Asia
| surface | 44,614,500 km² |
|---|---|
| population | about 4 billion |
| Population density | 90 inhabitants / km² |
| countries | 47 internationally recognized |
| Time zones | UTC +2 ( Turkey ) to UTC + 12 ( Russia ) |
Asia , part of Eurasia , is the largest continent in terms of area with around 44.6 million square kilometers, about a third of the total land mass . With over four billion people, more than half of the world's population , this part of the world is also the most populous. There are 47 internationally recognized states in Asia .
Asia played an important role early on in human history. Already around 900 BC originated here. With the New Assyrian Empire or 500 BC With the even larger Achaemenid Empire the first great empires .
etymology
The word "Asia" goes back to the Latin Asia in Greek Ἀσία ( Asía ). To this day one can only speculate about the further origin. Mostly it is assumed that it comes from the Assyrian assu "sunrise, east". The name Asía would therefore designate an eastern region that lies in the direction of sunrise, and would correspond to the Latin word Orient or the German “ Morgenland ”. The early Greeks initially only called the land mass of Asia Minor Asia , which later gave rise to the name of the Roman province of Asia . From Pliny the Elder ( Naturalis historia , around 77 AD) the name was then also related to the larger continent. In the long term, the old Asia became Asia minor .
In Greek mythology , Asia was the name of an Oceanid (or mother of such in Hesiod ), after which the geographical region should have been named. According to Aeschylus ( Promētheús desmṓtēs , around 470 BC) she is also the wife of the titan Iapetus and mother of Prometheus , according to Herodotus ( Historien , 5th century BC) his wife.
In today's common usage, the terms Asian and Asians refer primarily to things and people of East or Southeast Asian origin, for example in relation to cuisine , philosophy or architecture, sometimes including India , while the terms only very rarely refer to the Refer to countries west of India. While West Asia has been in close contact with Europe since ancient times, this was not the case with East Asia, so that this region in Europe represented the epitome of foreignness for centuries, also because countries like China and Japan separated themselves from the outside world and only had limited interest showed in exchange (see Sinocentrism , closure of Japan ).
geography
Asia is the largest continent on earth. With an area of around 44.6 million square kilometers (excluding Russia 31.7 million square kilometers), it comprises around a third of the total land mass. Together with Europe , Asia is also seen as part of the greater continent of Eurasia .
The continental landmass lies entirely in the eastern hemisphere and north of the equator with the exception of the southeasternmost islands in the Malay Archipelago , which are located in the southern hemisphere of the earth. The Chukchi Peninsula in eastern Siberia is located east of the 180th parallel, but the eastern time + 12h applies.
expansion
Asia is bordered by the Arctic Ocean to the north, the Pacific Ocean to the east and the Indian Ocean to the south .
In the west, Asia has no clear geographical or geological boundary with Europe . The most common definition of the border with Europe from north to south: the Ural Mountains , the Ural River , the Caspian Sea , the Caucasus or the Manytn lowlands , the southern coast of the Black Sea as well as the Bosphorus , the Sea of Marmara and the Dardanelles . From the Barents Sea to the Black Sea, this border is around 2700 km long.
With Africa Asia north of the Red Sea on the peninsula Sinai (Isthmus of Suez , 145 km wide) connected.
In the northeast, the mainland masses of Asia and North America are a little more than 80 km apart on the Bering Strait . In the southeast the Malay Archipelago forms the connection to Australia . The southernmost point is the Indonesian island of Pamana .
The northernmost mainland point of Asia and the world is Cape Chelyuskin on the Taimyr Peninsula (77 ° 43 ′ 21 ″ N), the easternmost point Cape Deschnjow on the Chukchi Peninsula (169 ° 39 ′ 7 ″ W). From there to the westernmost point of Asia, Cape Baba in Asia Minor (26 ° 3 ′ 50 ″ E), it is 8,223 km as the crow flies. The southernmost mainland point of the Asian continent is Cape Tanjung Piai on the Malay Peninsula (1 ° 15 ′ 57 ″ N).

structure
There are different approaches to the regional division of Asia. The following division into regions is used, among others, by the UN statistical agency UNSD . This division of Asia into regions by the United Nations is solely for statistical reasons and does not imply any assumption about political or other affiliations of the countries and areas.
