Federated States of Micronesia
| Federated States of Micronesia | |||||
| Federated States of Micronesia | |||||
|
|||||
|
Motto : Peace, Unity, Liberty
"Peace, Unity, Freedom" |
|||||
| Official language | Kosraean , Pohnpean , Yapese , Chuukes , Ulith , Woleaian and English | ||||
| Capital | Palikir | ||||
| Form of government | Federal Republic | ||||
| Government system | Parliament-bound executive power | ||||
| Head of state , also head of government | President David Panuelo | ||||
| surface | 702 km² | ||||
| population | 104,000 (UN, 2015) | ||||
| Population density | 160 inhabitants per km² | ||||
gross domestic product
|
2016 | ||||
| Human Development Index | 0.638 ( 127th ) (2016) | ||||
| currency | US dollar (USD) | ||||
| independence | November 3, 1986 (free association) November 22, 1990 final (from the USA ) |
||||
| National anthem | Patriots of Micronesia | ||||
| Time zone |
UTC + 10 ( Chuuk and Yap ) UTC + 11 ( Kosrae and Pohnpei ) |
||||
| License Plate | FSM | ||||
| Internet TLD | .fm | ||||
| Telephone code | +691 | ||||
The Federated States of Micronesia ( english Federated States of Micronesia ) are an island nation in the western part of the Pacific Ocean .
geography
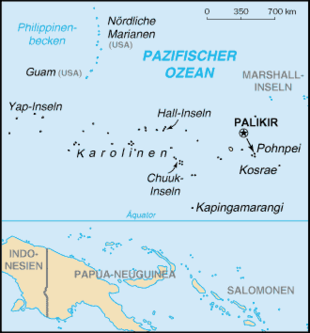
The state occupies most of the Carolines , which are a group of islands in Micronesia . The federation consists of the states of Chuuk , Kosrae and Pohnpei , which form the East Carolina, and the state of Yap , which together with the independent nation of Palau forms the West Carolina. The largest city in the country is Weno with about 17,624 inhabitants on the island of Moen in the east of the Chuuk Atoll ; The capital is Palikir on the island of Pohnpei.
The following islets represent the main islands and atolls of Micronesia: (from west to east)
- Ngulu
- Yap
- Ulithi
- Sorol
- Fais
- Eauripik
- Woleai
- Gaferut
- Olimaraoh
- Elato
- Lamotrek
- West Fayu (Pigailoe)
- Satawal
- Pikelot
- Pulusuk
- Puluwat
- Pulap
- Namonuito
- Fayu
- Chuuk Atoll (until 1990 Truk)
- Hall Islands
- Losap
- Namoluk
- Mortlock Islands
- Satawan
- Kapingamarangi
- Nukuoro
- Oroluk
- Sapwuahfik
- Pakin
- Ant
- Pohnpei
- Mokil
- Pingelap
- Kosrae
history

