Earth / dates and numbers
The earth in data and numbers provides an overview of the essential characteristics of the earth in terms of its planetoid , geographical , climatic and cultural properties, combined with a listing of the planet's geographical records .
Asteroid features
Data on the position in the solar system
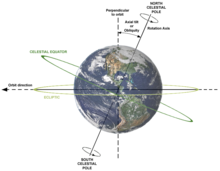
The Earth is the fifth largest and the sun third closest planet of the solar system . It moves in an elliptical orbit around the sun, with the point of the orbit furthest from the sun ( aphelion ) being reached around July 5th and the point closest to the sun ( perihelion ) around January 3rd. The mean value of the aphelion and perihelion distance is the major semi-axis of the ellipse and is about 149.6 million km. The sun's orbit is completed after 365.256 days ( sidereal year ).
| Data on the position in the solar system | ||
| Distance to the sun | Mean value ( semi-axes of the ellipse ) | 149.60 million km (1 AU ) |
| Distance to the sun | Greatest distance ( aphelion ) | 152.10 million km |
| Distance to the sun | Closest distance ( perihelion ) | 147.09 million km |
| Speed of rotation | Mean value (mean orbital velocity) | 29.78 km / s |
| Circulation speed in the perihelion | Maximum orbital velocity | 30.29 km / s |
| Circulation speed in aphelion | minimum orbital velocity | 29.29 km / s |
| Duration of the sun's orbit | Sidereal year | 365 days, 6 hours, 9 minutes and 9.54 seconds |
| Covered track | Sidereal period | 939,800,765.952 km |
| Duration of the sun's orbit | Tropical year | 365 days, 5 hours, 48 minutes and 45.26 seconds |
| Speed of the earth's rotation | at the equator | 0.463 km / s |
| Duration of one earth rotation | middle sidereal day | 23 hours, 56 minutes and 4.09 seconds |
| Duration of one earth rotation | mean sunny day | 24 hours, 0 minutes and 0 seconds |
Basic data of the earth
Due to the centrifugal force of the earth's rotation, the earth does not have an ideal spherical shape, but rather a flattening . The equatorial circumference is about 43 km longer than the circumference over the two poles. In addition, the earth's axis is inclined to the vertical axis of the ecliptic , which leads to climate-defining seasons .
Atmosphere of the earth
The earth's atmosphere comprises the troposphere (with a height between 8 km and 18 km) at the lowest level, the stratosphere (up to a height of 50 km) and mesosphere (with a height between 80 and 90 km) and in the uppermost areas the thermosphere . The layers close to the ground have a fairly uniform composition up to a height of about 90 km and form the homosphere . The transition between the earth's atmosphere and space is continuous and therefore no sharp upper limit can be drawn.
| Atmosphere of the earth | |
| Mass of the atmosphere | 5.15 x 10 18 kg |
| medium pressure at zero level | 1013.25 hPa |
| mean air density at zero level | 1.217 kg / m³ |
| Volume proportions of the air in the layers close to the ground (without water): | |
| nitrogen | 78.1% |
| oxygen | 20.9% |
| argon | 0.9% |
| other | <0.1% |
In addition, depending on the humidity , the atmosphere contains up to four percent by volume of water vapor with an average of 1.3% near the ground.
Structure and composition of the earth
The interior of the earth is made up of several shells. The elements iron, oxygen, silicon and magnesium make up approx. 93% of the weight of the earth, whereby the chemical composition of the individual earth shells differs considerably. In the center is the solid core of the earth with a radius of about 1250 km, which mainly consists of iron (86.3%) and nickel (7.3%). This is followed by the outer core of the earth with a thickness of around 2200 km, which consists of iron with an admixture of 10–15% sulfur and / or oxygen. Above it arches the 2900 km thick layer of the mantle made of viscoplastic rock ( silicates and oxides), which is enclosed by the relatively thin and hard crust . This also consists of silicates and oxides, but is also enriched with elements that do not occur in the earth's mantle.
| Mass percentage composition of the earth (excluding atmosphere) | |
| iron | 35.0% |
| oxygen | 30.0% |
| Silicon | 15.0% |
| magnesium | 13.0% |
| nickel | 2.4% |
| sulfur | 1.9% |
| aluminum | 1.1% |
| Calcium | 1.1% |
| other | <1.0% |
| Mass fraction of the composition of the earth's crust | |
| oxygen | 46.60% |
| Silicon | 27.22% |
| aluminum | 8.13% |
| iron | 5.00% |
| Calcium | 3.63% |
| sodium | 2.83% |
| potassium | 2.59% |
| magnesium | 2.09% |
| other | <1.0% |
Geographical features
Structure of the earth's surface
The earth's surface forms the boundary layer between the earth's crust - consisting of the oceanic or continental crust - on the one hand and the atmosphere on the other. The oceanic water area accounts for a total of 70.7%, while the land area that rises above sea level mainly comprises the continents with 29.3%.
The earth shows a clear division of its surface into the land hemisphere with the maximum land share and the water hemisphere , which is dominated by oceans.
| Structure of the earth's surface | ||
| Total area of the earth | 510,000,000 km 2 | 100.0% |
| Water surface | 360,570,000 km 2 | 70.7% |
| Land area | 149,430,000 km 2 | 29.3% |
| Land area excluding Antarctica | 135,281,639 km 2 (2011) | 100.0% |
| Agricultural area | 49,116,226 km 2 (2011) | 36.31% |
| Forest area | 40,274,680 km 2 (2011) | 29.77% |
| other areas (deserts, fallow land, mountains, built-up areas) |
41,313,584 km 2 (2011) | 30.54% |
| Inland waters (lakes, rivers) |
4,577,149 km 2 (2011) | 3.38% |
Overview
| Largest peninsula | Arabian Peninsula | 3 million km² |
| Largest island in a lake | Manitoulin in Lake Huron (to Canada ) | 2,777 km² |
| Largest island in a river | Ilha do Bananal in the Rio Araguaia (to Brazil ) | 19,162 km² |
| Longest mountain range | Mid-ocean ridge | 7000-8000 km long 1500 km wide |
Waters of the earth
The waters include, on the one hand, the seas , which are divided into five oceans including the secondary seas , and, on the other hand, the inland waters , which include all flowing and standing water within the continental borders.
Oceans
| rank | location | Surname |
Area in km² 1) |
Area in km² 2) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 |
|
Pacific Ocean 1) | 166,240,000 | 181,340,000 |
| 2 |
|
Atlantic Ocean 1) | 84,110,000 | 89,758,000 |
| 3 |

