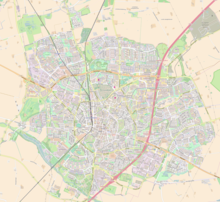
Lund
| Lund | ||||
|
||||
| State : | Sweden | |||
| Province (län): | Skåne County | |||
| Historical Province (landskap): | Gentle | |||
|
Municipalities : |
Lund Staffanstorp |
|||
| Coordinates : | 55 ° 42 ' N , 13 ° 12' E | |||
| SCB code : | 3584 | |||
| Status: | Crime scene | |||
| Residents : | 87,244 (December 31, 2015) | |||
| Area : | 26.3 km² | |||
| Population density : | 3317 inhabitants / km² | |||
| Postal code : | 220 02 - 228 20 | |||
| List of perpetrators in Skåne County | ||||
Lund [ lɵnd ] is a city in the southern Swedish province of Skåne län and the historic province of Skåne .
The so-called “student city” (more than a third of the population are students) is the eleventh largest city in Sweden and the third largest city in Skåne after Malmö and Helsingborg . It is characterized by numerous cafes, parks and old brick facades. The university town is considered the cultural center of the south and is the capital of the municipality of the same name . It is considered to be the fastest growing city in the country. As one of the oldest and most important cities of the Middle Ages, it is classified as an imperial interest .
geography
Lund is not far from the Öresund , about 17 km northeast of Malmö and only 60 km from the Danish capital Copenhagen , in the extreme southwest of Sweden , at 55 ° 42 '10 north latitude and 13 ° 11' 35 east longitude. The distances to some other Swedish cities are accordingly large. So Gothenburg about 250 km, Stockholm 600 km Umea almost 1200 km away. The city belongs to the transnational Öresund region and is part of the metropolitan region of Malmö (Greater Malmö) .
| Landskrona | Kävlinge | Eslöv |
| Copenhagen (Denmark) |

|
Södra Sandby |
| Malmo | Staffanstorp | Dalby |
Lund is located at the northwestern end of Romeleåsen , Sweden's southernmost eyrie , which extends 30 kilometers in a south-easterly direction to Ystad . Due to its location, Lund's highest point is in the northeast of the city, which slopes steadily to the southwest.
A small part (1 hectare ) of the area of the village with 9 inhabitants (2015) lies on the territory of the neighboring municipality of Staffanstorp to the south .
climate
Lund has a humid continental climate . Due to the proximity to the Öresund and the unprotected location on the Skåne peninsula, the weather is consistently windy, with wind mostly from south to south-west. This results in relatively small temperature fluctuations. The winters are mostly wet with little to no snow, and in summer the temperatures rarely exceed 25 degrees. The annual average temperature is 7.9 degrees, the annual precipitation is 655 mm.
history
etymology
It is believed that the name Lund comes from the Swedish word lund , which can be translated as wood or small forest . The allusion to a “holy hawthorn wood” is believed to have been located between the hamlets of Valkärra Torn and Östra Torn (now part of Östra Torn-Mårtens Fälad ), north of today's town of Lund.
Foundation and early history
Founded around 990 AD by the Danish Viking king Sven Gabelbart , Lund is the oldest city in Sweden, on a par with Sigtuna . Archaeological finds at Uppåkra indicate that the city was moved about five kilometers to the north after it was founded, probably on royal initiative. The finds give reason to believe that the city functioned as the central location for what was then southwestern Skåne even before the move. The settlement is also mentioned in the oldest history of the north as a city that was powerful due to shipping and trade.
The new location of the city was of strategic advantage as the better view of Romeleåsen and Moor - and swamps along the river Höje River gave additional protection. As in Uppåkra, the important country road ( Länsväg ) also ran past Lund in a north-south direction, but Lund was now also on the country road in an east-west direction, and it seems reasonable to assume that this gave the city new weight Schonens achieved. The founding of the city can therefore be seen in a series of attempts to create a unified Danish kingdom .
middle Ages

Lund was a suffragan diocese of the Archdiocese of Canterbury until the first half of the 11th century . This connection gradually dissolved when Lund became an ecclesiastical center with the growth of Christianity around 1050 and became a bishopric itself in 1060 , when Denmark was divided into new dioceses . From 1066, under Bishop Egino , Lund was subordinate to the Archdiocese of Hamburg- Bremen, within the boundaries of today's diocese, with the areas of Bornholm and Halland .