The islands have been around since at least the end of the 3rd millennium BC. Human settled. It is believed that a larger state developed in the region from the island of Yap in pre-colonial times .
The first Europeans arrived in Portugal in the 16th century to Micronesia. In 1696 the islands were taken over by Spain . After the Spanish-American War , Spain sold the islands to Germany in 1899 . The then German Empire made the islands part of its colony German New Guinea . A Sokehs uprising was forcibly suppressed by the Germans in 1911. At the beginning of the First World War , the islands were occupied by the Japanese army without resistance in 1914 . In 1920 they came to Japan as a League of Nations mandate .
During the Second World War , Truk served primarily as a base for the Japanese attacks on New Guinea , the Bismarck Archipelago and the Solomon Islands . On February 16 and 17, 1944, as part of Operation Hailstone, it was massively bombed by aircraft of the US Navy and a large part of the Japanese armed forces stationed there destroyed. With the so-called " island hopping " of the Americans, however, many other Japanese bases were bypassed and only handed over after the surrender of Japan .
In 1947 Micronesia became a UN Trust Territory . Under the name Trust Territory of the Pacific Islands (TTPI) it was initially administered by the US Navy, from 1961 by the US Department of the Interior . The TTPI enabled the USA to set up additional military bases away from the island of Guam and also to carry out nuclear weapon tests on the island groups. Atomic bombs were tested as early as 1946. In 1954, its stronger successor, the hydrogen bomb, was detonated for the first time on the Bikini Atoll in the Marshall Islands . In addition to military intentions, there were also civil ones: the UN required the US administration to raise national awareness among the tribal population and to promote economic development. In 1967 discussions began on the future of the islands, and in 1970 the Micronesians were finally granted the right to sovereignty.
On May 10, 1979, the four later states ratified the constitution of the thus founded Federated States of Micronesia and signed a treaty of free association with the USA, the Compact of Free Association (COFA), which stipulates their responsibility for defense and financial support . The contract came into effect on November 3, 1986. In 1991 the Federated States of Micronesia finally gained independence.
population
The fertility rate per woman in 2017 was 2.41 children. In the same year, there were 20 births and 4.2 deaths for every 1,000 inhabitants. The average life expectancy at birth in 2017 was 73.1 years (women: 75.3 years, men: 71.1 years). The median age was 25.1 years. Population growth in 2017 was −0.6 percent per year. The country has a high rate of emigration.
Population development
| year | population |
|---|---|
| 1950 | 32.001 |
| 1960 | 44,537 |
| 1970 | 61,431 |
| 1980 | 72,964 |
| 1990 | 96,331 |
| 2000 | 107,432 |
| 2010 | 103.616 |
| 2017 | 105,544 |
Source: UN
people
The largest and politically dominant ethnic group with about 48.8% of the population are the Chuukese . In addition, the Pohnpeianer are an influential ethnic group with 24.2% of the population. Other Micronesian ethnic groups are the Kosraeans with 6.2%, the Yapese with 5.2% and the Yap outer island inhabitants with 4.5% of the total population. 1.8% of the population are considered Asians ; 1.5% as Polynesians . Other ethnic groups make up 6.4% of the total population.
languages
The country has seven official languages: English , Yapese , Pohnpean , Kosraean , Chuukes , Ulith and Woleaian .
Other languages include Mokilesian , Mortlocke , Pingelapian , Puluwatesian , Satawalesian , Namonuito , Pááfang , Nukuoro , Kapingamarangisch and the Ngatik Men's Creole .
Most residents have at least a basic command of English. Many old residents speak Japanese fluently. Many speak one or more of the native languages. Some of these languages have been influenced by Spanish and German during history , then by Japanese, and more recently by English in particular.
religion
By and large, Micronesia is shaped by Christianity due to the German and Spanish colonial history. The Spanish rule meant that a large part of the population is still Roman Catholic today. During the German colonial period until 1914, Protestant missionaries from the German Empire were also deployed.
According to the 2000 census, 52.7% of the population are Roman Catholic and 40.1% are Congregationalists . Minorities are the Baptists and Seventh-day Adventists , who are 0.9% and 0.7% of the total population, respectively. Other denominations make up 3.8% of the population.
health
Statistically speaking, the fattest people in the world live in the Federation of Micronesia and Nauru . Over three quarters of the population is very overweight, which can be attributed to a local and local diet.
Life expectancy in Micronesia was 68.8 years from 2010 to 2015 (women: 69.9 / men: 68.0 years). Micronesia is therefore one of the countries in which the difference between men and women in life expectancy is very small.
Sports
The Micronesian national football team is not a member of FIFA or OFC . Micronesia has its own National Olympic Committee , which has been sending athletes to summer games since the 2000 Summer Olympics .
politics
The Federated States of Micronesia is a democratic federal state with a parliament-bound executive power as a system of government.
The Congress of the Federated States of Micronesia with 14 popularly elected members serves as the legislature . Each of the four states sends a member elected for four years, the other ten members of Congress each represent one of the constituencies determined by population for a legislative period of two years.
The head of state is the president, who is assisted by a vice-president. Both are elected for a four-year term by Congress from among the members sent by the states. Their seats in Congress will then be filled by a by-election. The President appoints a cabinet to carry out government business. There are no political parties in the Federated States of Micronesia .
The highest body of justice is the Supreme Court , which is divided into a procedural and an appeal body. The judges are appointed by the President on the proposal and with the approval of Congress.
President
The previous presidents of the country were:
- Tosiwo Nakayama (1979–1987)
- John Haglelgam (1987-1991)
- Bailey Olter (1991-1997)
- Jacob Nena (1997–1999, represented Olter since November 8, 1996)
- Leo Falcam (1999-2003)
- Joseph J. Urusemal (2003-2007)
- Manny Mori (2007-2015)
- Peter Christian (2015-2019)
- David Panuelo (since 2019)
Administrative structure
The Federated States of Micronesia are made up of four states. Each of these states has its own constitution , its own elected legislature and its own government. The individual state governments have considerable rights and maintain their own budgets .
| map | State | Islands | surface | Residents |
|---|---|---|---|---|