- North asia
- Central Asia
- Middle East (West Asia)
- South asia
- East asia
- South East Asia
In some publications, these limits are varied depending on the objective, subject, and background for which a split is used. Afghanistan was previously assigned to Central Asia, now to South Asia. There are also alternative or additional subdivisions or overlaps, for example for Northeast Asia .
Flora and fauna
The main vegetation zones or eco-zones (from north to south):
- Treeless tundra north of the Arctic Circle. The most important animals for the nomadic inhabitants like those of the Nenets are the reindeer .
- Forests of the temperate zone , including the boreal coniferous forest (taiga) in Siberia between the Arctic Circle and the course of the Trans-Siberian Railway and deciduous forests in the Far East and in the area of the Caspian Sea. The diverse fauna has (historical) importance for hunting, in addition to agriculture and cattle breeding, the use of wood is also important. Here live z. B. the rare Amur tigers and Amur leopards , as well as deer, wild boar, lynx and bears.
- Continental grasslands or steppes . The animal species that naturally inhabit these steppes include wild horses, saiga antelopes , Mongolian gazelles , wolves and ground squirrels .
- Low vegetation, rocky mountain landscapes and desert landscapes . Highland climate with large daytime temperature fluctuations and lots of sunshine. The mountains are populated by numerous mountain grazing animals such as ibex, gorals , serau and wild sheep. The most important predator of the Central Asian mountains is the snow leopard. The desert areas are home to half-donkeys, wild camels, cheetahs and gazelles.
- Tropical savannah areas and dry forests, preferably on the Indian subcontinent, but also in Southeast Asia. Characteristic large animals are lions, stag goat antelopes, Nilgau antelopes and various deer.
- Tropical rainforests . After clearing, the next step in destruction is often the cultivation of monocultures such as palm oil plantations, e.g. B. in Sabah (Malaysia) on Borneo .
- Tropical monsoon areas such as the Mekong Delta : Rice cultivation dominates here and poultry and pigs as farm animals as well as fishing.
Superlatives
Asia has a number of global geographic superlatives:
- Most populous country: China
- the largest share of the world's largest country in terms of area: Russia . This share of Russia itself is larger than the world's second largest country Canada.
- the highest mountain range : Himalayas , all mountains over 8000 meters high
- the deepest and oldest lake: the Baikal
- the largest inland lake: the Caspian Sea
- the deepest water: the Dead Sea
It is the continent with the most diverse vegetation, alternating from the permafrost soil of Siberia to the jungle of Southeast Asia . In addition to the extreme tundra , desert and tropical rainforest , all other vegetation zones on earth can also be found in Asia.
Another special feature are most of the world's intercontinental states, with both Asian parts of the country and territories in other parts of the world. These include Russia , Kazakhstan , Indonesia , Japan , Egypt and Turkey .
history
Asia is the cradle of numerous cultures , for example in China , Japan , India , Iran as well as Babylonia and Assyria in the Middle East . All so-called world religions originated in Asia.
Asia and Europe are linked by a long tradition of wars (e.g. Alexander the Great , the Persian Wars , the Crusades , the invasions of the Huns and the Turks ) and voyages of discovery (e.g. Sven Hedin ), but also many important trade connections, such as the Silk Road .
Asia has always been shaped by great empires and is not as fragmented as Europe. The Chinese culture has in the world, but especially in East Asia , its mark (paper, printing, compass, silk , porcelain u. V. M.). From India , the has Buddhism spread. North Asia (especially Siberia ) remained almost unpopulated for a long time, only when the Russian Empire continued to expand, larger cities were founded there. Central Asia was traditionally the home of steppe peoples ( equestrian peoples ), (for example the Mongols ), who in earlier times represented a threat to Europe. The Middle East has been shaped by Islam since the 7th century and has had a strong impact on North Africa .
population
Development of the population of Asia (in billions; excluding Russia, including Turkey)
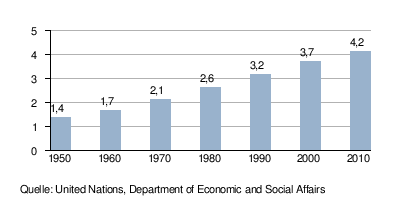
Around four billion people live in Asia, which corresponds to around 60% of the world's population. Both India and the People's Republic of China each have over a billion people. While Russia and Mongolia in particular are very sparsely populated, other countries are struggling with the effects of their population explosion .