With the Katedralskolan , the oldest school in Scandinavia was founded in 1085 . Knut the Great wanted to make Lund a second London, the metropolis of Scandinavia. The development into the new center of power was not without problems, however, as Dalby , about 10 km east of Lund, also competed for the bishopric and there began to build a cathedral church, which was never completed.
In 1103, Lund Cathedral, the oldest in Scandinavia, began, which further strengthened Lund's position and Dalby - like Uppåkra - lost its importance. A year later, Lund became an archbishopric , initially for the Nordic countries and, after Norway (1152) and Sweden (1164) became independent archbishoprics, also of Denmark . Up until the Reformation, the archbishop raised claims to supremacy over all Nordic prelates . In these times Lund was the spiritual and in a certain sense also the secular capital of the Danish Empire (metropolis Daniae) , whose coins were minted in Lund and whose kings were worshiped at St. Liborius level.
The city experienced its greatest heyday in the 13th and 14th centuries as Denmark's most important city. Knut I of Sweden celebrated his wedding here in 1177, in 1202 King Waldemar II (the victor) was crowned in Lund and in 1409 the wedding of Erich of Pomerania to Philippa, the daughter of Henry IV of England, was celebrated.
In the following years Lund remained one of the most important cities in Denmark, but lost its importance with the rise of Malmö in the 15th century: After the campaign of Charles VIII from Sweden to Scania in 1452 had dealt a severe blow to the prosperity of the city, it sank Reformation and the accompanying separation of religion and state into decline and insignificance. With the exception of the cathedral and the monastery church of St. Peter, the other churches were torn down, the houses fell into disrepair and squares remained undeveloped.
Early modern age
During the Second Northern War , Denmark declared war on Sweden in June 1657. This dispute ended in the Peace of Roskilde of 1658: Denmark had to vacate its property in what is now southern Sweden, so the city was ceded to Sweden together with all of Skåne in the same year.
The following war years under Charles XI. with the victory of the Swedes in the Battle of Lund on December 4, 1676 and under Charles XII. with the peace between Sweden and Denmark on October 6, 1679 accelerated the decline of the city. It took a long time for Lund to regain supraregional importance, especially thanks to the university founded in 1666 .
The main purpose of the establishment of the university was to tie the formerly Danish area to Sweden, which had an impact on the position of the formerly important city, at least in the medium term. Because from the end of the 17th century, Lund seemed to regain its former glory, especially through the university: Samuel von Pufendorf published his humanistic-democratic universal ethics on it in 1672.
Briefly seat of government 1716-18
Towards the end of the 17th and beginning of the 18th centuries, Sweden was ravaged by further wars, which made the situation in the city difficult. Fires raged in 1703 and 1711, and the bubonic plague from 1712 to 1713 . When between September 6, 1716 and June 11, 1718 Charles XII. resided in Kungshuset , Sweden was ruled from Lund. Two campaigns against Norway were planned and carried out. In the last years of the Great Northern War , diplomats from all over Europe came to Lund and the city gained new political importance.
industrialization
The industrial revolution and subsequent urbanization reached the city with the opening of the first section of the Södra stambanan from Malmö to Lund in 1856. However, unlike other cities in Sweden, Lund was not overly industrialized, despite its location on the railroad . A large part of the industry was initially concentrated in Malmö, and the old trade routes, which were gradually being replaced by railways, now had Malmö as their terminus. Other factors that contributed to the weak industrialization were the dominance of the university and the church. Since these institutions had always played a major role, a broad settlement of industry was avoided. Nevertheless, the construction of other railway lines began, such as the one to Trelleborg (1877), Bjärred (1901) and today's Västkustbana to Gothenburg (1888), originally a branch line to Kävlinge .