|
Indian Ocean 1) | 73,430,000 | |
| 4th |
|
Antarctic Ocean | 20,327,000 | |
| 5 |

|
Arctic Ocean | 12,260,000 | 14,090,000 |
| 1) without side seas | 2) with secondary seas |
The deepest sea sinks
The average sea depth is 3,800 m. That is about five times the mean altitude of the continents at 800 m (see hypsographic curve ). The deepest point of the sea floor is in the Mariana Trench, about 11,000 m below sea level.
| rank | Surname | region | Depth in m |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Witjastief 1 , Mariana Trench | Pacific | 11.034 (11.022 wire solder) 1 |
| 2 | Challenger Deep , Mariana Trench | Pacific | 10,984 ± 25 (10,863 wire solder) |
| 3 | Trieste Deep , Mariana Trench | Pacific | 10,916 |
1 controversial measurements from 1957
Tributaries
Nebenmeer is a generic term for inland , Mediterranean and marginal seas .
| rank | location | Surname | Area in km² |
|---|---|---|---|
| 6th |

|
Australasian Mediterranean | 9,080,000 |
| 7th |
|
American Mediterranean | 4,354,000 |
| 8th |
|
European Mediterranean | 2,500,000 |
| 9 |
|
Bering Sea | 2,160,000 |
| 10 |

|
Sea of Okhotsk | 1,390,000 |
| 11 |
|
Hudson Bay | 1,230,000 |
| 12 |
|
East China Sea | 1,200,000 |
| 13 |

|
Japanese sea | 1,010,000 |
| 14th |

|
North Sea | 580,000 |
| 15th |

|
Red Sea | 450,000 |
| 16 |
|
Black Sea | 424,000 |
| 17th |

|
Baltic Sea | 390,000 |
| 18th | |||
|
|
Persian Gulf | 240,000 | |
|
|
Gulf of Saint Lawrence | 240,000 | |
| 19th |
|
Gulf of California | 160,000 |
| 20th |