Health and life expectancy correlate with the wealth of nations. A higher standard of living also means more resources for our own health as well as for public health.
The residents of Macau, Singapore, Hong Kong and Japan have the highest average age among Asians. Saudi Arabia, the United Arab Emirates, Brunei, China, Malaysia, Thailand, the Philippines and Indonesia are around the world average in terms of life expectancy. The shortest life expectancy in Asia is found in India, Bangladesh, Burma, Cambodia, Laos, Bhutan and Afghanistan.
Malaria is common in South Asia and Southeast Asia. There is still no effective vaccine against malaria. By insect sprays the disclosure of which might be somewhat curbed, but these are too expensive for large sections of the population affected.
AIDS is widespread. The HI virus is particularly common in Russia, India, Nepal, Myanmar, Thailand, Cambodia, Vietnam and Malaysia. In contrast, in Japan, Mongolia, Sri Lanka, Bangladesh, Bhutan, Afghanistan, Turkmenistan and in the Middle East, only relatively few people have AIDS. These figures should be viewed with caution, however, as the HIV infection rate is an average for the entire country, but occurs more frequently in large cities.
languages
Hundreds of individual languages are spoken in Asia. The important language families and language groups include (selection):
- Slavic languages
- Caucasian languages
- Semitic languages
- Iranian languages
- Oghuz languages
- Kipchak languages
- Uighur languages
- Siberian Turkic languages
- Sinitic languages
- Indo-Aryan languages
- Dravidian languages
- Tibeto-Burmese languages
- Tai Kadai languages
- Austro-Asian languages
- Korean language
- Japanese ryūkyū
- Malayo-Polynesian languages
See also section Eurasia: Europe and Mainland Asia in the article Language families of the world .
economy
The breakdown into North Asia ( Russia ), West Asia (W), Central Asia (Z), South Asia (S), Southeast Asia (SO) and East Asia (O) results in the following picture:
- After Africa, Asia has the most developing countries . These include Vietnam (SO), Cambodia (SO), Laos (SO), Myanmar (SO), Bangladesh (S), Bhutan (S), Nepal (S), Pakistan (S), Afghanistan (S), Tajikistan (Z ), Uzbekistan (Z), Kyrgyzstan (Z), Georgia (W), Armenia (W), Azerbaijan (W), Yemen (W), Mongolia (O) and (still) the People's Republic of China (O) and India ( S).
- The countries "bought" into the industrial age include the oil producing countries Iran (S), Iraq (W), Kuwait (W), Saudi Arabia (W) and the United Arab Emirates (W) (and perhaps soon the oil-rich areas too the former Soviet Union).
- The industrialized nations are Japan (O), Singapore (SO), the Republic of China (Taiwan) (O), South Korea (O), Israel (W), and the two colonies Hong Kong and Macau that have been returned to the People's Republic of China (O) . These countries are now among the world's leading countries in the fields of high technology . Even Malaysia (SO) is making successful efforts to catch up to the top.
- The richest country in the world, Qatar (W), is in Asia.
Industrial nations
In terms of both exchange rate-based gross domestic product and purchasing power parity, China is the largest economy in Asia and the second largest in the world. In Asia, Japan, India and South Korea follow. The economy of Japan was the fastest growing economy in Asia for decades. While Japan's economic situation has worsened since the 1990s, China and India show above-average economic growth of more than 10 and 7 percent per year, respectively , in the global comparison . Japan handed over the role of Asia's leading economic nation to China in 2010. Nevertheless, it is the leading industrial nation in Asia and (besides Russia, which is largely part of Europe) the only country on the continent that is a member of the group of eight leading industrialized countries. In terms of purchasing power parity, India also has a larger GDP than Japan today (2015).
Tiger states


After the Second World War , and intensified from the 1960s onwards, economic growth was initially concentrated on the countries and areas along the Pacific coast, from which Japan, South Korea and Taiwan as well as the former British colonies of Hong Kong and Singapore, which closely followed the United States economy tied. In the 1980s, several states in East and Southeast Asia developed from emerging economies to industrialized countries with rapid economic growth : the so-called " tiger states " Hong Kong (at that time still a crown colony of the United Kingdom ), Taiwan, Singapore and South Korea. In 1997/98 the rapid boom in many of these countries came to an end with the Asian crisis , which - starting in Thailand - was primarily a financial and currency crisis. Since then, the economies of these countries have continued to grow, but the very high growth of up to ten percent has weakened to five to six percent.