The university also experienced a new boom: new faculties were founded and new buildings, such as the main administration building, were erected. At the beginning of the 19th century, famous personalities such as Esaias Tegnér , Carl Adolph Agardh and Pehr Henrik Ling lived and worked in the city.
After 1945
After the end of the Second World War , the city experienced strong population growth; in 1950 about 35,000 people lived in Lund. Former arable land such as Norra Fäladen , Östra Torn-Mårtens Fälad and Klostergården have been developed into new districts. In 1951 the new building for the Lund University Hospital, founded in 1768, was opened. The range of courses at the university was also expanded and the Lund Technical University ( Lunds tekniska Högskola, LTH ) was founded in 1961 . In 1983, construction began on Sweden's first industrial park, Ideon , which is now a company park primarily for information and biotechnology companies .
Cityscape
When Lund was the seat of the archbishop in the 12th and 13th centuries, many church buildings were built in and outside the city . At times there were 27 churches and monasteries in Lund. In the course of the Reformation, however, a large part of the religious buildings was demolished. The medieval city center is still most evident through the structure of the street network, which has been preserved to this day and, seen as a whole, has the shape of a human heart, which is typical of urban planning in the Middle Ages. The streets of the inner city district Centrum also consist exclusively of cobblestones , which despite the busy bus traffic are not being replaced by ordinary asphalt , but are constantly being renewed. Other features include a number of medieval buildings such as the cathedral, the royal house ( Kungshuset ), Krognoshuset and the cathedral school from 1085.
The construction of half-timbered houses was not unusual until the 18th century , which shows the influence of northern Germany, for example. The majority of today's houses date from this very time. Towards the end of the 18th century, many old houses were expanded or replaced by multi-storey buildings, such as the main building of the cathedral school or the grand hotel . From 1902 to 1907 the new university library was built on the Helgonabacken . Other university buildings were added in the university district. In the city center in particular, but also in and around the university campus, there are still many brick facades.
In the 1960s, there was a plan for Genombrottet , the breakthrough of a four-lane road directly through the city center. This plan was mainly supported by the bourgeois parties, but in later years it was abandoned and in 1968 it was decided to stop the project. In some of the places where the demolition began, you can still find larger fallow land today . The relocation of shopping centers to the outskirts of the city was also rejected for a long time. This is how Nova Lund , the first and so far only such facility, came into being in 2002.
Outside the center ( Centrala staden ), Lund is characterized by buildings of the university and the technical university, as well as houses with a suburban character. There are older residential buildings in the districts of Värpinge and Östra Torn-Mårtens Fälad , among others .
City structure
Lund divided into 14 administrative districts : Centrala Staden , Gunnesbo , Järnåkra-Nilstorp , Klostergården , Kobjer , Linero , Möllevången , Norra Fäladen , Nöbbelöv , Östra Torn-Martens Fälad , Tuna , Vallkärratorn-Stångby , Värpinge and Väster .
Places
The most important square and center of the city is Stortorget south of the cathedral. This is dominated by the town hall ( Rådhuset ) as well as some shops and cafes. Kyrkogatan leads past the square . To the right of the town hall is the building of the town hall ( Stadshallen ), in which, in addition to a concert hall, there are meeting rooms that are used for meetings of the city council .
The place Mårtenstorget is an old trading post regularly on the markets are held. It is located about 200 m southeast of the town hall. The space also serves as a parking space for cars. Other places are Botulfsplatsen between Stortorget and Mårtenstorget , Clemenstorget north of the train station, Bantorget with the Grand Hotel and Knut den Stores torg and Krafts torg .
Parks

|

|
|
|
View of Lundagård from the west. On the left the tower of the Kungshuset .
|
Tulips in the botanical garden
|
There are several parks in Lund, with Lundagård being the central one. The park with its dense mature trees is located between the cathedral in the south and the university in the north, where the university square forms a natural continuation. To the west it is bounded by Kyrkogatan , Lund's old main street. To the east it borders on the Tegnérsplatsen and the Krafts torg . The history of the park is closely related to that of the city. A park for the Danish king was laid out in it around 1000 AD . The park, at that time still surrounded by a wall, housed the bishop's residence (Kungshuset) , the royal mint and several economic houses.
