the dam on the E.ON site, a work of art called “Electrified rotary clothespins” by the artists Gerhard Hesse from Edertal-Wellen and Kanae Kato from Osaka, Japan, was installed. It was about the contrast between nature and technology. The rotary clothes dryers glowed red from dusk until midnight.
Since June 12, 2014, the barrier wall has held the German record as the longest permanently illuminated object.
Transport links
You can reach the Edersee on several state or county roads , by the west in north-south direction at Herzhausen the reservoir tangent B 252 , from just north running B 251 and the slightly northeast leading past the reservoir B 485 branch:
Both federal highways connect between Herzhausen in the west - past the dam and along the Affolderner See - and Affoldern and Mehlen in the east a continuous road ( L 3084 − L 3086), which partly runs along the north bank of the reservoir and in sections the route with the Ferienstrasse divides German half-timbered road . Along its south bank there is a dead end from the west from Herzhausen via Harbshausen to Asel-Süd and from the east from Hemfurth-Edersee via Rehbach to Bringhausen .
There are also numerous cycling and hiking trails in the Ederseeregion. In the past, the Ederseebahn, leading from Korbach through the Edertal below the dam to Bad Wildungen, ran east and north past the reservoir several kilometers away from the Edersee ; its closed section Korbach - Buhlen was converted from 2008 to 2012 into the Ederseebahn cycle path .
Movies and games
- (Die) Schicksalsmauer am Edersee - A project of the century and its consequences hrfernsehen, 2014. youtube, published January 19, 2014, video (44:49) - Author: Eckhard Braun, bilderbogen.hr.de. Documentation about prehistory, construction, destruction, control and maintenance today.
- A film by a soldier, shot privately on May 17, 1943, shows the heavily damaged dam (see section Severe damage in World War II ) and the effects of the water flowing out along the Eder a few hours after the attack on the wall.
- The attack was the 1954 made-for the BBC British feature film in May 1943 - The destruction of the dams ( The Dam Busters ) by Michael Anderson readjusted. The location of the action is the reservoir and the region for the crime scene Like Lilly once did with Ulrich Tukur (2010) and the dam wall and lake in Matthias Schweighöfer's film Schlussmacher (2013).
- The attack on the dam is part of the computer game Call of Duty 1. However, the mission there is purely fictional and has nothing in common with the real attack.
- The area around the Edersee and the Edersee itself serve as the setting for the ZDF series The Lost Daughter (2020).
gallery
Arid Edersee near "Alt- Asel "; Cliffs Usually Below Water Level (2008)
Stream bed of the advertising at low water in the Edersee (2008)
Long exposure of the illuminated Edertalsperre at the blue hour in October 2016
Left dam tower with coat of arms: Imperial eagle seen from the clock head
Right dam tower with coat of arms: ( Imperial crown , star, cross) seen from the clock head
See also
Individual evidence
- ↑ DIN 4048-1 Hydraulic Engineering, Terms, Dams, Jan. 1987.
-
↑ Edersee - The Edertalsperre ( memento of the original from April 9, 2018 in the Internet Archive ) Info: The archive link was automatically inserted and not yet checked. Please check the original and archive link according to the instructions and then remove this notice. , on info-waldeck.de; according to sources from local "*" - note: information from Wilhelm Soldan, who led the state building supervision during the construction of the barrier wall - see: - The Waldecker dam in the Eddertal , Ewert'sche Verlagsbuchhandlung, Marburg 1914 - Hermann Bing: Waldeckisches Lesebuch , 3rd edition, Wilhelm Bing Verlag, Korbach 1990
- ↑ Grandson of the government builder Pietsch visited the barrier wall , August 10, 2014, accessed on January 6, 2015, on hna.de.
- ↑ When the lost villages appear (Drei Videos vom Edersee-Atlantis), HNA, September 5, 2016 , accessed on November 9, 2016
- ↑ Mike Burkhardt (ed.): Far away times, near goals. Experience history in and around Kassel. Kassel University Press, Kassel 2010, ISBN 978-3-89958-952-8 , p. 87.
- ↑ https://www.vde-kassel.de/de/veranstaltungen/berichte-zu-vergangene-veranstaltungen/vde-detailsseite-standard excursion to the Edersee barrier wall , 28 Sep. 2016, picture report by VDE Kassel from December 26, 2016, accessed on October 23, 2018
- ↑ Drained water - the wave from the Edersee spills into politics ( memento from August 1, 2012 in the web archive archive.today ), from August 16, 2011, from faz.net
- ↑ The E.ON power plants at Edersee ( memento from September 5, 2012 in the web archive archive.today ), from michael-kranz.de
- ↑ List of power plants. Federal Network Agency , March 7, 2019, accessed on September 17, 2019 .
- ↑ Pictures of the low water level of the Eder reservoir August 23, 2003 ( Memento from September 22, 2007 in the Internet Archive )
- ↑ Wildcat photographed for the first time in Kellerwald-Edersee , March 20, 2009, on faz.net
- ↑ Climbing Park Edersee (official homepage)
- ^ Association Sperrmauer Museum Edersee e. V. , on dambusters.de
- ^ Hermann Hauschild: Recordings of the destruction of the Edertalsperre on May 17, 1943 , on youtube.com
- ↑ https://www.hna.de/lokales/frankenberg/korbach-ort55370/korbach-kulisse-fuer-zdf-serie-verlorene-t Zeiten- 13445312.html
literature
- Literature about Edersee in the Hessian Bibliography
- Roland Gööck: When the barrier broke - A report on the destruction of the Edertalsperre on May 17, 1943 and the reconstruction in the Edertal . Wilhelm Bing Verlag, Korbach 1953.
- Peter Franke, Wolfgang Frey: Dams in the Federal Republic of Germany. 1987, ISBN 3-926520-00-0 .
- Ulrich Klein: The Edertalsperre and the beginning of the electricity supply in Northern Hesse 1914–1922. In: Hessian homeland. 61 (2011), pp. 69-76.
- Cycling map - Leporello Eder cycle path, Edersee circular path. Scale 1: 50,000, 2008, ISBN 978-3-89920-509-1 . http://d-nb.info/991446003
- Andrea Rabini (Red.): Festschrift 100 years Edertalsperre. Waterways and Shipping Office Hann. Münden (Ed.), 2014 (PDF; 5.68 MB)
Web links
- Waterways and Shipping Office Hann. Münden (owner and operator)
- Edersee holiday region
- Edersee Touristic GmbH
- Edersee weather station , private weather station, water levels and temperatures