Developing countries

Large parts of Asia are still dominated by agriculture , with rice cultivation and fishing being of particular importance.
Countries with few raw materials or countries that have been thrown back by war and corrupt governments such as Afghanistan , Bangladesh , Myanmar , Laos , Cambodia , Vietnam and the former Soviet republics in Central Asia are still characterized by agriculture according to their topography.
Most of today's Central and North Asian states were part of the Soviet Union until its collapse in 1990/91 and were thus organized according to a planned economy . The economies of these countries are largely determined by agriculture and heavy industry .
The wealth of raw materials in some regions, such as oil and gas in the Caspian Sea region or those in the tundra of Siberia, is gaining importance in the global struggle for these resources, whereby the curse and blessing for the inhabitants are often close together (environmental pollution, corruption and wars).
Gulf States
In Southwest Asia, oil production is the main industry. The world's largest known reserves are located on the Arabian Peninsula and in the surrounding regions on the Persian Gulf, with the Kingdom of Saudi Arabia having the most extensive oil fields. Other important producing countries are Iran and Iraq. The emirates of Kuwait and Qatar, which are small in terms of area, the United Arab Emirates and the Kingdom of Bahrain are among the richest countries in the world due to the sale of crude oil with a relatively small population.
Religion, mythology and philosophy
Several regions of Asia, including Mesopotamia , the valley of the Indus (see Indus culture ), Iran and China , are considered to be the " cradles of civilization ". With the development of civilizations and the early advanced civilizations in these areas, the development of religions went hand in hand. All religions generally referred to as “ world religions ” have their origins in Asia. With over 1 billion followers, Islam is the largest religion in Asia and comprises more than a quarter of all inhabitants of the continent. Muslims make up the majority of the population in more than half of all countries in Asia.
Middle East
The facility in Göbekli Tepe in today's Turkey is one of the earliest monuments of human religious sentiment . Originated around 9000 BC BC, although the origins are likely to go back much further than the Neolithic Revolution and with it the beginning of agriculture and cattle breeding, Göbekli Tepe is considered the oldest known temple complex in the world. Finds in Nevalı Çori on the Euphrates in what is now the Turkish province of Şanlıurfa date from around the same time , where comparable sculptural works, such as anthropomorphic figures and depictions of animals that indicate religious use, have been found.

In Mesopotamia ( Mesopotamia ;. See " Fertile Crescent ") is the fourth millennium, developed from around v. The Sumerian religion . It is one of the oldest known religions and had a decisive influence on the later developing belief systems of the Canaanites (forerunners of the Hebrews ), Akkadians , Babylonians , Assyrians , Hittites , Hurrites , Ugarites and Aramaeans . In addition to a number of the main and original gods, the Sumerians worshiped city gods at a time when some of the first cities such as Ur and Byblos arose there (see list of historical city foundations ) and thus already had a pantheon of gods. The Gilgamesh epic , one of the earliest written records of mankind, has its origins in this era and tells of the encounters between King Gilgamesh and the gods and his search for immortality. The Enūma eliš (written around the 12th century BC) is again one of the most original creation myths . Sumerian myths, such as the story of the Flood , also found their way into Judeo-Christian traditions.
Probably in Bactria originated between 1800 BC. BC and 700 BC Chr. Of Zoroastrianism , one of the oldest, though originally dualistic , monotheistic ( Ahura Mazda ) religions, which has survived to this day.
The judges (approx. 1250 BC) and the patriarchs , who are considered the earliest traditions in Jewish history, had their origins in Mesopotamia, where the ancestors of the Hebrews lived as a nomadic people. Abraham , the progenitor of Israel, is said to have come from Ur himself. The Jewish religion is traditionally recorded in the Torah as a written and an oral teaching ( Talmud and others).