Due to the geographical proximity to important university buildings such as the main building and the building of the Academic Association ( AF-Borgen ), the park can nevertheless be described as the academic center of the city. The Lunda Carnival has been held here every four years since 1849 , an important student custom with pageants.
The city park ( Stadsparken ) is located southwest of the city center. It was built between 1909 and 1911 around the Högevall , a city wall from the Middle Ages. In the park, which is heavily frequented by the population when the weather is nice, there are several sculptures by various artists. The city park has been a member of the European Garden Heritage Network - EGHN since June 2011 .
The Botanical Garden ( Botaniska trädgården ) is the third park in the city area. It was laid out at the beginning of the 18th century and is now home to thousands of different plant species and several buildings that are used by the university. Below is a greenhouse with nine climate zones .
In the south of the city there is Sankt-Lars-Park, a park in the area of the former Sankt-Lars-Hospital used as a psychiatric clinic .
Population development
| year | population |
|---|---|
| 1570 | 817 |
| 1610 | 1,145 |
| 1650 | 1,535 |
| 1690 | 1,251 |
| 1730 | 1,530 |
| 1770 | 2,078 |
| 1810 | 3,100 |
| 1850 | 6,709 |
| 1890 | 15,023 |
| 1930 | 24,520 |
| 1950 | 34,039 |
| 1970 | 52,359 |
| 1995 | 71,450 |
| 2005 | 76,188 |
| 2010 | 82,800 |
Towards the end of the 17th century, the population in the ecclesiastical city increasingly decreased in the course of the Reformation and secularization. The city was not to recover from this until the 19th century. Even the establishment of the university in 1666 did not ensure the expected population growth in the medium term. Esaias Tegnér referred to Lund around 1800 as an "academic farming village".
Strong demographic changes did not take place until the middle of the 19th century . Founded primarily by the settlement of industrial companies and businesses, the city developed into a commercial and financial center for the surrounding towns and the region. The inauguration of Södra stambanan in 1856, a railway line from Malmö via Nässjö to Falköping, was of great importance . The better connections ensured above-average population growth at that time. From the 20th century on, the expansion of the university and the health sector in particular ensured growth.
politics
The administrative authority of the city is the municipality of Lund (Lunds kommun) . However, their area extends beyond the boundaries of the actual city in terms of settlement geography ( Tatort ) and includes outlying localities. Lund is the main town ( centralort ) of the municipality and thus the seat of the municipal administration.
During the 2006–2010 electoral period, the city and the municipality were ruled by a bourgeois majority of conservatives , liberals and the center ( Kommunfullmäktige ).
coat of arms
The city's coat of arms has been in use since the mid-14th century. The blazon speaks of a silver shield, inside a red wall with battlements and a tower standing on a green background . On top of it, and on both sides, another tower. Contrary to the blazon, the coat of arms is shown in today's use with a golden, curved wall crown , such as the coat of arms of the city of Helsingborg . This crown is supposed to symbolize the free middle class .
What exactly the coat of arms represents cannot be fully determined. A church building could be shown, this is indicated by the cross-like recess in the middle of the main tower. However, due to the fortified walls and towers, a castle also seems possible.
The coat of arms was established in this form by King Gustav V in 1913 . It has been used by the municipality of Lund since 1971 .
traffic
Trunk roads

The European route 22 , Sweden's oldest motorway ( Swedish motorväg ) , has passed through Lund since 1953 when coming from Malmö . There are also connections to all major highways, such as Riksväg 16 , which connects Lund to European route 6 , and Länsväg 108 with a connection to the E 65 .