|
Chuuk |
294 | 127 km² | 48,651 |

|
Kosrae |
5 | 110 km² | 6,616 |

|
Pohnpei |
163 | 346 km² | 35,981 |

|
Yap |
145 | 118 km² | 11,376 |
State budget
The state budget in 2007 comprised expenditures equivalent to US $ 152 million , which was offset by income equivalent to US $ 166 million. This results in a budget surplus of 2.2% of GDP . The country receives millions of dollars in dollar payments from the US every year.
In 2006, the share of government expenditure (as a percentage of GDP) was as follows:
- Health : 13.3%
- Education : 7.3% (2000)
- Military : 0.0% (Micronesia has no military, defense is the task of the USA )
Membership in international organizations
Micronesia is a member of the following organizations:
ADB , AKP , AOSIS , ESCAP , FAO , G 77 , IBRD , ICAO , IDA , IFC , IFRCS , IOC , IOM , IPU , ITSO , ITU , IWF , MIGA , OPCW , PIF , Sparteca , SPC , UNCTAD , UNO , UNESCO , WHO , WMO .
economy
As a developing country, the Federated States of Micronesia are characterized by subsistence agriculture and fishing . The sale of licenses for commercial fishing in territorial waters to foreign fishing fleets is the largest independent income item. The largest source of income is financial grants from the USA, which are paid under the Association Agreement. Israel also supports the Federation in the areas of education, agriculture and medical care.
The mining of high-quality phosphate ore forms another economic mainstay. So far, there are no larger industries, smaller companies mainly produce products for the domestic market. Only textiles and souvenirs manufactured on a small scale are of minor economic importance for exports .
There is tourist potential, which is underdeveloped due to the isolation of the islands and the lack of infrastructure .
The unemployment rate was 16.1 percent (as of 2010).
literature
- Ellen Boneparth, M. James Wilkinson: Terminating Trusteeship for the Federated States of Micronesia and the Republic of the Marshall Islands. Independence and Self-Sufficiency in the Post-Cold War Pacific . In: Pacific Studies . tape 18 , no. 2 , 1995, ISSN 0275-3596 , p. 61-78 (English).
- Hermann Mückler : Traditional and modern mobility on atoll islands. For spatial orientation, navigation, boat building and migration in Micronesia . In: Communications of the Anthropological Society Vienna . tape 133 , 2003, ISSN 0373-5656 , p. 125-137 .
- Glenn Petersen: Lessons Learned: The Micronesian Quest for Independence in the Context of American Imperial History. In: Micronesian Journal of the Humanities and Social Sciences. 3, 2004, ISSN 1449-7336 , pp. 45-63 ( online ; PDF; 275 kB).
Web links
- Official website of the government of the FSM
- Official website of the Congress of the FSM
- Legal Information System of the Federated States of Micronesia
- Database of cataloged literature on the social, political and economic situation in the Federated States of Micronesia
- Country and travel information from the Federal Foreign Office (Germany)
Individual evidence
- ↑ a b UN Statistics Division, World Statistics Pocketbook 2015, p. 130 ( Memento from January 1, 2016 in the Internet Archive )
- ↑ [1]
- ↑ [2] United Nations Development Program ( UNDP ),
- ↑ Harenberg State Lexicon , Dortmund 2000.
- ↑ a b c d e CIA World Fact Book Micronesia. Retrieved May 10, 2014 .
- ^ A b World Population Prospects - Population Division - United Nations. Retrieved July 28, 2017 .
- ↑ a b c The World Factbook
- ↑ The Fischer World Almanac 2010: Figures Data Facts. Fischer, Frankfurt, September 8, 2009, ISBN 978-3-596-72910-4 .
- ^ The World Factbook - Central Intelligence Agency. Accessed August 6, 2018 .
Coordinates: 7 ° N , 152 ° E