With Jesus of Nazareth (cf. Jesus Christ ) about 7 to 4 BC The founder of Christianity , who himself is in the tradition of the Jewish religion, was born in Palestine . After his death, the teaching of his disciples was first spread in the Middle East and, within the Roman Empire , in southern Europe. Various traditions of the Christian Orient developed in Asia, some of which, such as Nestorianism , penetrated as far as Central Asia and China. Starting from the Byzantine Empire , the ancient oriental churches spread to the Near East and India, as well as the Orthodox churches that still predominate in large parts of North Asia .
The history of Islam began in the 6th century with the work of Muhammad on the Arabian Peninsula . According to the teaching of Islam recorded in the Koran , he is considered the last prophet in human history and the perfecter of biblical prophecy . In Asia, Islam spread in the course of Islamic expansion in the Middle East and in large parts of Central and South Asia to the Malay Archipelago in the southeast.
South and East Asia

Hinduism , which still predominates in India today, emerged towards the end of the Indus culture around 2000 BC. The teachings are based on the Vedas , holy scriptures, the oldest of which, the Rigveda , from around 1200 to 1000 BC. Was put together. Hinduism encompasses a large number of sometimes very different schools of faith and views. There is neither a common creed nor institutions that have equal authority for all believers. Unifying features are the central deities Brahma , Shiva and Vishnu ( Trimurti ) - which, however , are viewed very differently in the teaching traditions such as Shivaism , Vishnuism or Shaktism - and the belief in the constantly repeating cycle of life ( samsara ) and reincarnation . Like Indian philosophy , Hinduism had an early formative influence on those countries that were under the influence of Indian culture and found its way into the worlds of belief in South and Southeast Asia.
At the turn of the sixth to the fifth century BC, Siddhartha Gautama lived in northern India , who, according to tradition, attained enlightenment at the age of 35 and thus became a Buddha ("awakened", "enlightened"). Coming from the Vedic tradition and leaving it behind, he became the founder of Buddhism . At around the same time Mahavira founded the doctrine of Jainism in India .
Buddhism first became known on the Indian subcontinent , Sri Lanka and Central Asia . Southern Buddhism ( Theravada ) spread to the countries of Southeast Asia. Northern Buddhism ( Mahayana ) reached Central and East Asia via the Silk Road , as well as the countries of the Himalayan region from northern India, where, in interaction with the already widespread belief systems such as Bon , further traditions developed; for example Vajrayana (Tibet), Chan (China) or Zen (Japan) and Amitabha Buddhism (East Asia).
In China, the philosophers Laozi (also Lao Tse , Lao-tzu ; 6th century BC, whether it actually existed is not definitively clarified) and Confucius (also Kong Tse , Kǒng Fū Zǐ ; approx. 551 BC). BC to 479 BC) established the teaching traditions of Daoism and Confucianism , which still have a formative influence on the world of thought and society in East Asia and also influenced the development of Buddhism in these regions (cf. Buddhism in China ).
The religion in Japan was characterized early on by the syncretism of different belief systems. To date, Shinto and Buddhism (Zen, Amidism), which reached Japan in the 5th or 6th century, are the most widespread religions. Contents of the Chinese teachings Daoism and Confucianism were taken up and integrated by Shinto and Buddhism. Since the end of the Second World War, there has been a particularly high level of religious tolerance in Japan, which has led to a strong growth in new religious groups.
At the turn of the 15th to the 16th century , Guru Nanak founded Sikhism in Punjab , in northwest India . Often referred to as the secession or reform movement of Hinduism or as syncretism between Hinduism and Islam, Sikhs describe their faith as a cross-religious path of life that is not based on dogmatic boundaries, but on lived wisdom.
Officially founded on September 7, 1926 in southern Vietnam , Caodaism ( Đạo Cao Đài ) is now the third largest religion in the country after Buddhism and Catholicism. The founder of the religion was Ngô Văn Chiêu , who received the teachings of this religion, which includes various contents from several Asian religions and Christianity, through spiritualistic sessions.
In the 20th century, personalities as diverse as the Indian Mahatma Gandhi , with his doctrine of non-violence ( ahimsa ) derived from Indian philosophy , and the Chinese revolutionary Mao Zedong , with his communism- based Maoism , had a decisive influence on the politics of both largest countries in the world according to their population and beyond.