Railways and public transport
The important train connection in the direction of Malmö (part of Södra stambanan ) has existed since 1856 , and today it continues with the Öresund connection over the Öresund Bridge to Copenhagen and Helsingør . This, as well as the routes Helsingør - Kalmar , Helsingør - Gothenburg and Helsingør - Karlskrona , is served by the Öresundståg , which is jointly organized by the southern Swedish transport associations Blekingetrafik, Hallandstrafik, Länstrafik Kronoberg, Kalmar Läns Trafik, Skånetrafik and Västtrafik as well as the Danish Trafik . Most of the routes were operated by DSB First. On 11 December 2011, DSB First with the acquisition of the Swedish routes by Veolia in DSB Øresund renamed.
Furthermore, the so-called Pågatåg runs as a local train as well as long-distance and regional trains of the state railway company SJ to Gothenburg and Stockholm . Since the railway lines of Västkustbanan and Södra stambanan cross in Lund, it is possible to reach the three largest cities in Sweden (Stockholm, Gothenburg and Malmö) without having to change trains.
The public transport is used with the well-developed bus network of Lund Stadsbuss (operated by Nettbuss ). There are around 400 bus stops in the city. Within the city, the eleven main lines are served by environmentally friendly low-floor buses, 90% of the vehicles run on natural gas . In addition, there is extensive regional bus transport to many cities in Skåne, including Malmö, within the Skånetrafik transport association.
In mid-December 2015, the municipal council decided to build a tram , which will connect Lund C station with the Science Village in the northeast of the city with a stretch of around 5.5 kilometers. The start of operations is planned for 2020. Two more lines are planned in the medium term.
Air traffic
Lund is not far from Malmö Airport , which is particularly important for domestic Swedish flights. In addition, the proximity to the much larger Copenhagen-Kastrup Airport is of great importance. This can be reached in 35 minutes by Öresundståg, while Malmö Airport is connected to public transport by the Flygbuss . In addition, there is the Hasslanda airfield about two kilometers away from Lund , but it is used exclusively for sport flights.
Bicycle traffic
As in any medium-sized university town, the bicycle is the most important means of transport in Lund. Around 22,000 cyclists pass through the city center every day, 90% of the residents have access to a bicycle. The municipality as the administrative authority has been promoting the expansion of the road network and increasing security with around 80 million SEK since 1998. Lundahoj has been a bicycle travel center at Lund C since 1996 with 780 covered and guarded bicycle parking spaces and a bicycle rental service. The project is financed by state grants, with support from INTERREG III B of the European Regional Development Fund (ERDF) .
Sights and culture
Thanks to its location, Lund is the starting point for excursions through Skåne, as well as for day trips to Malmö or Copenhagen. The Romanesque Lund Cathedral (domkyrkan) is a landmark of the city that can be seen from afar . A special feature are the numerous water towers , of which the Gamla Vattentornet is the largest with a height of around 75 m.
In terms of culture, the city offers several theaters, cinemas and countless cafes for its size, in which readings or film screenings take place. Also worth mentioning are the art museum Skissernas museum ( museum of sketches ), the art gallery Lund , the open-air museum cultures as well as the Mejeriet ( dairy ), a cultural center where concerts take place. The city of Lund applied for European Capital of Culture 2014, but was defeated by Umeå in the final selection. The Lund Chamber Choir is one of the representative choirs of Lund Cathedral.
education and Science
The University of Lund is now one of the largest universities in Scandinavia with around 35,000 students and is the fourth oldest Swedish university founded after the universities in Uppsala (founded in 1477) and Tartu (founded 1632 in today's Estonia ) as well as the Royal Academy of Åbo (founded 1640), which later became the University of Helsinki . Between 1425 and 1536, the Studium generale in Lund was a precursor to the university. The current university was only founded in 1666 in an effort to Swedishize the former Danish province of Skåne .
Important faculties are the medical faculty with the university hospital , as well as the natural science faculty and the technical faculty. The university also houses the national synchrotron radiation source MAX-lab (MAX-I, II, III, built in 1986, 1997 and 2008), which were closed in 2015 and are being dismantled. Instead, the new MAX IV synchrotron radiation source outside of Lund is due to go into operation in June 2016. In 2019, the European Spallation Source (ESS) will follow in the immediate vicinity .