|
Irish Sea | 100,000 |
| Others | 290,000 | ||
Largest natural lakes
| rank | Surname | region |
Area in km² |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Caspian Sea | Azerbaijan - Russia - Kazakhstan - Turkmenistan - Iran | 386,400 |
| 2 | Lake Superior | USA / Canada | 82,414 |
| 3 | Lake Victoria | Kenya - Tanzania - Uganda | 68,894 |
For reservoirs see: List of the largest reservoirs on earth
The deepest lakes
| rank | Surname | region | Depth in m |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Baikal lake | Russia | 1642 |
| 2 | Lake Tanganyika | Tanzania - DR Congo - Zambia - Burundi | 1470 |
| 3 | Caspian Sea | Azerbaijan - Russia - Kazakhstan - Turkmenistan - Iran | 1025 |
The longest rivers
| rank | flow | continent |
Length in km |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Amazon | South America | 6992 |
| 2 | Nile | Africa | 6852 |
| 3 | Yangtze River | Asia | 6380 |
The highest waterfalls
| rank | waterfall | Region / country | height |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Angel somersault | Venezuela | 979 m |
| 2 | Tugela Falls | South Africa | 948 m |
| 3 | Yumbilla | Peru | 870 m |
Land masses of the earth
Continents
The surface of the earth measures 510 million km². The share of the land area is around 148.9 million km² (29%). The country is spread over continents and islands.
Depending on the method of counting, a distinction is made between up to seven continents: Asia , Africa , North America , South America , Antarctica , Australia / Oceania and Europe (Europe, as the large western peninsula of Asia, has probably never been an independent unit in the context of plate tectonics).
The categorical demarcation between Australia as the smallest continent and Greenland as the largest island was only established purely conventionally.
| rank | location | continent | surface |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 |
|
Eurasia (excluding the polar islands) |
54.5 million km² |
| 2 |
|
America (excluding polar regions) |
38.3 million km² |
| 3 |
|
Africa | 29.3 million km² |
| 4th |
|
Antarctic | 13.2 million km² |
| 5 |
|
Oceania | 7.7 million km² |
Islands of the earth
| rank | location | island | Area in km² |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 |

|
Greenland | 2,130,800 |
| 2 |
|
New Guinea | 785.753 |
| 3 |

|
Borneo | 743.330 |
- The most populous island is Java ( Indonesia ) with 131.193 million inhabitants.
- The island with the highest population density is Santa Cruz del Islote ( Colombia ) with approx. 100,000 people / km².
- The largest river island that lies entirely in a river is Ilha do Bananal , 19,162 km².
- The largest inland lake island is the Manitoulin in Canada, 2,766 km²
- The largest atoll is Kwajalein , approx. 303 km circumference, 1,683 km² lagoon area, 16 km² land area
- The largest coral island is Kiritimati , 624 km² land area
- see also: List of the largest islands in the world
The deepest depressions
| rank | Surname | region |
Depth in m below sea level |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Bentley subglacial moat | Antarctica | 2496 |
| 2 | Shores of the Dead Sea | Israel , West Bank , Jordan | 420 |
| 3 | Shores of the Sea of Galilee | Israel , Syria | 212 |
The highest elevations (mountains) above sea level
| rank | mountain | Mountains / land |
Height in m |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Mount Everest | Himalaya / China , Nepal | 8848 |
| 2 | K2 | Karakoram / Pakistan | 8611 |
| 3 | Kangchenjunga | Himalaya / India , Nepal | 8586 |
The highest point on the equatorial line is on the southern flank of the Cayambe in Ecuador .
The highest volcanoes
| rank | Name 1) | Mountains / State |
Height in m above sea level |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Nevado Ojos del Salado | Andes / Argentina , Chile | 6893 |
| 2 | Tupungato | Andes / Chile | 6550 |
| 3 | Guallatiri | Andes / Chile | 6071 |
The largest deserts
| rank | Desert (region) | Area in km² |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | Antarctica ( Antarctica ) | 13,200,000 |
| 2 | Sahara ( North Africa ) | 8,700,000 |
| 3 | Greenland | 2,160,000 |
Climatic features
overview
The temperature extremes measured on earth are −89.2 ° C (measured on July 21, 1983 in the Vostok station in Antarctica at an altitude of 3420 meters) and +56.7 ° C (measured on July 10, 1913 in Death Valley at 54 m below sea level ).
The mean temperature near the ground is 15 ° C. The speed of sound at this temperature is about 340 m / s in the air at sea level.
| Highest air temperature | Death Valley | +56.7 ° C (on July 10, 1913) |
| Lowest air temperature | Vostok , Antarctica | −89.2 ° C (on July 21, 1983) |
| Most rainy place | Cherrapunji , India | 26,470 mm within 12 months |
| The place with the lowest rainfall | Arica , Chile | Average of 0.8 mm per year |
Cultural characteristics
overview
| Country with the poorest population | Vatican city | 829 inhabitants (March 2011) |
| Country with the smallest area | Vatican city | 0.44 km² |
| Country with the lowest population density | Greenland | 0.026 inhabitants / km² (2013) |
| Longest border between two countries | USA / Canada | 8890 km |
| Longest coast in a country | Canada | approx. 200,000 km |
countries
See the full list of countries in the world
The largest countries in terms of area
| rank | location | country | Area in km² |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 |
|
|
17,098,242 |
| 2 |
|
|
9,984,670 |
| 3 |
|
|
9,826,675 |
The most populous countries
| rank | country |
Population in millions |
|---|---|---|
| 1 |
|
1380 |
| 2 |
|
1314 |
| 3 |
|
326 |
Countries with the greatest population density
| rank | country | Inhabitants / km² |
|---|---|---|
| 1 |
|
15,250 |
| 2 |
|
6,744 |
| 3 |
|
1,884 |
(cf. Germany 230 inhabitants / km²)
Metropolitan areas with the most inhabitants
| rank | Surname |
Population in millions (as of 2009) |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | Tokyo Metropolitan Area , Japan | 36-43 |
| 2 | Jabodetabek , Indonesia | 26-28 |
| 3 | Shanghai , China | 24-26 |
The highest cities
| rank | city | Country (region) | Height in m |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | La Rinconada | Peru | 5099 |
| 2 | Wenzhuan | China ( Tibet ) | 5019 |
| 3 | El Aguilar | Argentina | 4895 |
Most spoken languages
| rank | language | Distribution area (selection) | Speakers in millions | of which as mother tongue |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | English | Great Britain , Ireland , USA , Australia , New Zealand , Ghana , South Africa , Canada , Jamaica , Kenya , Cameroon , Gambia , Belize | 1500 | 375 |
| 2 | Standard Chinese | North, East and Central China | 1100 | 982 |
| 3 | Hindi | India | 650 | 460 |
The spread of religions
| rank | distribution | religion | Main distribution areas |
Followers (in millions) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 |