Countries of Asia by region
| country | Capital | Area (km²) | Population 2016 |
|---|---|---|---|
| North asia | |||
|
|
Moscow | 13,122,850 (Asian part only) | around 38 million (only Asian part) |
| East asia | |||
|
|
Beijing | 9,572,419 | 1,380,000,000 |
|
|
Taipei |
35,980 | 23,500,000 |
|
|
Tokyo | 377.835 | 126,900,000 |
|
|
Ulaanbaatar | 1,565,500 | 3,000,000 |
|
|
Pyongyang | 122,762 | 25,000,000 |
|
|
Seoul | 99,392 | 50,700,000 |
| South asia | |||
|
|
Kabul | 647,500 | 32,200,000 |
|
|
Dhaka | 144,000 | 160,400,000 |
|
|
Thimphu | 47,000 | 800,000 |
|
|
New Delhi | 3,287,590 | 1,314,100,000 |
|
|
Times | 298 | 300,000 |
|
|
Kathmandu | 147.181 | 28,000,000 |
|
|
Islamabad | 803.940 | 199,000,000 |
|
|
Colombo | 65,610 | 20,900,000 |
| South East Asia | |||
|
|
Bandar Seri Begawan | 5,770 | 400,000 |
|
|
Jakarta | 1,912,988 | 255,700,000 |
|
|
Phnom Penh | 181.040 | 15,400,000 |
|
|
Vientiane | 236,800 | 6,900,000 |
|
|
Kuala Lumpur | 329,750 | 30,800,000 |
|
|
Naypyidaw | 676,600 | 52,100,000 |
|
|
Manila | 300,000 | 103,000,000 |
|
|
Singapore | 682 | 5,500,000 |
|
|
Bangkok | 513.115 | 65,100,000 |
|
|
Dili | 15.007 | 1,200,000 |
|
|
Hanoi | 331,690 | 91,700,000 |
| Middle East | |||
|
|
Cairo | 60,000 (only the Sinai) | ≈1,300,000 (only on Sinai) |
|
|
Yerevan | 29,800 | 3,000,000 |
|
|
Baku | 86,600 | 9,700,000 |
|
|
Manama | 711 | 1,400,000 |
|
|
Tbilisi | 69,700 | 3,800,000 |
|
|
Baghdad | 437.072 | 37,100,000 |
|
|
Tehran | 1,648,195 | 78,500,000 |
|
|
Jerusalem | 22,380 | 8,400,000 |
|
|
Sanaa | 527.970 | 26,700,000 |
|
|
Amman | 89,342 | 8,100,000 |
|
|
Doha | 11,437 | 2,400,000 |
|
|
Kuwait City | 17,820 | 3,800,000 |
|
|
Beirut | 10,452 | 6,200,000 |
|
|
Muscat | 309,500 | 4,200,000 |
|
|
Ramallah | 6.220 | 4,500,000 |
|
|
Riad | 2,240,000 | 31,600,000 |
|
|
Damascus | 185.180 | 17,100,000 |
|
|
Ankara | 779.452 | 67,000,000 |
|
|
Abu Dhabi | 83,600 | 9,600,000 |
|
|
Nicosia | 9,251 | 775.927 |
| Central Asia | |||
|
|
Nur-Sultan | 2,717,300 | 17,500,000 |
|
|
Bishkek | 198,500 | 6,000,000 |
|
|
Dushanbe | 143,100 | 8,500,000 |
|
|
Ashgabat | 488.100 | 5,400,000 |
|
|
Tashkent | 447,400 | 31,300,000 |
* is politically and culturally assigned to Europe
** contested state
Since 2008, Abkhazia and South Ossetia have been recognized as two other states by Russia and four non-Asian states, but the remaining states continue to regard them as part of Georgia. The Turkish-occupied Turkish Republic of Northern Cyprus is only recognized by Turkey. Nagorno-Karabakh , which was split off from Azerbaijan with Armenian help , is not recognized by Armenia itself, but it is recognized by Abkhazia and South Ossetia. The autonomous region of Kurdistan in northern Iraq originally aspired to independence, but has agreed on autonomy within Iraq in a basic agreement with the central government in Baghdad. The state of Palestine , which emerged from the Palestinian Autonomous Territories, is an observer state in the UN, but not a UN member state. As early as 1988, the founding of the Palestinian state was recognized by over 100 states (including the GDR and the Vatican) with which Palestine maintains diplomatic relations. The Islamic State , which has been spreading across large parts of Iraq and Syria since 2014 at the latest and which calls into question the state structure of Western Asia that emerged in the 20th century, is not internationally recognized .