With the family archive of Alfred Nobel , which is kept in the Lund State Archives, one of Sweden's six world document heirs exists in Lund. The National Archives, one of five national archives in Sweden, holds, among other things, an extensive collection of Danish writings from the time before the Peace of Lund .
economy
In 1951 Tetra Pak AB was founded in Lund , the main factory of which is still located here. Alfa Laval , another major company based in Lund, was part of the Tetra Pak Group between 1991 and 2000, but has since been partially spun off again. The medical technology company Gambro is also based in Lund. In addition, the Sony Mobile company has its main location in the city.
In 1983, the IDEON science park was the first of its kind in Scandinavia. Small and medium-sized companies from the IT , biotechnology and high-tech sectors are settling in the Tuna district on an area of around 100,000 m 2 today . It works closely with Lund University, especially with the Technical University ( LTH ). Notable companies include Deloitte , Skandia and QlikTech .
media
In the past two daily newspapers were published in Lund : Lunds Dagblad and Folkets Tidning . Both no longer exist. Currently the largest newspaper is the Malmöer Sydsvenskan , the Skånska Dagbladet has an editorial office in Lund. The newspaper Lundaliv has existed for 15 years and provides information about news and trends from Lund. Furthermore, the free newspaper metro is selling well. The student channel Steve is broadcast on local television , with Radio AF there is also a student channel on radio.
Sports
Lund can be described as a handball city. Two clubs from the city alone play in the first division: H 43 Lund and LUGI HF , the latter becoming Swedish champions in 1980. Since 1978, Lundaspelen has been hosting what it claims to be the largest youth handball tournament in the world. Lund hosted the 2011 men's handball world championship .
The Lunds BK football team plays in Division 2 Södra Götaland , Sweden's fourth division. Well-known players like Martin Dahlin and Roger Ljung already played in the club.
In basketball, the LUGI ( Lunds Universitets Gymnastik och Idrottsförening ) and Eos Lund IK departments should be mentioned, the latter playing in the second division. The Lundaspelen, a basketball tournament organized by Eos Lund with around 300 participating teams, has taken place every year since 1979. The Innebandymannschaft the LUGI plays in the fourth Swedish League.
The most important sports facilities are the general sports hall ( Lunds Idrottshall ), the Färs och Frosta Sparbank Arena, the Ballhaus ( Bollhuset ) where ball sports are at home, the Eos Hall, as well as the Victoria Stadium and the sports field ( Centrala idrottsplatsen ).
Personalities
literature
- K. Arne Blom: Medeltidens Lund. Lund 1999, ISBN 91-973770-0-7 .
- Bengt Liljegren: Karl XII i Lund: När Sverige styrdes från Skåne (Illustrerad historia). Lund 1999, ISBN 91-88930-51-3 .
- Ragnar Blomqvist: Lunds Historia, Medeltiden. Lund 1951, ISBN 91-40-30125-7 .
- Ragnar Blomqvist: Lunds Historia, Nyare tiden. Lund 1978, ISBN 91-40-04391-6 .
Web links
- Official website (English, Swedish)
- Tourist information (German, English, Swedish)
- Illustration of the city in 1588 in Civitates orbis terrarum by Georg Braun and Frans Hogenberg
Individual evidence
- ↑ a b c Statistiska centralbyrån : Land area per crime scene, folkmängd och invånare per square kilometer. Vart femte år 1960 - 2015 (database query)
- ↑ Sydsvenskan: Lund växer mest av storstädera ( Memento of the original from March 27, 2008 in the Internet Archive ) Info: The archive link was inserted automatically and has not yet been checked. Please check the original and archive link according to the instructions and then remove this notice.
- ↑ Svenska Dagbladet: Efter Lund är Malmö awned the stad som växer mest i Sverige.
- ↑ Riksintressen för kulturmiljövården - Skåne län , Riksantikvarieämbetet page 24.