|
Christianity | Europe , Oceania , parts of Africa , North and South America | 2200 |
| 2 |

|
Islam | Europe , Middle East , North Africa , Indonesia | 1387 |
| 3 |
|
Hinduism | India , Indonesia , Nepal | 1050 |
Others
| Highest natural cold water geyser | Geyser Andernach near Andernach , Germany | 60 m |
| Highest navigable lake | Lake Titicaca , Peru , Bolivia | 3812 m |
| Deepest cave (level difference) | Voronya (also: Krubera Cave ), Georgia | 2191 m |
| Narrowest strait | Euripos Canal , Evia , Greece | 40 m |
| Biggest gorge | Dihang Gorges , Tibet ( People's Republic of China ) | approx. 500 km long, approx. 21 km wide (?), max. 6000 m deep. |
| Biggest cave | Mammoth Cave , United States of America | 590 km corridor length |
| Largest cave room | Sarawak Chamber , Malaysia | 600 m × 400 m × 100 m (L / W / H) |
| Largest monolith | Mount Augustus , Australia | 92 km² |
| Largest coral reef | Great Barrier Reef , Australia | approx. 2000 km long, 260,000 km² |
| Largest atoll (excluding dry land, submarine) | Saya de Malha Bank , western Indian Ocean | approx. 35,000 km² |
| Largest atoll (by area / circumference / diameter) | Great Chagos Bank, Chagos Islands | 12,642 km² |
| Largest tidal range | Bay of Fundy , Canada | over 16 m |
| Largest ice cave | Eisriesenwelt in Werfen , Austria | approx. 42 km corridor length |
Individual evidence
- ↑ NASA (NSSDC): Earth Fact Sheet
- ↑ [1] (PDF; 76 kB)
- ↑ Lexicon of Geosciences: Erdkern
- ↑ [2]
- ↑ [3]
- ↑ a b c d e according to FAOSTAT - FAOSTAT
- ↑ a b c d e Global Weather & Climate Extremes at wmo.asu.edu , accessed on December 22, 2013.
literature
- Harenberg country lexicon. Harenberg Lexikon Verlag, ISBN 3-611-01061-8