Economic and political alliances and organizations
The Arab League was founded as an association of Arab states on March 22, 1945 in Cairo, where it is also based. It consists of 22 member states: 21 nation states in Africa and Asia as well as Palestine. The main objective of the Arab League is to promote relations between the member states in the political, cultural, social and economic fields. The independence and sovereignty of the member states and Arab external interests should be preserved and disputes within the league should be settled. Decisions of the league are only binding on those states that have approved them. Member states from Asia are: Bahrain, Iraq, Yemen, Jordan, Qatar, Kuwait, Lebanon, Oman, Palestine, Saudi Arabia, Syria and the United Arab Emirates. Within the league, Saudi Arabia, Kuwait, Bahrain, Qatar, the UAE and Oman form the Gulf Cooperation Council .
In September 1960, Iran, Iraq, Kuwait, Saudi Arabia and the South American state Venezuela founded the OPEC ( Organization of Petroleum Exporting Countries ) in Baghdad , which later also the oil producing countries Qatar (1961), Indonesia (1962) and the United Arab Emirates (1967 ) joined. The OPEC member states from Asia, Africa and South America together produce around 40% of global oil production and have around three quarters of the world's oil reserves. The goals of OPEC are a common oil policy in order to protect itself against a fall in prices and at the same time secure global oil supplies. Petroleum production is regulated by setting production quotas for the individual OPEC members. In addition to OPEC, a number of countries are also represented in the OAPEC ( Organization of Arab Oil Exporting States ), which was created in 1968 by Kuwait, Libya and Saudi Arabia as an amalgamation of politically conservative Arab countries in Asia and North Africa and an antipole to OPEC. Other members from Asia today are Bahrain, Iraq, Qatar, Syria and the United Arab Emirates.
The ASEAN ( Association of Southeast Asian Nations ) was established on August 8, 1967 as a political, economic and cultural Association of Southeast Asian Nations Thailand, Indonesia, Malaysia, Philippines and Singapore. The aim was and is to work together to promote economic recovery, social progress and political stability in the region. Founded in the time of the “ Cold War ”, the alliance was capitalist- market economy and geared towards cooperation with the western industrialized nations from the beginning and was in competition with the communist- planned economy People's Republic of China. The Sultanate of Brunei joined ASEAN in 1984, Vietnam in 1995, Myanmar and Laos in 1997 and Cambodia in 1999. Papua New Guinea has observer status. On January 1, 2003, with the establishment of the ASEAN Free Trade Area (AFTA), a free trade area was created to which all member states of ASEAN belong. Australia and New Zealand are in negotiations to join this free trade agreement . ASEAN plus Drei refers to the joint conference of the ASEAN countries with China, Japan and South Korea. In Thailand, the Chiang Mai Initiative was founded in 2000, which stipulates close cooperation between ASEAN plus three countries in the financial sector.
Iran, Pakistan and Turkey founded the Organization for Economic Cooperation (ECO) in 1985 , from which a free trade area should emerge. Since the dissolution of the Soviet Union, Afghanistan, Azerbaijan, Kazakhstan, Kyrgyzstan, Tajikistan, Turkmenistan and Uzbekistan have also joined the cooperation alliance. It is of international importance primarily due to the wealth of mineral resources in some member countries and the strategic location as a transit corridor for these goods both to Europe and to China.
On the initiative of the USA, Japan and Australia, the Asia-Pacific Economic Community (APEC) was created in 1989 , the aim of which is to establish a free trade area encompassing all Pacific countries in two steps: the free trade agreements are to apply to the industrialized nations of the regions from 2010 and from 2020 also for developing countries. The Asian members of the APEC are Brunei, the People's Republic of China, Indonesia, Japan, Malaysia, Papua New Guinea, the Philippines, Russia, Singapore, South Korea, Taiwan, Thailand and Vietnam.
The Asia-Europe Meeting (ASEM) provides advice and multilateral discussions between Europe and Asia on cooperation in business, politics, education and culture. The proposal for this meeting came from the then Prime Minister of Singapore Goh Chok Tong and was implemented in March 1996. Members from Asia are: Brunei, the People's Republic of China, Indonesia, Japan, Cambodia, Laos, Malaysia, Myanmar, Philippines, Singapore, South Korea, Thailand and Vietnam.