- ↑ Statistiska centralbyrån : perpetrators 2015 som delas av commungräns (Excel file)
- ↑ Temperatures och nederbörden i Sverige 1961 - 1990: referensnormaler / Hans Alexandersson och Carla Eggertsson Karlström. - Utgåva 2. - Norrköping: Sveriges meteorologiska och hydrologiska institut, 2001. - 71 pages: Kt .; 30 cm. - (Meteorologi / SMHI; 99.2001)
- ↑ Svenskt local dictionary. 2003, p. 199.
- ↑ Overview map of the city districts ( Memento of the original from September 30, 2007 in the Internet Archive ) Info: The archive link has been inserted automatically and has not yet been checked. Please check the original and archive link according to the instructions and then remove this notice.
- ↑ Lund City Park ( Memento of the original from September 27, 2011 in the Internet Archive ) Info: The archive link has been inserted automatically and has not yet been checked. Please check the original and archive link according to the instructions and then remove this notice. on the EGHN website
- ↑ Stockholm University , Institute for City and Community History : Lunds befolkningsutveckling 1570-1995 ( Memento of the original from 23 September 2010 in the Internet Archive ) Info: The archive link has been inserted automatically and has not yet been checked. Please check the original and archive link according to the instructions and then remove this notice.
- ↑ Tatorternas landareal, folkmängd och invånare ( Memento of the original from January 25, 2007 in the Internet Archive ) Info: The archive link was inserted automatically and has not yet been checked. Please check the original and archive link according to the instructions and then remove this notice.
- ↑ oresundstag.se
- ↑ DSB First skiftede navn til DSB Øresund, March 26, 2013, in Danish. Archived from the original on April 12, 2013 ; accessed on January 2, 2016 .
- ↑ Lund Stadsbuss ( Memento of the original dated February 14, 2007 in the Internet Archive ) Info: The archive link was inserted automatically and has not yet been checked. Please check the original and archive link according to the instructions and then remove this notice. (Swedish)
- ↑ Lund gets a tram.
- ↑ Lundacyklisten i siffror ( Memento of the original from February 10, 2008 in the Internet Archive ) Info: The archive link has been inserted automatically and has not yet been checked. Please check the original and archive link according to the instructions and then remove this notice. (Swedish)
- ↑ Cyklist ( Memento of the original of February 10, 2008 in the Internet Archive ) Info: The archive link was automatically inserted and not yet checked. Please check the original and archive link according to the instructions and then remove this notice. (Swedish)
- ↑ Hoj is slang for bicycle
- ↑ Lundahoj - cykelresecentrum ( Memento of the original from December 14, 2007 in the Internet Archive ) Info: The archive link was automatically inserted and not yet checked. Please check the original and archive link according to the instructions and then remove this notice. (Swedish)
- ↑ uu.se ( Memento of the original from May 14, 2011 in the Internet Archive ) Info: The archive link was inserted automatically and has not yet been checked. Please check the original and archive link according to the instructions and then remove this notice.
- ↑ ut.ee
- ↑ Åbo is the Swedish name of Turku
- ↑ helsinki.fi
- ↑ maxlab.lu.se ( Memento of the original dated July 16, 2011 in the Internet Archive ) Info: The archive link was inserted automatically and has not yet been checked. Please check the original and archive link according to the instructions and then remove this notice.
- ↑ ESS in Lund ( Memento of the original dated June 3, 2011 in the Internet Archive ) Info: The archive link was inserted automatically and has not yet been checked. Please check the original and archive link according to the instructions and then remove this notice. (PDF; 1.3 MB)
- ↑ IDEON - en berättelse om framgång ( Memento of the original from January 11, 2004 in the Internet Archive ) Info: The archive link was inserted automatically and has not yet been checked. Please check the original and archive link according to the instructions and then remove this notice.
- ↑ Allt you behöver är en god idé ( Memento of the original from July 19, 2007 in the Internet Archive ) Info: The archive link was inserted automatically and has not yet been checked. Please check the original and archive link according to the instructions and then remove this notice.
- ↑ Lundaspelen ( Memento of the original from October 31, 2013 in the Internet Archive ) Info: The archive link was inserted automatically and has not yet been checked. Please check the original and archive link according to the instructions and then remove this notice.