In 1997 the group of eight developing countries (D-8) was founded, which includes Egypt and Nigeria as well as the Asian states of Bangladesh, Indonesia, Iran, Malaysia, Pakistan and Turkey. The aim of the D-8 is to improve its position in the world economy, to diversify trade relations and to create new trade relations, to increase participation in decisions at international level and thus to ensure better living conditions for people in developing countries .
The Shanghai Cooperation Organization (SCO; also: Shanghai Organization for Cooperation , SOZ) emerged in 2001 from the Shanghai Five Group , which was primarily intended to serve the military cooperation of the member countries and the reduction of the military presence at the common borders. Uzbekistan was added to the original member states of the People's Republic of China, Russia, Kazakhstan, Kyrgyzstan and Tajikistan when the SCO was founded. Mongolia, India, Pakistan and Iran are in observer status. India in particular is encouraged to become a full member. In addition to improving political stability in the region, for which an anti-terror network ( Regional Antiterrorism Structure , RATS) was set up, a common foreign policy and the creation of a free trade area are sought in the long term.
In the run-up to the fifth ministerial conference of the World Trade Organization (WTO) in Cancún ( Mexico ), the G20 (at times also G21 , G22 or G20 + ) was created on August 20, 2003 as a common platform for developing and emerging countries and a counterweight to the USA and the EU . Along with Brazil, the People's Republic of China and India are the leading forces in this. Indonesia, Pakistan, the Philippines and Thailand are also members.
Since 2002, 30 Asian countries from all regions have been cooperating in the Asian Cooperation Dialogue . Annual meetings of the foreign, finance and economic ministers in particular are intended to contribute to increased cooperation.
Other major Asian organizations are: the Organization of the Islamic Conference , the Asian Development Bank ( Asia Development Bank , ADB) and the Asian Human Rights Commission .
See also
- Asian highway project
- Eurasisches Magazin - online magazine with the topic of Europe and Asia.
- Transnational pollution in East Asia
- List of Asian TV channels in Europe
- List of geographical records by continent # Asia
Web links
- Database of literature on the social, political and economic situation in Asia
- Asia House Foundation in Cologne , an association of non-governmental organizations working on Asia, offers a wide range of information on different countries and regions with a focus on social developments, human rights and the environment.
- Federal Agency for Civic Education: Focus on Asia
- Jochen Buchsteiner: New forces in Asia - repercussions for Europe. Discussion paper for the Salzburg Trilogue 2006 on the economic, political and cultural consequences of the “Pacific Century”. Bertelsmann Foundation, Gütersloh, August 2006 (PDF; 912 kB)
- Culture in Asia: art, religion, cult, festivals, calendar, architecture, history (by Dr. Bernhard Peter) (a broad information forum about various Asian countries that combines essays, photo galleries and travel reports)
- ZNet's Resource on Asia ( Memento from July 20, 2008 in the Internet Archive )
- Extensive map collection of Asia
- Perry-Castañeda Library Map Collection: Historical Maps of Asia (University of Texas, Austin)
- a resource of the Asia Society (Engl.)
- Asian expatriates resources (Engl.)
- Many pictures from Asia from Dubai to Vietnam
Individual evidence
- ^ Entry "Asia" in the Online Etymology Dictionary .
- ↑ Standard Country or Area Codes for Statistical Use (M49 Standard). UN Statistica Division, accessed on May 2, 2020 (click on "Geographic Regions"). Quote: "The assignment of countries or areas to specific groupings is for statistical convenience and does not imply any assumption regarding political or other affiliation of countries or territories by the United Nations."
- ↑ United Nations, Department of Economic and Social Affairs: World Population Prospects: The 2010 Revision , data available online
- ↑ Statistics life expectancies
- ↑ Frankfurter Allgemeine Zeitung of March 8, 2013, pages 6–7: Die Welttreligionen
- ^ Time Almanac (powered by Encyclopaedia Britannia) 2010, page 508. Chicago 2010
- ↑ DSW data report 2016. (PDF) World Population Foundation, accessed on October 29, 2017 .